Edexcel A Level Chemistry, topic 6: Organic Chemistry 1
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
What are the options for types of bonds around a carbon atom? (5)
Four single
Two single and one double
One single and one triple
Two double
Three single and one ionic
What is a hydrocarbon?
a compound made of hydrogen and carbon only
What is a general formula?
The simplest algebraic formula of a member of a homologous series
What is a homologous series? (3)
A series of organic compounds with the same functional group, but each successive member differing by CH2
What is a functional group?
a group of atoms responsible for the characteristic reactions of a particular compound.
What are the six different formulas used to represent molecules? (6)
Empirical
Molecular
Structural
Displayed
Skeletal
3D displayed
What is a structural formula? (2)
The minimal written detail that shows the arrangement of atoms in a molecule
What is the displayed formula?
Diagram showing the relative positioning of the atoms and bonds between them
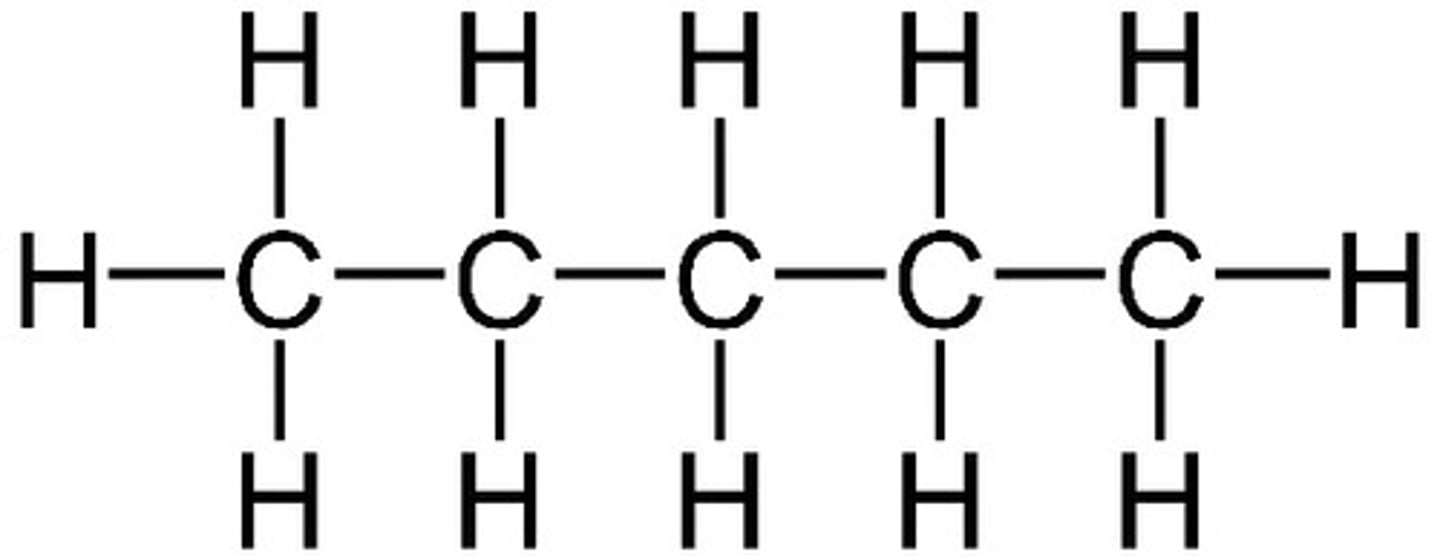
What is a skeletal formula?
Diagram showing the bonds of the carbon skeleton only with any functional groups

General formula for alkanes
CnH2n+2
Functional group for alkenes
C=C
General formula for alkenes
CnH2n
Functional group of halogenoalkanes
-X, where X is a halogen
General formula for halogenoalkanes
CnH2n+1X
General formula for cycloalkanes
CnH2n
Functional group of alcohols
-OH
Suffix for alcohols (2)
-ol, or if another functional group is present a prefix of hydroxy-
Functional group for aldehydes
CHO
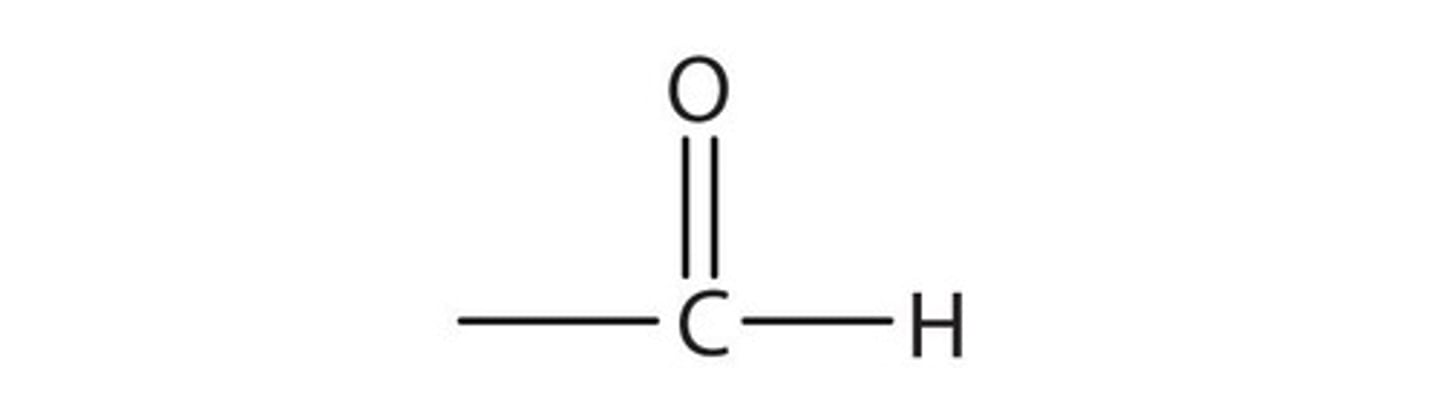
suffix for aldehydes
-al
Functional group for ketones
C=O
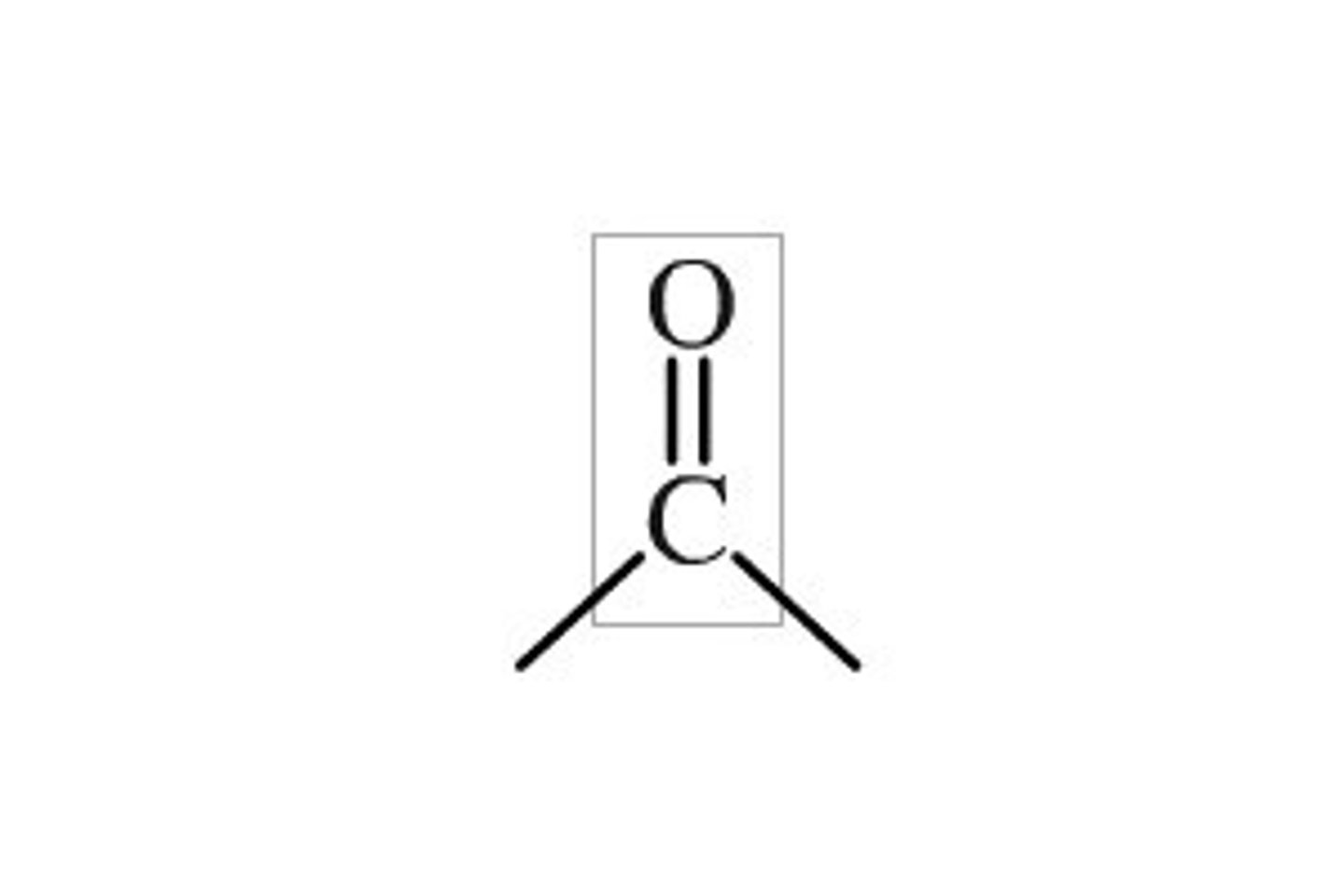
Suffix for ketones
-one
Functional group of carboxylic acids
COOH
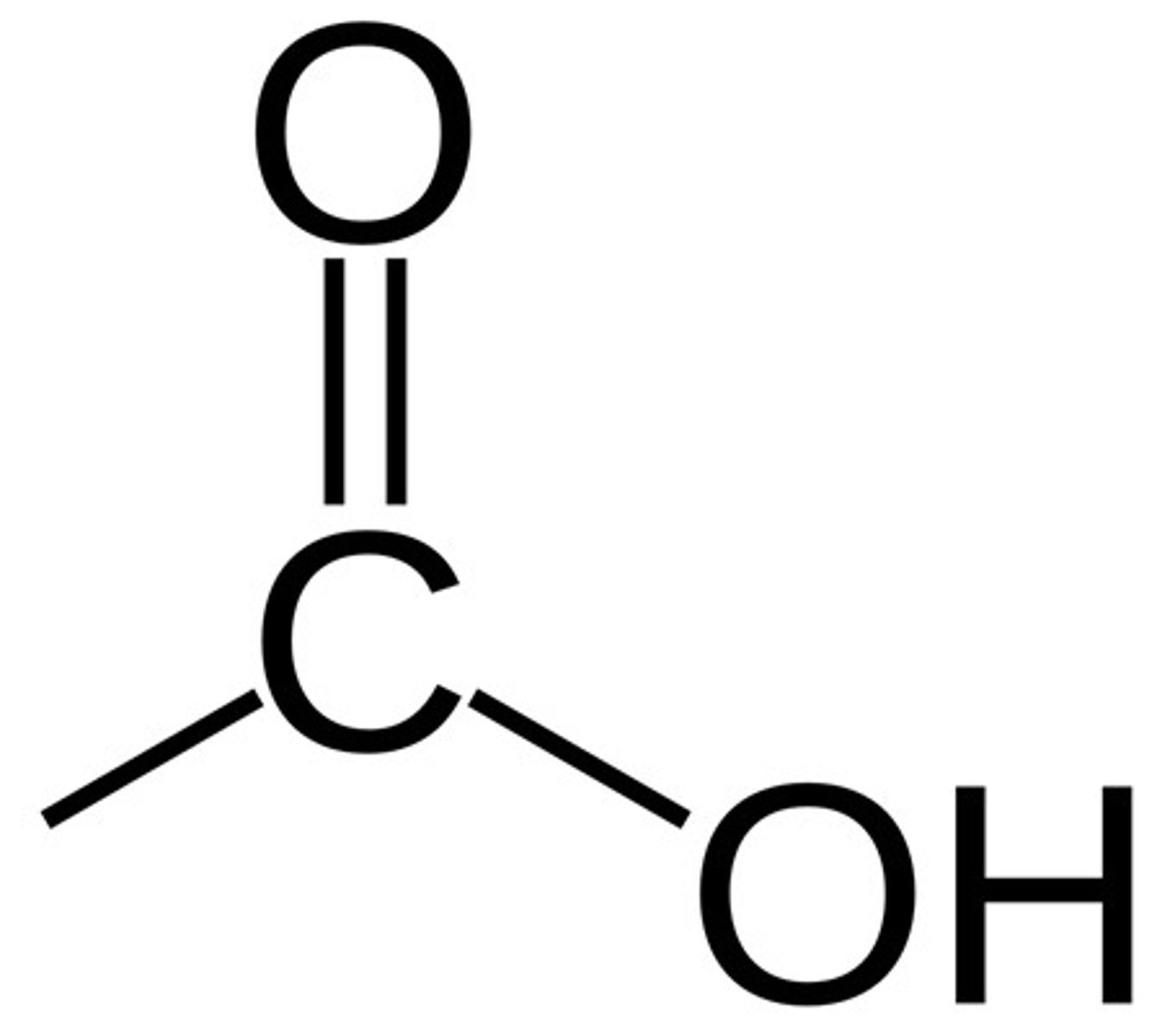
Suffix for carboxylic acids
-oic acid
What does aliphatic mean?
Straight chain of carbons
What are the steps for naming an organic compound? (3)
Identify longest unbranded carbon chain to give stem name
Name any substituent groups, if more than one order alphabetically
Identify position of substituent groups
What are the rules for identifying the position of substituent groups? (4)
Count from the end that gives the lowest numbers
If two of the same on one carbon, repeat number and add di- as prefix to group
If more than one of same on diff carbons, number and add di-, tri- or tetra-
Commas between numbers, dashes between numbers and letters
What is the general formula of cycloalkanes?
CnH2n
What is the first member of the cycloalkane homologous series? (+formula)
Cyclopropane, C3H6
What is an unsaturated hydrocarbon?
Have at least one double or triple C-C bond
What is a saturated hydrocarbon?
Single C-C bonds only, alkane
What is an alkene?
An unsaturated hydrocarbon
What is the general formula of alkenes?
CnH2n
How is the naming of alkenes different from that of alkanes?
Must specify the location of the double bond
What is structural isomerism?
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural
What are the different types of structural isomerism? (3)
Carbon-chain isomers
Positional isomers
Functional-group isomers
What are carbon chain isomers? (+ one example) (5)
The length of the main carbon chain
Similar chemical properties because same functional group
Slightly different physical properties
More branches results in lower boiling point
Butane and methylpropane
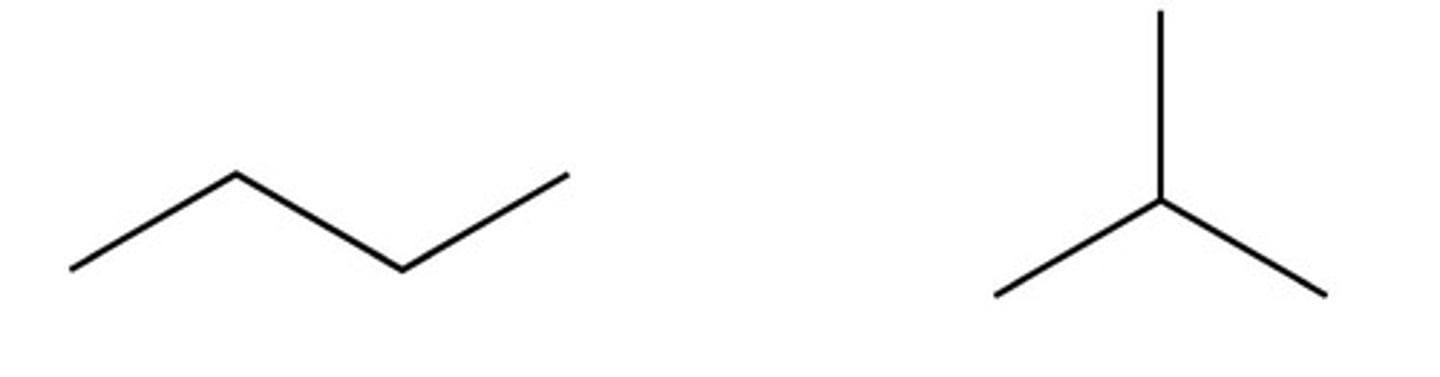
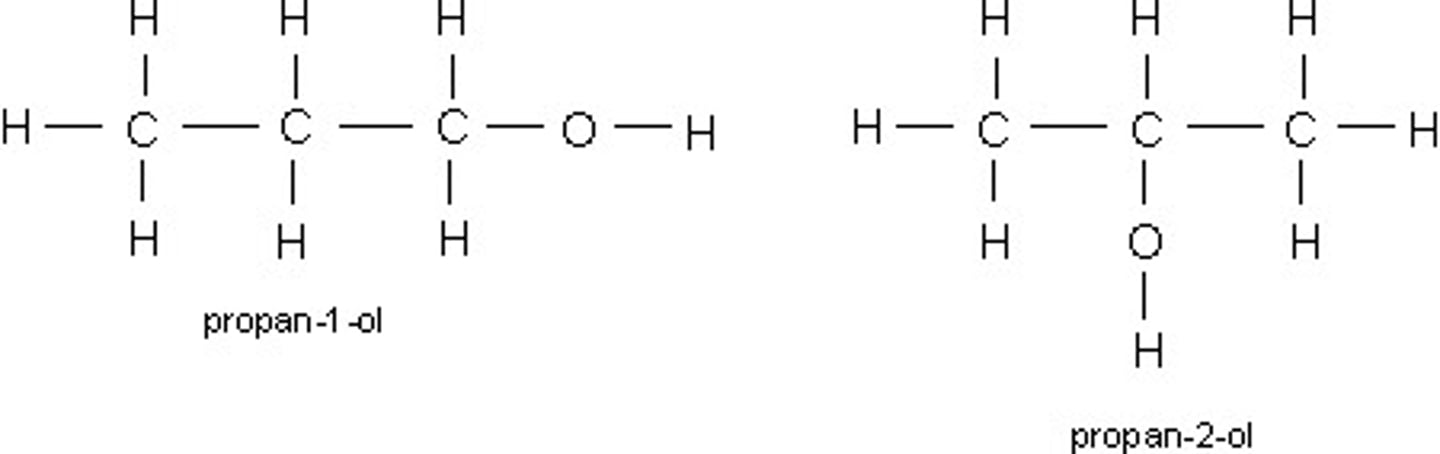
What are positional isomers? (+ one example) (4)
The functional group is in a different location on the carbon framework
Similar chemical properties
Different physical properties
Propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol
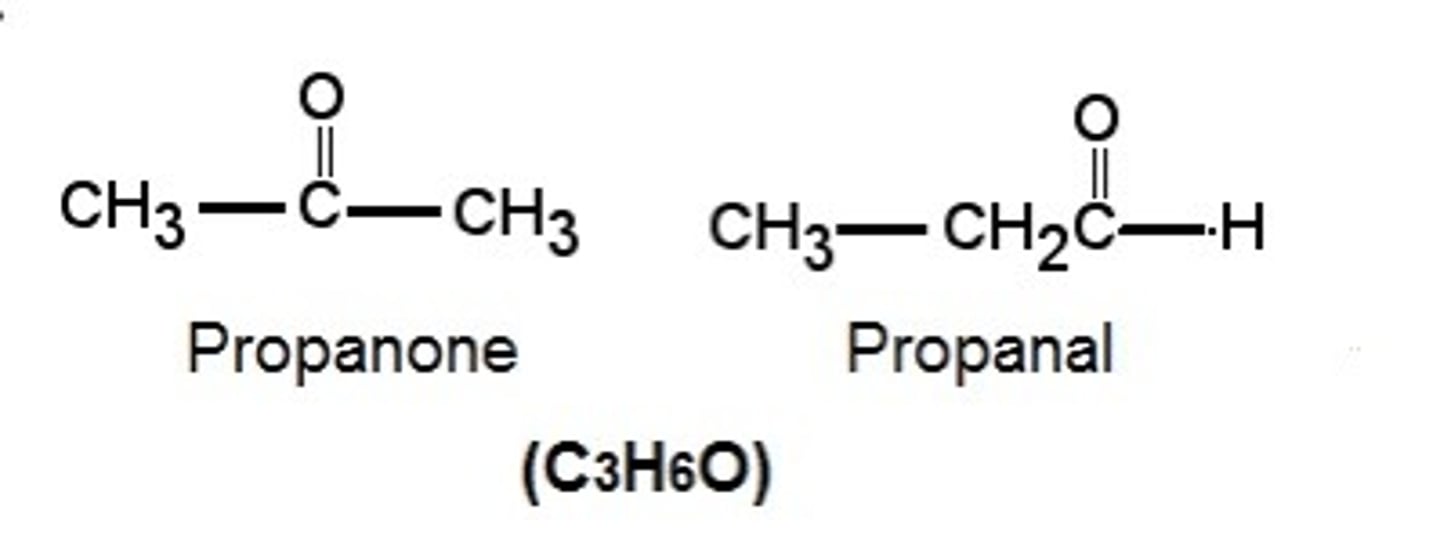
What are functional-group isomers? (+ one example) (4)
A different functional group but same molecular formula
Different chemical properties
Different physical properties
Propanone and propanal
What is stereoisomerism? (1)
Atoms making up the isomers are joined in the same order but have a different arrangement
What must happen for a geometric isomer to be able to occur?(3)
There must be restricted movement somewhere in the molecule, often a double bond or in a cyclic compound
Why does a C=C bond result in the potential for geometric isomers? (3)
The pi bond formed by sideways overlap of p orbitals fixes the carbon atoms in position resulting in no free rotation
What is a trans isomer?
The priority groups are on opposite sides of the carbon chain
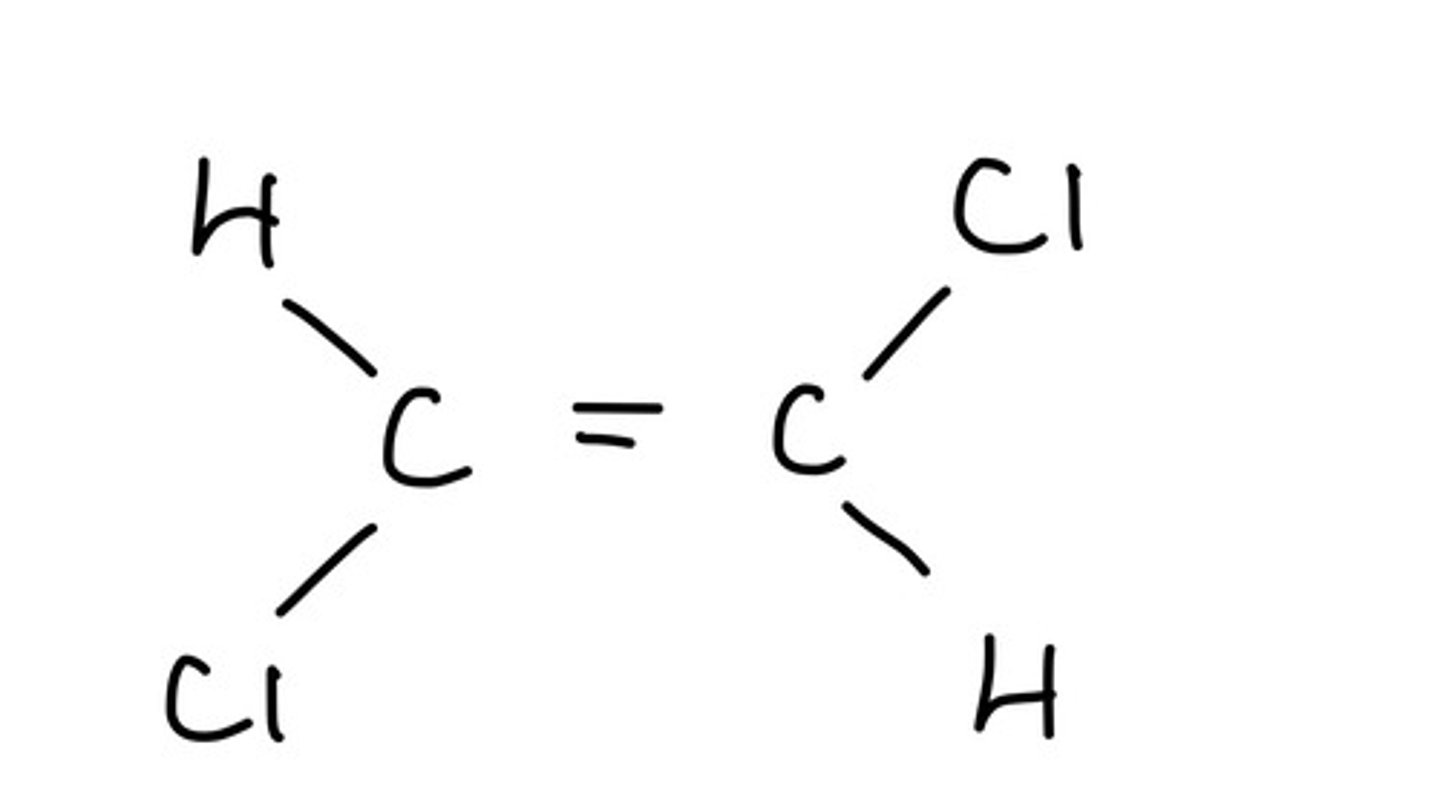
What is a cis isomer?
The priority groups are on the same side of the carbon chain
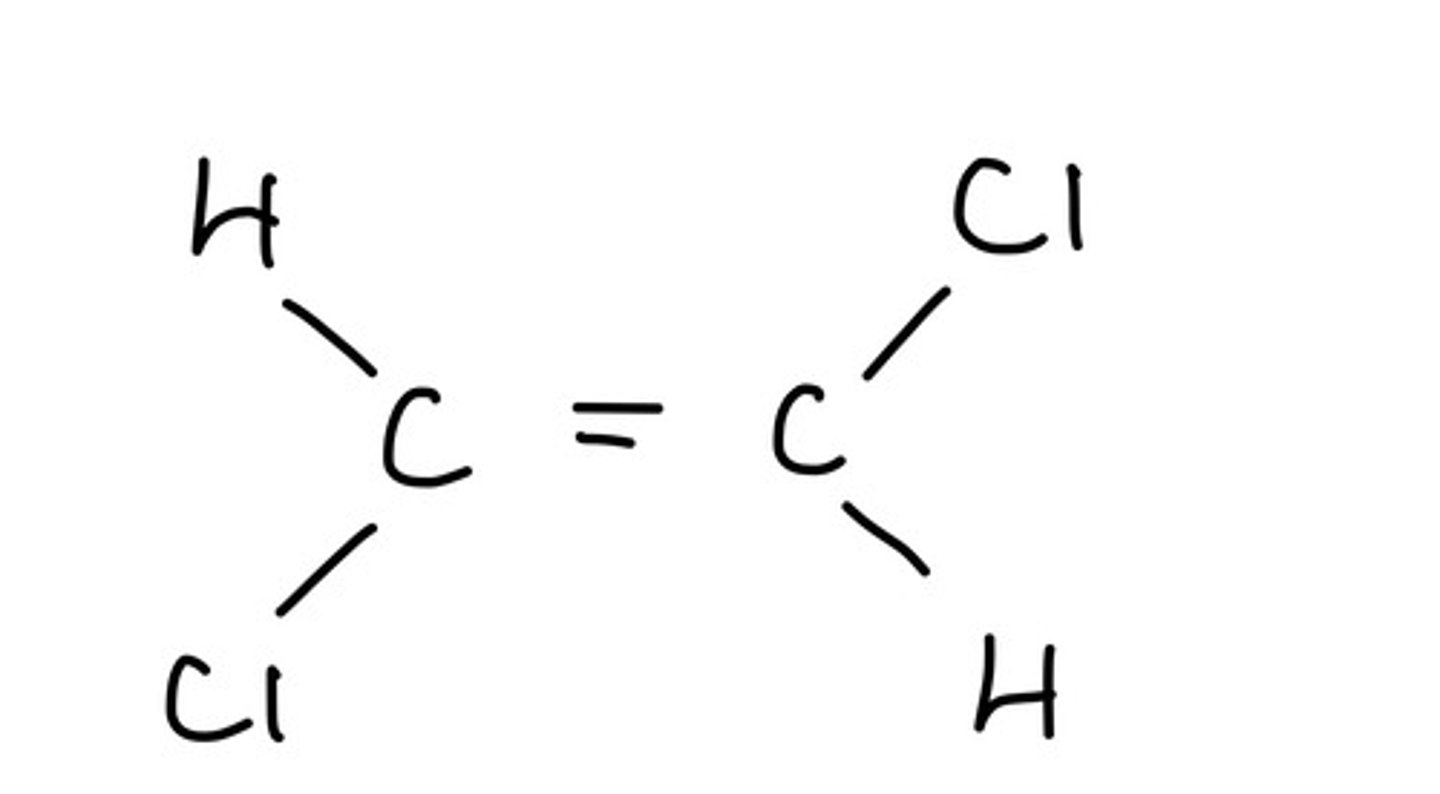
What is an E (entgegen) isomer?
The priority groups are on opposite sides of the carbon chain
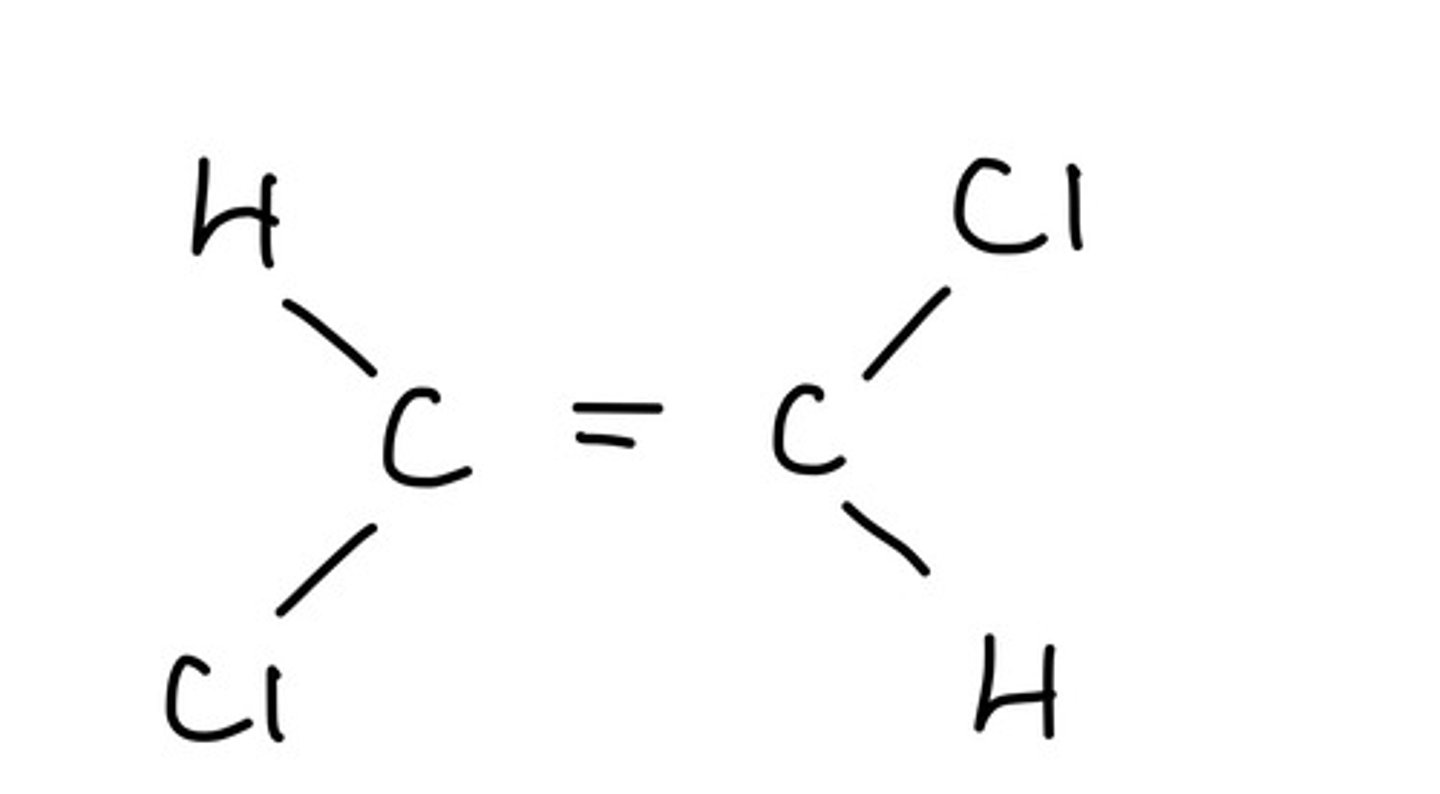
What is a Z (zusammen) isomer?
The priority groups are on the same side of the carbon chain
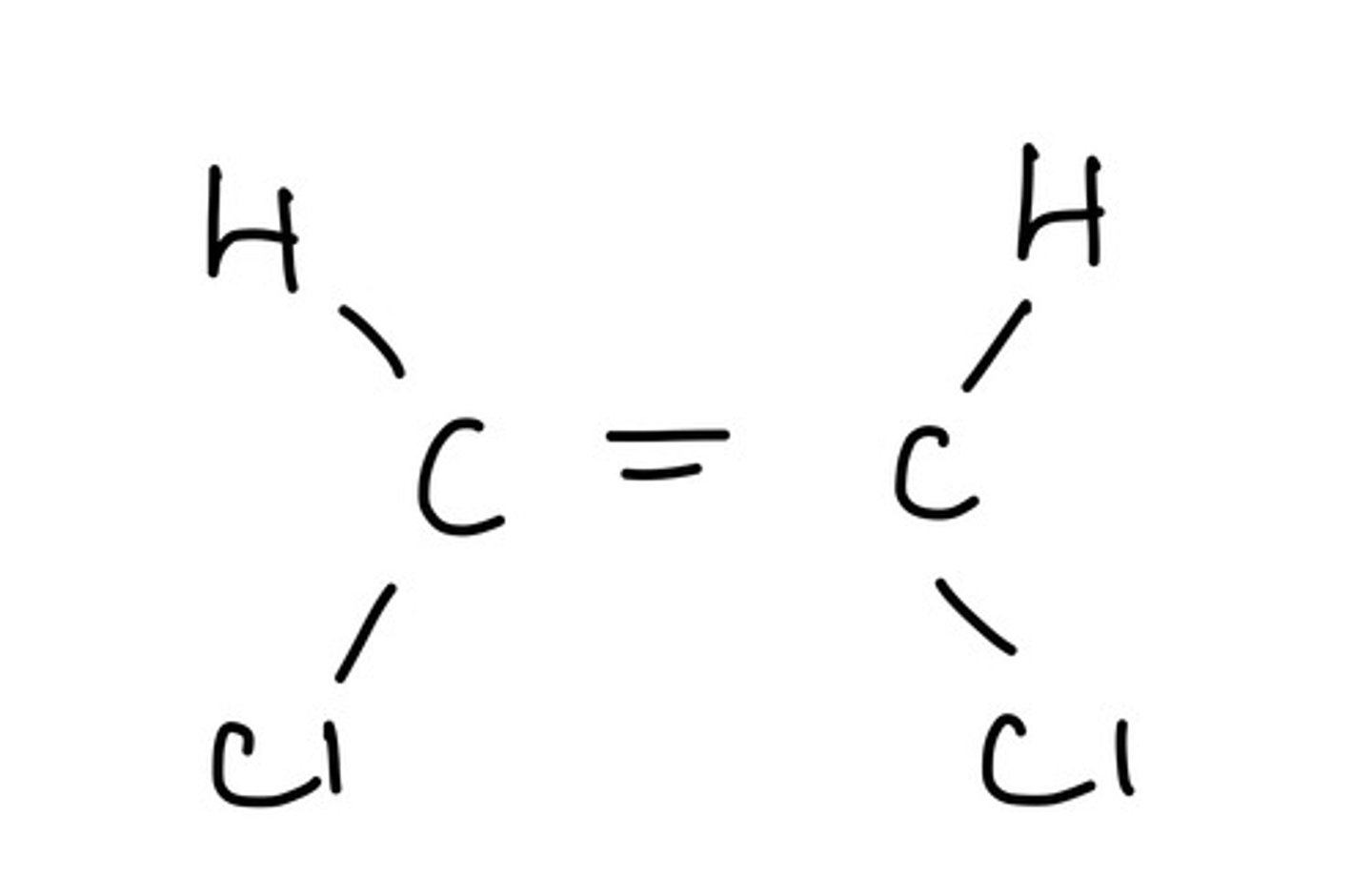
When can cis/ trans or E/ Z notation be used in isomers?
When there is a priority and a non priority group on each side of the double bond
How do you identify a priority group (in the context of isomerism)?
The priority group has the largest atomic mass
What is the effect of geometric isomerism on physical properties?(2)
Z (cis) isomer has a higher boiling point
E (trans) isomer has a higher melting point
Why do Z isomers have higher boiling points than E?(2)
Both have same number of electrons (so Wan der Vaals the same) but Z isomers can be polar because they aren’t symmetrical
Why do E isomers have higher melting points than Z?(3)
The straighter shape of E isomers mean they can pack better than the U of Z isomers so intermolecular forces between Z isomers aren’t as strong as they should be
What is an addition reaction?
A molecule with a C=C double bond reacts with an other molecule to form one product
What is an elimination reaction?
A small molecule is lost from a larger molecule to produce two molecules, one with a C=C double bond
What is a substitution reaction?
An atom or small group is lost from a molecule to be replaced by a different atom or group
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
A covalent bond in a molecule is broken by adding a molecule of water, slitting it into two parts
What is heterolytic fission?(3)
When the covalent bond breaks, both electrons go to one species to form a cation and an anion (X-Y → X+ + Y-)
What is homolytic fission?(3)
When the covalent bond breaks, one electron goes to each species to form two radicals (X-Y → .X + .Y )
What do dots before a chemical symbol indicate?
Unpaired electrons
What a free radical substitution reaction?(3)
An atom or group in a molecule is replaced by a free radical, producing another free radical
What is a radical?
A species with an unpaired electron
What is the the first step of a free radical substitution reaction?
Initiation
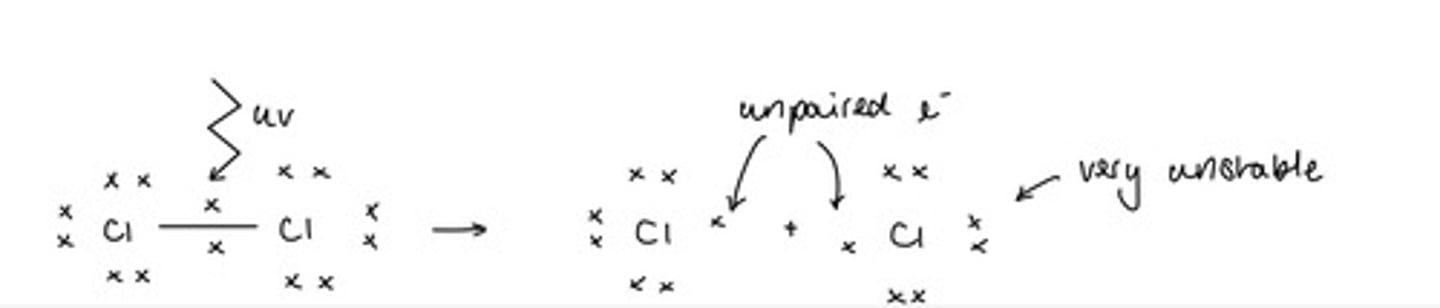
Describe the initiation step of a free radical substitution reaction (using CH4 and Cl2 as examples)(4)
UV light provides energy to split Cl2 into free radicals by homolytic fission
Waves must be of a high enough energy to break the sigma (σ) bond
The radicals are so unstable that no more energy is needed
A chain reaction forms
A Cl-Cl bond breaks feather than a C-H because is has a lower bond enthalpy
What is the second step of a free radical substitution reaction?
Propagation
Describe the propagation step of a free radical substitution reaction (using CH4 and Cl2 as examples)(6)
The free radicals from the initiation step react with CH4 to form HCl and a .CH3 radical
Then the new .CH3 radical reacts with a Cl2 molecule to form CH3Cl and another .Cl radical
The new .Cl radical can now trigger another set of reactions
Unwanted side reactions also occur:
.Cl + .Cl → Cl2
.Cl + .CH3 → CH3Cl
.CH3 + CH3 → C2H6
What is the third step of a free radical substitution reaction?
Termination
Describe the termination step of a free radical substitution reaction (using CH4 and Cl2 as examples)(7)
As the concentration of Cl2 and CH4 falls, more free radicals react with each other
More side reactions
.Cl + .Cl → Cl2
.Cl + .CH3 → CH3Cl
.CH3 + CH3 → C2H6
Slows Down main reaction
When there are no radicals left, the reaction stops
What is the evidence for the free-radical mechanism?(using CH4 and Cl2 as examples)(2)
Production of C2H6 as a minor byproduct
Need for high frequency UV waves to produce 2.Cl from Cl2
What are the limitations of a free radical substitution reaction to produce the major product?
Will not just produce the desired product
Produces a range of side products (may not be useful)
What are the by products of the free radical substitution of CH4 and Cl2?(3)
Cl2
CH3Cl
C2H6
What is the hybridisation of orbitals in alkenes?(3)
One s-orbital and two p-orbitals combine to form three new sp² orbitals
All three are equivalent
Remaining p-orbital is unchanged
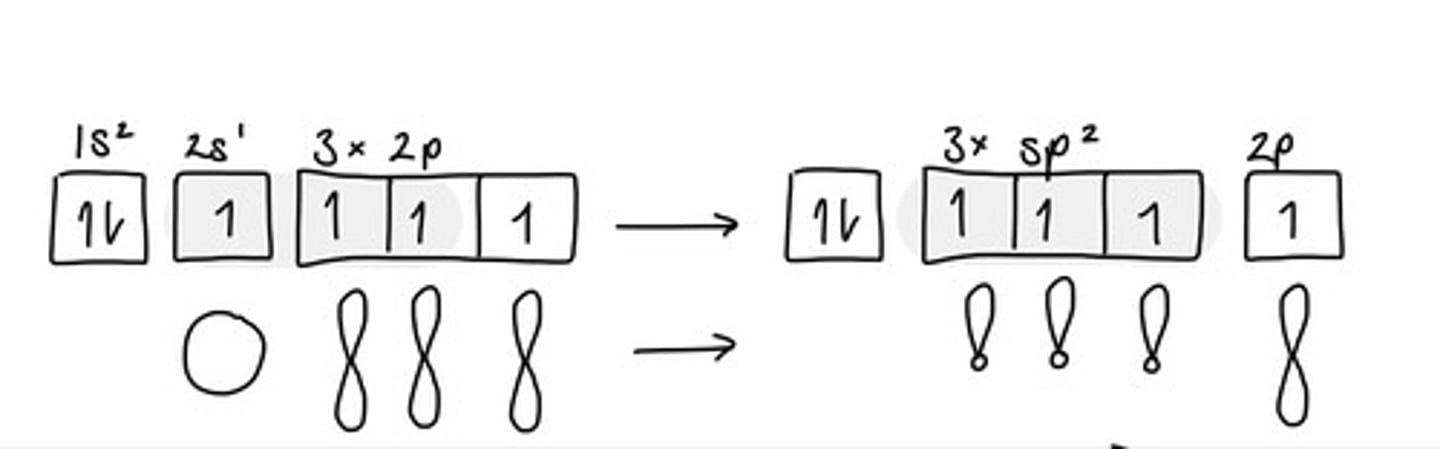
How do carbon atoms form double bonds?(3)
Hybridised sp² orbitals (one form each C) overlap to form a single C-C bond (σ bond)
2p orbitals overlap to form the second bond (π bond)
For maximum overlap, 2p orbitals overlap in a line
What are the main reactions of alkenes?(5)
Hydrogenation
Halogenation
Hydration
Addition of hydrogen halides
Oxidation to diols
What is common in all reactions of alkenes?(3)
Opening of a double bond to form a saturated product
Addition reactions
High electro density in the π bond attracts electrophiles
What is hydrogenation?
Electrophilic addition of H2 to an alkene across the C=C double bond
What are the conditions of hydrogenation?
Hydrogen gas
Nickel catalyst
150 degrees C
What are some of the uses of hydrogenation?(4)
Manufacturing margarine
Reduces the number of double bonds in polyunsaturated veg oils and fats
Increases solidity of the fat so easier for use in cooking
Produces partially hydrogenated oil/fat
What is halogenation?(3)
Electrophilic addition of a halogen to alkene across the C=C double bond
Often with bromine water to test for double bonds
Forms dihalogenoalkane
What are the conditions for halogenation?
Room temp
What is an electrophile?
An electron deficient species that can accept a lone pair of electrons
What is the meaning of curly arrows in reaction mechanisms?(2)
Show the movement of a pair of electrons
Always from an electron pair or a double bond
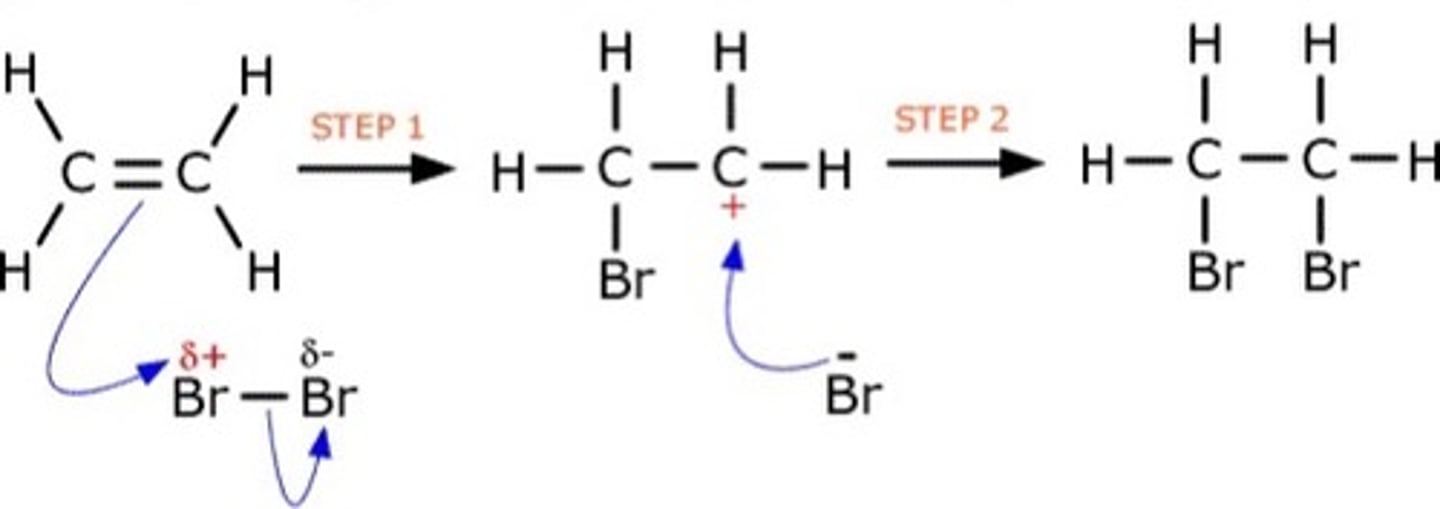
Describe the mechanism for halogenation (use bromine and ethene as examples)(8)
As Br2 approaches the C=C bond, high electron density of the bond induces a dipole in Br2
Delta positive Br in now an electrophile
A pair of electrons from C=C are accepted by the electrophile (this is electrophilic attack)
C=C bond breaks to accept Br atom
Br-Br bond breaks through heterolytic fission
Creates a Br- ion and a carbocation intermediate
Br- will now attack C+ to form a second bond
Creates 1,2-dibromoethane
What is the general term for an oxidising agent?
[O]
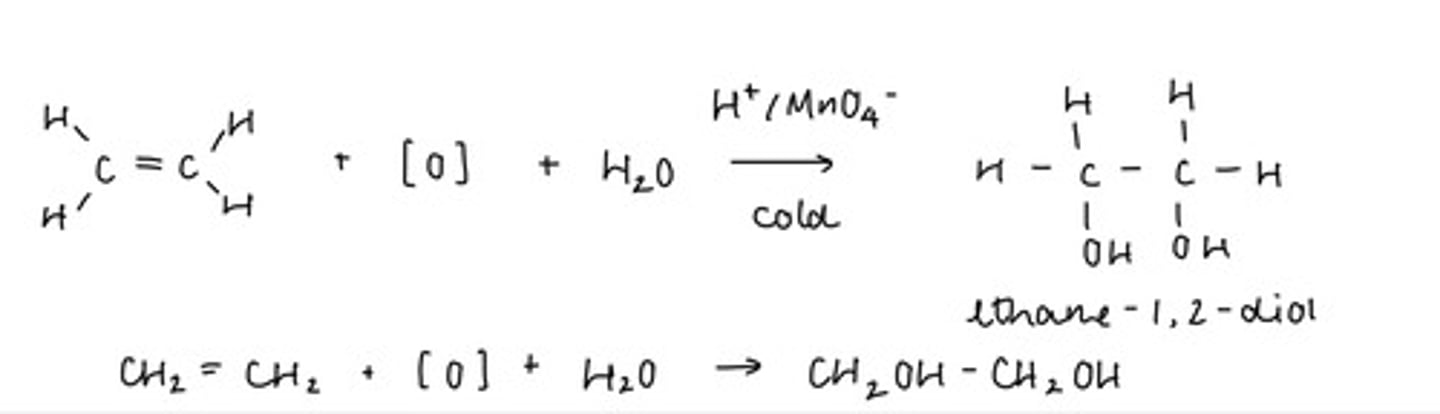
Describe addition using acidified manganate (vii) (5)
An alkene reacts with water and an oxidising agent
Cold, dilute, acidified manganate (vii) used as a catalyst
Double C=C bond is oxidised to form a diol (two OH groups)
O of OH provided by MnO4- and water
H of OH provided by water
What is hydration of an alkene?
Alkene reacts with steam to form an alcohol
What are the conditions of hydration?
Concentrated phosphoric acid catalyst
600 K
6MPa (pressure)
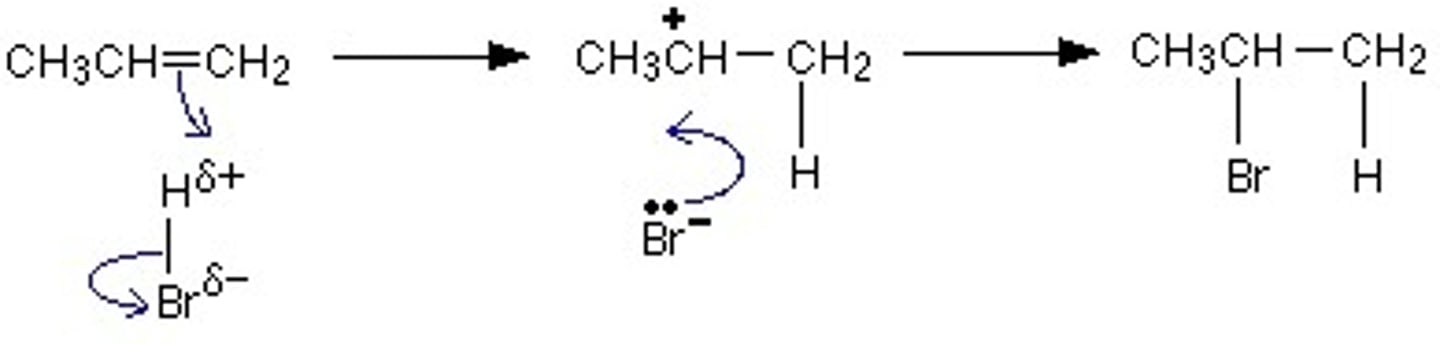
Describe the mechanism for electrophilic addition of a hydrogen halide (use hydrogen bromide and propene as examples)
As HBr approaches the C=C bond, high electron density of the bond induces a dipole in HBr
Delta positive H in now an electrophile
A pair of electrons from C=C are accepted by the electrophile (this is electrophilic attack)
C=C bond breaks to accept H atom
H-Br bond breaks through heterolytic fission
Creates a Br- ion and a carbocation intermediate
Br- will now attack C+ to form a second bond
Creates 2-bromopropane as major product
When is there more than one possible addition product in electrophilic addition with an alkene?
If the alkene is unsymmetrical
What are the three types of carbocations (+explain)?
Primary: C+ is bonded to one other C atom
Secondary: C+ is bonded to two other C atoms
Tertiary: C+ is bonded to three other C atoms
What is the most stable type of carbocation?
Tertiary
What will the major carbocation intermediate be in an electrophilic addition reaction?
The one where the C+ is bonded to the highest number of other C atoms (the most stable one)
Why are tertiary carbocations more stable than secondary etc?
More alkyl groups 'push' the electrons in the covalent bonds towards the C+, stabilising it
State Makovnikov's rule
When compound HX is added to an unsymmetrical alkene, the hydrogen becomes attached to the carbon atom with the most hydrogen atoms attached to it
How are radicals formed?
By homolytic fission of a covalent bond
What is crude oil?(4)
Mixture of hydrocarbons, mainly alkenes
Varying viscosities, volatilities and carbon chain length
All dissolved in each other
Not very useful in raw form so must be separate and processed
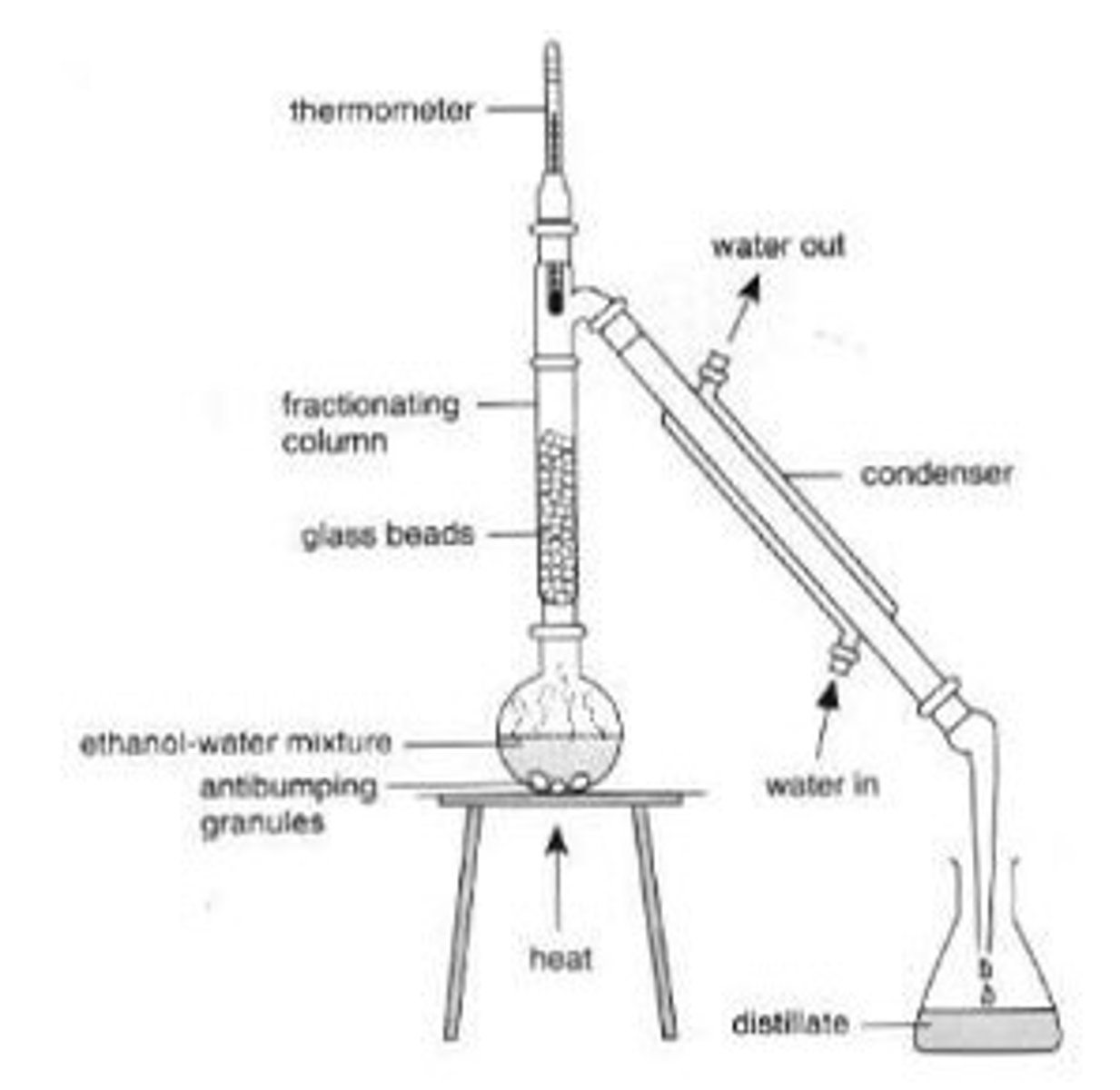
What is fractional distillation?
Process of separating a mixture into different components (fractions) based on boiling points.
Describe the fractional distillation of crude oil (4)
Heated crude oil is led into a fractionating column
Decreases in temperature the further you go up
As soon as crude oil reaches the fractionating column, each fraction will evaporate
Once cool enough, each fraction will condense and fractions can be collected
What is cracking?(3)
Vaporising and breaking up large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller, more useful alkanes and alkenes
Combust more cleanly and are more volatile
Either high pressure and temperature with no catalyst, of lower pressure and temperature with a zeolite catalyst (500 degrees C)
What is reforming?(3)
Turning small hydrocarbons (often 5-10 carbon atoms) into cyclic hydrocarbon and hydrogen
Changes physical and chemical properties
Requires high pressure, temperature and either platinum or rhenium catalyst
What is a catalytic converter?(2)
Exhaust emission control system
Reduces toxic gases and pollutants form an internal combustion engine into less toxic pollutants by catalysing redox reaction
How do catalytic converters work?(3)
Reduce nitrogen oxides into N2 and O2
Oxidise CO into CO2 and water
Require oxidative and platinum or rhodium catalyst
What are alternative fuels?
Any material or substance that can be used as a fuel, other than conversational fuels such as fossil fuels and nuclear material