RAD-L5: Interpreting and Reporting Radiographs
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
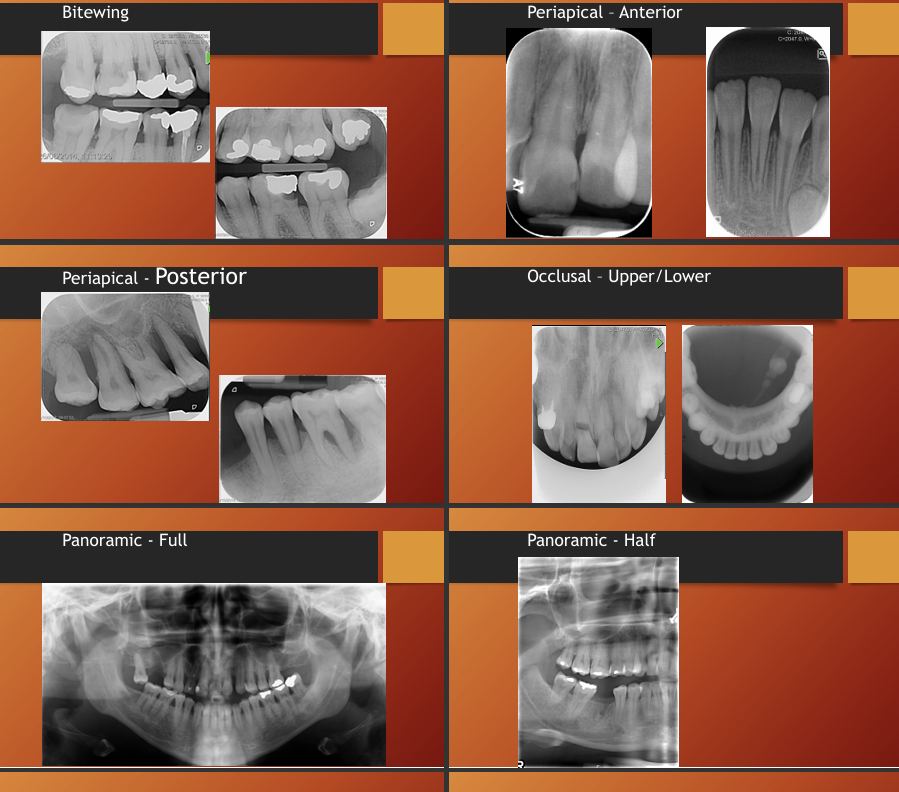
What are some radiographs taken in dentistry?
Bitewing
periapical - anterior and posterior - allows you to see entire root
occlusal - upper and lower - may help see cracks in teeth
panoramic - full and half (sometimes if you are looking for a specific tooth you can do half, but if there is a problem that is not specific on one side it might be better to do a full so you can see if there is also anything wrong in the other side as well as its provides a good comparison)
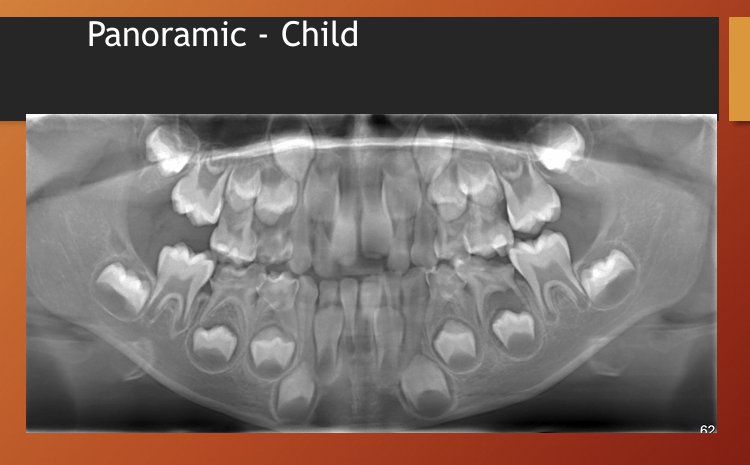
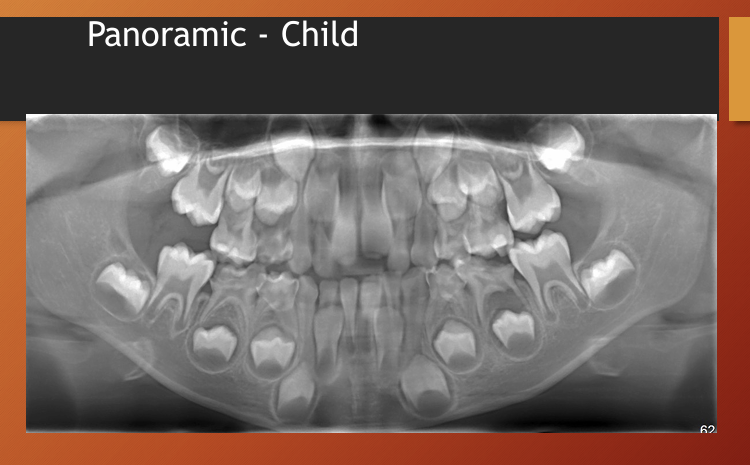
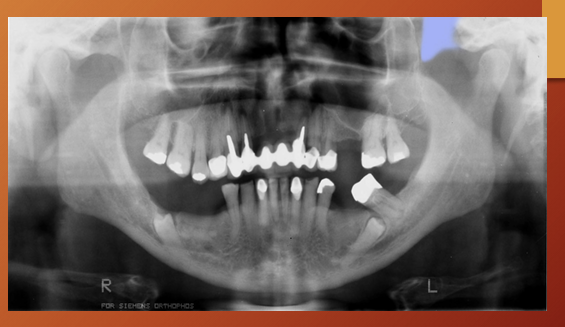
What id the age of this patient?
child
what are some steps to interpreting a radiograph? (7)
•Good quality radiographs
•Good viewing conditions
•Systematic approach
•Decide if anatomy, artefact or pathological
•Describe the area of interest
•If Pathological you need a differential diagnosis
•Remember: no definite diagnosis unless with Histology

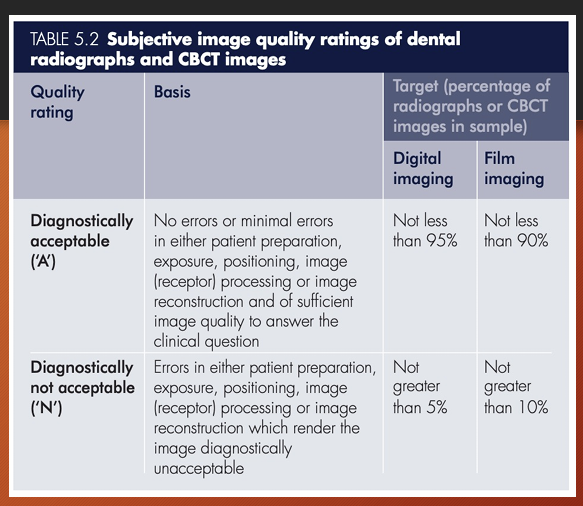
What are the gradings for quality of a radiograph
diagnostically acceptable and diagnostically unacceptable
What are 3 considerations for optimum viewing conditions ?
Screen - (even, uniform, bright light) - variable intensity to allow view film of different density
viewing room - (dark and quiet)
magnifying glass - see fine details (if conventional film)
what are 3 features of display devices that are important/
resolution, contrast ratio, luminance - PACS - guideline
DICOM - digital imaging and communication in medicine - about display devices
Which background colour would make this radiograph more discernible? white or black?
black
What are 2 further viewing methods for conventional film?
Warday viewing box - additional central bright light source for viewing overexposed dark films
SDI X-ray reader - intraoral film viewer with built in magnification
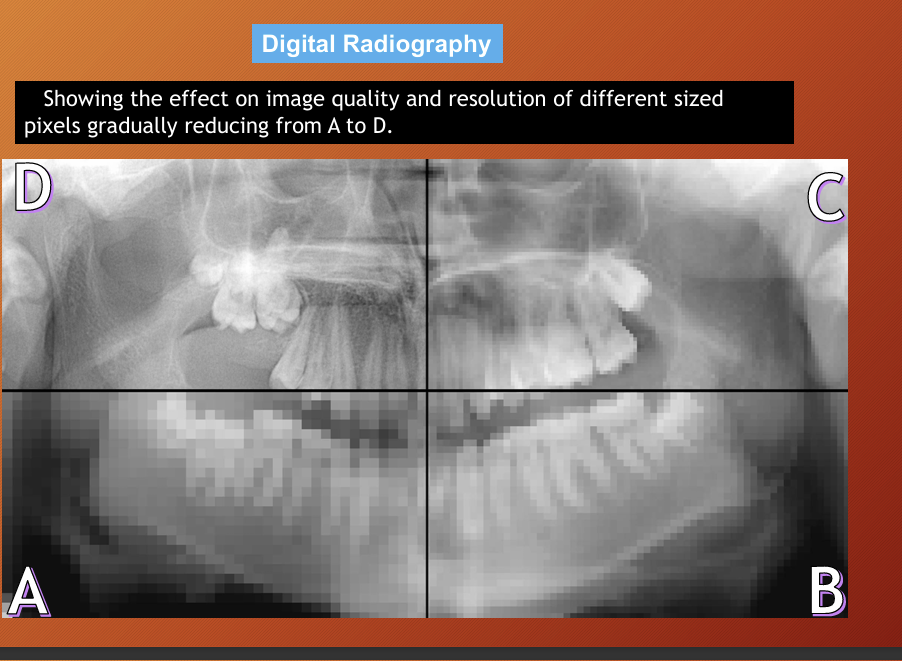
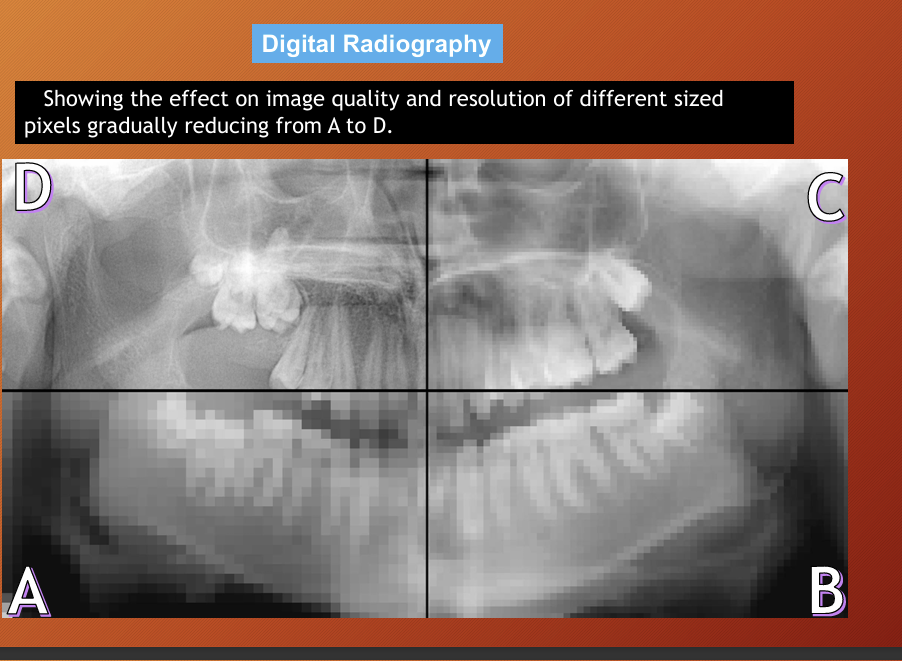
resolution of digital radiography
number and size of pixels and the grey scale available
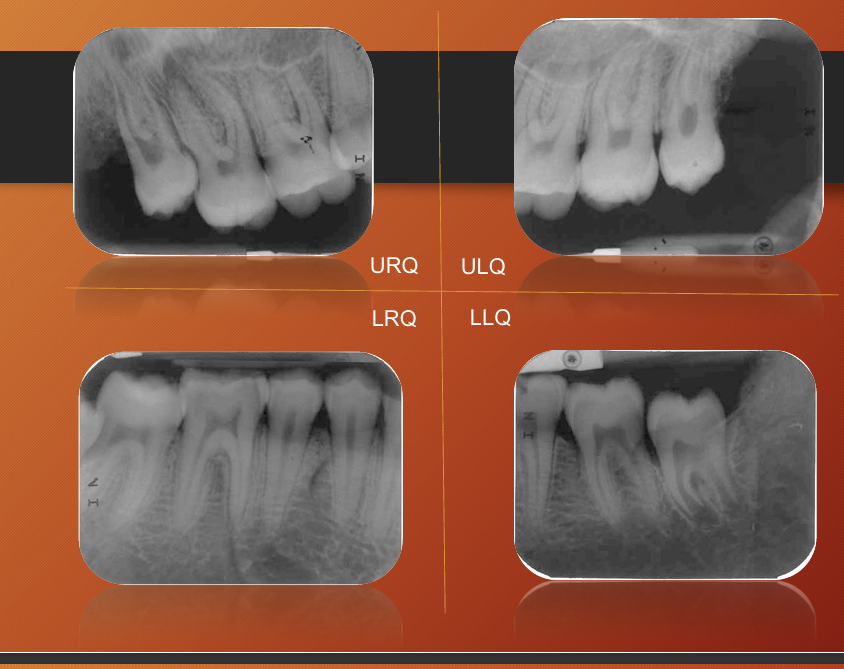
What may give you better quality instead of doing 1 panoramic?
4 periapical better than one panoramic
why are there limitations to radiograph?
what are the terms for white, black and grey areas and why do they occur?
final image is a 2D image from a 3D image - variety of black, white and grey superimposed shadows and is referred to as shadowgraphs
white = radiopaque = very dense objects, have totally stopped the X-ray beam
Black = radiolucent = low density object, x-ray has passed through completely
grey = x ray beam as partly passed and partly stopped
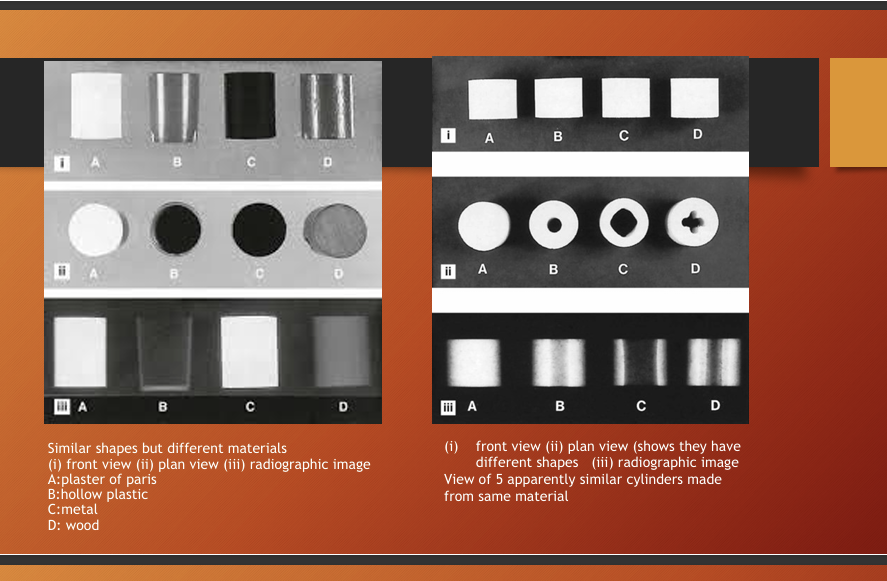
What is this image showing?
the radiograph produced can differ based on the shape, type and thickness or density of the material
again the main limitation of radiographs is?
view 2D image of a 3D object
3 main factors when critically assessing radiographs?
technique
exposure factors
processing
What are some questions when considering the technique? (7)
which techniques was used?
how much distortion is present?
is the image foreshortened or elongated?
is there any rotation or asymmetry?
how good are the image resolution and sharpness?
has the film been fogged?
which artefactual shadows are present?
What are some questions for exposure factors?
Is the radiograph correctly exposed for the specific reason it was requested?
is it too dark and so possibly overexposed?
is it too light/pale and so possibly underexposed?
how good is the contrast?
What are some processing questions?
is the radiograph correctly processed?
is it too dark and so possibly overdeveloped?
is it too pale and so possibly underdeveloped
is it underfixed? - dirt and emulsion still present?
why is a good quality radiograph important?
a poor quality radiograph is a poor diagnostic aid, or has no diagnostic value at all - means you have to repeat and expose the patient to more radiation
systemic approach? 3
looking at:
normal anatomy
errors/artefacts
pathology
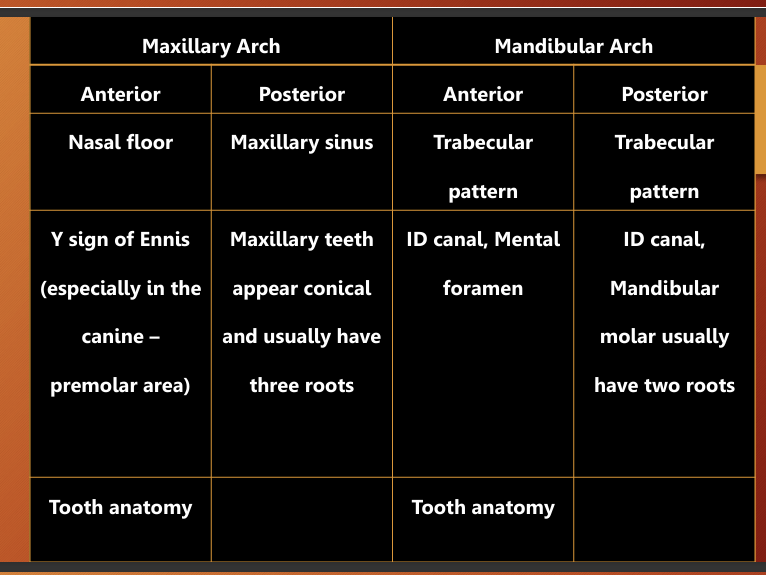
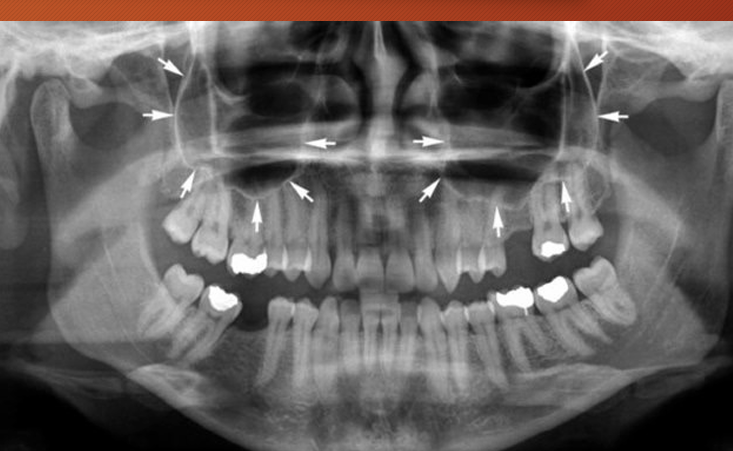
What are different anatomy you can see
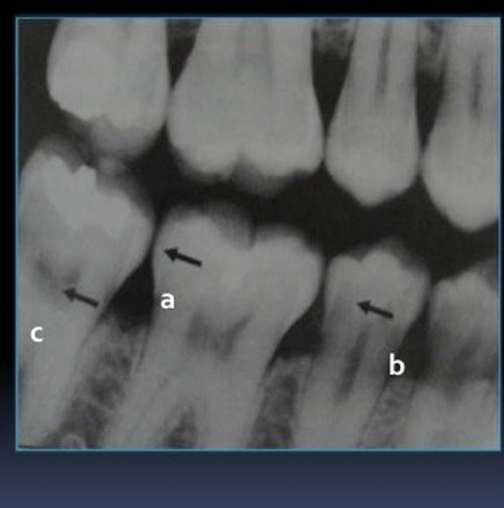
Which anatomy of the teeth is it pointing at?
a - enamel
c- pulp
b- dentin
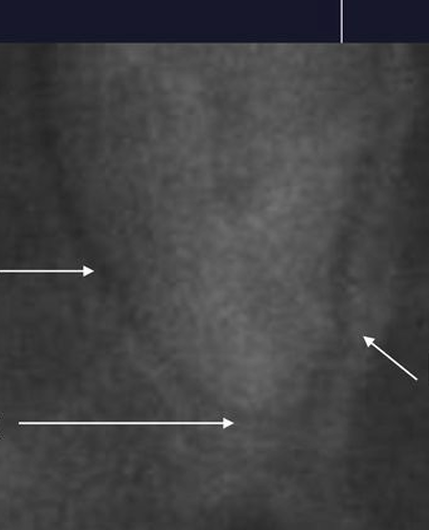
What part of the tooth is being pointed at?
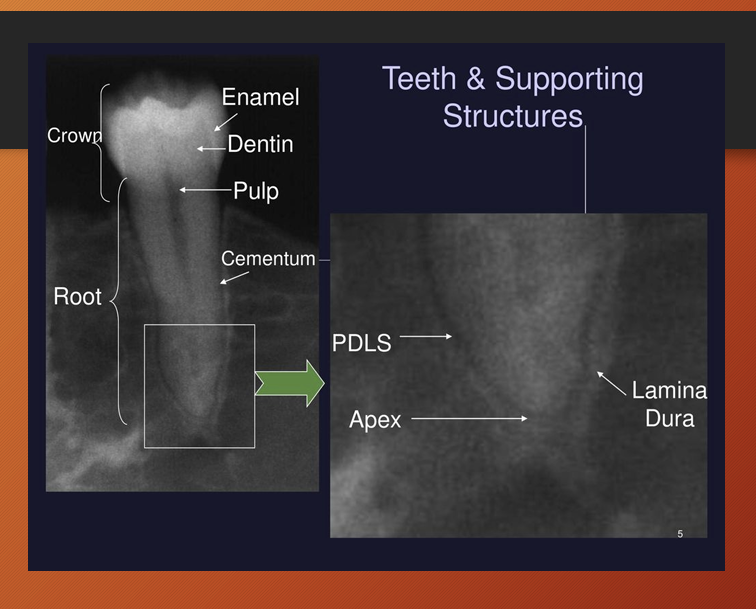
What is the lamina dura?
it is a thin radiopaque layer of dense bone - cortical bone - surrounding the tooth socket
it is thicker than the surrounding trabecular bone - hence appears whiter
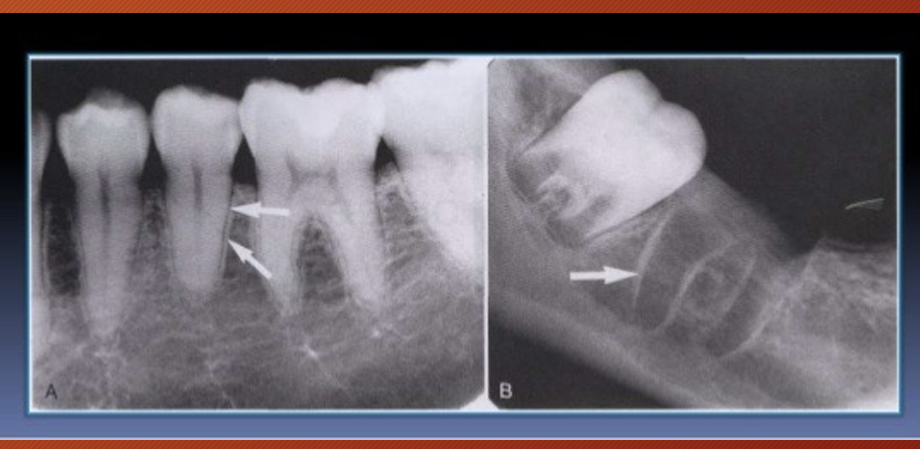
What is being pointed at?
the alveolar crest

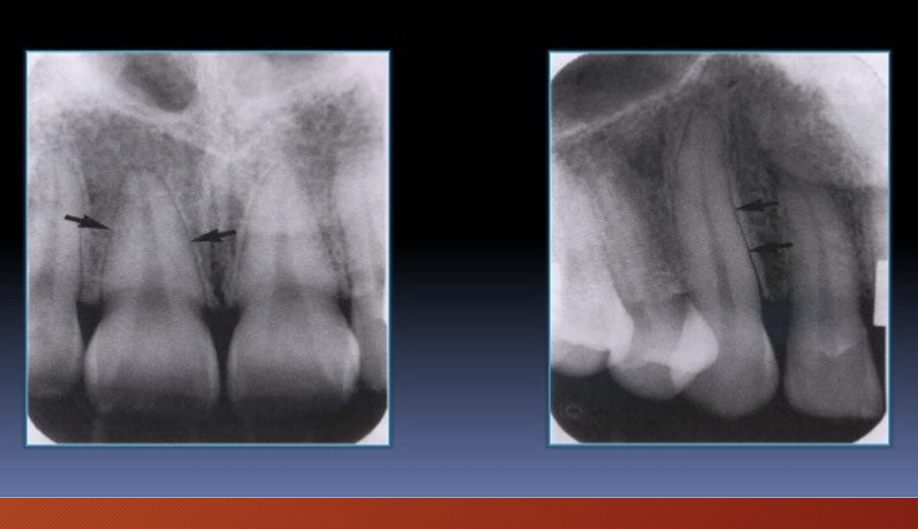
What is being pointed at?
periodontal ligament space - primarily composed of collagen - appears as radiolucent space between root and lamina dura
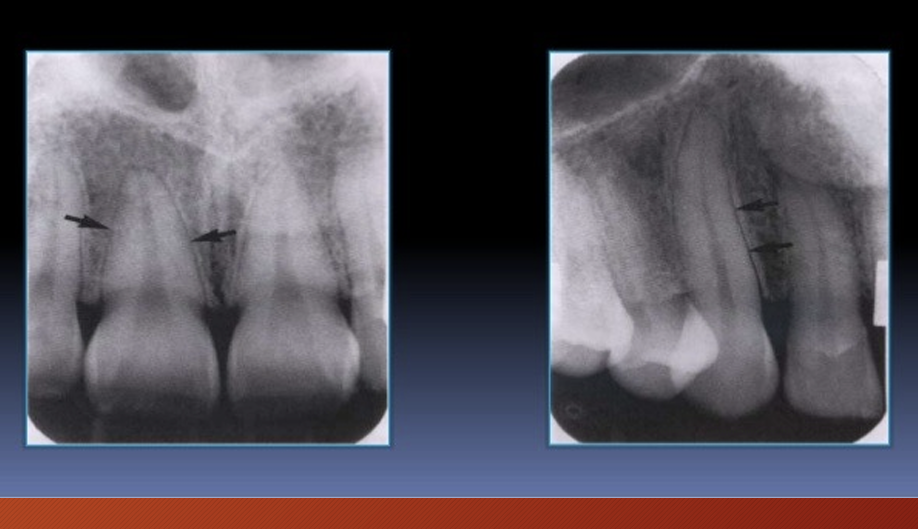
What is this?
cancellous bone - aka trabecular bone or spongiosa
lies between the cortical plates in both the jaws
it is composed of thin radiopaque plates and rods
surrounding many small radiolucent marrow spaces
in posterior maxilla it is similar to anterior maxilla but marrow spaces are larger
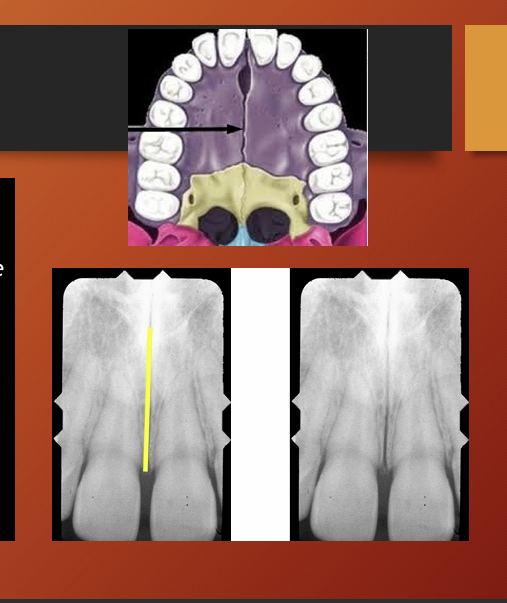
what are some anatomical land marks of the maxilla, list some (13)
intermaxillary suture
anterior nasal spine
incisive foramen
nasal fossa and nasal septum
superior foramina of nasopalatine canal
lateral fossa
nose
nasolacrimal canal
zygoma and zygomatic process of maxilla
nasolabial fold
pterygoid plates
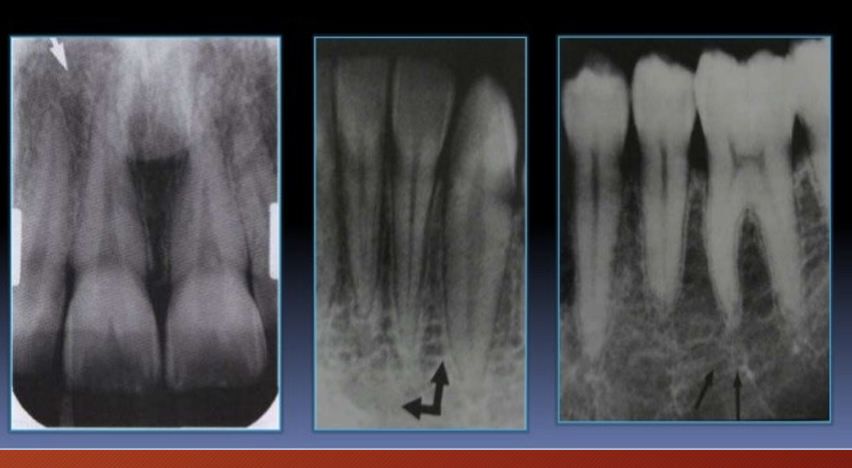
What is this ?
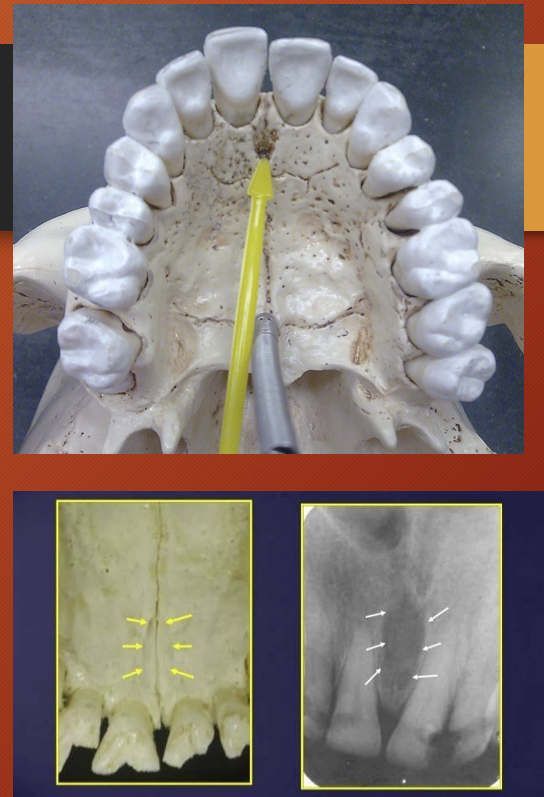
intermaxillary suture aka the median suture
in a panoramic it appears as a thin radiolucent (black) line in the midline between the two portions of maxilla
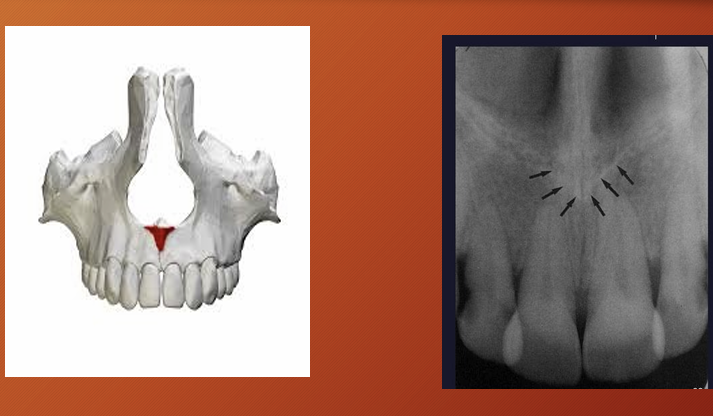
What is this?
anterior nasal spine
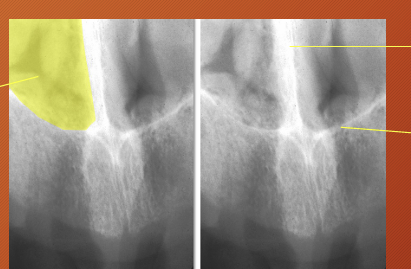
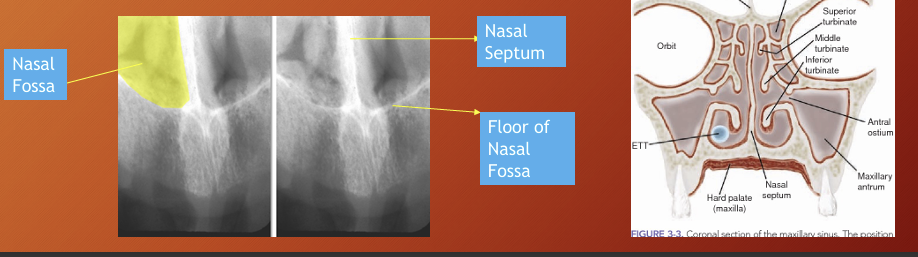
What is this image showing?
the nasal septum divides the nasal cavity into 2 fossae
What is this?
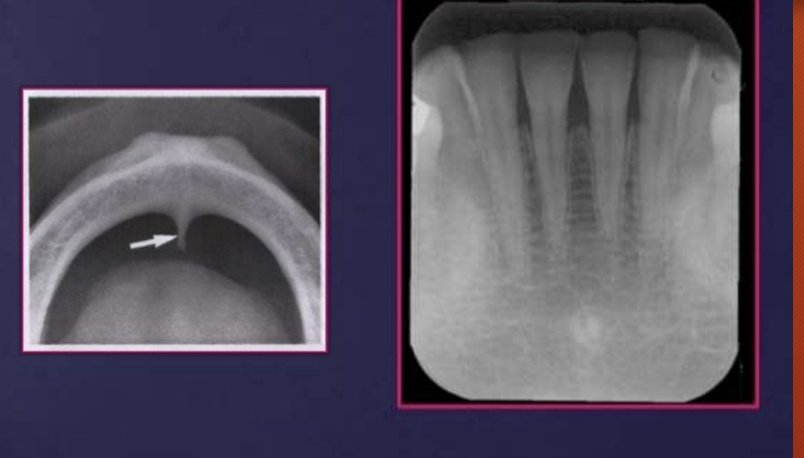
incisive foramen - also called nasopalatine foramen or anterior palatine foramen
it is the opening of the nasopalatine canal
the bone is thinner so appears darker in this case there is nothing wrong with the patient, the incisive foramen can be bigger so this is not an abnormality
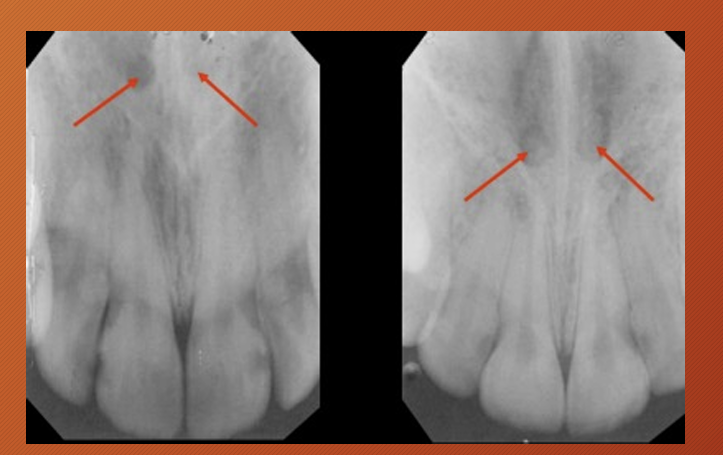
What is this?
superior foramina of nasopalatine canal
What is this?
lateral fossa
a gentle depression in the maxilla near the apex of the lateral incisor
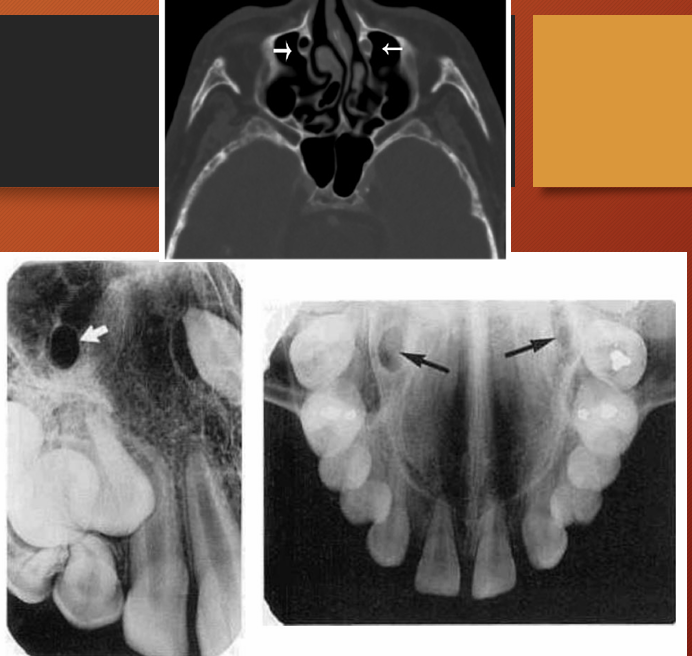
What is this?
nasolacrimal canal
the canal containing the nasolacrimal duct
What is this?
radiographic features of nose - soft tissues of the nose
What is this ?
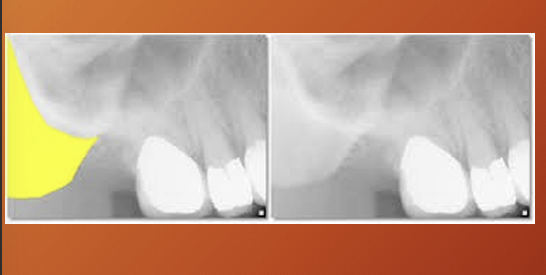
maxillary sinus - air containing cavity lined by mucous membranes
important to rake a full panoramic so you can compare one side to the other
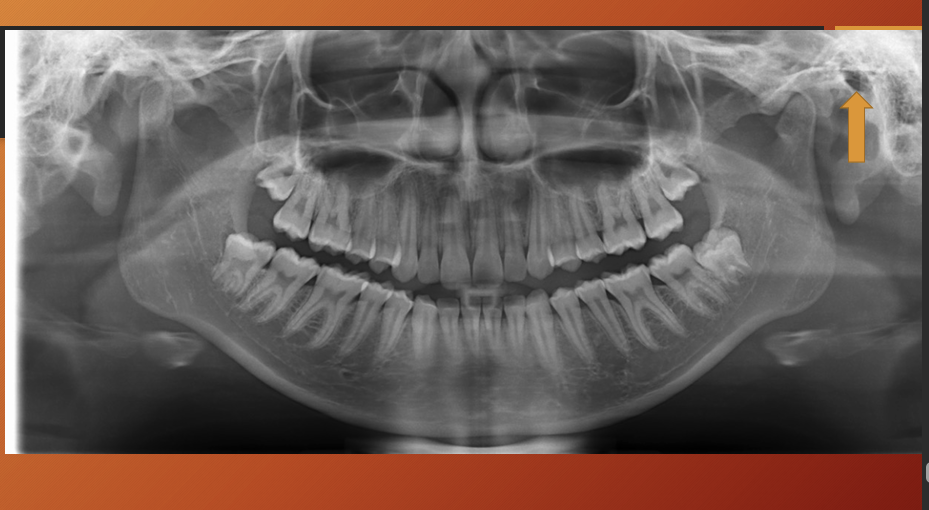
What has happened to the maxillary sinus in this image?
pneumatization - physiological process of expansion of sinus wall into surrounding bone , usually in an area where teeth have been lost prematurely
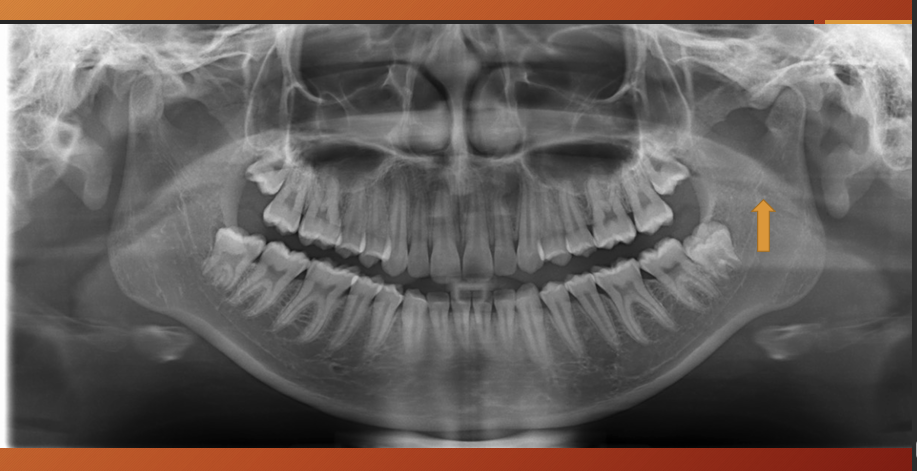
What is this?
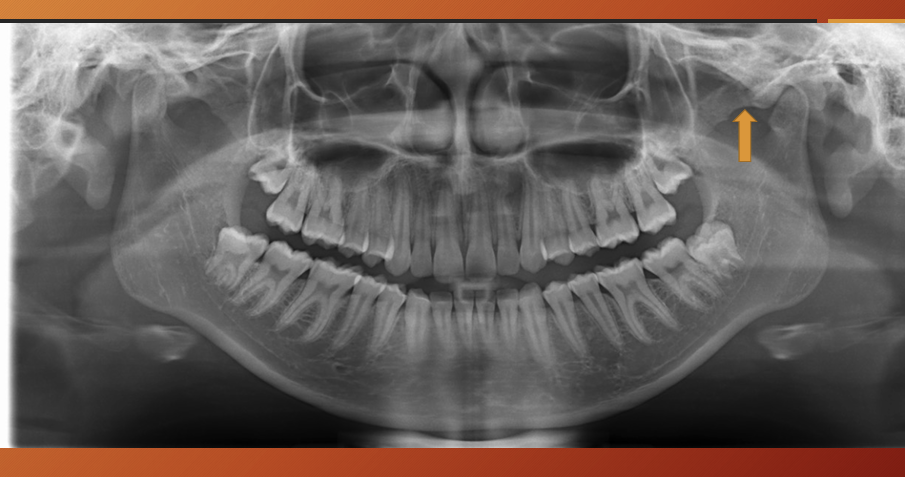
zygomatic process
What is this?
Zygomatic bone - zygoma
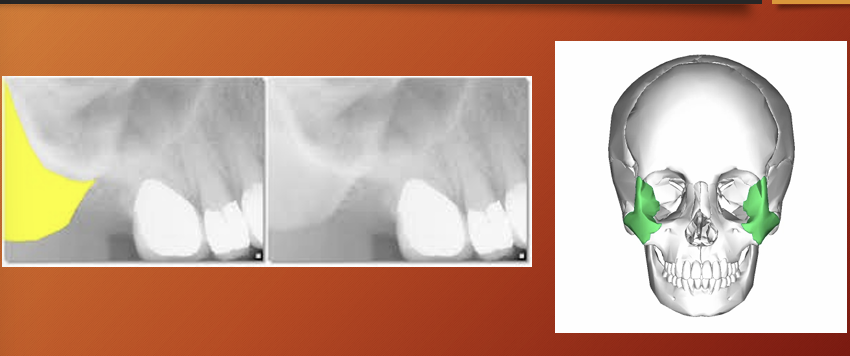
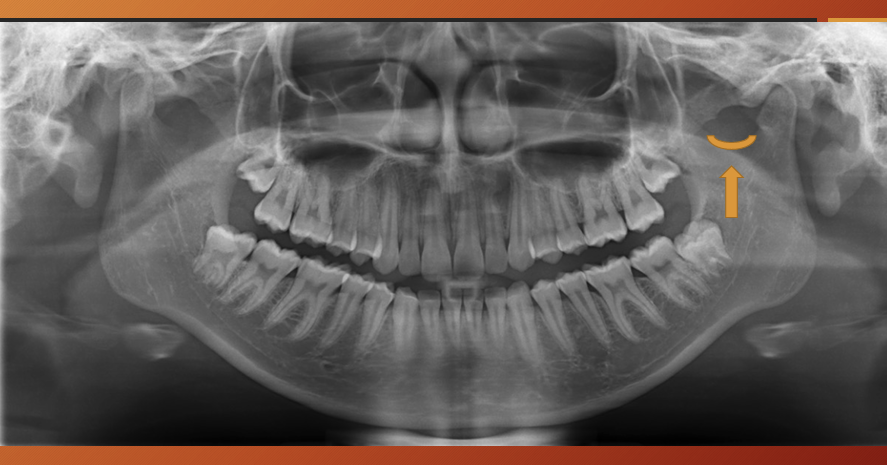
What is this?
pterygoid plates
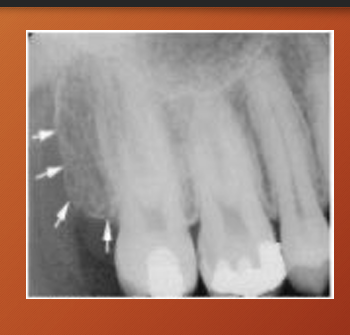
What is this?
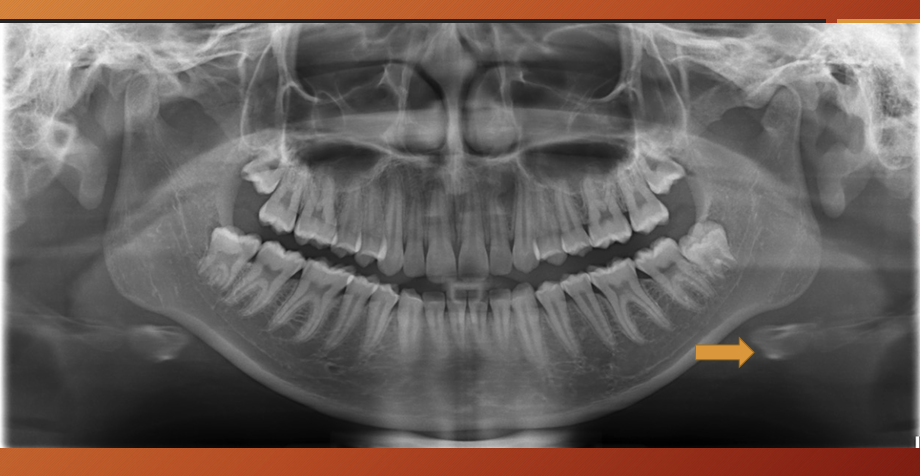
Maxillary tuberosity
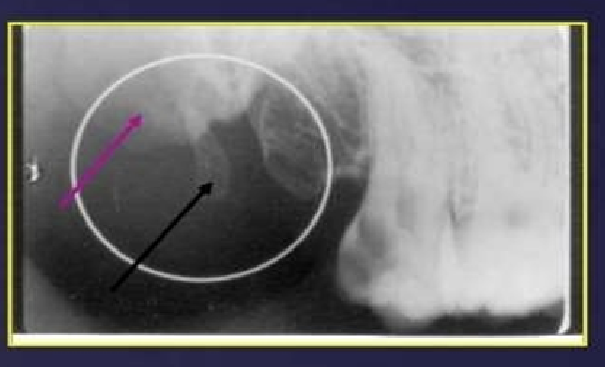
What is this?
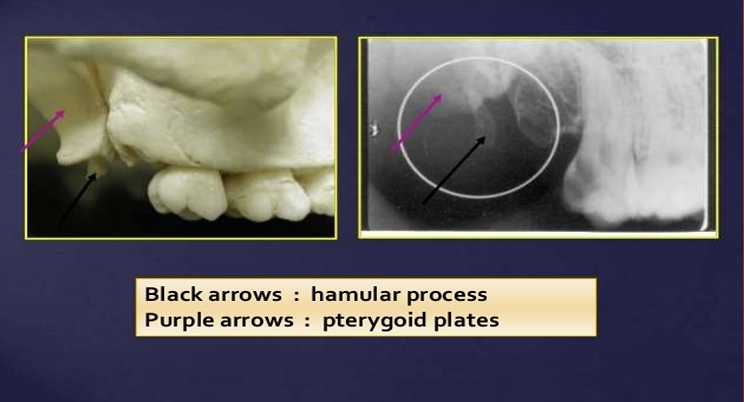
What is this ?

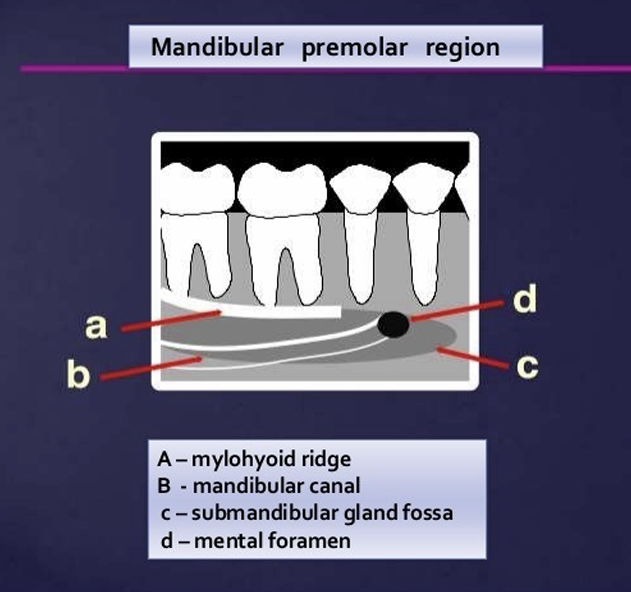
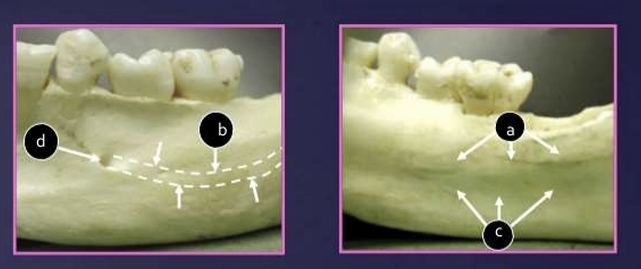
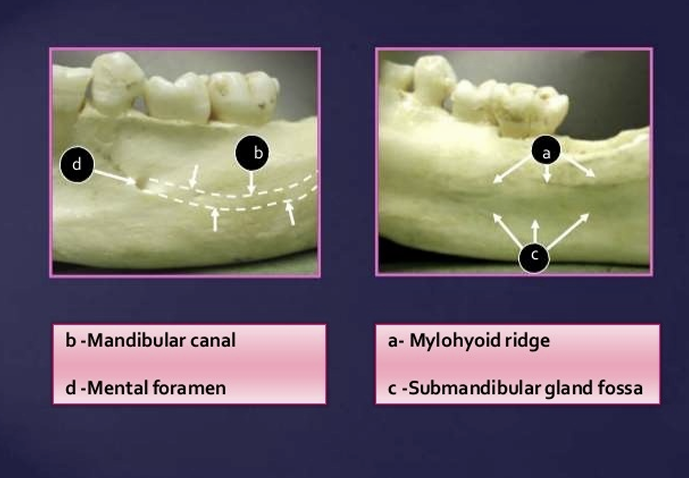
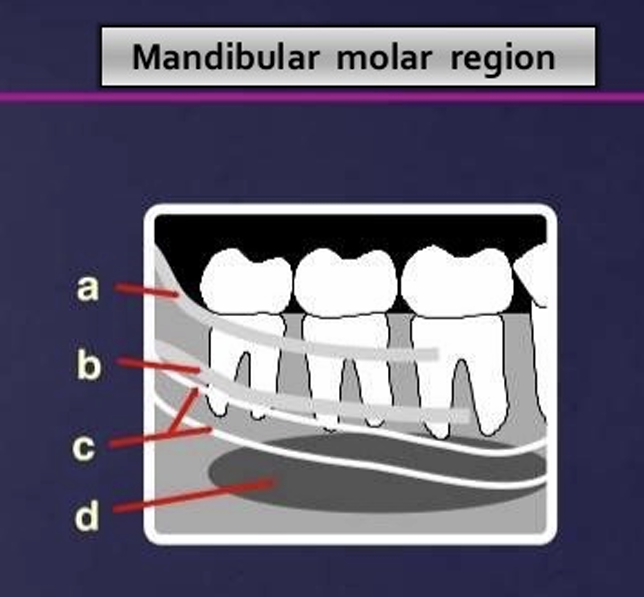
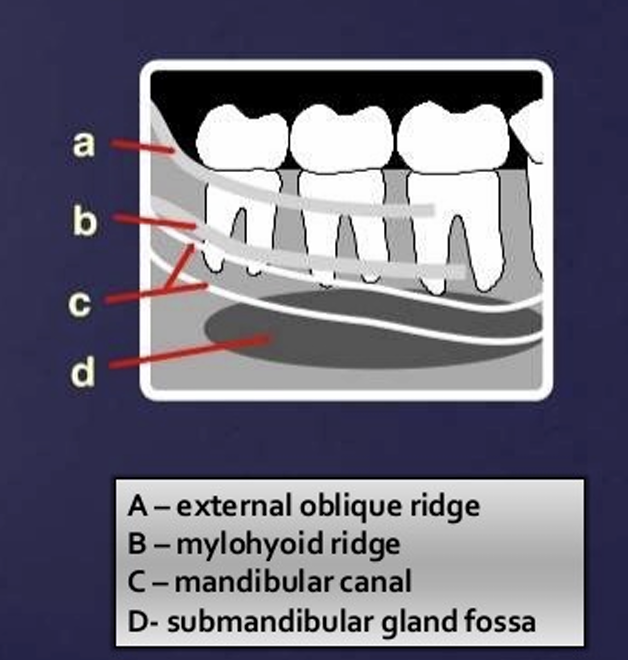
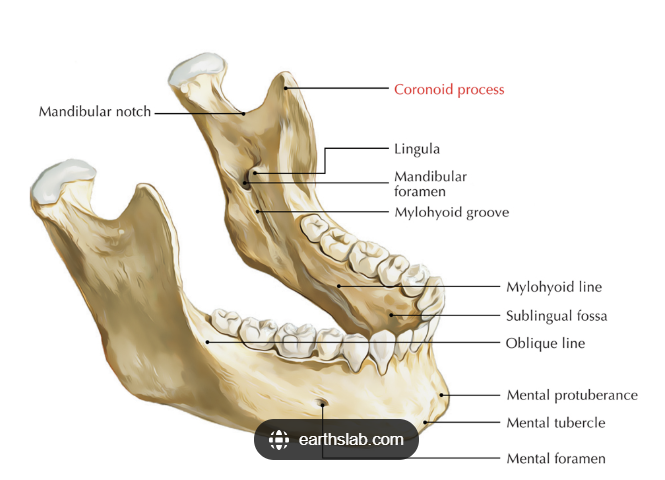
What are some landmarks of the mandible?
lingual foramen
genial tubercle
mental foramen
external oblique line
internal oblique line
mylohyoid line
mandibular foramen
inferior alveolar canal
submandibular gland fossa
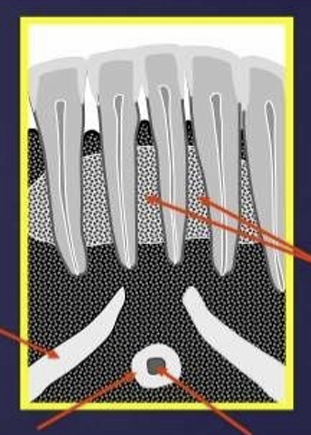
Label
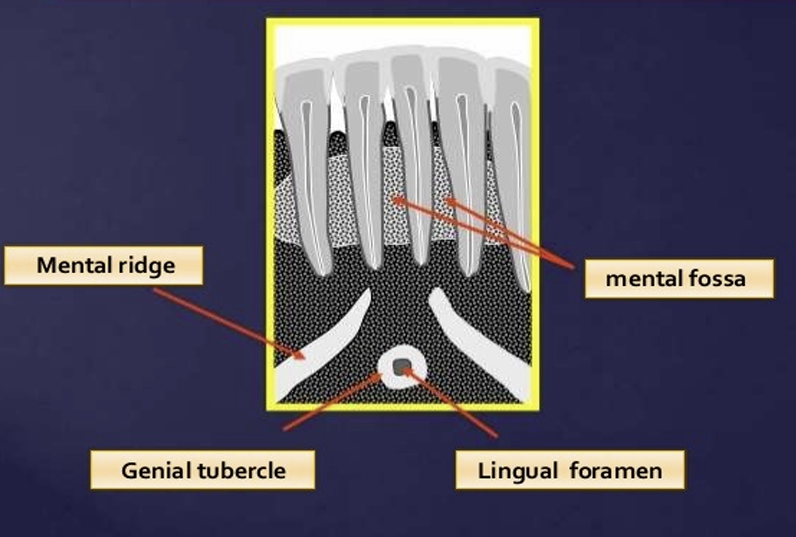
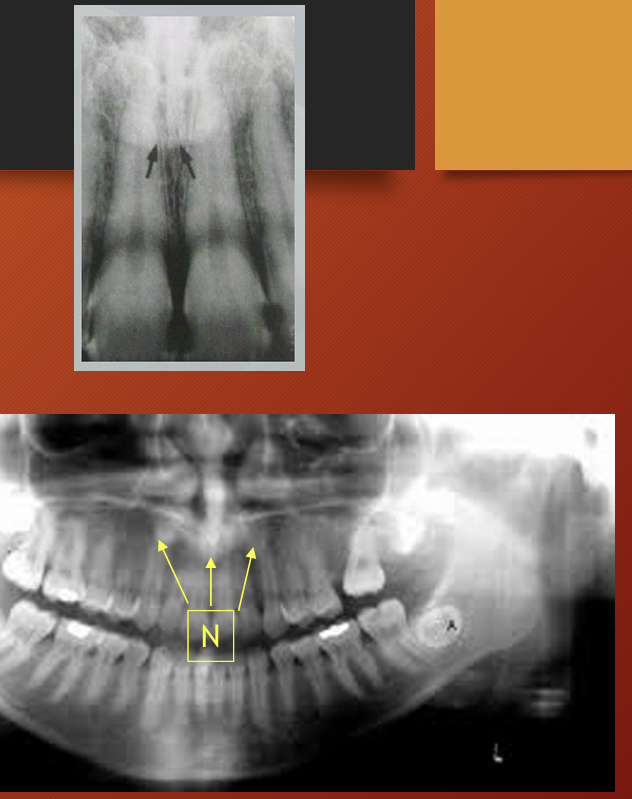
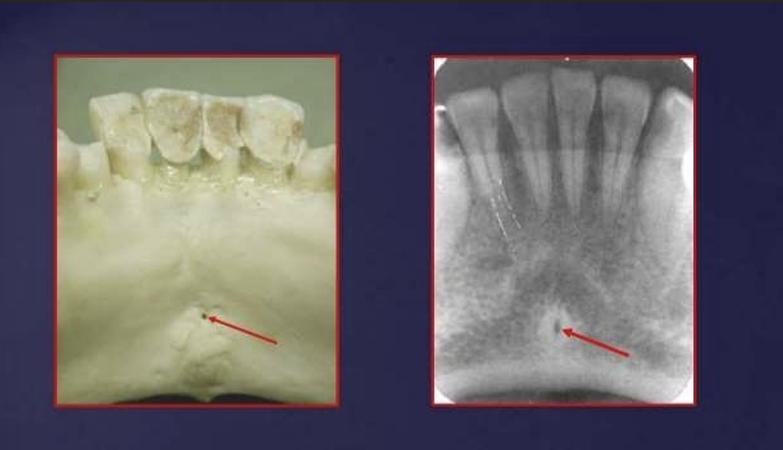
What is the lingual foramen and genial tubercles?
lingual foramen: radiolucent ‘hole’ in centre of genial tubercles
lingual nutrients pass through this foramen
in the image you can see the mental fossa, and mental ridge
the genial tubercles appear where?
as radio-opaque circles that surround the lingual foramen just below the apices of the incisors
What is this?
mental ridge
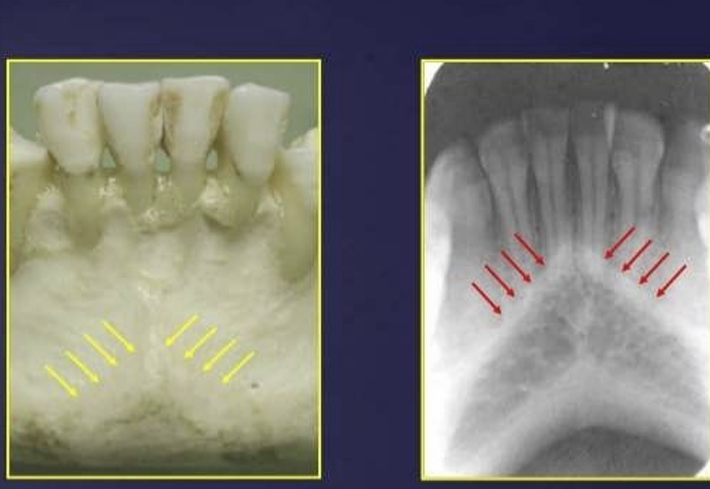
What is this?
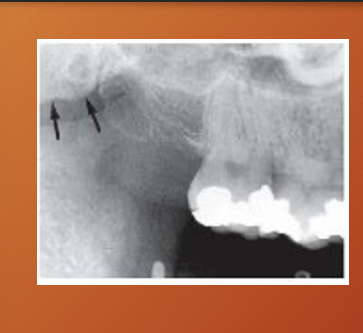
nutrient canals - often seen in patients with thin bone and in those with high blood pressure or advanced periodontitis
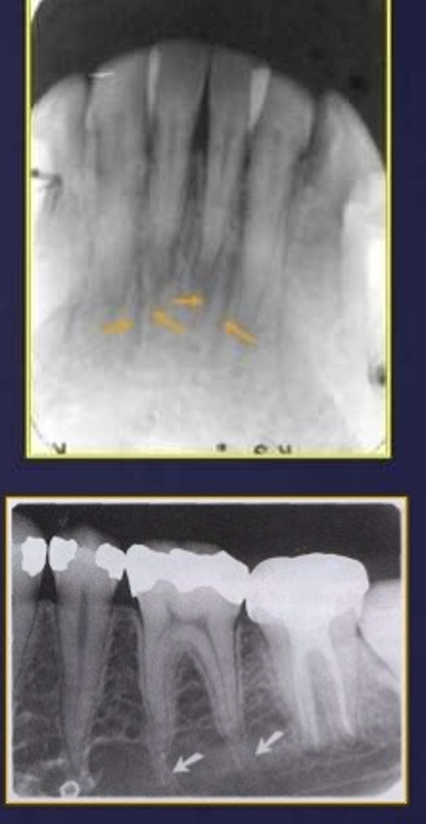
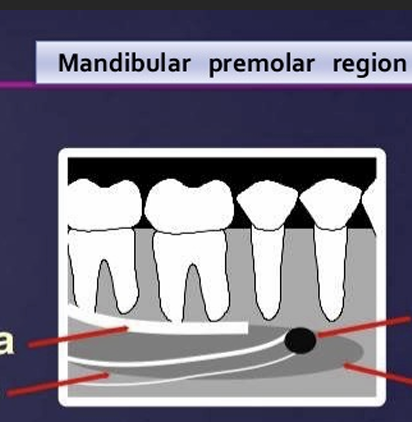
What is this?
mental foramen
it appears as radiolucent, ill defined area between the apices of bicuspids - pre-molars
it represents the anterior terminates of the mandibular canals
What is this?
label
What is this?
mental foramen
What is this?
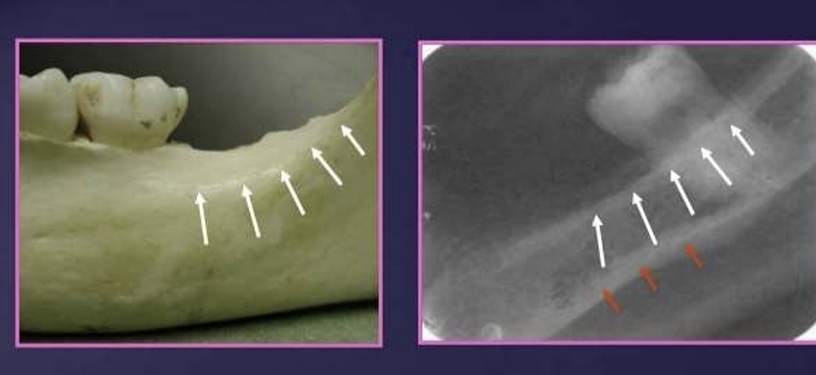
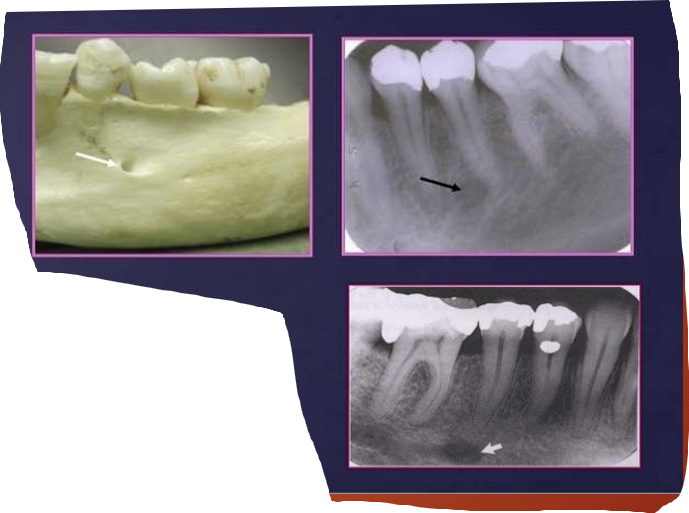
What is the white and red arrow pointing at?
White arrow is the external oblique ridge
red arrow - mylohyoid ridge
Where does the external oblique ridge start and end?
external oblique ridge - a continuation of the anterior border of ramus passing downwards and forwards on the buccal side of the mandible
it appears are a radio-opaque lines which usually ends anteriorly in the area of the first molar
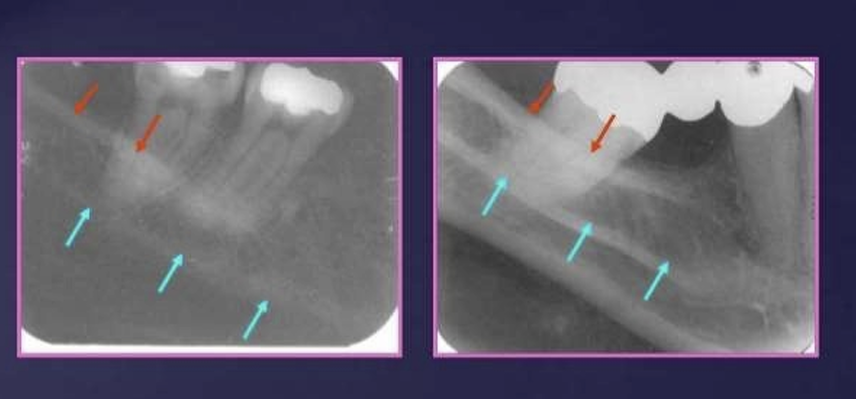
What is the relationship of the external oblique ridge and the mylohyoid ridge?
usually run parallel to each other
with the external oblique ridge always being higher on the film
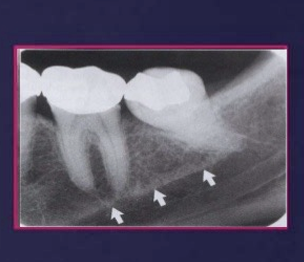
What is this?
internal oblique ridge
How does it appear on a radiograph?
it appears as an oblique line descending downwards and forwards from coronoid process, in a horizontal position , stops at the third molar area or become continuous with the mylohyoid line
placed below the external oblique ridge
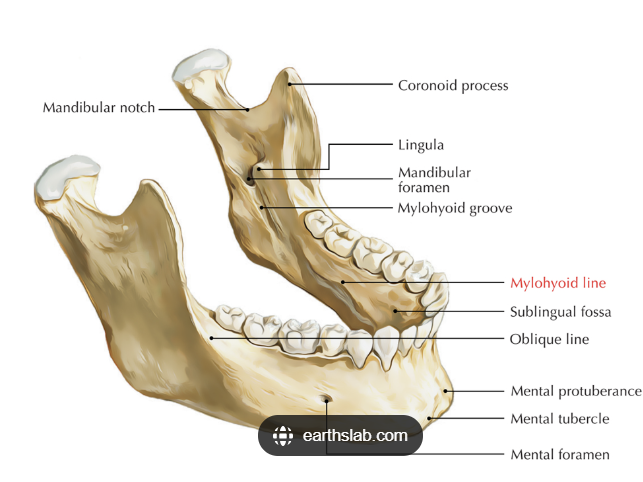
the mylohyoid ridge (internal oblique) extends from which surface of the mandible?
located on the lingual surface of the mandible , extending from the third molar area to premolar region
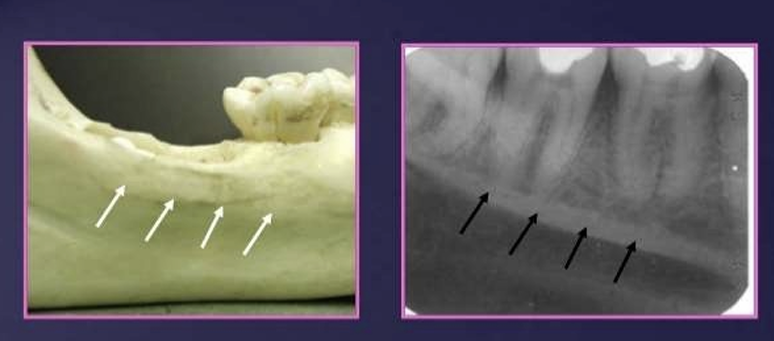
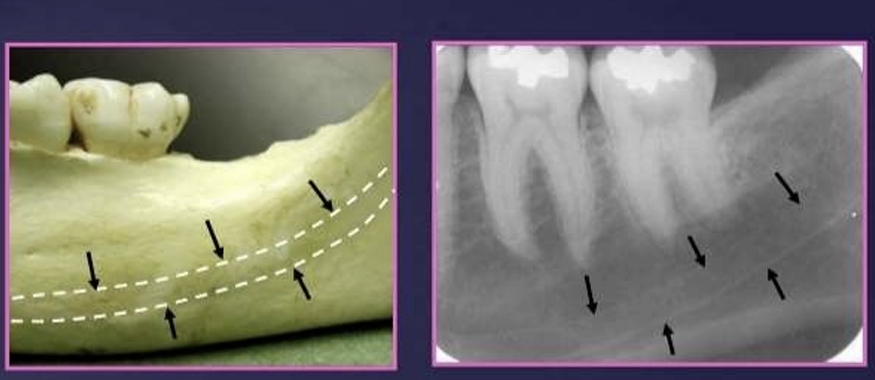
What does the mandibular canal contain?
arises at the mandibular foramen on the lingual side of the ramus and passes forwards and downwards, moving from the lingual side in the third molar region to the buccal side in the premolar region
it contains the inf alveolar nerves and vessels
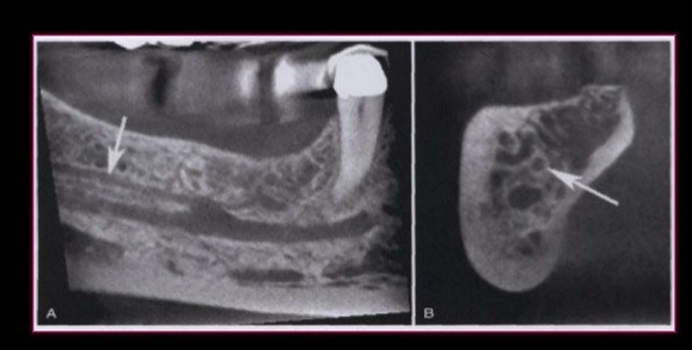
bifid mandibular canal
a) cone beam scan
b) cross section
pterygomaxillary fissure
pterygoid plate
earlobe
shadow of the spine
EAM
hyoid bone
mandibular notch
articular eminence, actually its the mandibular fossa of teh temporal bone
mandibular foramen
41 - soft palate
21- hard palate
43 - posterior pharyngeal wall?
46 - nasopharyngeal air space
40 - tongue
nasopharyngeal airspace
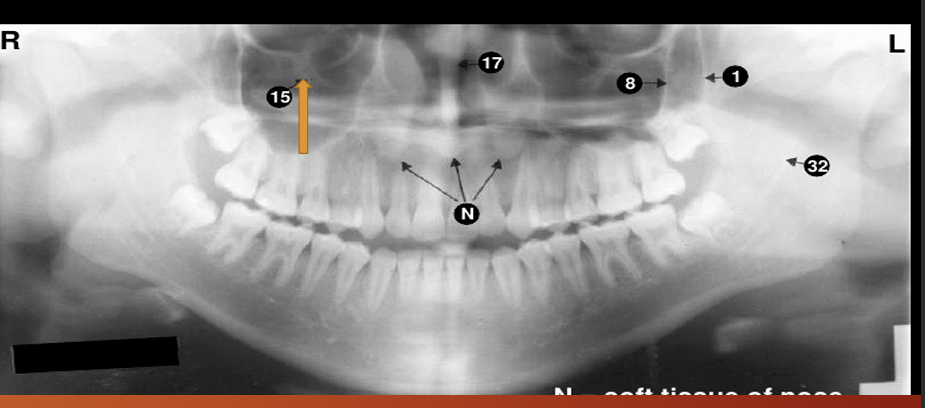
15?
15 - infraorbital canal
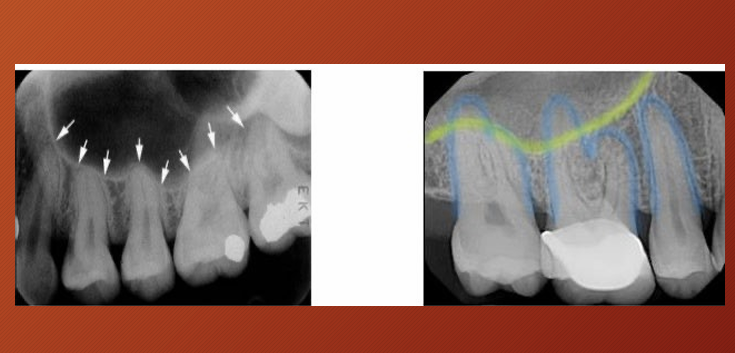
radiographic scoring of dental caries?
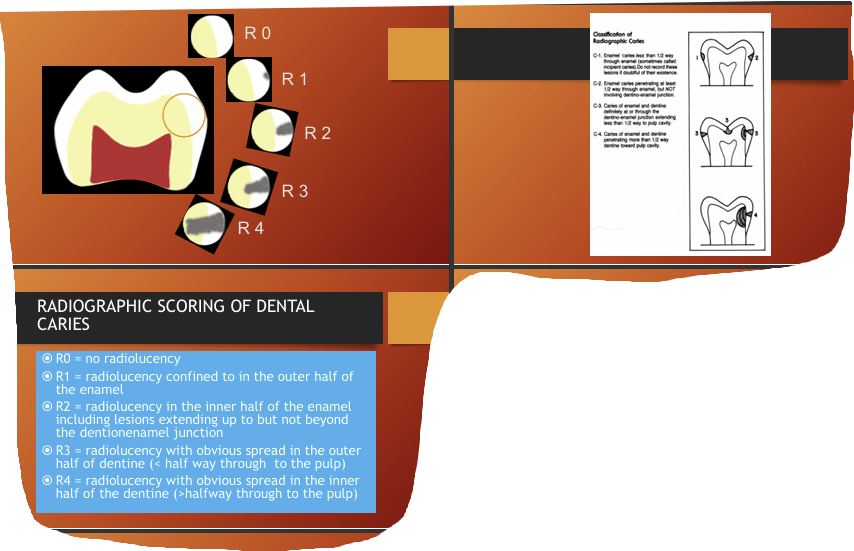
What are some factors affecting appearances of caries? (5)
•Buccolingual thickness of the tooth
•Superimposition of structures-2D imaging of 3D structure
•X-ray beam not paralleled
• Incorrect exposure factors
•Cervical burnout/Mach band effect
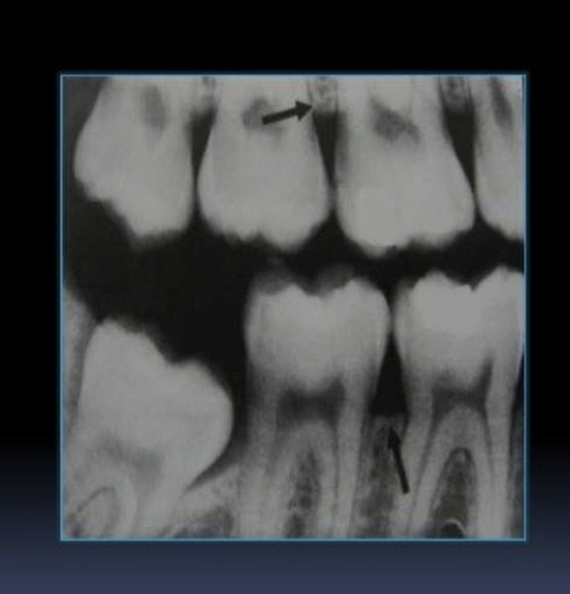
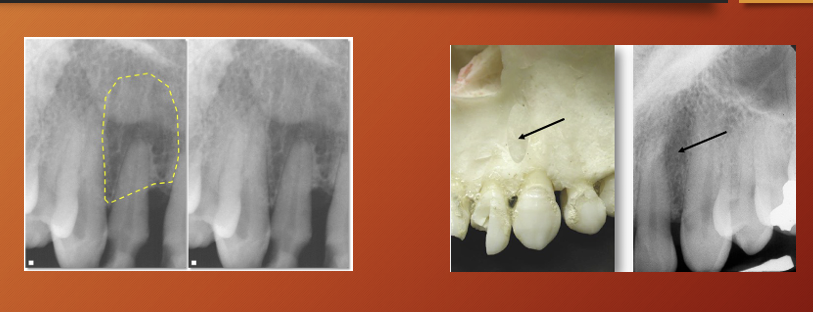
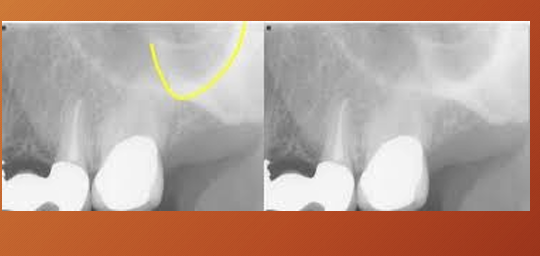
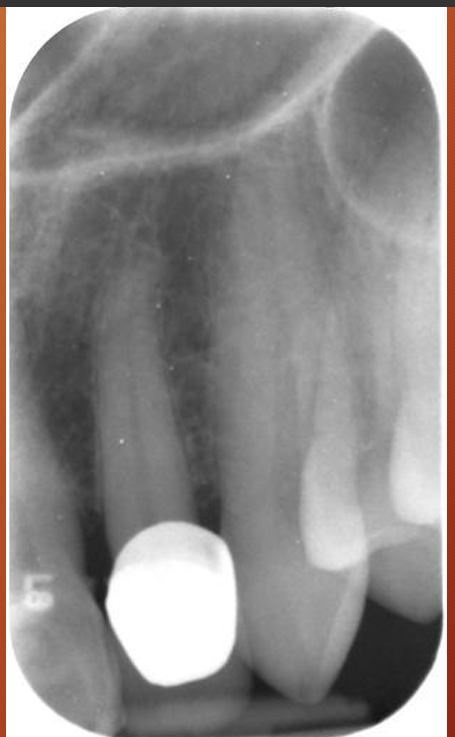
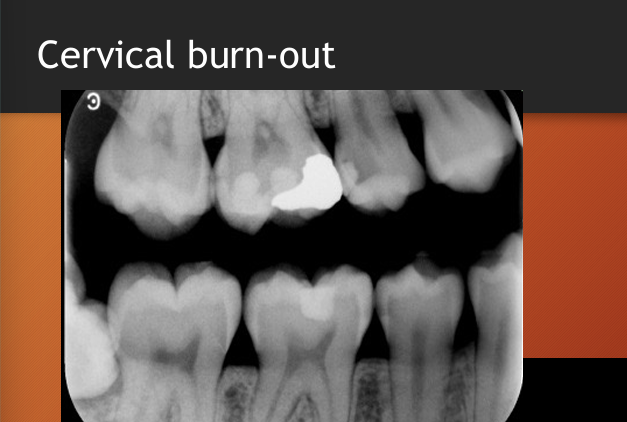
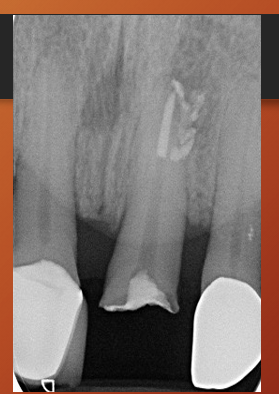
What is cervical burnout?
artefactual phenomenon,
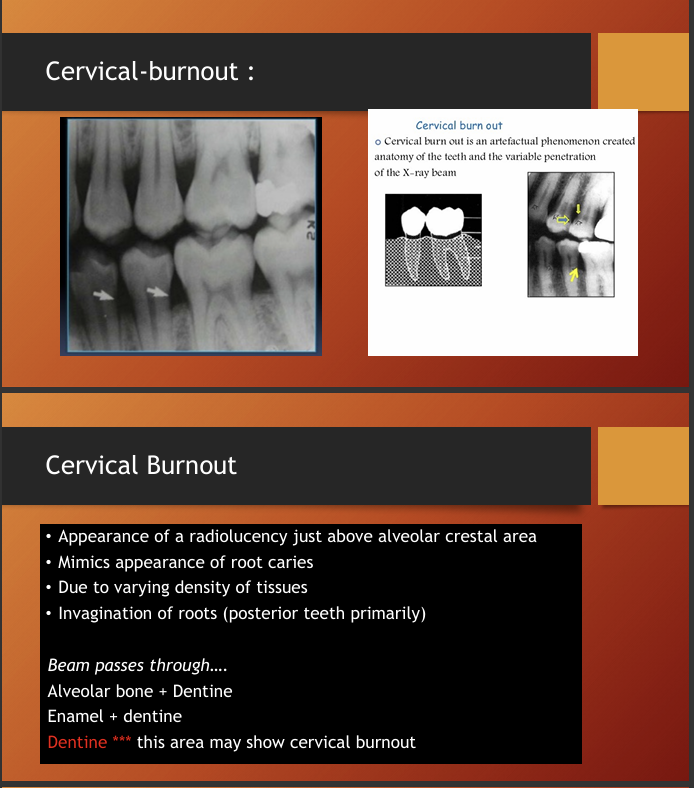
so cervical burnout should not be confused with what?
root caries
What are Mach bands?
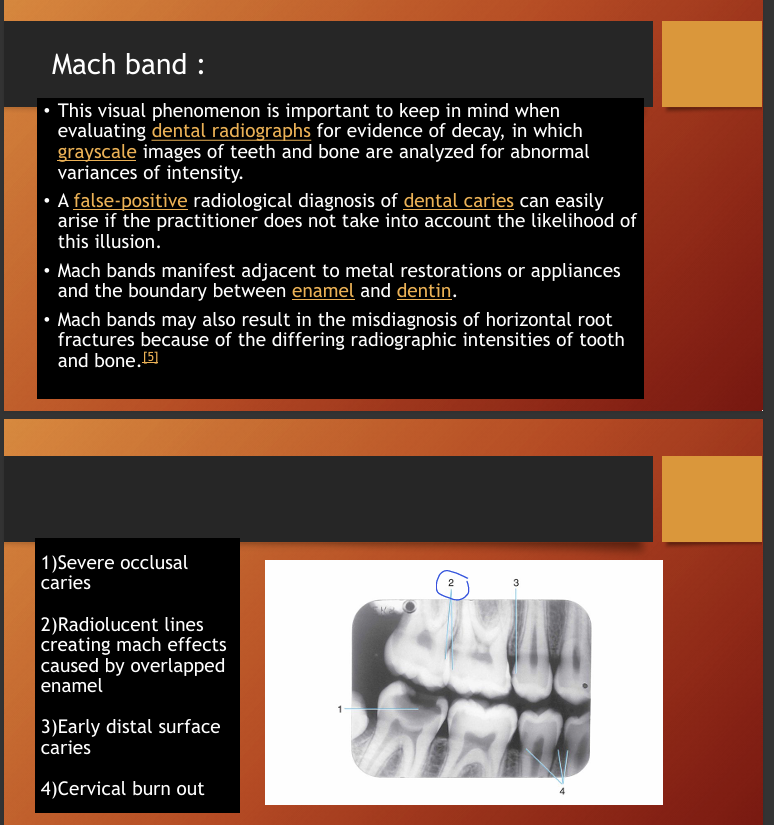
Mach bands in this image?
the line around the crown looks black but its an optical illusion
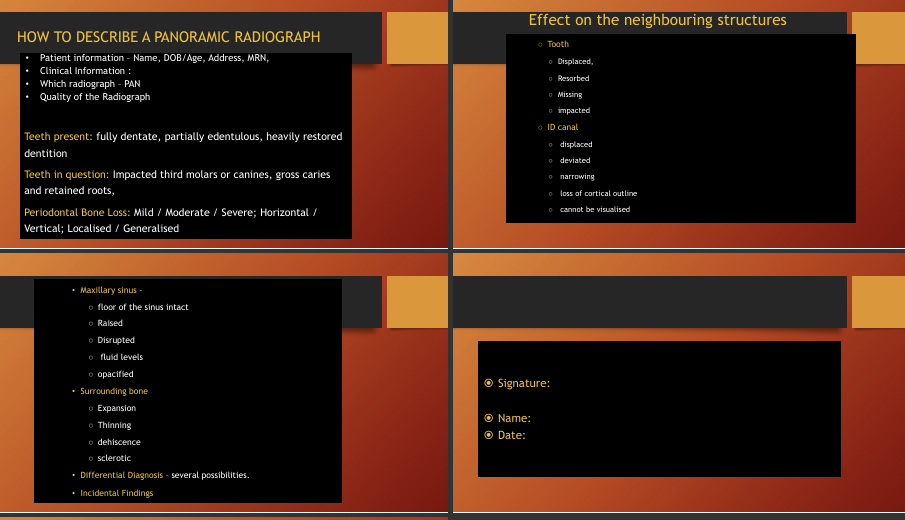
How do you describe a radiographic description of a lesion?
size/extension - e.g UR 1 to UR 2
shape - round/oval/irregular
effects such as resorption

How do you request a radiograph?

What is included in a radiological report?

How to describe a panoramic ?