APUSH - GREAT DEPRESSION/FDR/NEW DEAL
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Causes of the Great Depression
1. tariffs and war debt policies- cut down the
foreign market for American goods.
2. Stock market speculation- buying stock on margin with borrowed money
3. Bank failures- too many people withdrew their money
4. Fed. Reserve raised interest rates to banks to curb stock market
5. growing personal consumer debt

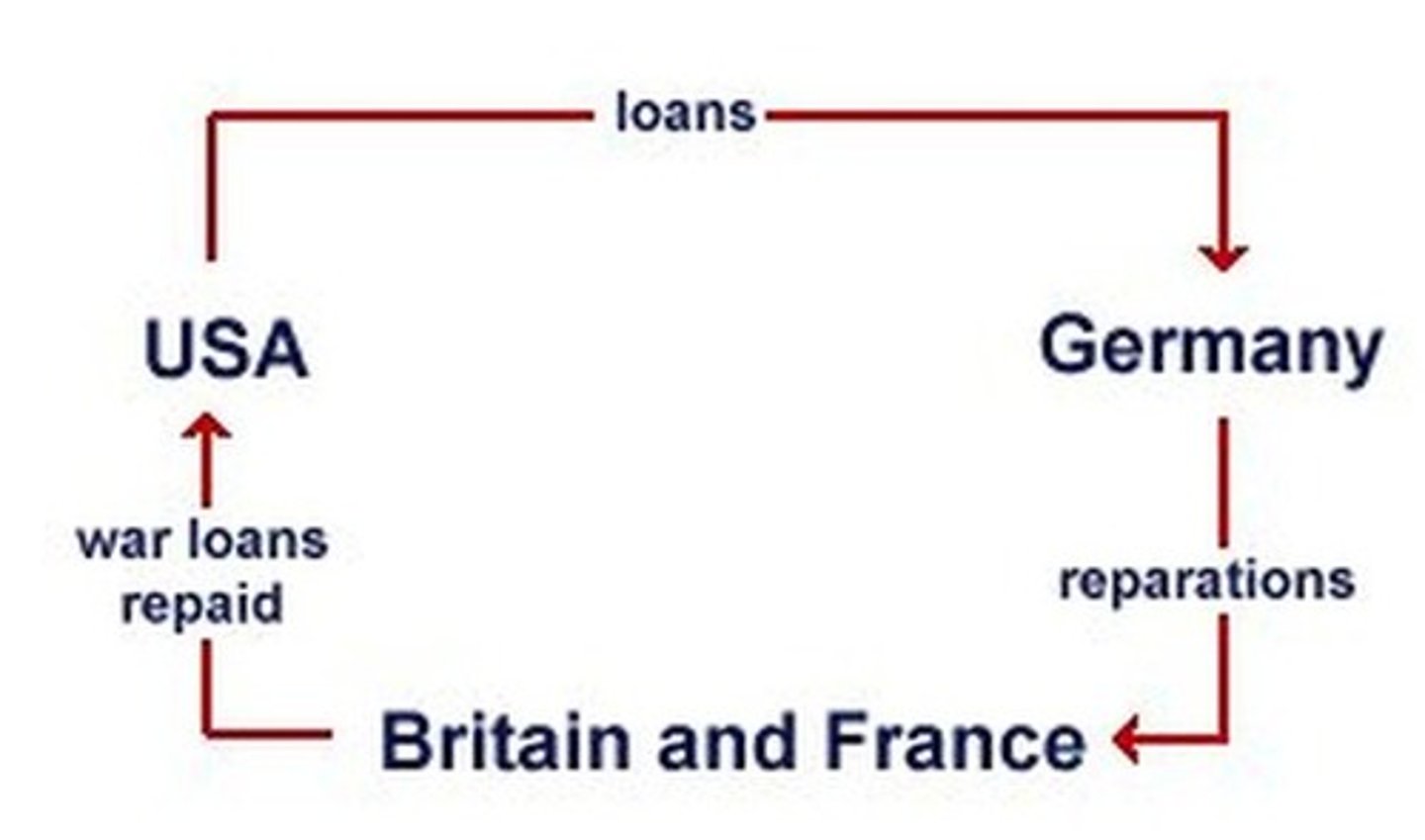
Dawes Plan
A plan to revive the German economy- United States loaned Germany money to pay reparations (war debt) to England and France, who would then pay back loans from the U.S. This circular flow of money was a success.
effects of the Great Depression
- banks failed- too many withdrew their cash
- businesses and factories failed- could not repay debt - sales declined
- millions of Americans were out of work/ lost their land and homes - no way to pay their debt
- poverty and homelessness
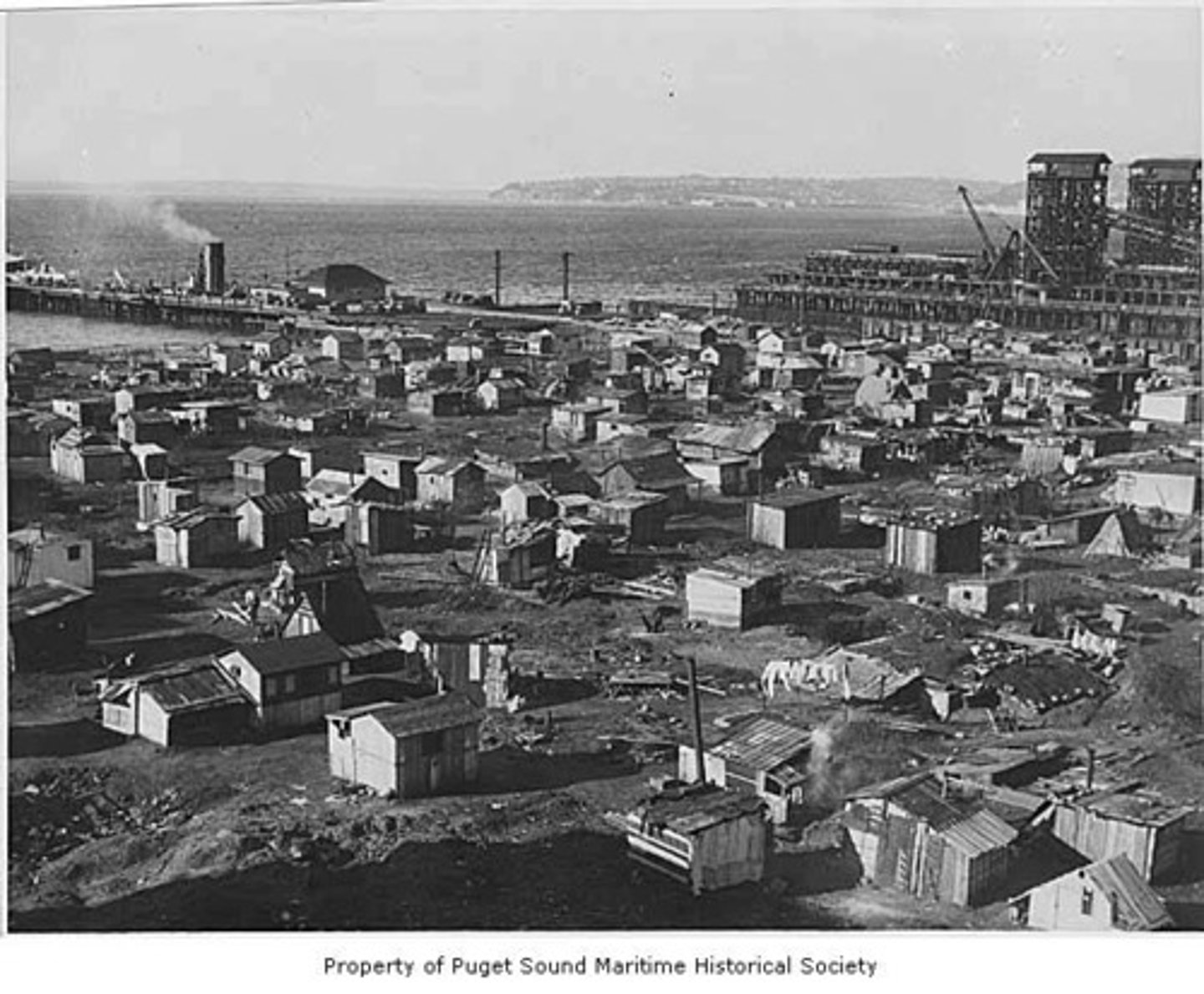
-Hoovervilles
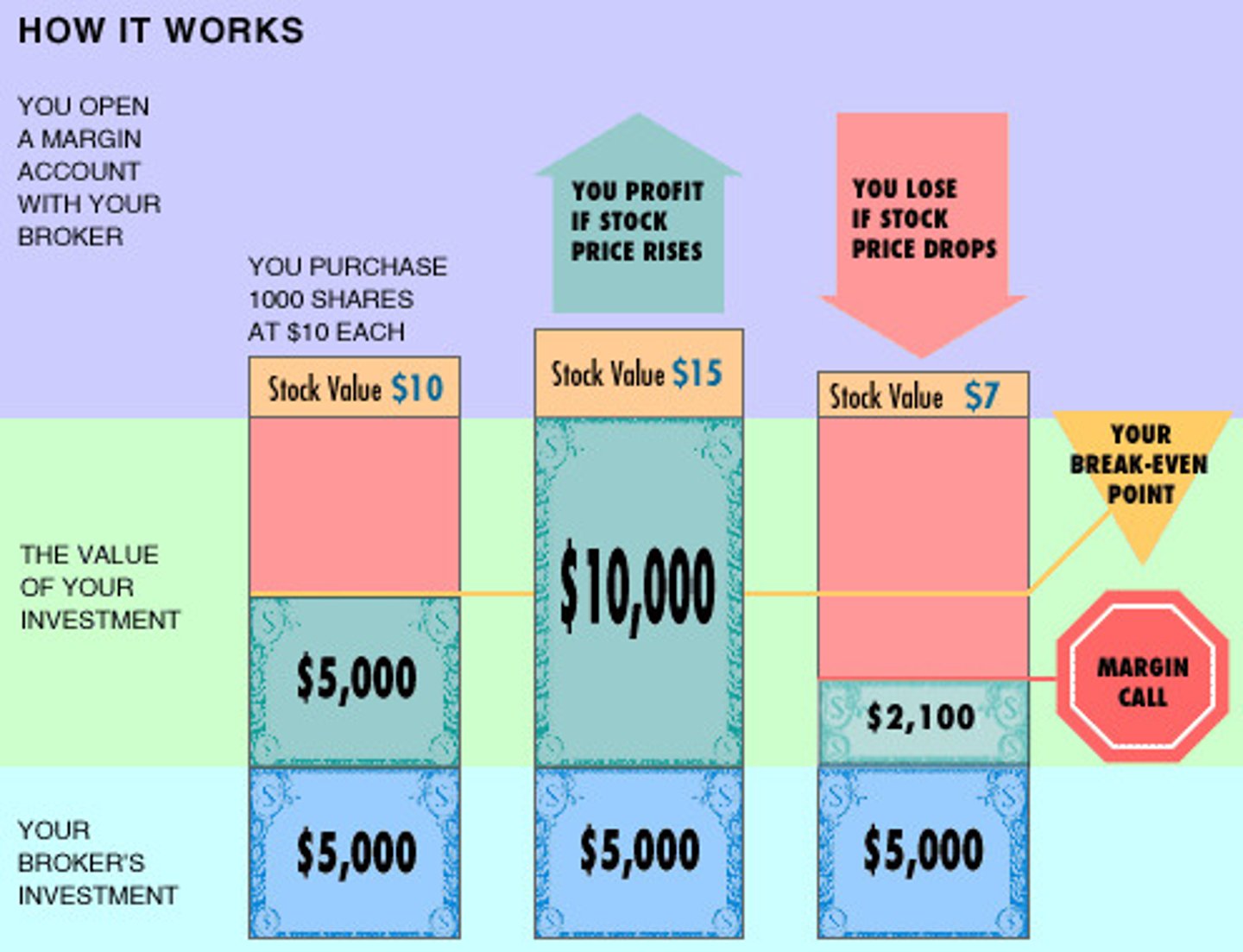
buying on margin
Purchasing stock little money down - with the promise of paying the balance at sometime in the future as stock increases in value- essentially borrowing money to buy stock
Black Tuesday
October 29, 1929--massive sell off of stocks- worst market crash in American history- beginning of the Great Depression.

Herbert Hoover
Elected president- 1928. Republican- approach to economy known as voluntarism (avoid destroying individuality/self-reliance by government coercion of business)- 1929 the stock market crashed- tried to fix it through creating the Emergency Relief and Construction Act and the Reconstruction Finance Corporation- lost reelection to FDR by a landslide

RFC
Agency set up under the Hoover administration to make loans to banks and other lending institutions.
Reconstruction Finance Corporation

Great Depression
(1929-1939) The dramatic decline in the world's economy due to the United State's stock market crash of 1929, the overproduction of goods from World War I, and decline in the need for raw materials from non industrialized nations. Results in millions of people losing their jobs as banks and businesses closed around the world.

New Deal
Federal government projects financed by the government to help the public and put people back to work

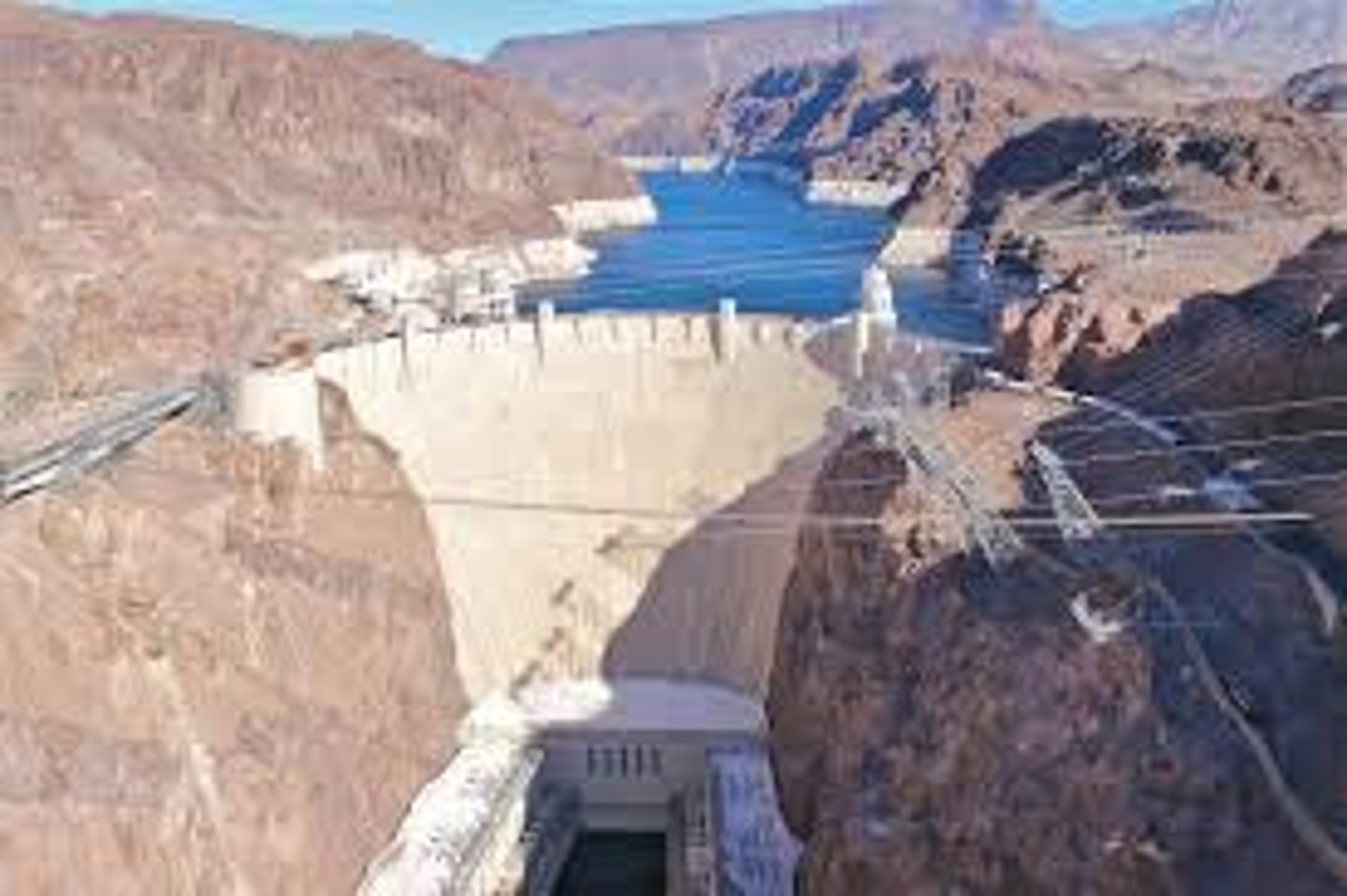
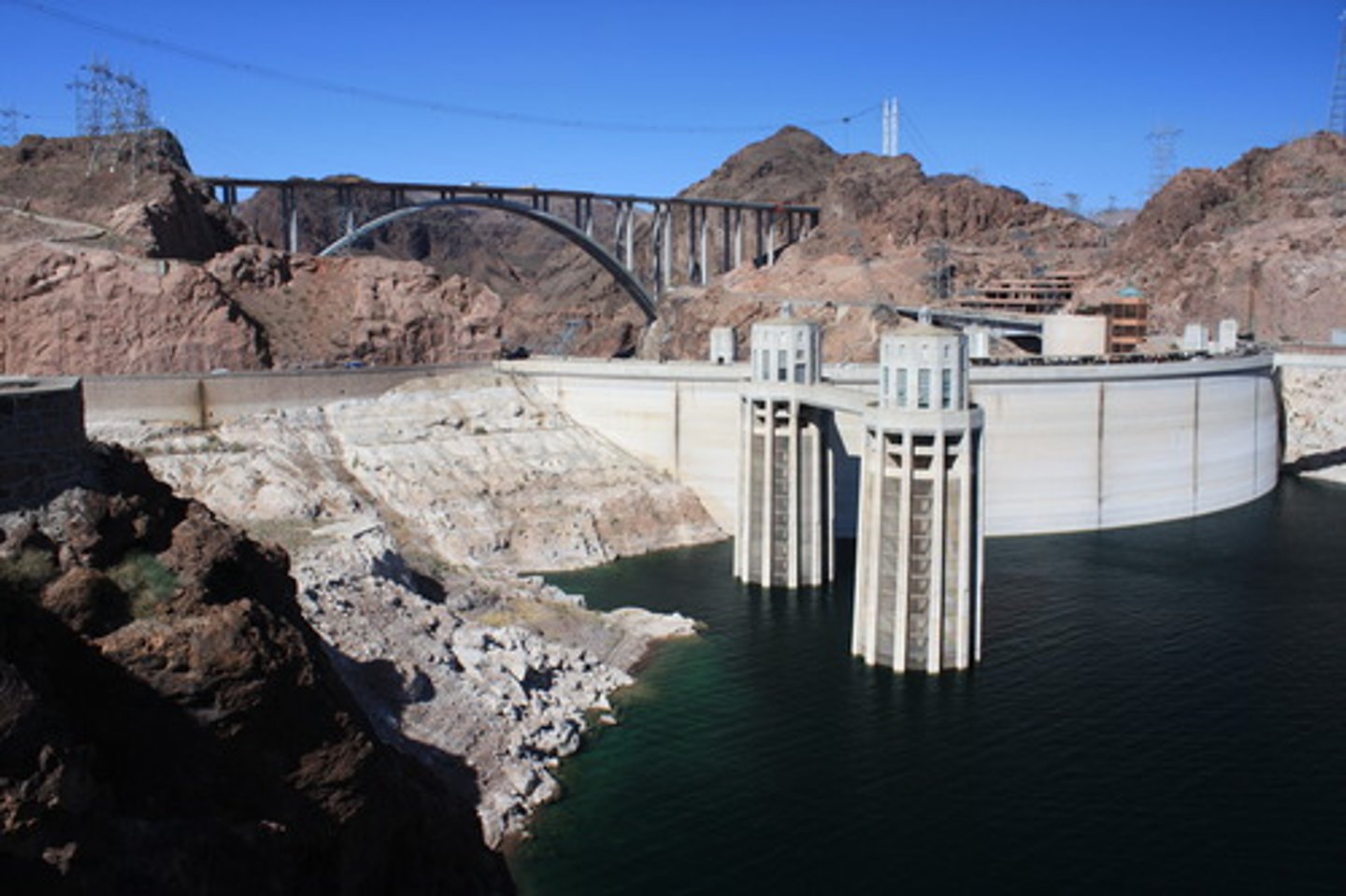
Hoover Dam
massive public-works program; brought employment and hydro-electric power to the Southwest. Initiated by President Hoover- similar to programs Roosevelt used in the New Deal.

Hoovervilles
Depression shantytowns, named after the president whom many blamed for their financial distress

bank holiday
All banks ordered to close until new laws could be passed. An emergency banking law was rushed through Congress. The Law set up new ways for the federal government to funnel money to troubled banks It also required the Treasury Department to inspect banks before they could re-open.

Fireside Chats
Informal radio conversations Roosevelt had with the Amercian people to keep spirits up. It was a means of communicating with the people on how he would take on the depression. Mass media
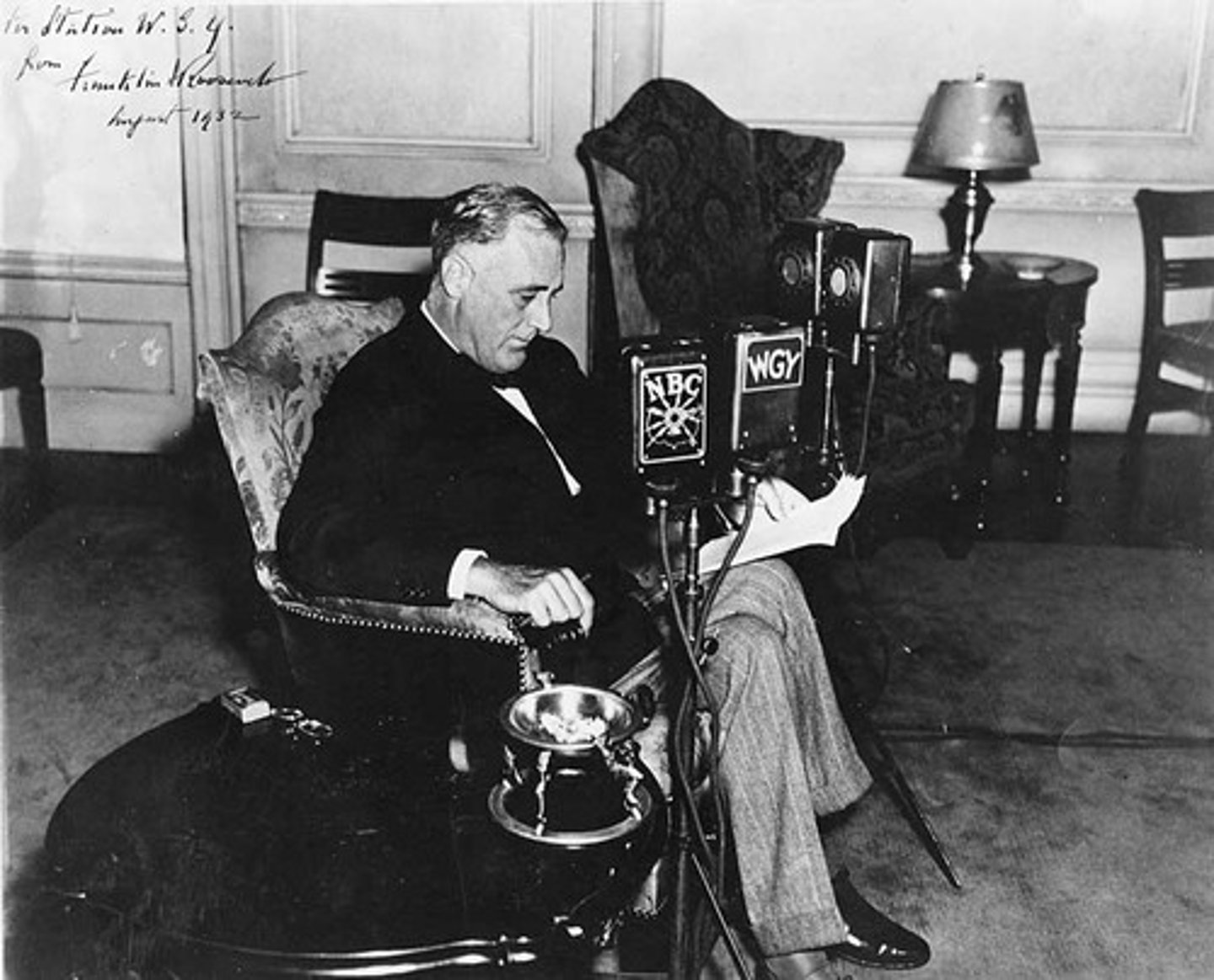

Hundred Days
Special session of Congress from March 9, 1933 to June 16, 1933, called by President Franklin D. Roosevelt- important social legislation was enacted. relief, recovery, and reform
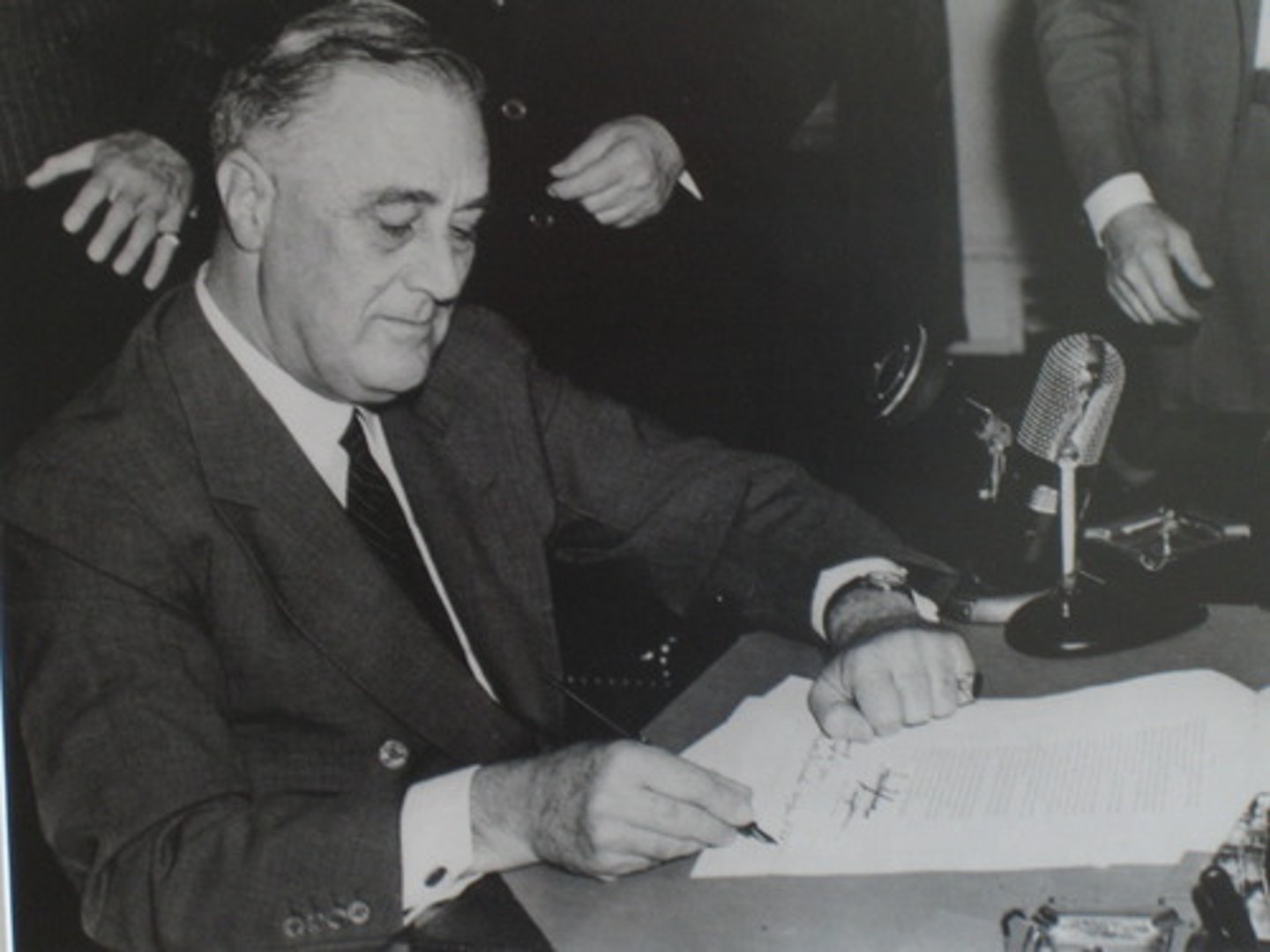

New Deal
President Franklin Roosevelt's programs to combat economic depression enacted a number of social insurance measures and used government spending to stimulate the economy- RELIEF, RECOVERY, AND REFORM

First New Deal, 1933
FDR established to serve the "three Rs" Relief for the people out of work, Recovery for business and the economy as a whole, and Reform of American economic institutions

Second New Deal, 1935
Began in 1935 - Created Works Progress Administration WPA which put over 3 million people to work paid by the government. Most important legacies: Social Security and Wagner Act

Pros of Roosevelt's New Deal
- Federal government has a duty to help all citizens.
- helped the nation through the worst days of the Great Depression.
- when people in other countries turned to dictators to solve problems, the New Deal saved the America's democratic system.

Cons of Roosevelt's New Deal
- many believed that the government should not interfere in business or in people's private lives.
- New Deal spending led to increases in the national debt.
- The New Deal did not end the Great Depression
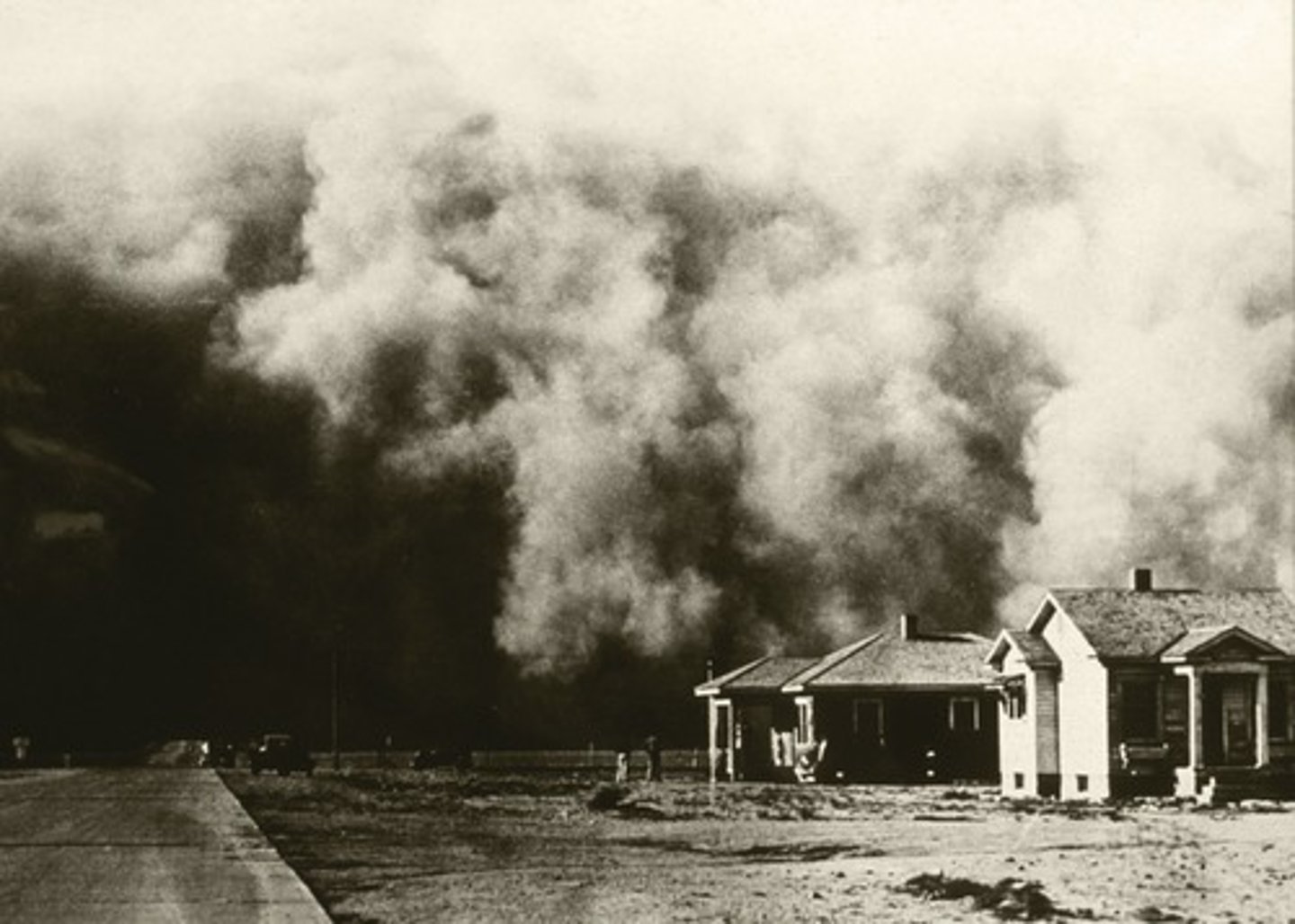
Dust Bowl
Region of the Great Plains that experienced a drought in 1930 lasting for a decade, leaving many farmers without work or substantial wages. Many families migrated to the west in search of jobs and new opportunities.

FDR
32nd President of the United States, the President of the United States during the Depression and WWII. He instituted the New Deal. Served from 1933 to 1945, he was the only president in U.S. history to be elected to four terms

SEC- Securities and Exchange Commission
Federal government agency that oversees the exchange of securities (stocks and bonds) to protect investors and their savings and investments

Wagner Act
1935 - National Labor Relations Act; granted rights to unions; allowed collective bargaining

FDIC- Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
Federal guarantee of savings or bank deposits initially of up to $2500, raised to $5000 in 1934, and frequently thereafter; continues today with a limit of $100,000

Glass-Steagall Act
Passed by Congress 1933- prohibited banks from engaging in investment banking services. The law also created the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), which insures bank deposits up to $250,000. Also known as the Banking Act of 1933.

PWA Public Works Administration
Part of the New Deal programs. Put people to work building or improving public buildings like schools, post offices, dams etc.-

AAA Agricultural Adjustment Administration
Attempted to regulate agricultural production through farm subsidies ($ to decrease the amount of crops produced); ruled unconstitutional in 1936; disbanded after World War IIAgricultural

WPA- Works Progress Administration
Work Progress Administration: Massive work relief program funded projects ranging from construction to acting; disbanded by FDR during WWII

TVA- Tennessee Valley Authority
Created in 1933 in order to provide navigation, flood control, electricity generation, fertilizer manufacturing, and economic development in the Tennessee Valley, a region particularly impacted by the Great Depression

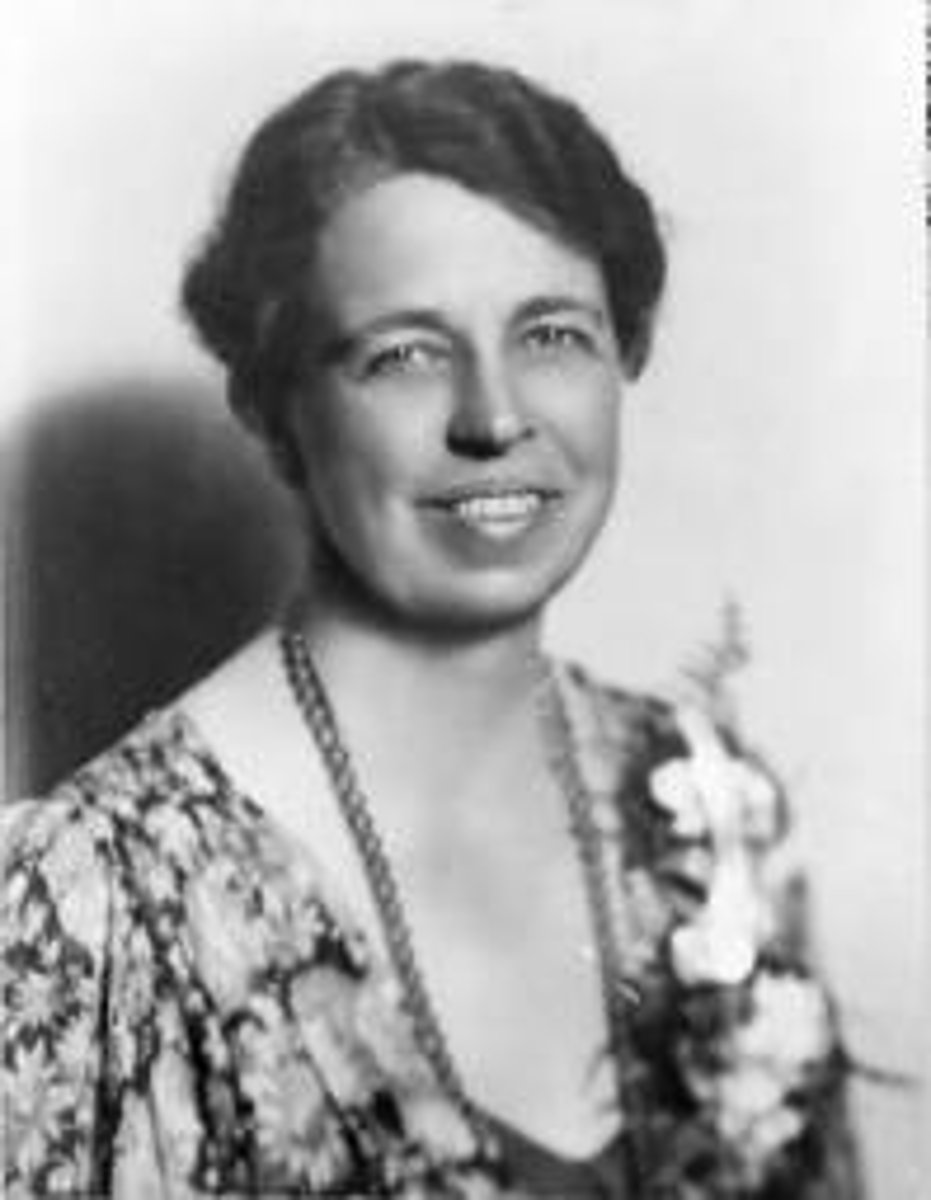
Eleanor Roosevelt
First lady of the United States from 1933-1945.
Was a great supporter of civil rights and opposed the Jim Crow laws. She also worked for birth control and better conditions for working women

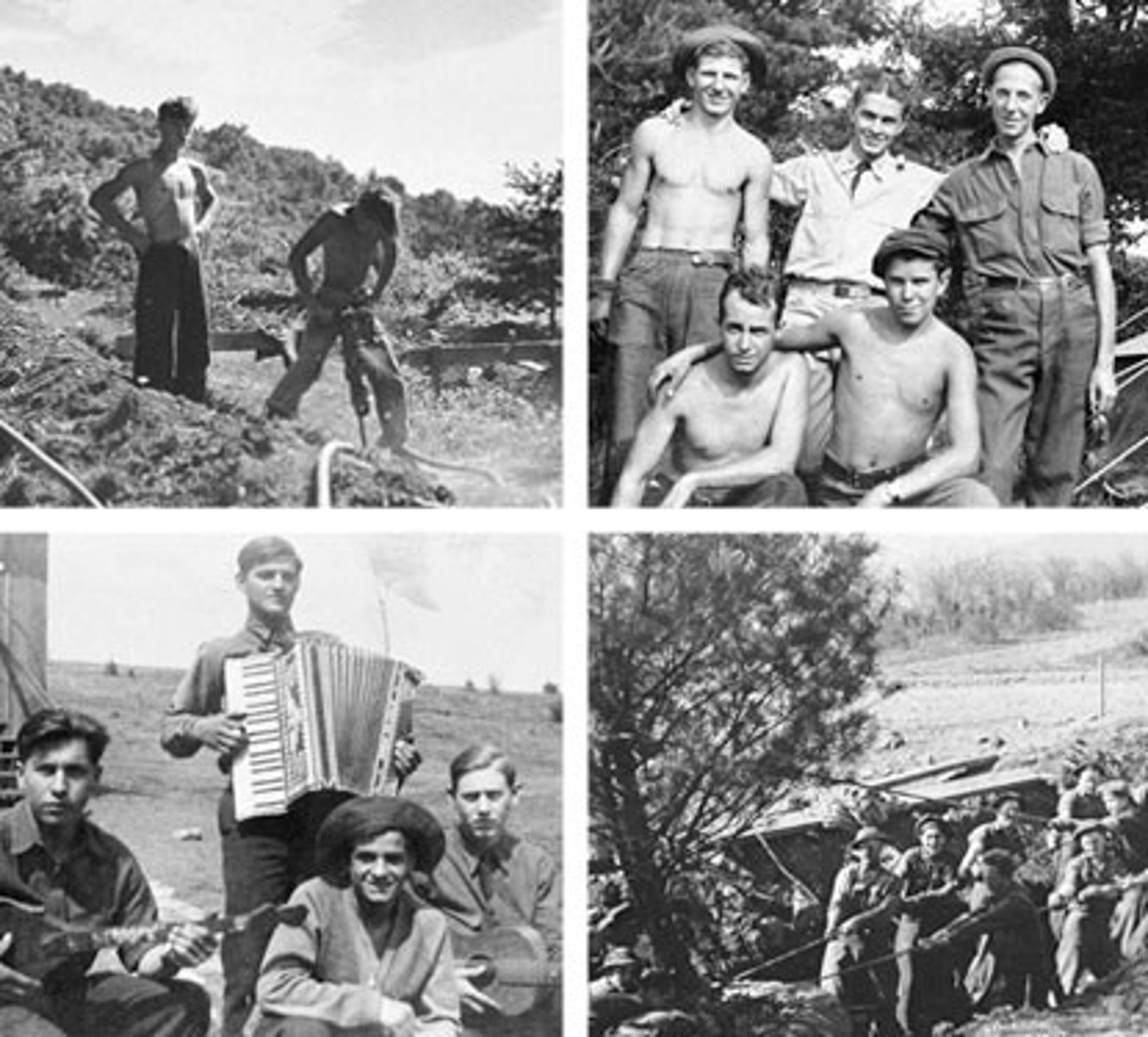
CCC Civilian Conservation Corp
New Deal program for young men between the ages of 18 and 25 -volunteered to be placed in camps to work on regional environmental projects, mainly west of the Mississippi; they received $30 a month, of which $25 was sent home; disbanded during World War II- built the Appalachian Trail.

Social Security Act
1935 New Deal program- guaranteed retirement payments for enrolled workers beginning at age 65; set up federal-state system of unemployment insurance and care for dependent mothers and children, the handicapped, and public health

Fair Labor Standards Act
1938 Act which provided for a minimum wage and restricted shipments of goods produced with child labor

deficit spending
Spending more money than the govt. receives in revenue
Used by FDR to finance the New Deal
Kenysian economic model.

John Maynard Keynes
British economist who said deficit spending was acceptable because in difficult times the government needed to spend well above its tax revenues in order to initiate economic growth, "priming the pump". His ideas and theories influenced FDR's New Deal policies to put people back to work.

Huey P. Long
Immensely popular governor and senator of Louisiana; provided tax favors, roads, schools, free textbooks, charity hospitals, and improved public services for Louisiana citizens; cost: corruption and personal dictatorship; formed national organization (Share Our Wealth)

CWA
Civil Works Administration
-emergency work relief program- put more than four million people to work during the winter of 1933-34

FHA Federal Housing Authority
Expanded private home ownership among moderate-income families through federal guarantees of private mortgages, the reduction of down payments from 30 to 10 percent, and the extension of repayment from 20 to 30 years; continues to function today.

court packing
Attempt by FDR to appoint one new Supreme Court justice for every sitting justice over the age of 70 who had been there for at least 10 years. Wanted to prevent justices from dismantling the new deal. Plan died in Congress and intensified opposition to FDR's New Deal

John Steinbeck
American novelist who wrote The Grapes of Wrath. (1939) A story of Dust Bowl family (the Joads) who travel to California to look for a better life. Novel addresses the despair and loss of hope and dignity associated with the Depression

The Grapes of Wrath
1939- Steinbeck tells the story of a poor farmer family who were evicted (in large part due to Dust Bowl in Oklahoma- migrate to CA to find work- Captured the attention of the nation to hardships faced by migrant farmers during the Depression.
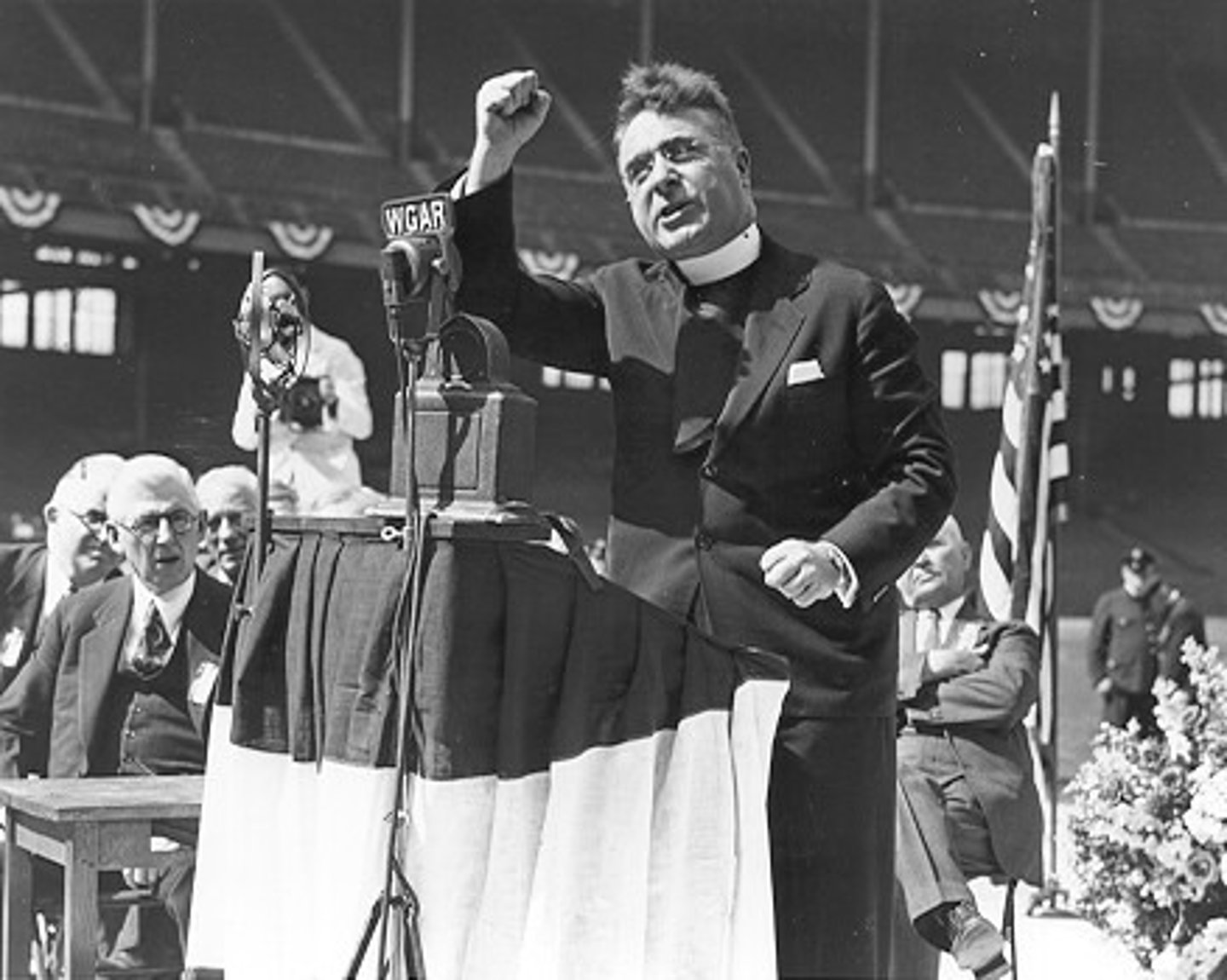
Father Coughlin
Catholic priest from Michigan who was critical of FDR on his radio show. His radio show morphed into Anti-Semitic rants during WWII and he was eventually kicked off the air; he was popular among those who opposed FDR's New Deal.

Woody Guthrie
American songwriter and folksinger who flourished in the 1930s, writing songs about social injustice and the hardships of the Great Depression years- two of his best-remembered songs are "This Land is Your Land" and "So Long, It's Been Good to Know Yuh."
