CCIV: BST
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
mesoderm; notochord and neural tube
somites form from ________ on either side of the _________ and ________
sclerotome
ventromedial portion of the somite
dermomytome
dorsolateral portion of somites
vertebrae and ribs
the sclerotome (ventromedial of the somite) forms the ?
myoblasts and dermis
the deromyotome (dorsolateral of the somite) forms the?
late week 4 to early week 5
when do limb buds begin to elongate?
myogenic cells (myoblasts)
originate from somite and migrate into limb buds
cylindrical myotubes containing myofilaments (muscle fibers)
what do myoblasts fuse into?
weeks 4-8
when do the hands and feet develop?
end of week 6
when are hand plates visible and are forming digital rays?
digital rays
by the end of week 6, hand plates are visible and form ?
week 7
when do toe buds form?
apoptosis
the loose mesenchyme between digits must undergo _________ to create separate digits by the end of week 8
week 8
by when must loose mesenchyme (webbing between digits) must undergo apoptosis to create separate digits ?
week 7
when does osteogenesis of long bones begin?
week 12
by when are ossification centers present in all long bones?
weeks 7-8
what week ? (hand plate present with elongated digits, but webbing still present, toes are starting to form)
intramembranous
bone formation in which mesenchymal cells differentiate directly into osteoblasts between two membrane sheaths and osteoblasts secrete osteoid
intramembranous
what type of bone formation for flat bones?
endochondral
bone formation in which mesenchymal cells condense and differentiate into chondrification centers in the late 5th week; cartilage models of bones form; by week 8 primary ossification centers form within cartilage models
late week 5
when do mesenchymal cells condense and differentiate into chondrification centers for endochondral bone formation?
week 8
when do primary ossification centers begin to form within cartilage models in endochondral bone formation
endochondral
which type of bone formation for long, short, and irregular bones?
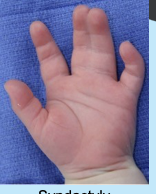
syndactyly
failure of webbing to degenerate creating fused digits
syndactyly
polydactyly
supernumerary digits
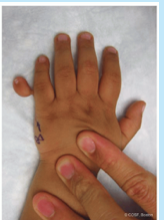
cleft hand (foot)
failure of the digit rays to form and becomes only 2-3 opposing parts
cleft hand
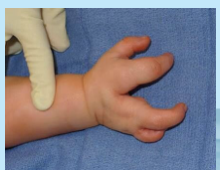
congenital talipes (clubfoot)
clubfoot; many different types
uncertain etiology - sometimes hereditary but often environmental factors
multifocal inheritance pattern
talipes equinovarus
most common type of congenital talipes with foot turned medially and inverted

congenital talipes (clubfoot)
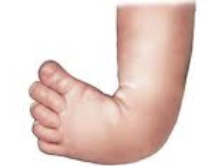
amelia
complete absence of limb from suppression of limb bud development in the early 4th week
meromelia
partial absence of a limb from arrest or disturbance of growth during the 5th week
Genetic factors (trisomy 18)
Mutant genes = skeletal dysplasias (achondroplasia), bradydactyly, or osteogenesis imperfecta
Environmental factors (thalidomide)
Vascular disruption and ischemia
what are common causes of limb defects (4)
long
what type of bone: humerus, radius, ulna, metacarpals, phalanges, femur, fibula, tibia
short
what type of bone: tarsal, carpals
irregular
what type of bone: vertebrae, sacrum
flat
what type of bone: cranial, sternum, scapula, ribs
sesamoid
what type of bone: patella
pivot
what type of joint: neck (C1-C2)
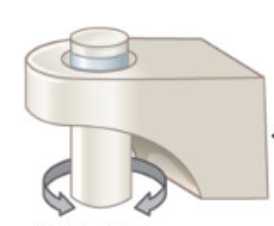
hinge
what type of joint: elbow
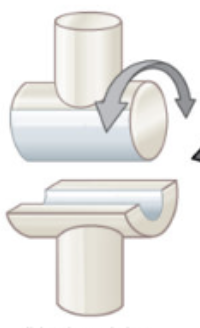
saddle
what type of joint: thumb
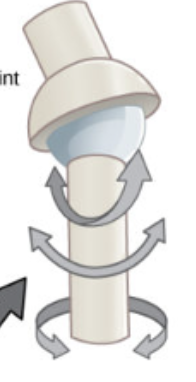
ball and socket
what type of joint: hip
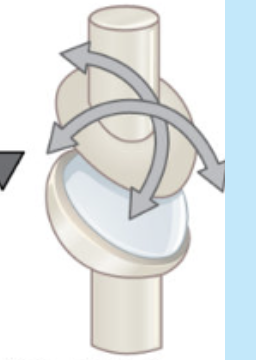
condylar
what type of joint: wrist
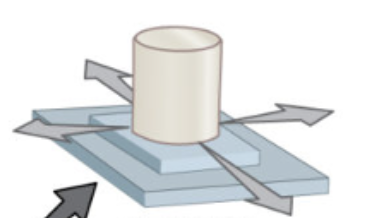
plane
what type of joint: between tarsal bones of foot
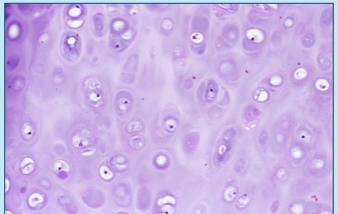
hyaline cartilage
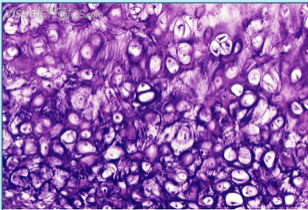
elastic cartilage
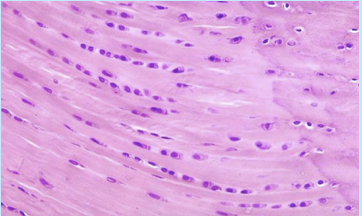
fibrocartilage
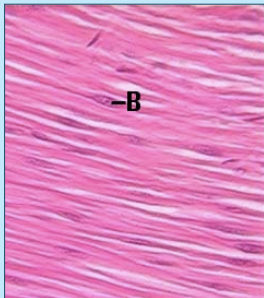
smooth muscle
skeletal muscle
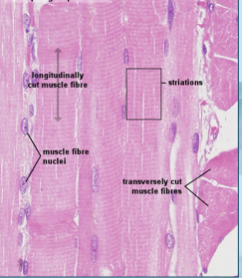
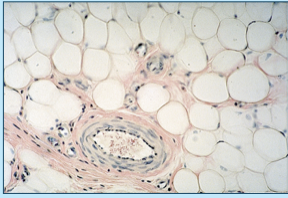
adipose tissue
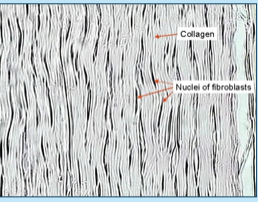
dense fibrous tissue
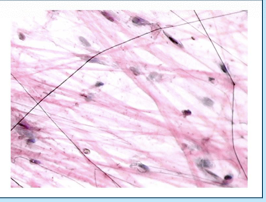
loose fibrous tissue
eburnation
the result of long term bone-on-bone movement making the surface smooth and glistening (ivory-like)
DJD/osteoarthritis
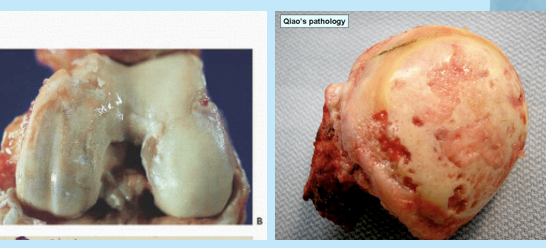
DJD/osteoarthritis
older patients, obese, athletes
bone components within joint are in contact after wear and tear → damaged articular cartilage and underlying bone
femoral heads, knee bones, humeral heads
eburnation, surface pitting/distortion, subchondral cysts, osteophytes
avascular necrosis
trauma, infection, alcoholism, steroid use, sickle cell disease
almost always femoral heads
cartilage over the infarct separates from underlying bone
buckling, distortion, minimal eburnation
avascular necrosis
crescent-sign on x-ray
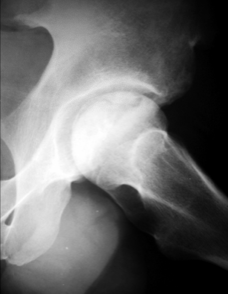
avascular necrosis
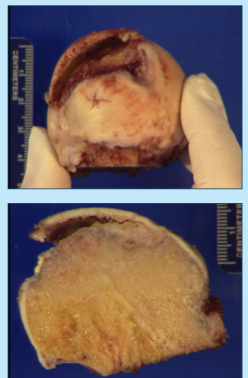
osteophytes
overgrowth on periphery of bony joint components, result of DJD
loose bodies
detached osteophytes from injury, wear and tear
gout
transient attacks of acute arthritis initiated by crystallization of urate within and around joints
primary
gout from overproduction/reduced excretion of uric acid from diet or enzyme deficits (90%)
secondary
gout from overproduction/reduced excretion of uric acid from renal disease or neoplasm (10%)
gout
synovium thickened, fibrotic, and forms pannus which destroys the underlying cartilage
tophi = aggregations of urate crystals
chalky white substance grossly
needle-shaped crystals with birefringent light
gout
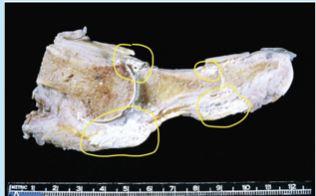
gout
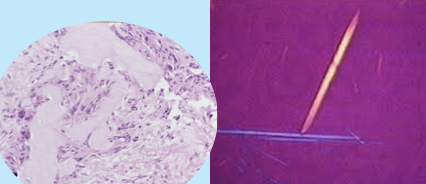
false (chalky substance will not be present in formalin-fixed tissue so MUST use alcohol)
T/F: gout can be placed in formalin
true (formalin will not dissolve but DECAL WILL)
T/F: pseudogout can be placed in formalin
pseudogout (chondrocalcinosis)
calcium pyrophosphate (CPP) crystals
more common
commonly affects knees
mimics tophi with no destruction of underlying bone
chalky white substance grossly
oval/block-shaped crystals
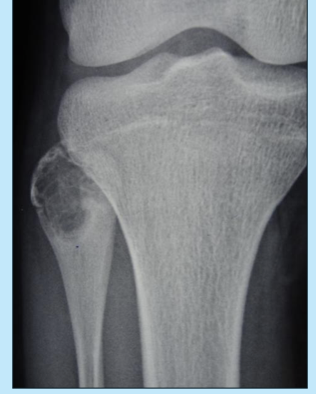
aneurysmal bone cyst
first 2 decades of life
multiple blood-filled spaces separated by thin, tan-white septa and covered with a thin layer of bone
treated by curettage (or en bloc in certain situations)
aneurysmal bone cyst
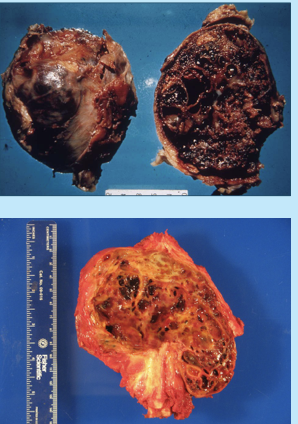
osteomyelitis
inflammation of the bone/bone marrow which leads to infection
injury site, surgical site, ulcer
bone softening, instability, abscesses
loss of blood supply → distal degeneration
can spread into vasculature and cause sepsis/death
wet/dry ulcers, gangrene, eschars, skin sloughing, mummification
osteomyelitis
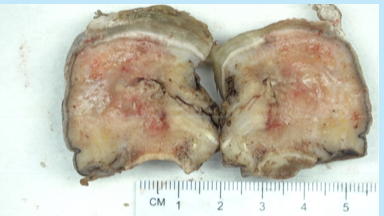
incidental ribs (multiple myeloma is most important dx!)
what specimen is often received for thoracic outlet syndrome?
assess if there is osteomyelitis present
check margin viability
determine if PVD is present
why would we gross a specimen for osteomyelitis
wrist
where are ganglion cysts most commonly found?
synovial cyst
herniation of the synovium through a joint capsule
baker’s cyst
cyst in the popliteal synovium
morton’s neuroma
compression neuropathy in the foot
osteoma
sessile, bosselated, round/oval tumors growing from subperiosteal cortex
usually bones of the face/skull
slow growing, often incidental
gardner’s syndrome
multiple osteomas present
osteoma
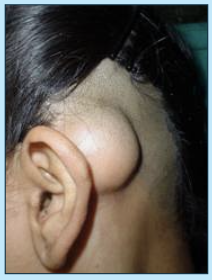
osteoma
osteoid osteoma
< 2 cm
appendicular skeleton, posterior spine, talus
severe nocturnal pain relieved by aspirin
severe underlying reaction of bone
treated by radioablation (not usually received in surg path)
osteoblastoma
> 2 cm
spine
dull achy pain that is not responsive to aspirin
no bony reaction
excised
giant cell tumor
uncommon, benign but locally aggressive
20-40 years old
most common in knee and arise from epiphysis
destroys overlying cortex producing a large bulging ST mass with a thin shell of reactive bone
large red-brown masses with cystic degeneration
giant cell tumor
multinucleated osteoclast-like giant cells with a background of mononuclear cells with nuclei identical to giant cells
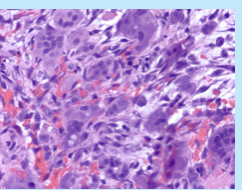
giant cell tumor
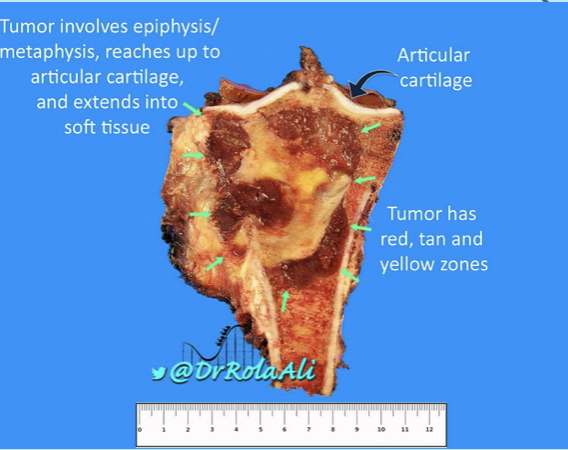
osteochondroma
benign, most common bone neoplasm
late teens, early adults
endochondral origin - metaphysis near growth plate
hyaline cartilage-capped tumor with “bony stalk”
most common in knee
osteochondroma
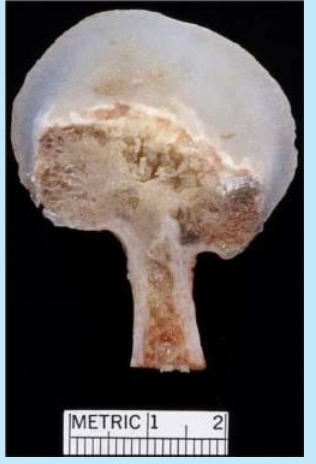
osteochondroma
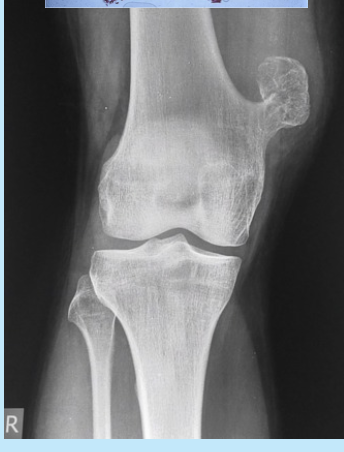
chondroma
benign neoplasm of hyaline cartilage
incidental and asymptomatic
20-50 years
chondroma
well-circumscribed lucencies, with focal opacities if calcified
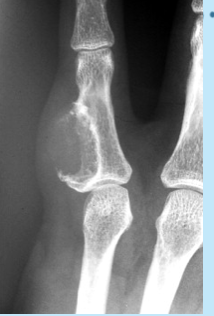
enchondroma
chondroma within the medullary cavity
chondroma
“scalloping” from nodules pushing into endosteum
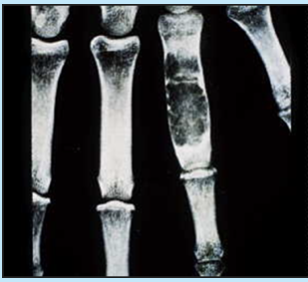
maffucci syndrome
endochondrmatosis associated with ST hemangiomas which can become large and cause deformities
chondroblastoma
very rare bone tume (<1%)
teens, male > female
benign but aggressive
“chicken wire” pattern of calcifications on histo
bone currettage
typical specimen received for chondroblastoma
chondroblastoma
well-defined lucency with scattered calcs