CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 7: Animal nutrition
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Balanced diet
A balanced diet provide all 7 classes of nutrients in the right amount

Explain how age, gender and activity affect
the dietary needs
A child needs more energy than an adult because they have a higher basal metabolic rate (BMR) the energy is used for growth, to make new cells
Malnutrition
Daily intake of food does not meet amount required for 7 classes of nutrients
Starvation
Starvation is the result of a severe or total lack of nutrients needed for the maintenance of life.

Constipation
Lack of roughage or fibre. Roughage adds bulk to our food and keep it moving down alimentary canal, constipation is the result of lack of roughage thus making it hard to defecate

Obesity
Having too much body fat in the body
Causes:
-high intake of fatty foods
-high intake of processed foods
-too little exercise
-emotional stress leading to 'stress eating'

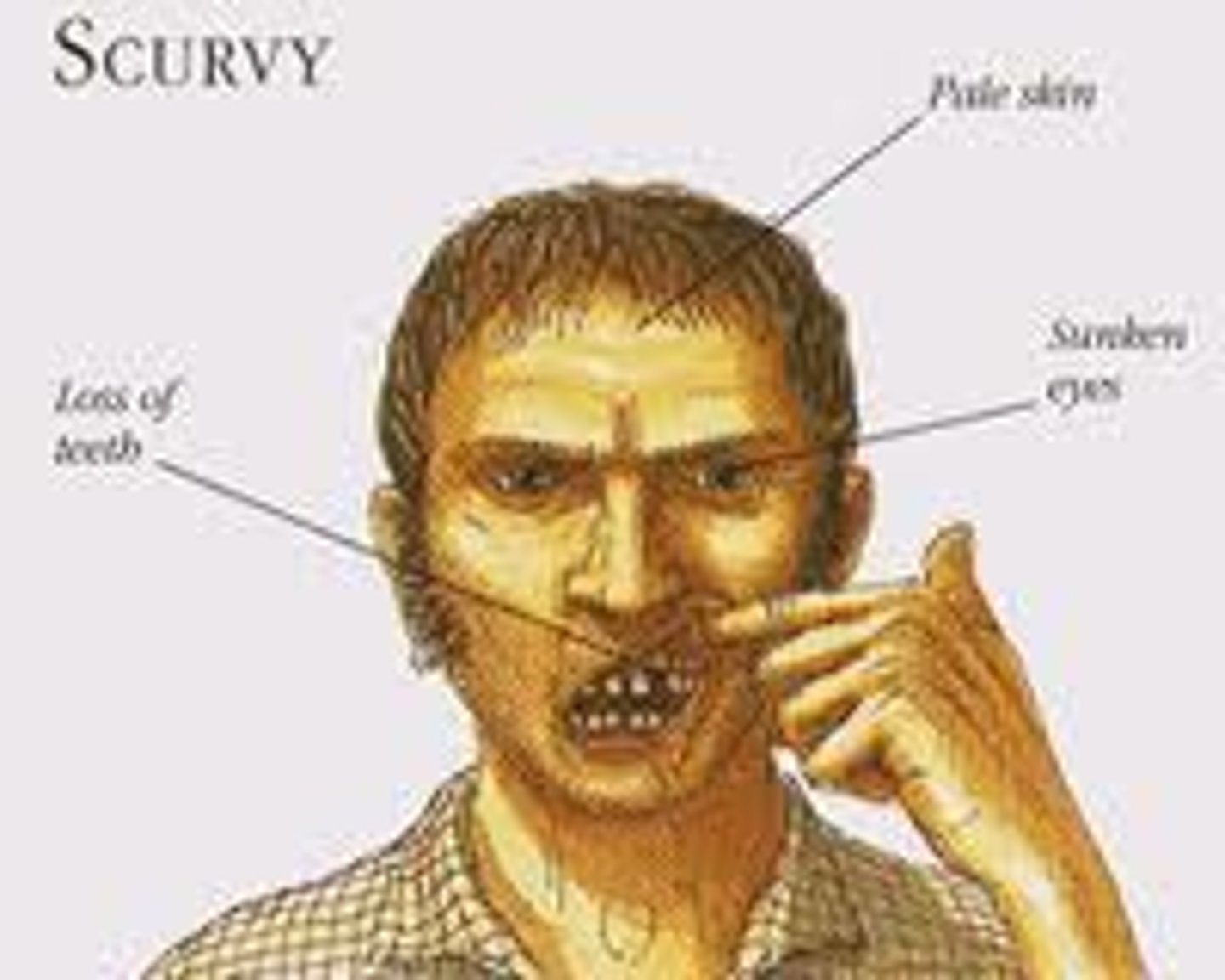
Scurvy
Lack of vitamin C, symptoms include bleeding and weak gums, poor wound healing
Dietary importance of carbohydrates
To provide energy

Dietary importance of fats
Helps in dissolving fat soluble vitamins (A,D,E,K)

Dietary importance of proteins
Used for growth and repair

Dietary importance of vitamin C
Needed for healing wounds

Dietary importance of vitamin D
Needed for absorption of calcium and promote bone growth

Dietary importance of calcium
Building and maintaining bones

Dietary importance of iron
Helps in transport of oxygen in red blood cell

Dietary importance of fibre (roughage)
Add bulk to food to promote bowel movement (prevent heart disease, diabetes and weight gain)

Dietary importance of water
Used for all bodily functions including digestion

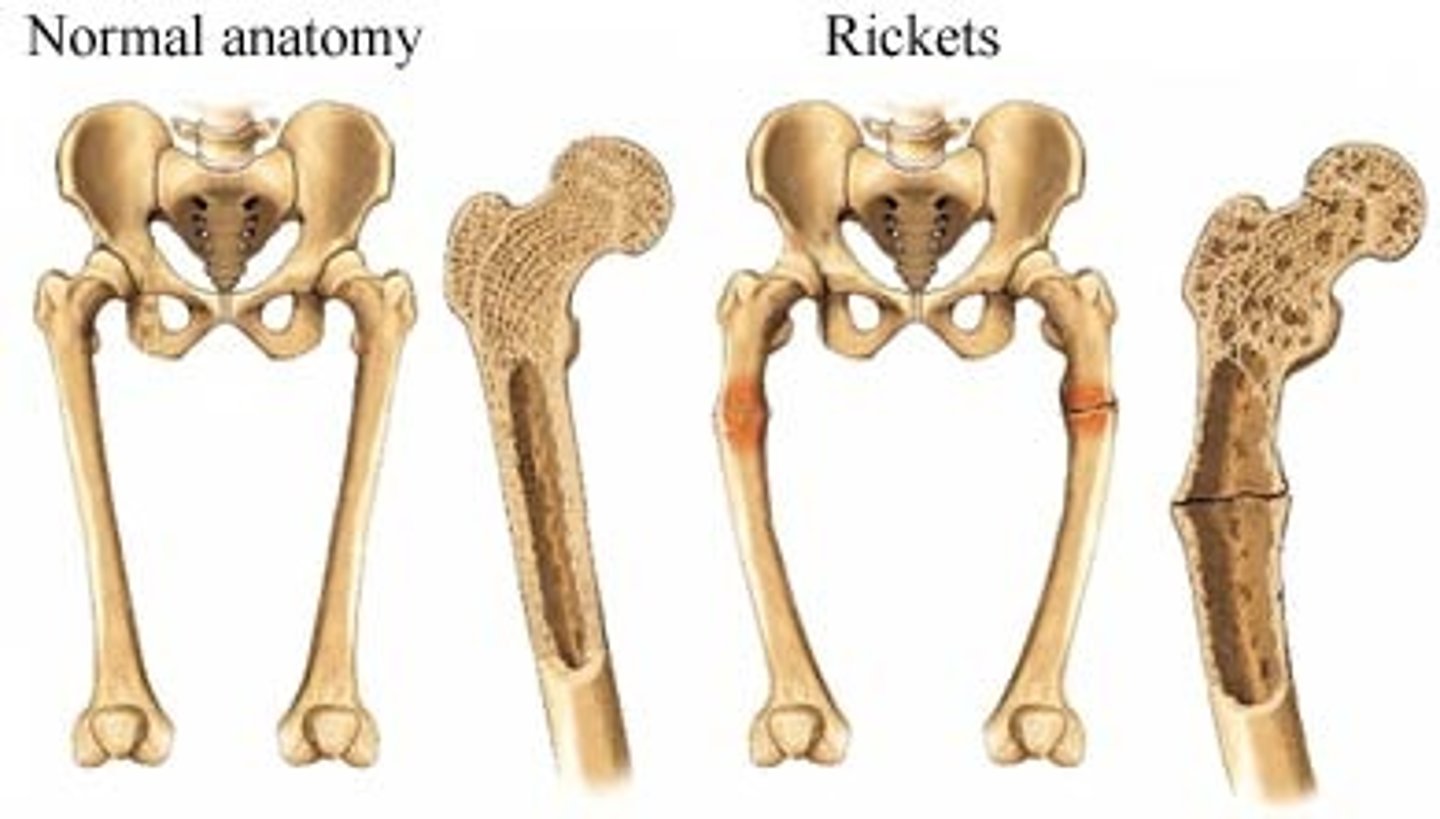
Rickets
Lack of calcium causes brittle bones
Anaemia
Lack of iron or haemoglobin in blood causes tiredness
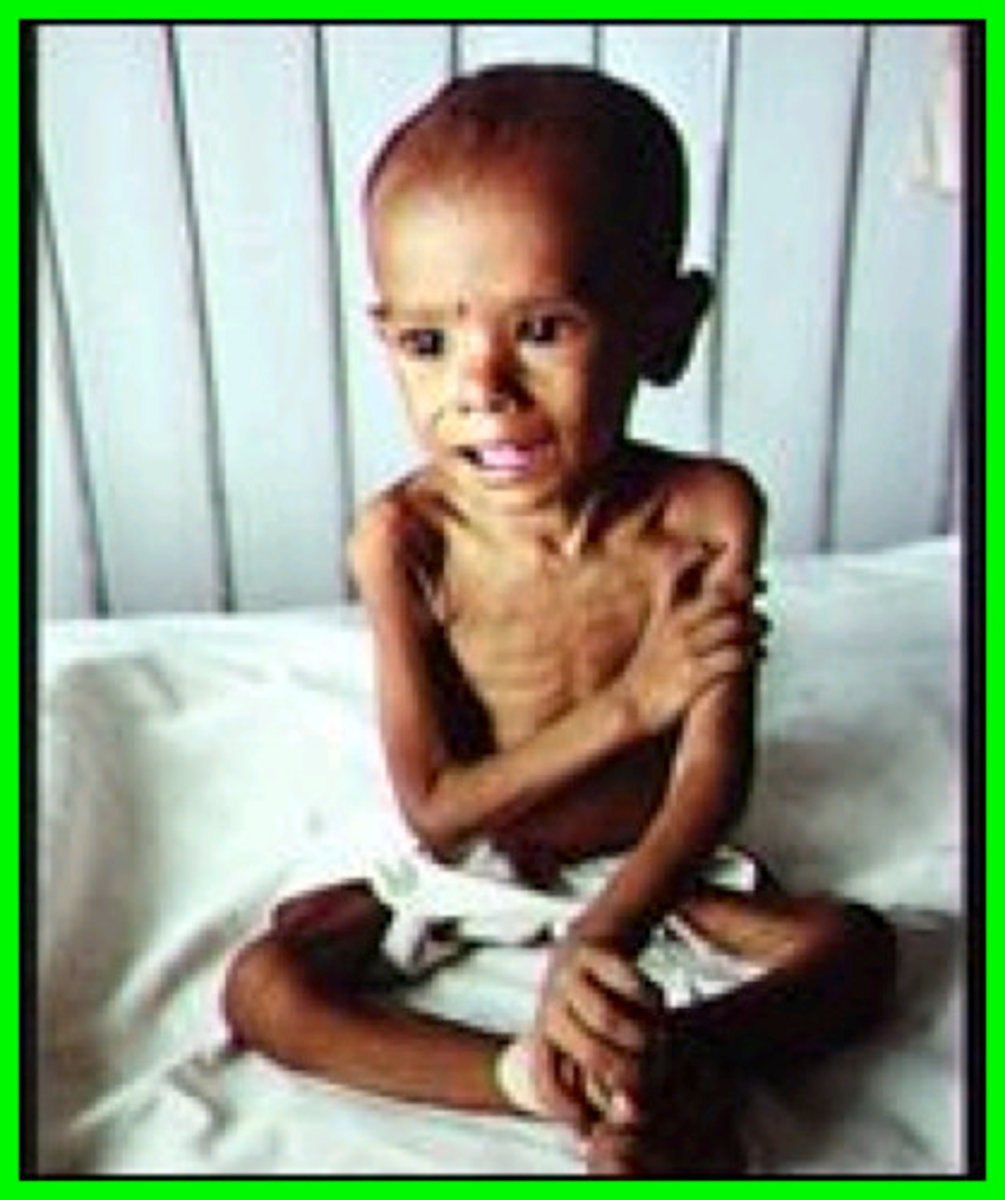
kwashiorkor
Lack of protein, symptoms are oedema (swelling of abdomen and legs), fat accumulation in liver, dry hair
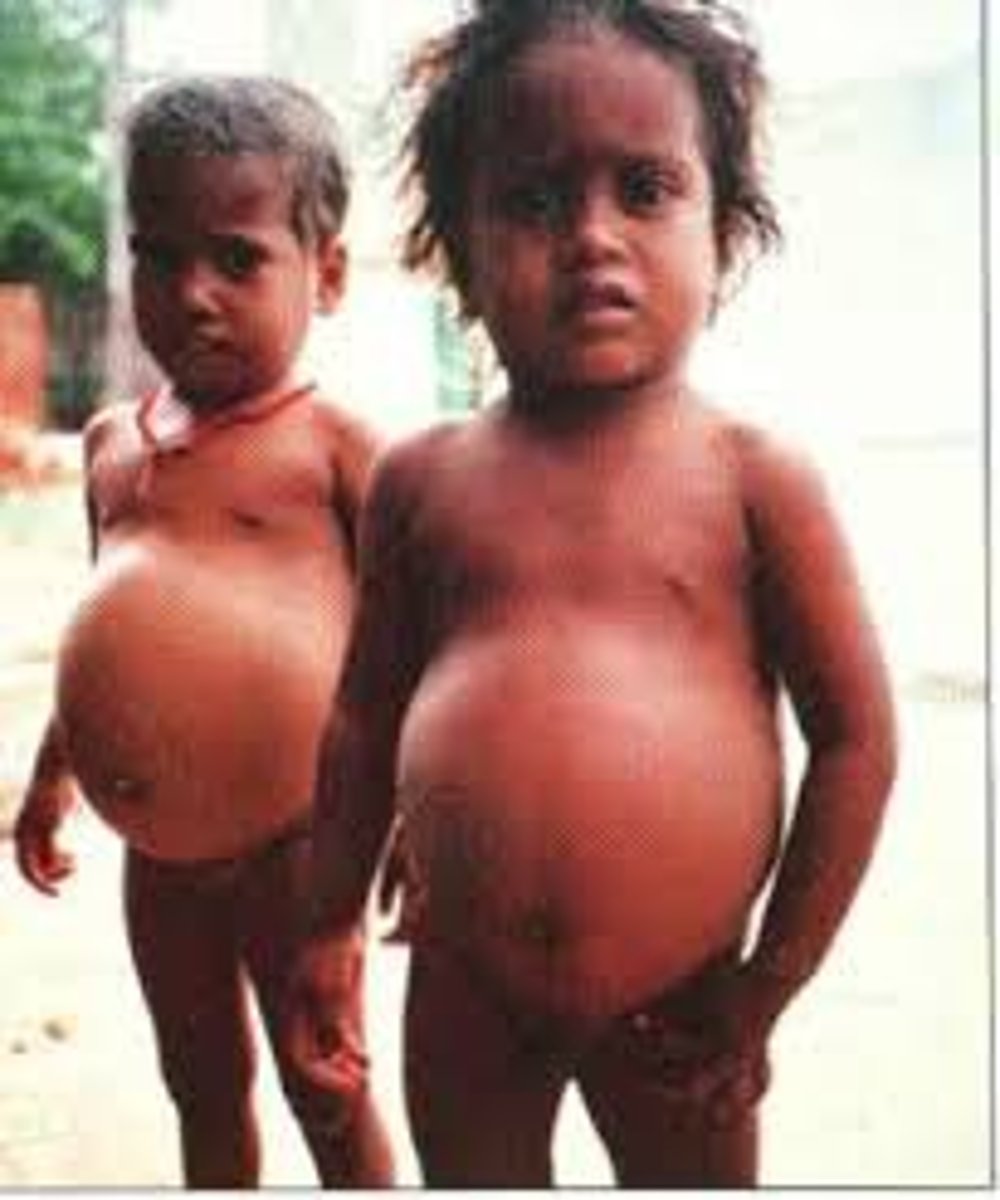
marasmus
Lack of protein, symptoms are very low body mass, thin limbs, little muscle and fat
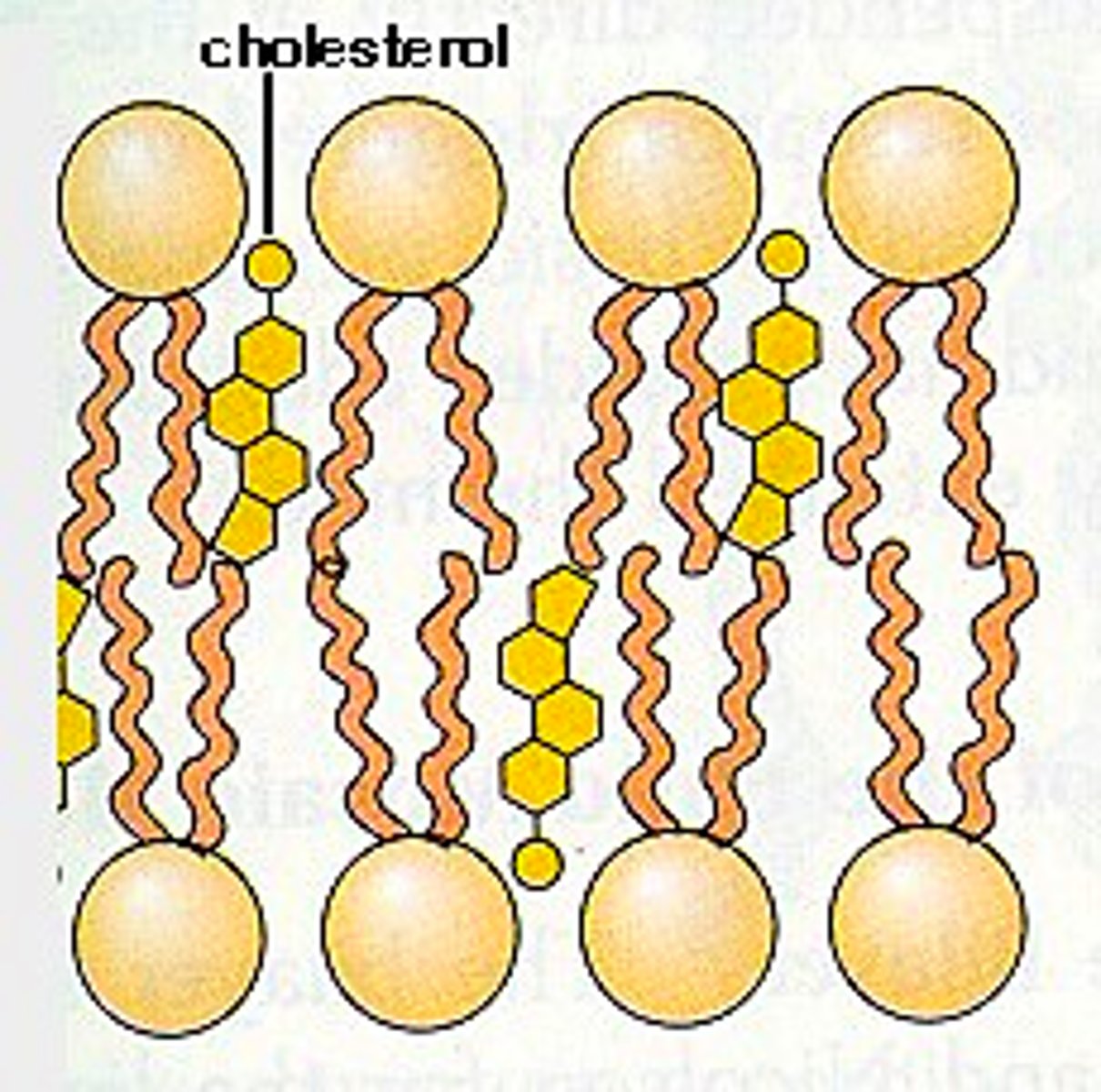
Cholesterol
Stick to arteries causing blockage
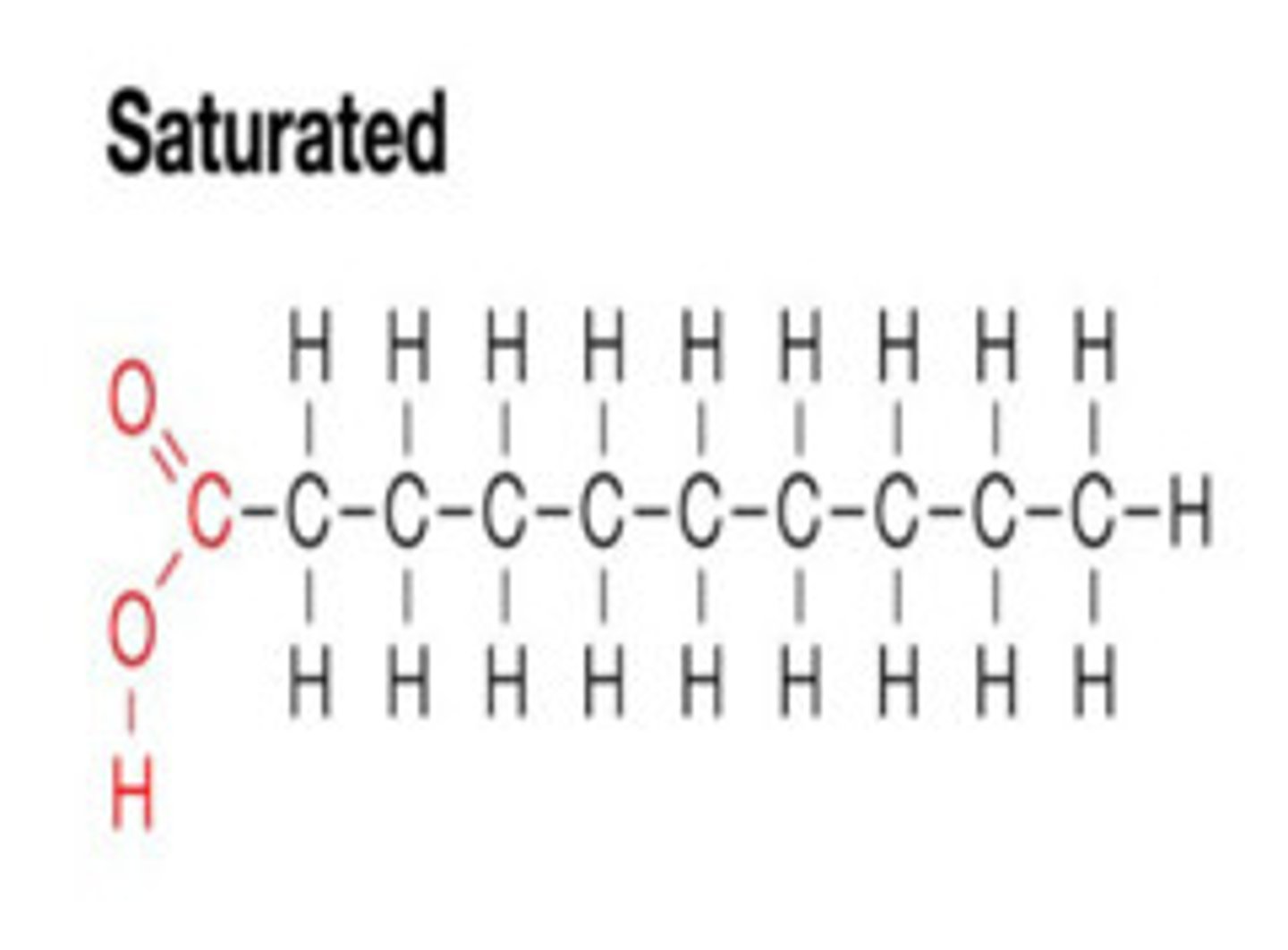
Saturated fats
Fat molecules with no double bonds, mainly comes from animal fats
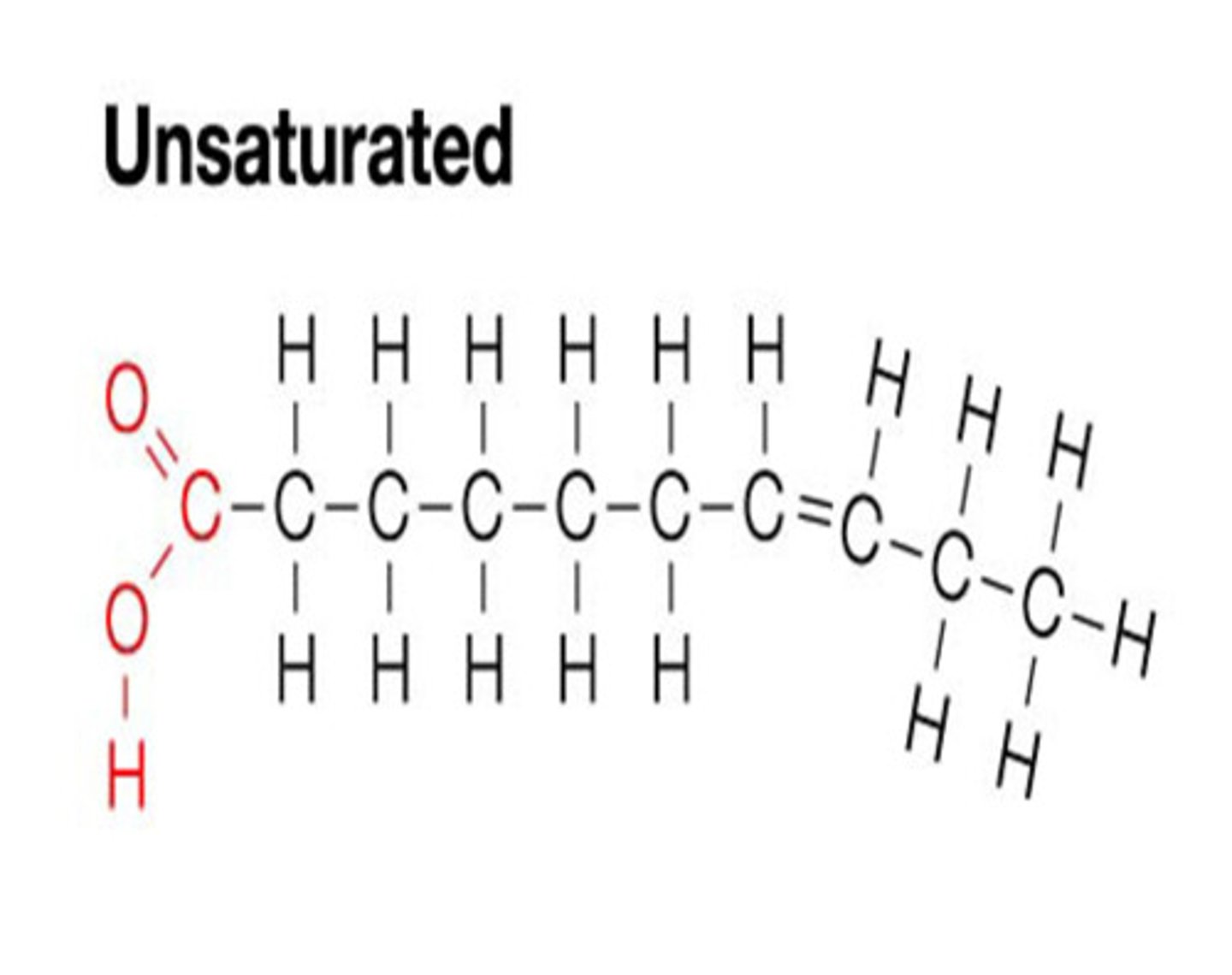
Unsaturated fats
Two types of unsaturated fats
-mono-unsaturated fats: have little effect on blood cholesterol
-poly-saturated fats: help reduce cholesterol concentrations
Ingestion
The taking of substances into the body through the mouth

Digestion
Chemical or mechanical process of breaking down foodstuffs to substances that can be absorbed.
Absorption
the movement of small food molecules and ions through the wall of the intestine into the blood
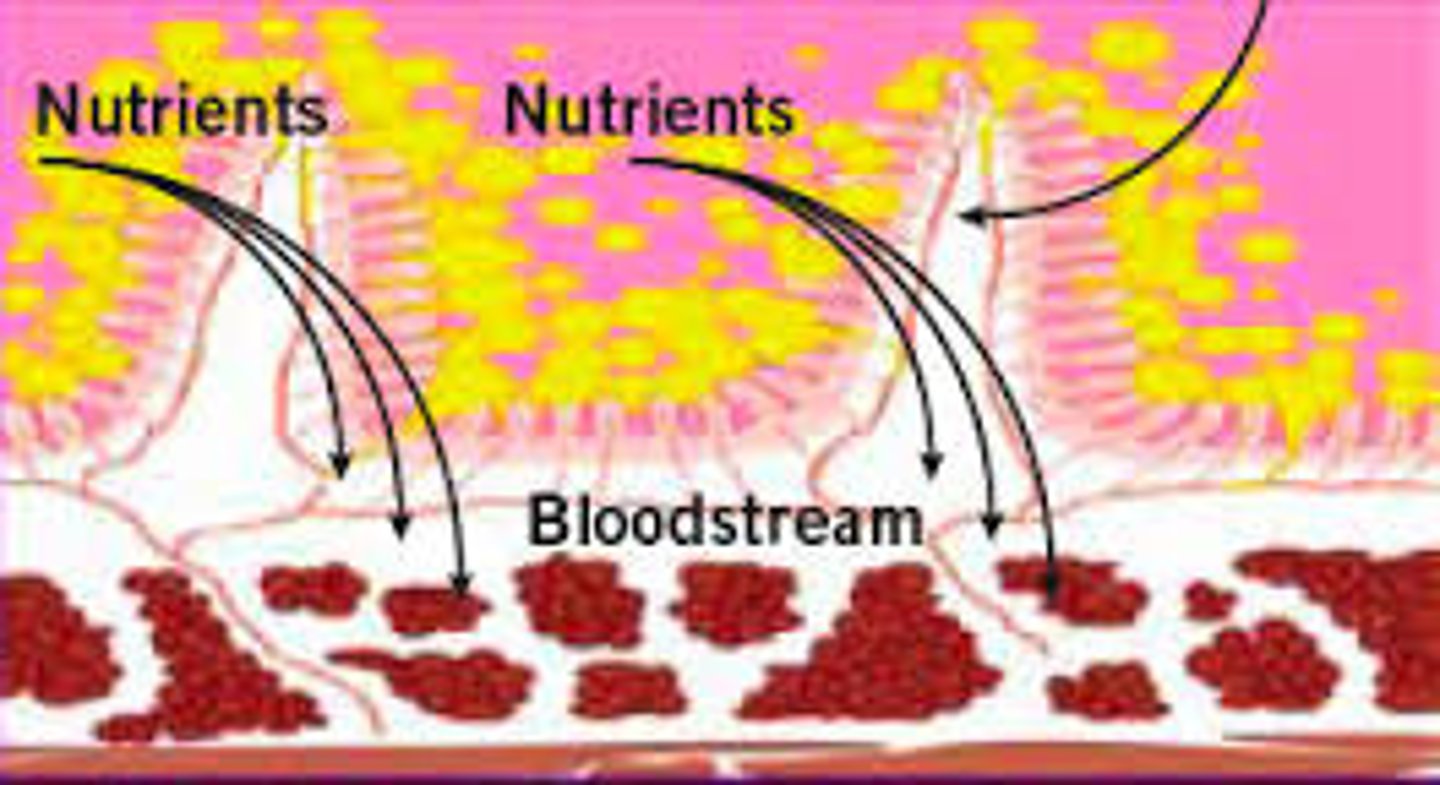
Assimilation
the movement of digested food molecules into the cells of the body where they are used, becoming part of the cells
Egestion
the passing out of food that has not been digested or absorbed, as faeces, through the anus
Chemical digestion
the breakdown of large, insoluble molecules into small, soluble molecules
Mechanical digestion
the breakdown of food into smaller pieces without chemical change to the food molecules

diarrhoea
the loss of watery faeces
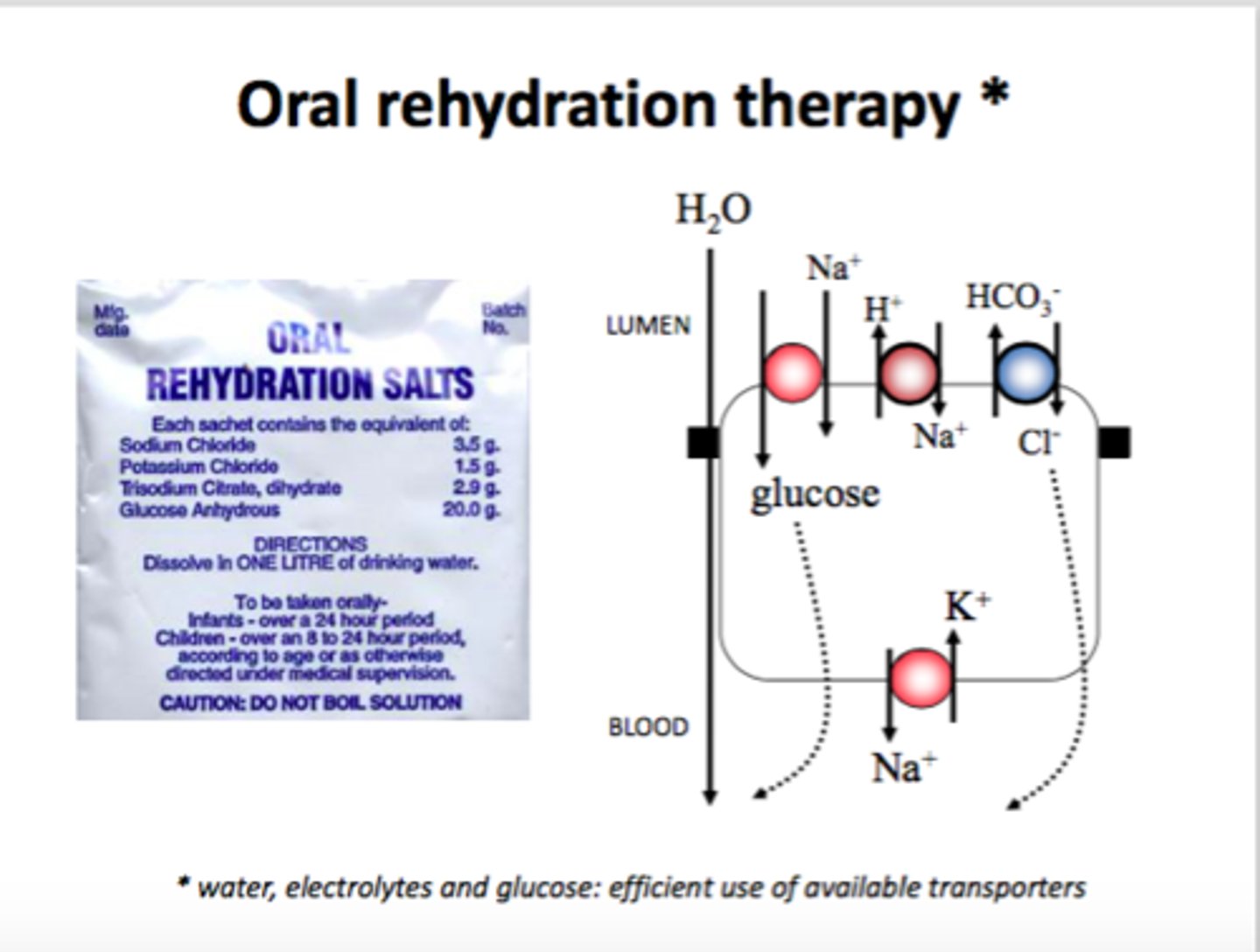
Oral rehydration therapy
ORT solutions contain:
-contains water to rehydrate blood and other tissues
-sodium ions to replace ions lost from blood and tissue fluid
-glucose to provide energy for uptake of sodium ions from intestine
-ions of potassium and chloride to replace ions lost in diarrhoea
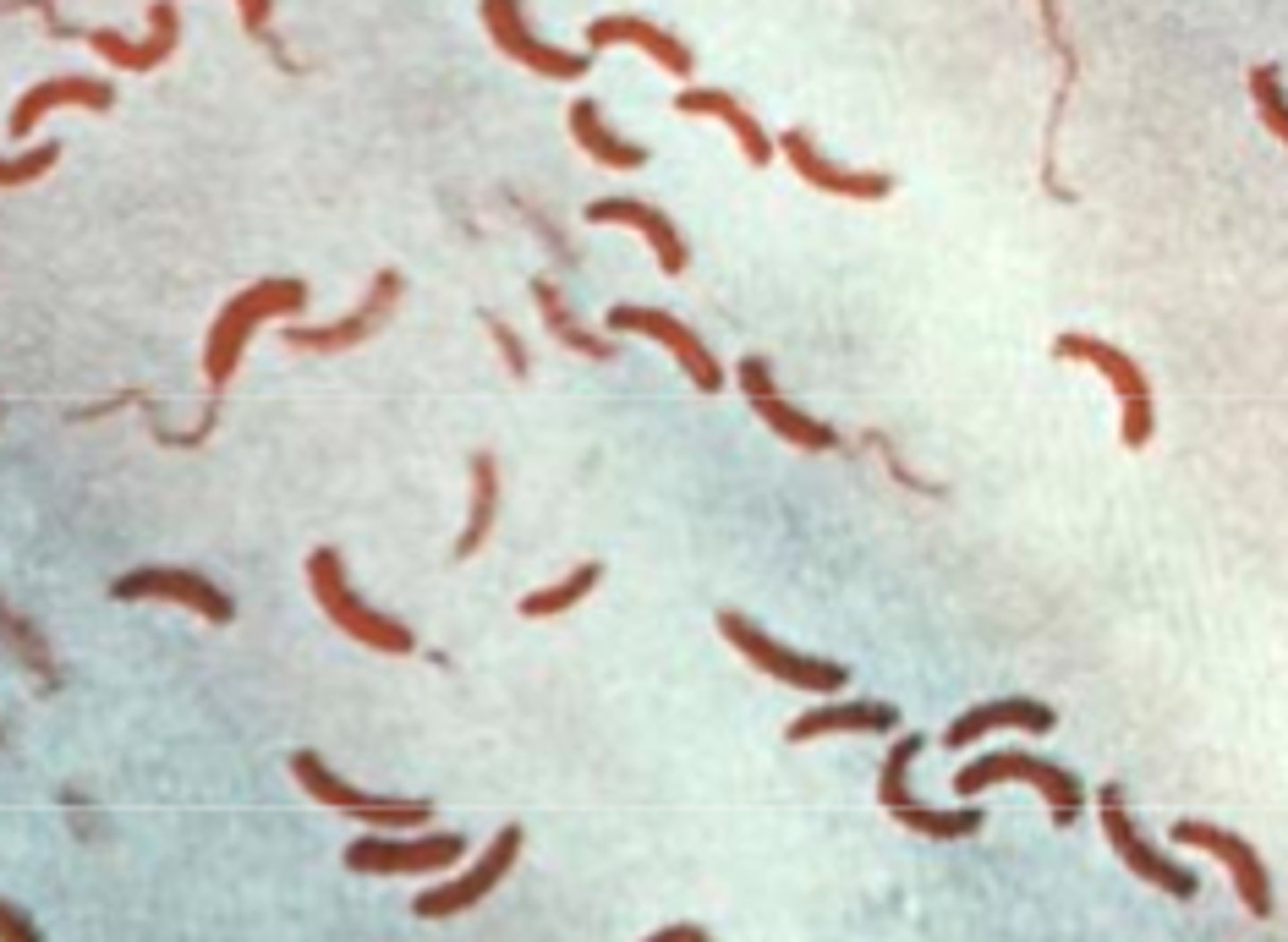
cholera
Cholera bacterium produces a toxin that causes secretion of chloride ions into the small intestine, causing osmotic movement of water into the gut, causing diarrhoea, dehydration and loss of salts from blood
protease
Enzyme that breaks down protein found in stomach, small intestine and pancreas
lipase
Enzyme that breaks down fats, found in pancreas and small intestine
amylase
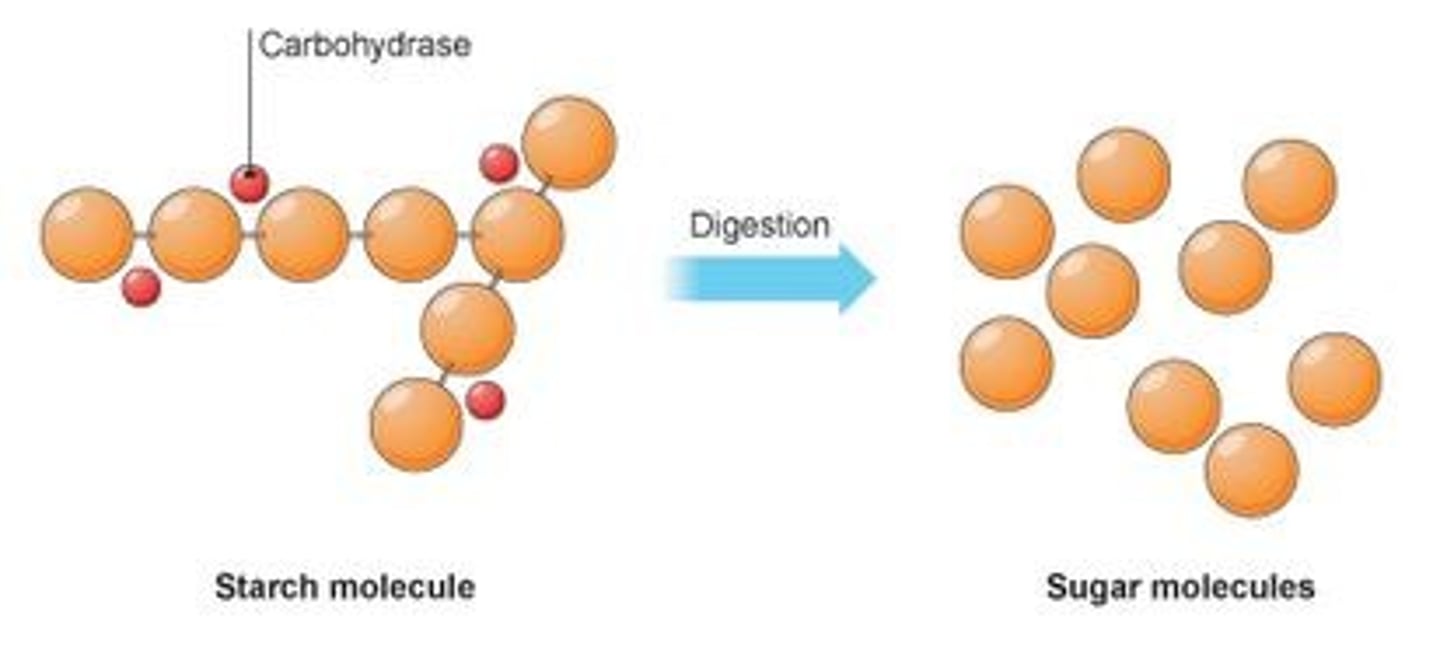
Enzyme that breaks down starches into saccharides which is further broken down into the simple sugar glucose
Alimentary canal
passage from where food travels from the mouth to the anus. Includes esophagus, stomach and intestines
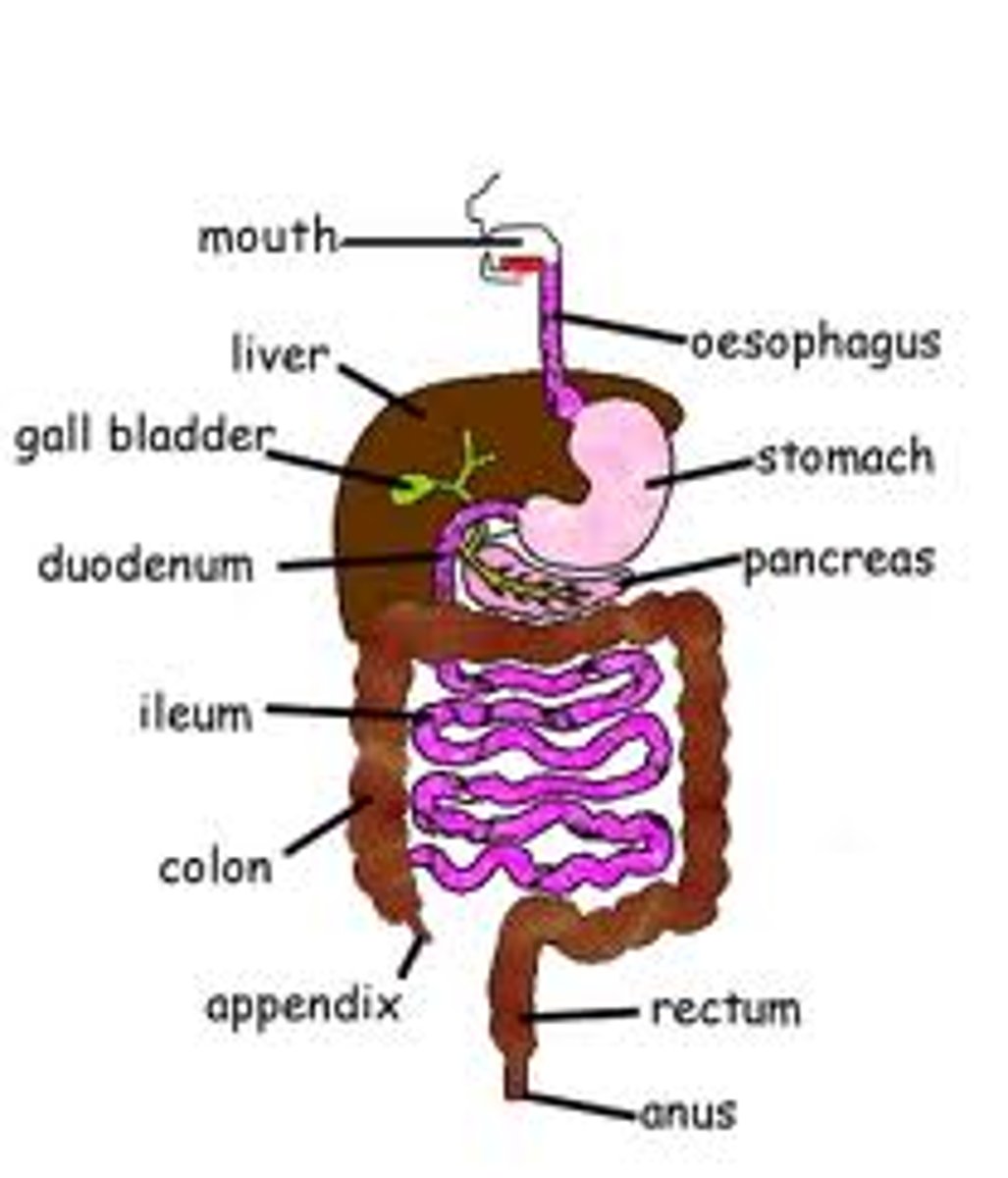
mouth
A medium used for mechanical digestion, breaking large food pieces into smaller pieces particles to increase surface area for chemical digestion

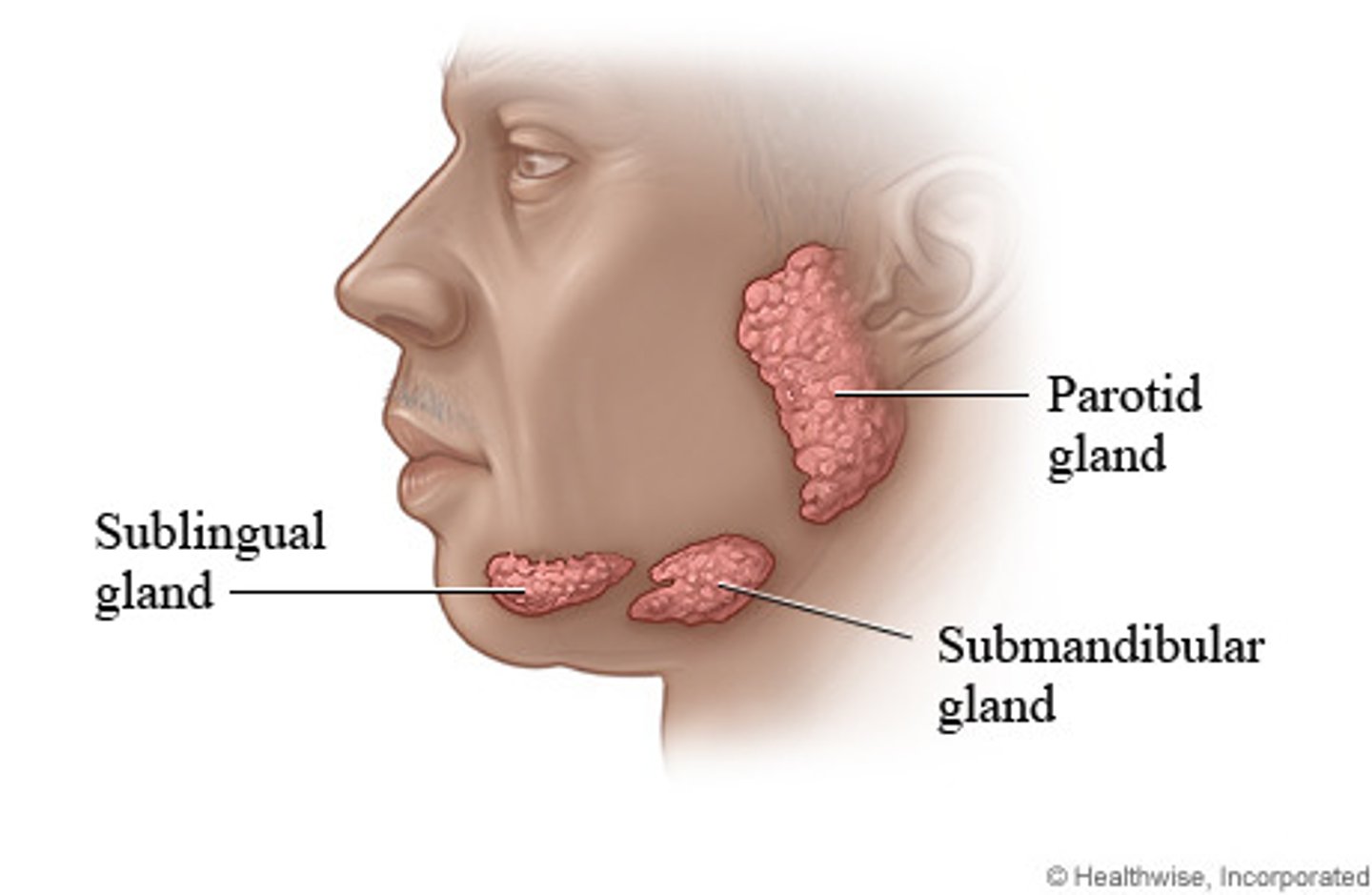
salivary glands
Produce saliva and enzyme amylase that breaks catalystses breakdown of starch to maltose
oesophagus
Food is rolled into a ball called a bolus and moved down to the stomach by peristalsis

stomach
Contains hydrochloric acid that kills bacteria and enzyme pepsin that digests protein into polypeptides
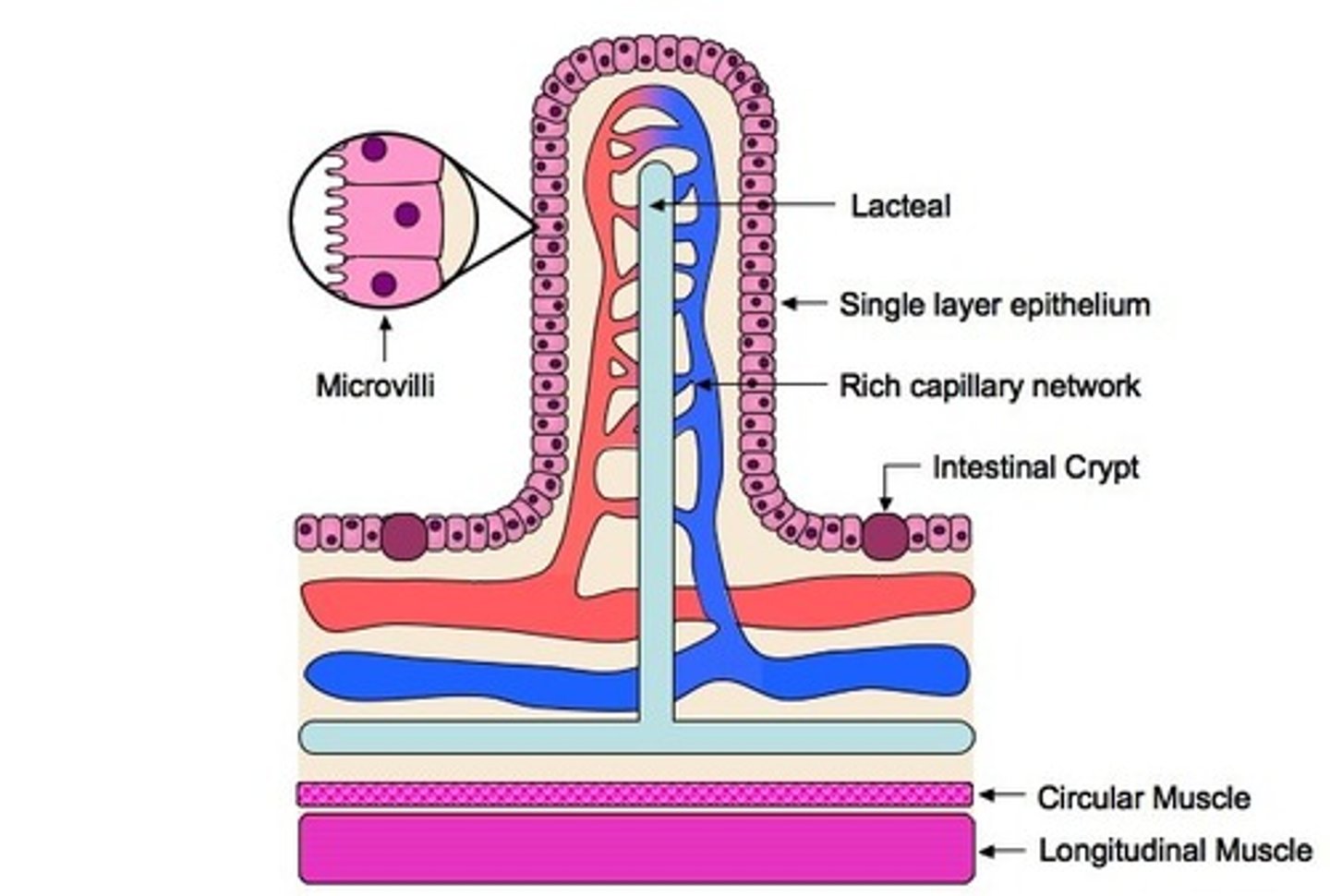
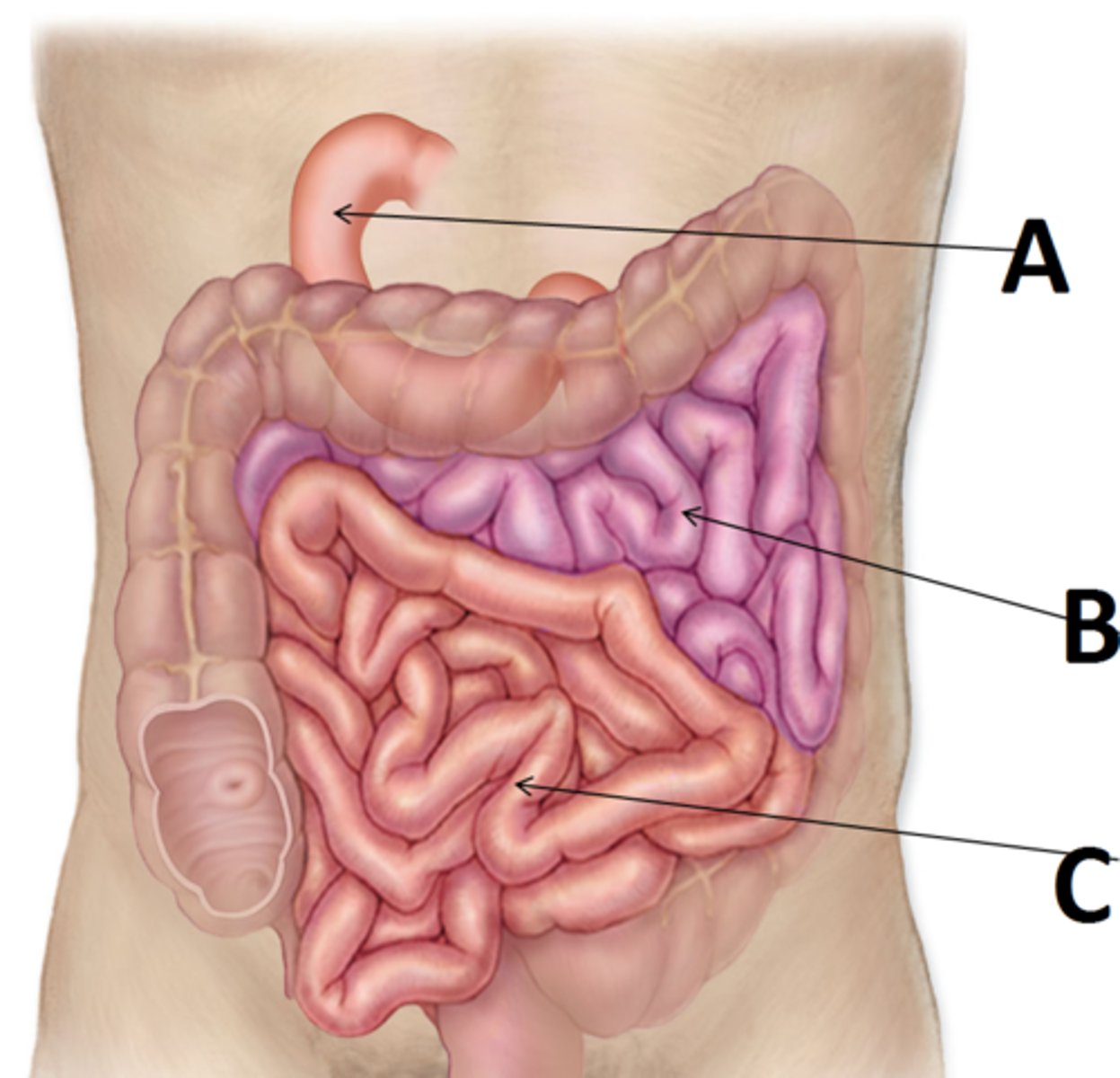
small intestine
contains villi for absorption of digested food
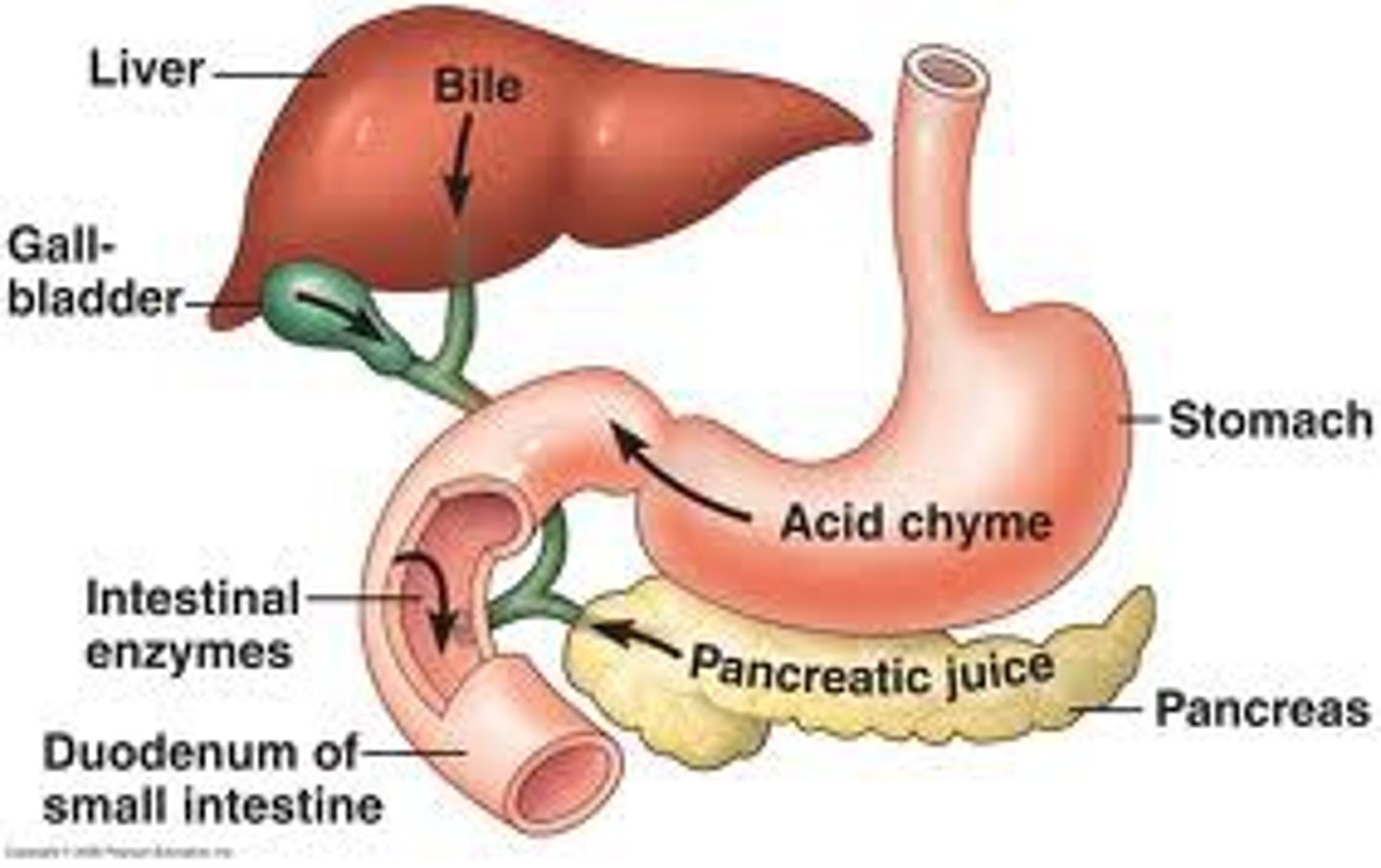
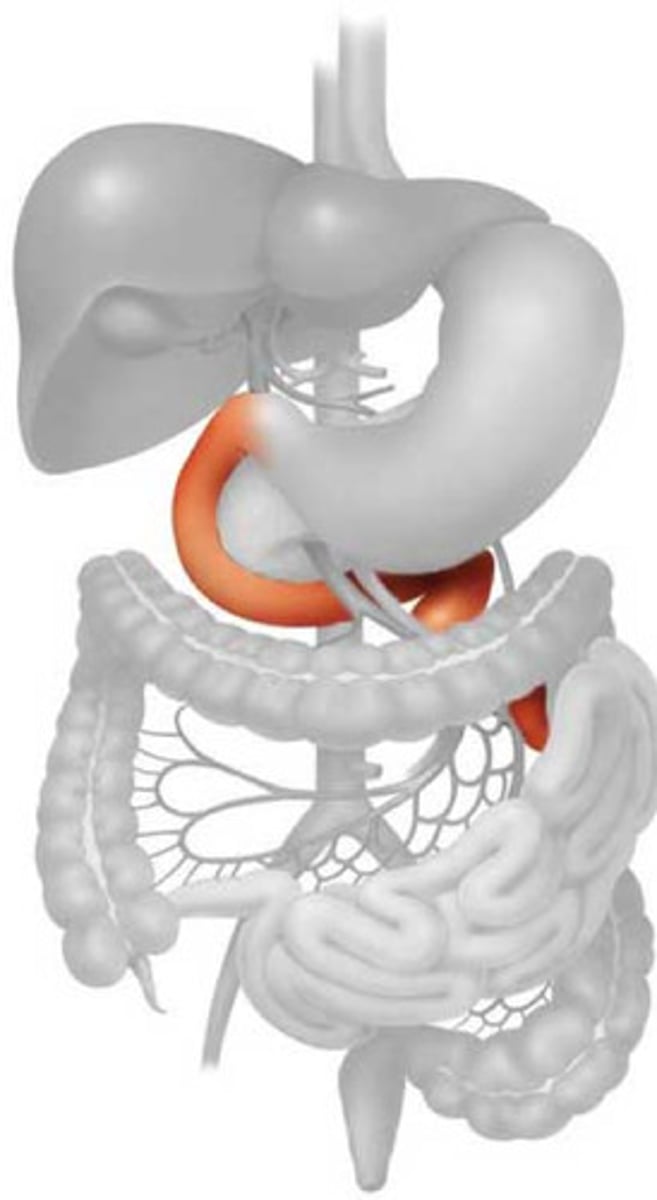
duodenum
connected to pancreas that secretes pancreatic juice that contains enzymes (amylase, trypsin, lipase) bile is also secreted from the gall bladder (bile made in liver and stored in gall bladder), bile is alkaline and neutralises the acid from the stomach as enzymes secreted from pancreas works in alkaline conditions. Bile also emulsifies fat by breaking large fat globules into smaller fat globules
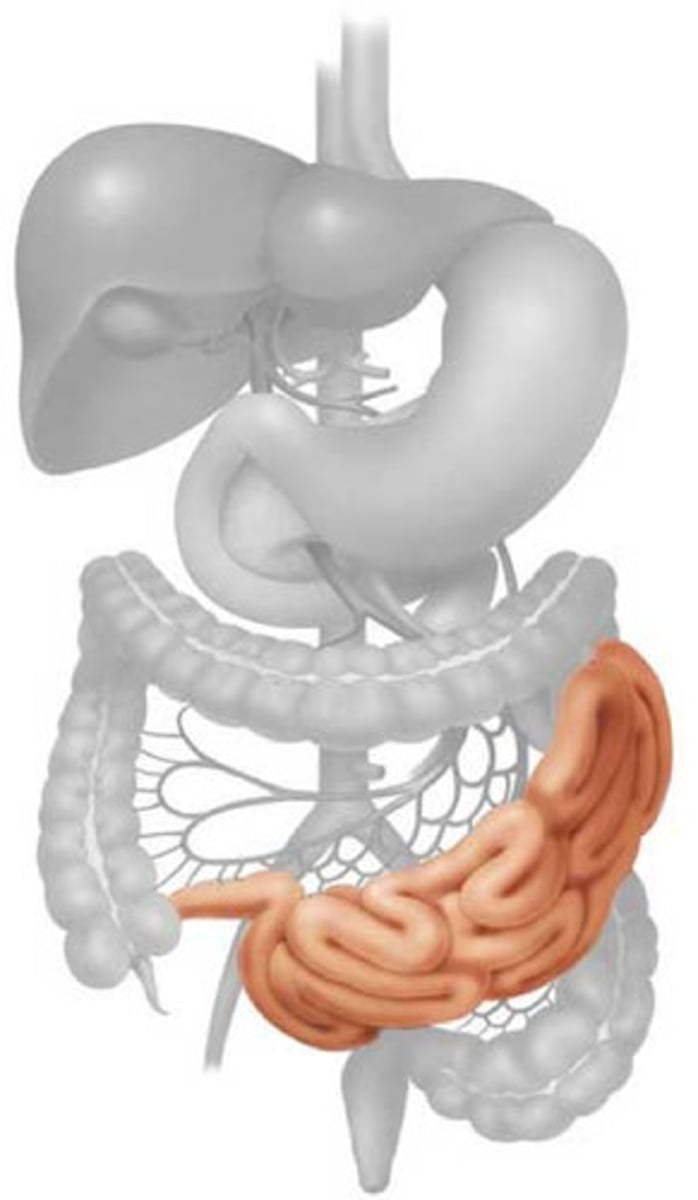
ileum
Final segment of the small intestine; fine tune oraganic absorption (B12,iron,etc) picks up/absorbs any nutrients not already absorbed
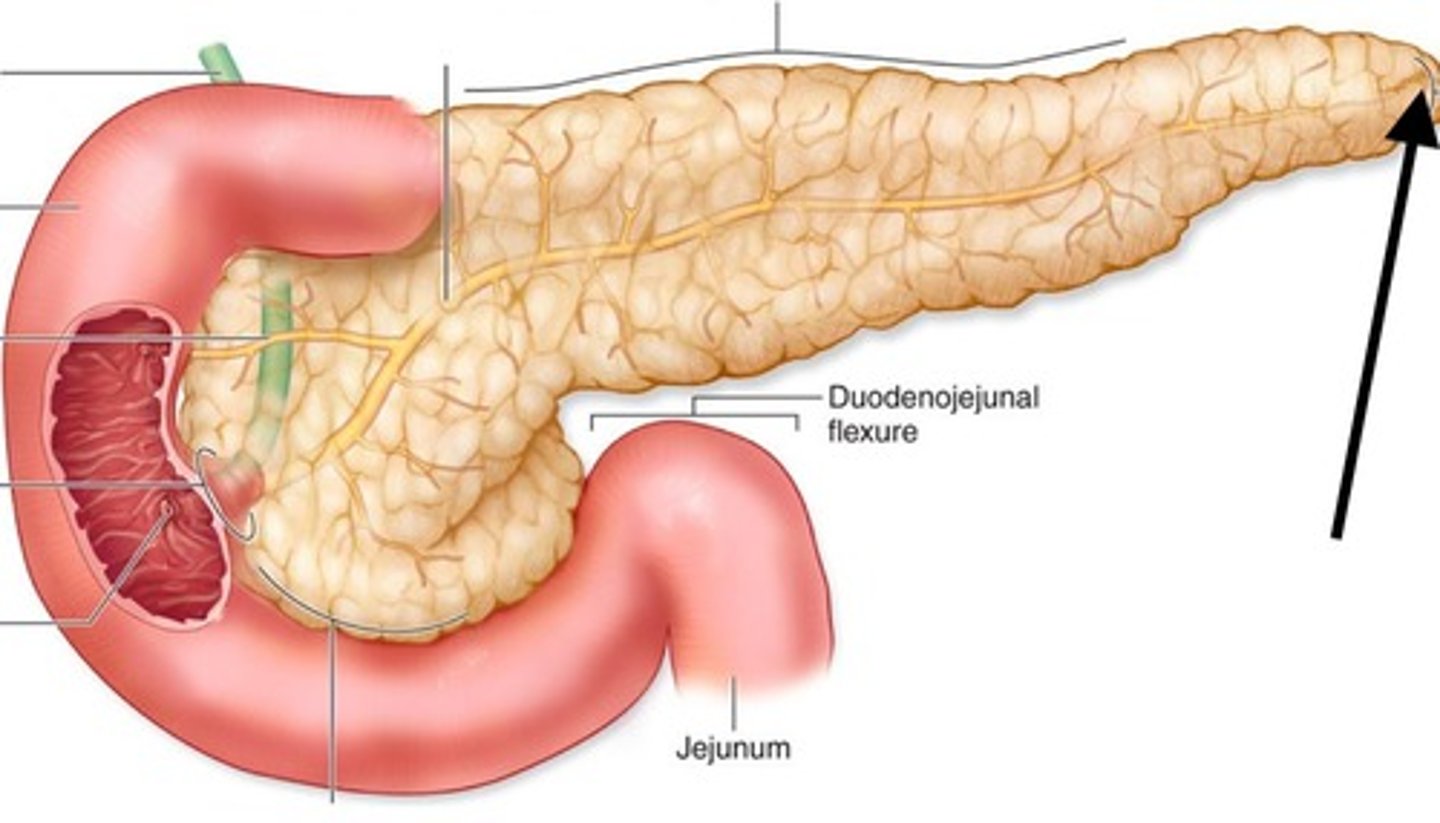
pancreas
-connected to duodenum
-secretes enzymes (amylase, trypsin, lipase)
liver
-process nutrients absorbed from small intestine
-produces bile to be stored in gall bladder
-produces cholesterol
-undergoes deamination
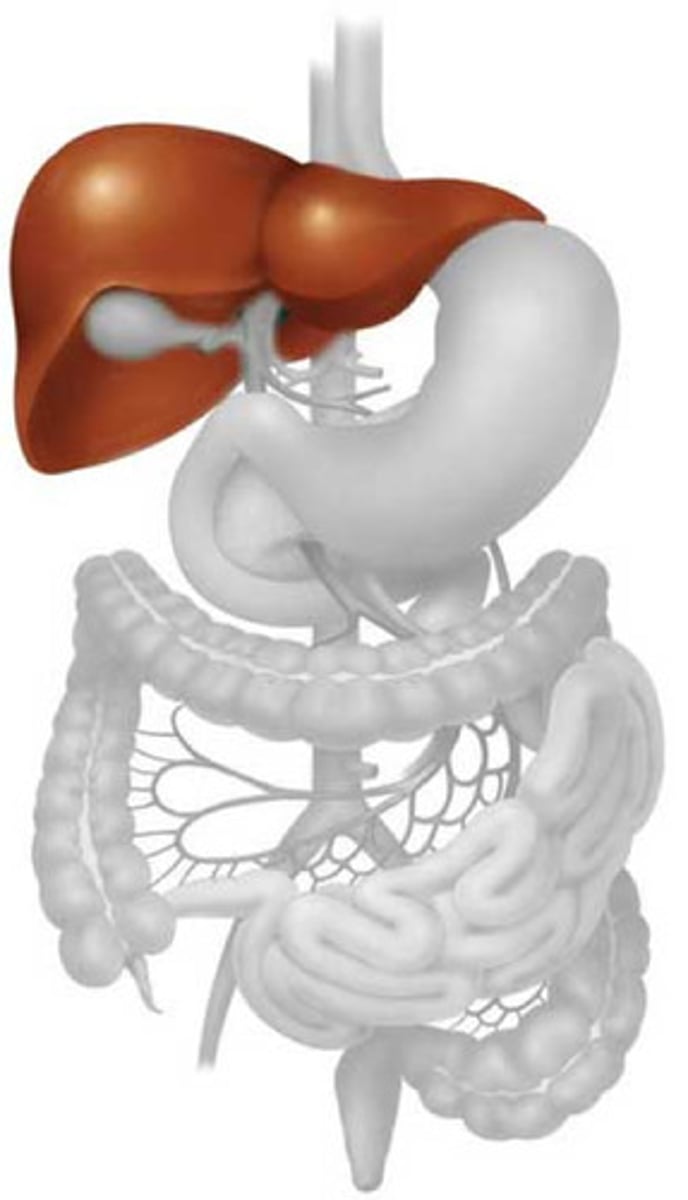
Deamination
Amino acids can't be stored in the liver, thus liver breaks down the amino acid, one molecule is converted into carbohydrate and the other molecule is ammonia (NH4) which combines with carbon dioxide to form urea that is carried to the kidneys and filtered out, excreted in urine
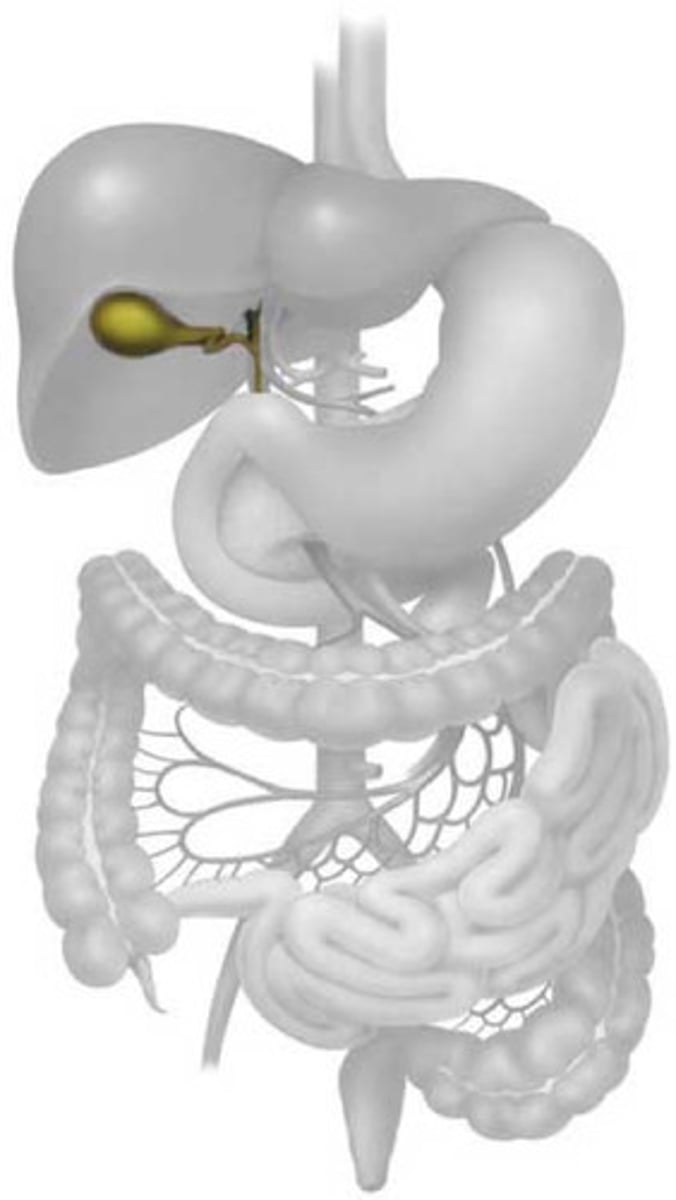
gall bladder
stores bile produced by liver to be secreted to duodenum to neutralise acidic food from stomach
large intestine
Absorb water
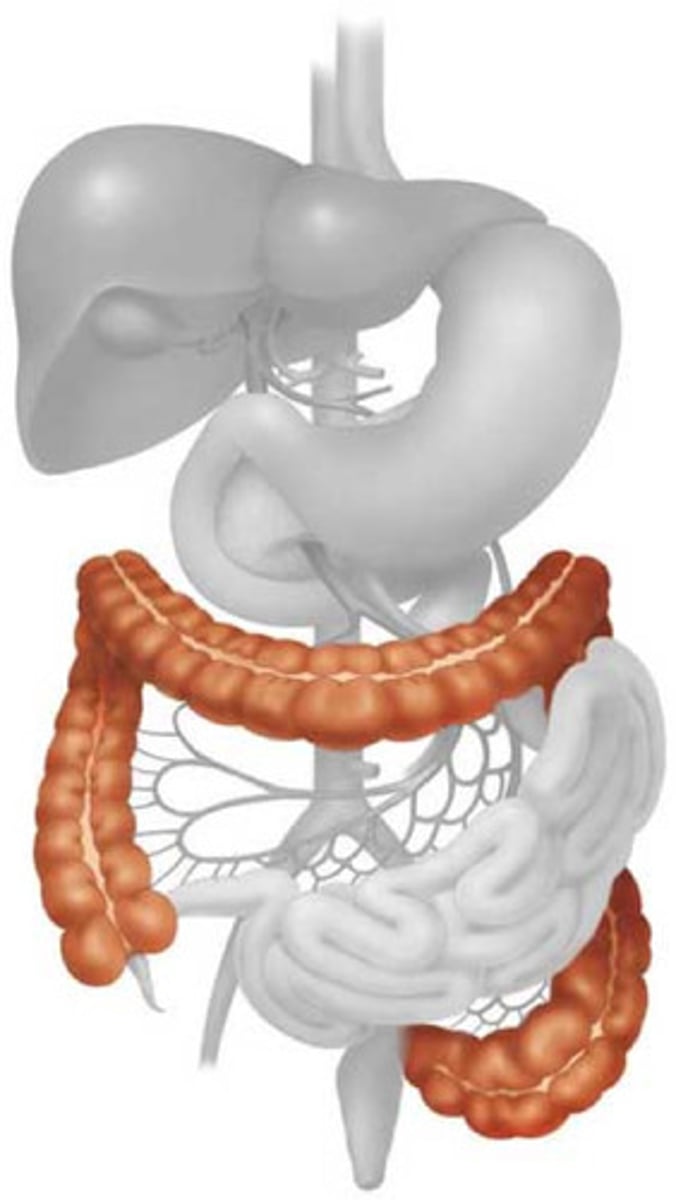
colon
Absorb water
rectum
Stores undigested food
anus
Faeces are egested through anus, passing out indigestible food through anus is called egestion
incisors
Chisel shaped for biting and cutting
canines
Pointed for piercing and tearing
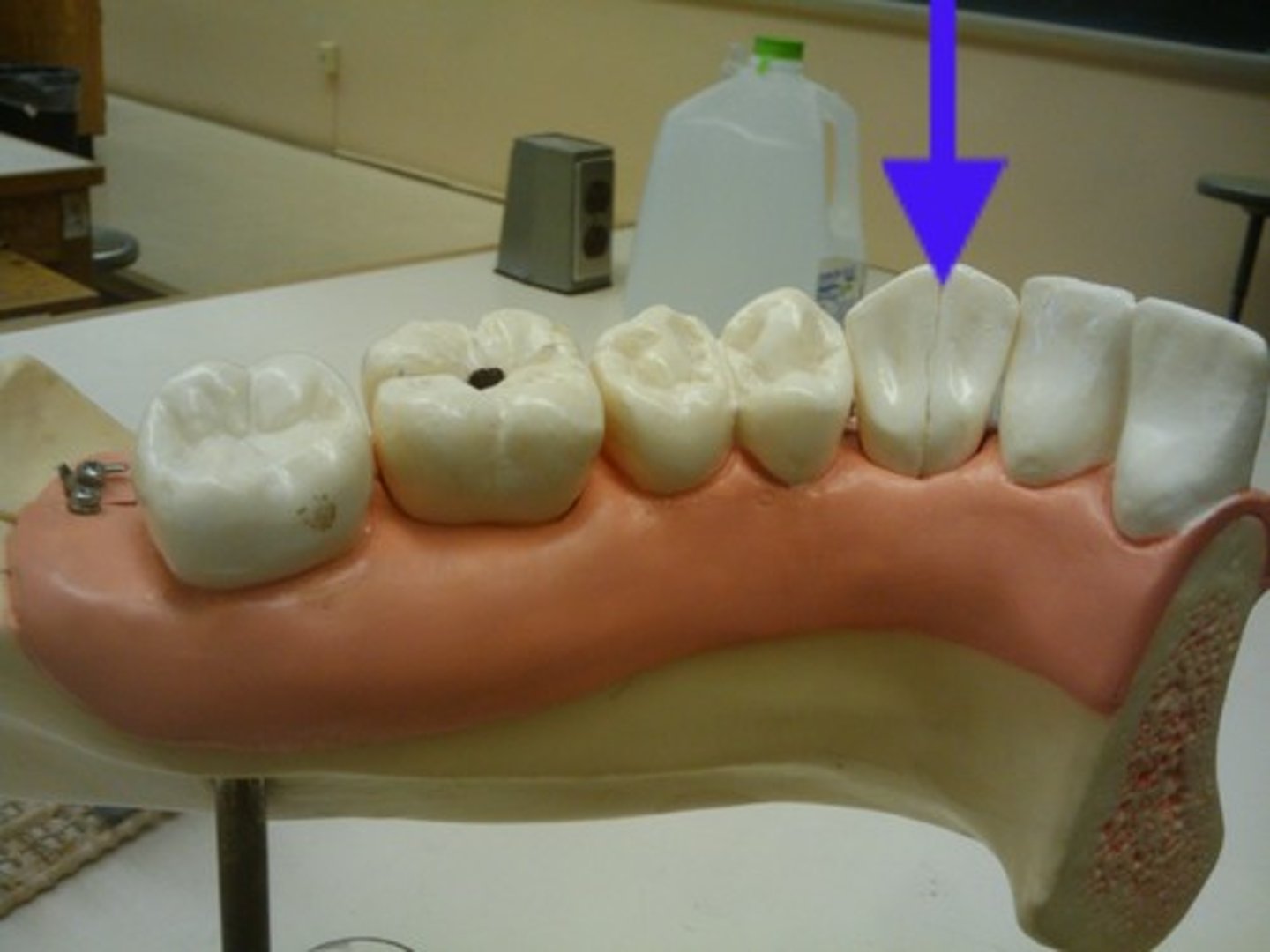
molar
Like premolars are for grinding and chewing food
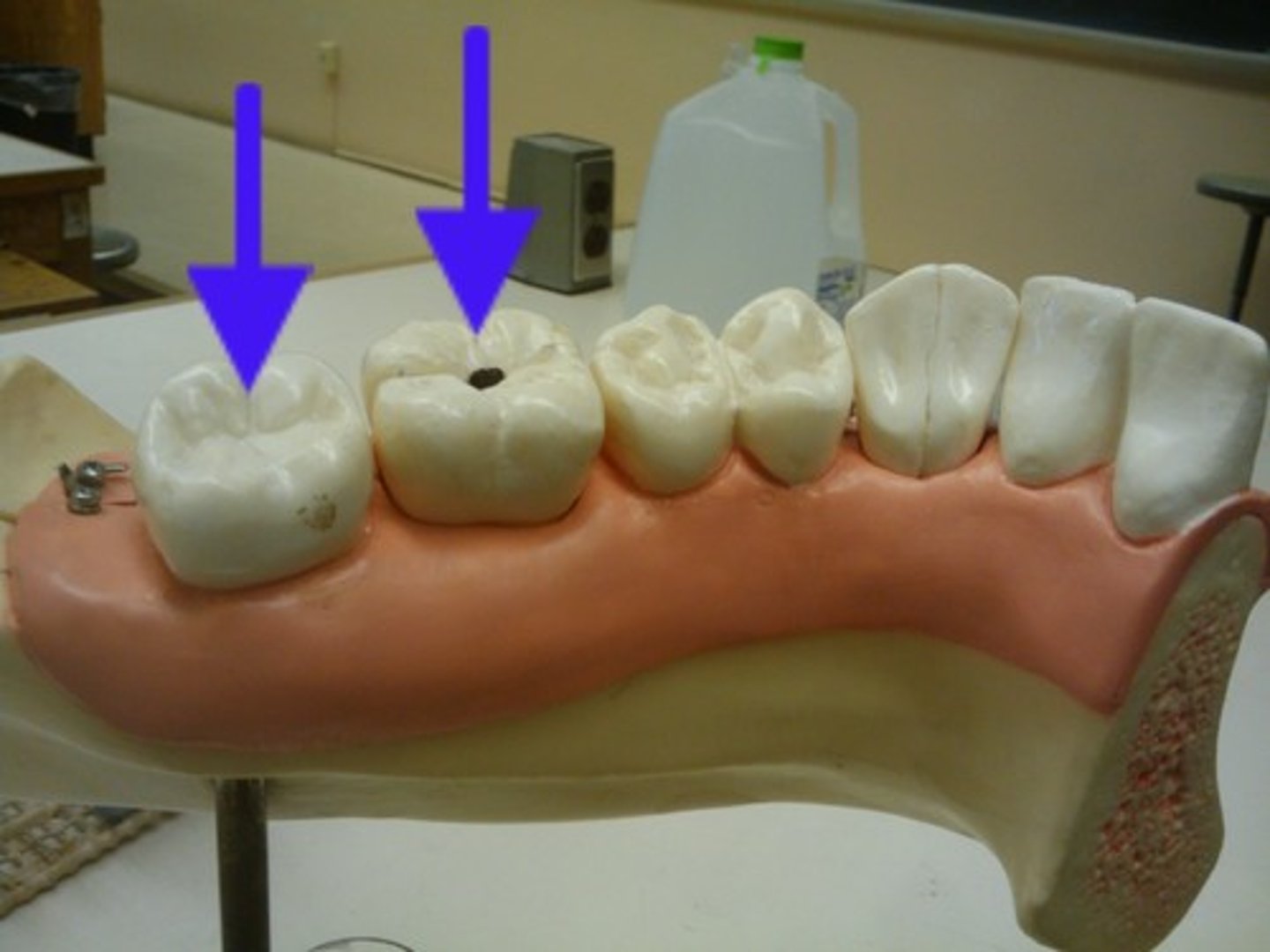
premolar
Have uneven 'cusps' used in chewing, grinding
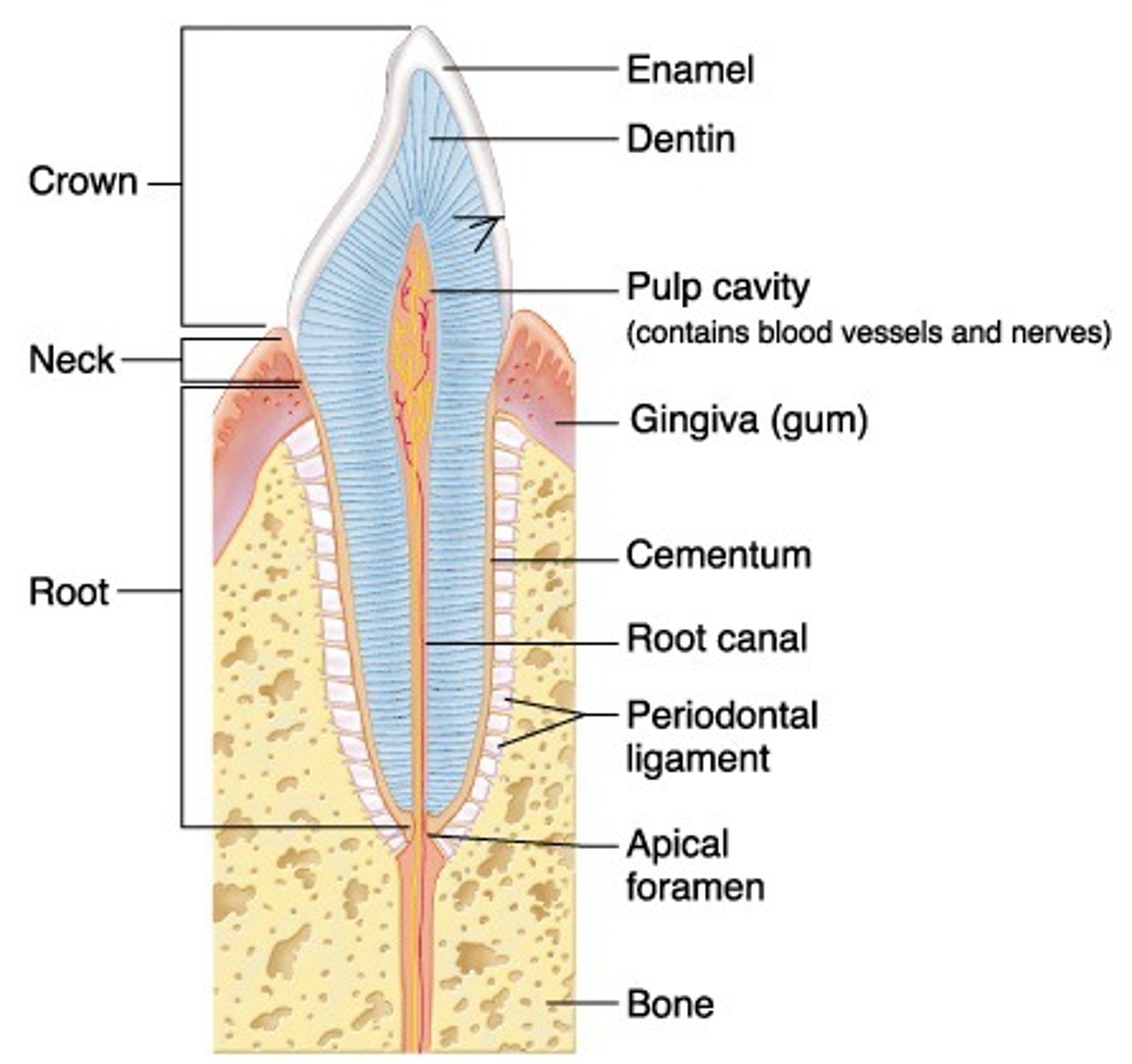
Structure of human tooth
Crown:
-enamel: hard outer layer
-dentine: bone in structure
-pulp cavity: contains nerve and blood vessels
Root:
-cement: fixes root of tooth into bony socket in the jaw
Causes of dental decay
a coating of bacteria and food on teeth, the bacteria respiring sugars in the food, producing acid which dissolves the enamel and dentine
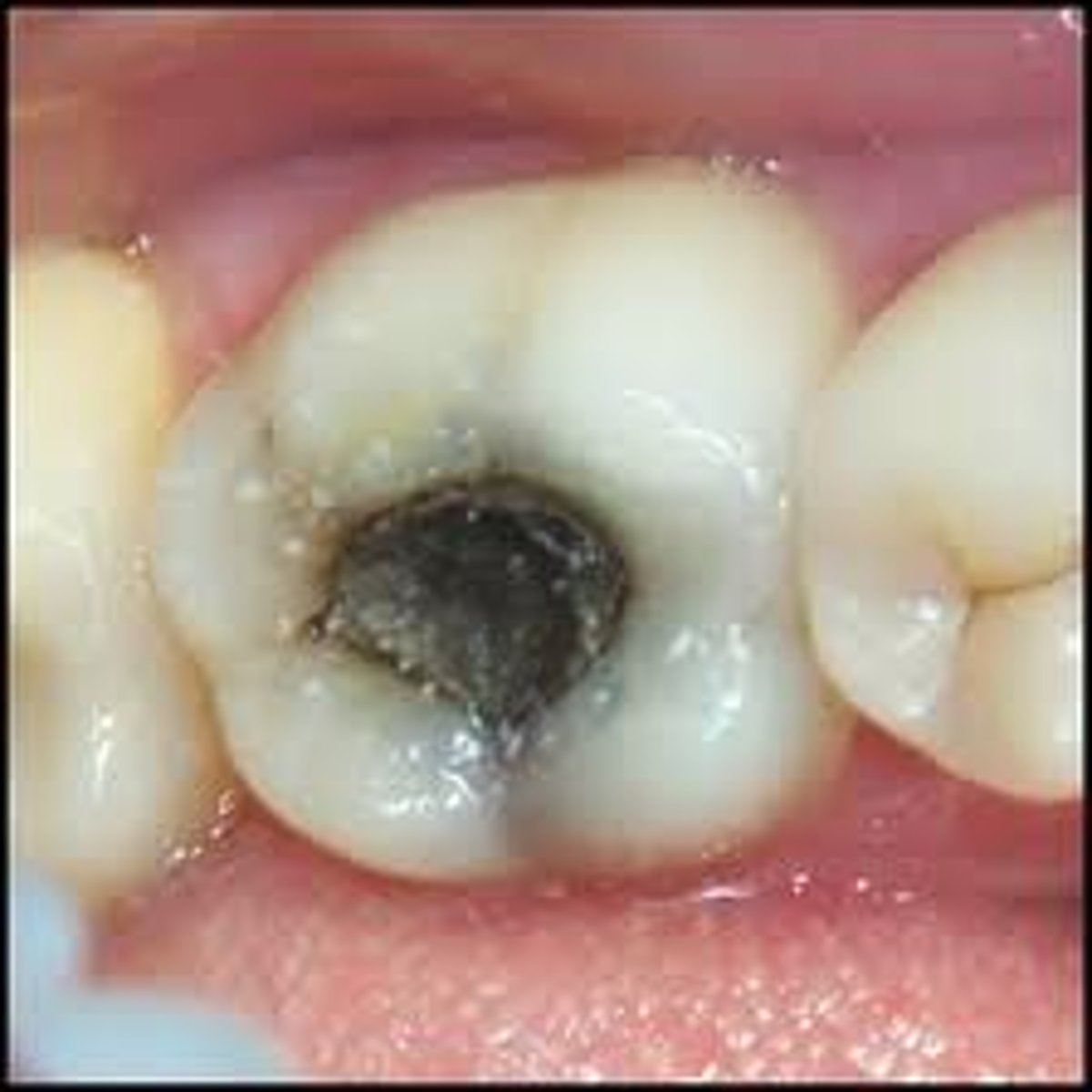
proper care of teeth
-Brush teeth with tooth paste that contains flouride
-Eat less sugary foods to prevent bacteria to multiply and cause tooth decay
the digestion of starch in the alimentary canal
- amylase is secreted into the alimentary canal by salivary gland and breaks down starch to maltose
- maltose is broken down by maltase to glucose on the membranes of the epithelium lining the small intestine
Functions of the hydrochloric acid in gastric juice
- denaturing enzymes in harmful microorganisms in food
- giving the optimum pH for pepsin activity
Function of bile
- neutralising the acidic mixture of food and gastric juices entering the duodenum from the stomach, to provide a suitable pH for enzyme action
- emulsifying fats to increase the surface area for the chemical digestion of fat to fatty acids and glycerol by lipase
Vili
increasing the internal surface area of the small intestine to better absorb nutrients