U3: The Integumentary System
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Integumentary System
the organ system that provides protection to the outer body
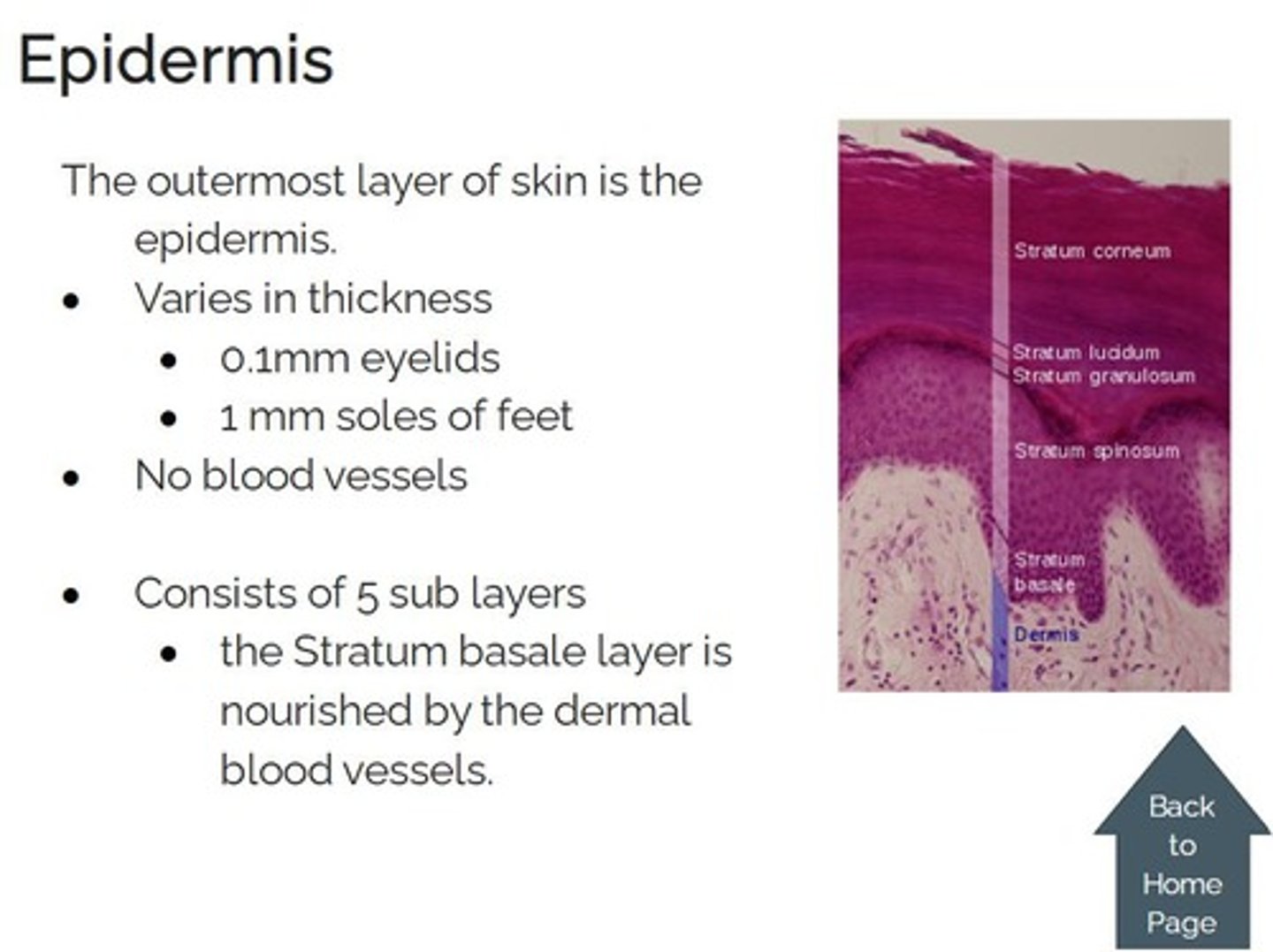
Epidermis
the outermost layer of the skin
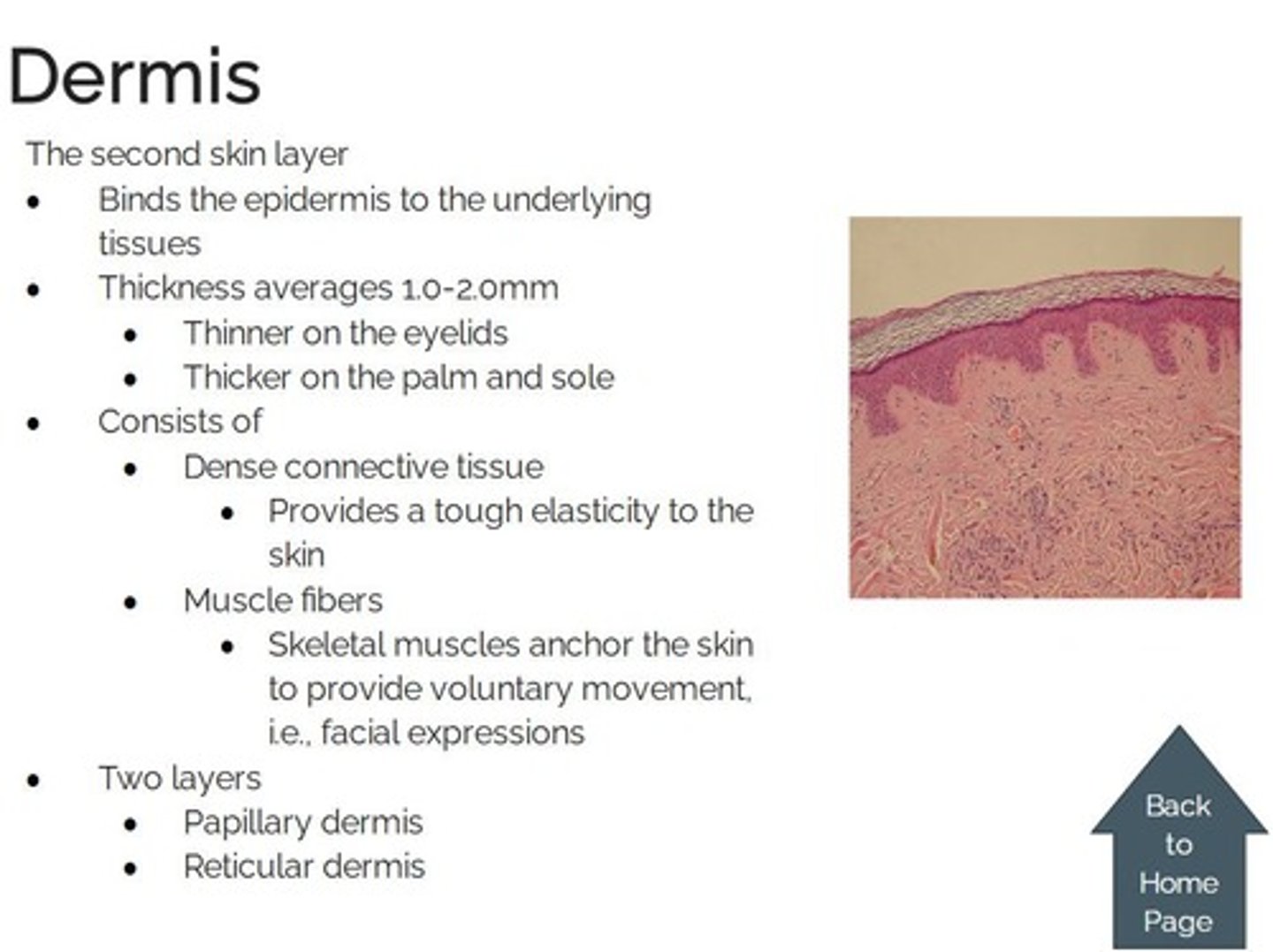
Dermis
the second layer of the skin composed of elastic connective tissue, blood vessels, lymph vessels, nerves, involuntary muscle, hair follicles, sweat, and oil glands
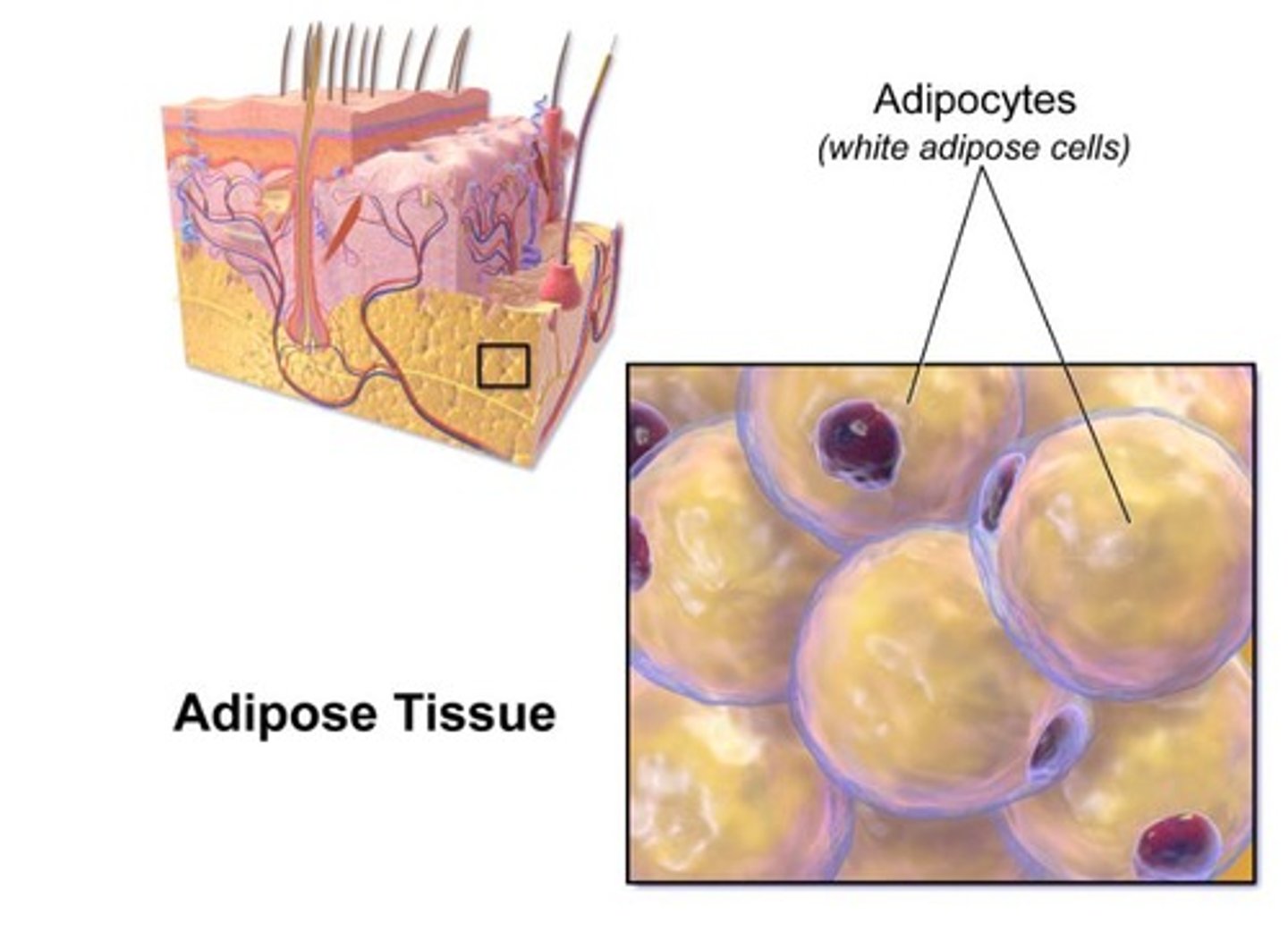
Hypodermis
also known as the subcutaneous fascia is the innermost layer of the skin consisting of connective tissue and adipose (fatty tissue)
Sebaceous Glands
oil glands

Sudoriferous Glands
sweat glands
Macules
flat spots on the skin such as freckles
Papules
small, firm skin elevation caused by inflammation, fluid accumulation, or hypertrophy of tissue
Vesicles
a small abnormal elevation of the outer layer of skin enclosing a watery liquid
Pustules
a small circumscribed elevation of the skin containing pus and having an inflamed base
Crusts
an encrusting deposit of serum, cellular debris, and bacteria present over or about lesions in some skin diseases
Wheals
a suddenly formed elevation of the skin surface with associated burning or itching
Ulcer
a break in the skin or mucous membranes with loss of surface tissue; may extend into the dermis and cause bleeding and/or scarring.
Keratinization
the process in which the cytoplasm of the outermost cells of the mammalian epidermis is replaced by keratin
Inflammatory Response
A normal response to injury characterized by swelling, warmth, and pain, aimed at increasing nutrients and oxygen supply for healing.
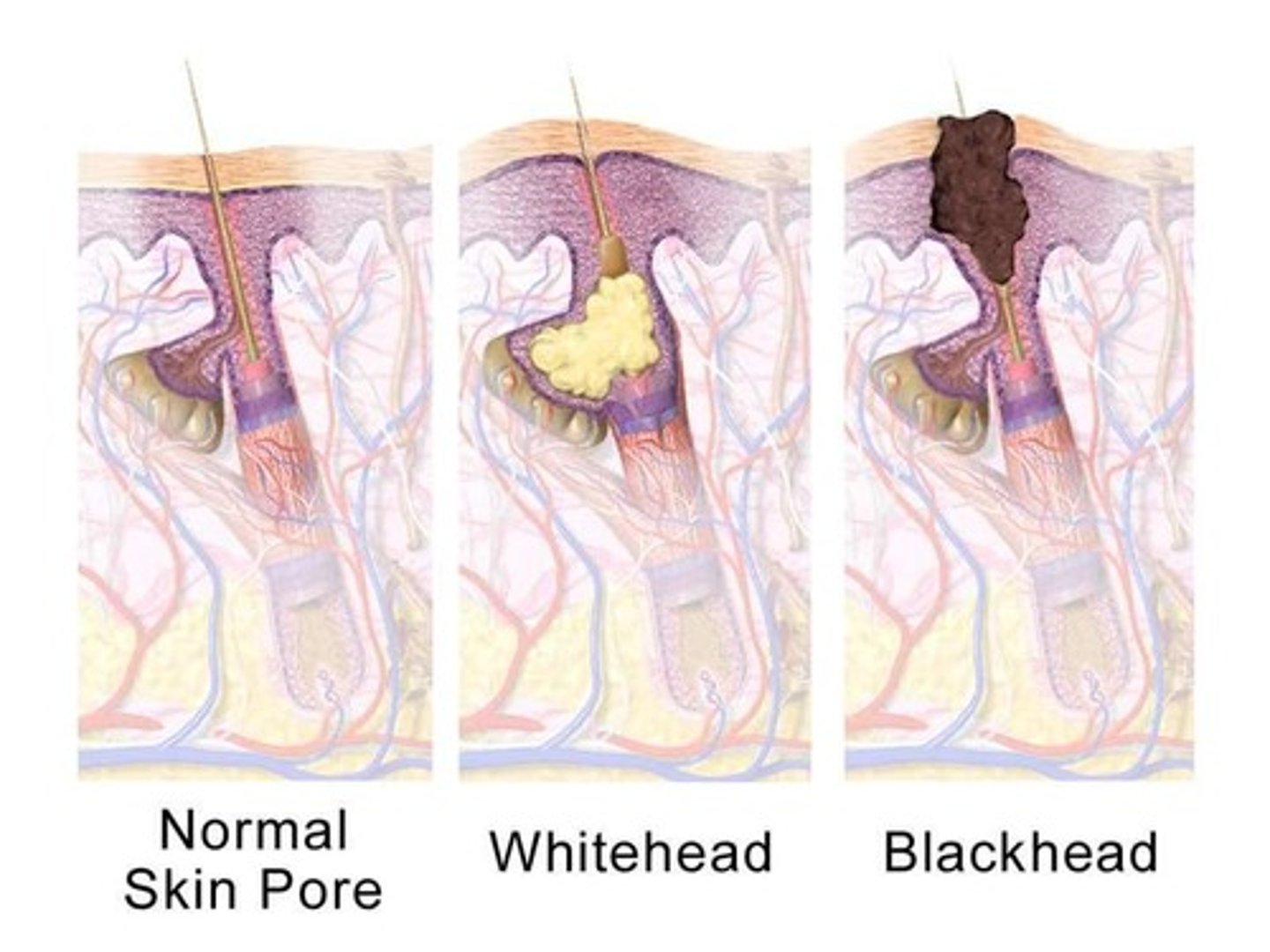
Acne
A disease linked to the sebaceous glands, where sebum can occlude the duct opening leading to pimple development, affecting an estimated 80 percent of people at some point in their lives.
Eczema
A skin condition characterized by dry, scaly, itchy, and recurring rashes, which can lead to rough, dark, leathery patches of skin over time.
Psoriasis
A skin condition that may be misunderstood due to a lack of knowledge about its disease process.
Skin Cancer
The most common form of cancer in the United States, with common types including squamous cell, basal cell, and melanoma.

Melanoma
A type of skin cancer that forms in the melanocytes and holds the greatest life-threatening potential among skin cancer types.
Aging Integumentary System
Visible changes in the skin that affect homeostasis and appearance, including thinning skin and decreased elasticity.
Epidermal Layers
The outer layers of skin that show signs of aging, such as larger, fewer, and less elastic cells.
Fatty Layer
The layer under the skin that thins with age, leading to more prominent wrinkles and decreased capacity to endure temperature changes.
Capillary Blood Supply
Blood vessels supplying the skin that shrink with age, decreasing support for sweat glands.
Sweat Glands
Glands that help regulate body temperature, which become less effective with aging, increasing the risk of heatstroke.
Nerve Endings
Sensory structures in the skin that decrease with age, leading to reduced sensitivity to pain and increased injury risk.
Healing Process
The biological process that slows with age due to diminished blood supply and nutrient delivery for tissue repair.
Melanocyte Production
The process that slows with age, leaving skin more vulnerable to ultraviolet radiation.
Vitamin D Synthesis
The skin's ability to produce Vitamin D, which decreases with age, placing individuals at risk for skeletal injury and depression.

Homeostasis
The body's ability to maintain stable internal conditions, which can be disrupted by aging skin.
Skin Integrity
The overall health and condition of the skin, which deteriorates with age.
Injury
Any damage to the skin that triggers the inflammatory response and healing process.
Environmental Irritants
External factors that, combined with genetics, may predispose individuals to specific skin conditions.
Chronic Inflammation
A prolonged inflammatory response that can lead to skin conditions like eczema.
Skin Disease
Any condition affecting the skin, including acne, eczema, psoriasis, and skin cancer.
Pain Response
The body's reaction to injury, which can diminish with age, increasing injury risk.