fields and their consequences ^_^
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Is force a vector or scalar quantity?
● Vector
● It has both a magnitude and an
associated direction
what are some similarities between electrostatic and and gravitational forces?
inverse square force laws
potential concept
equipotential surfaces
use of field lines
what are some differences between electrostatic and gravitational forces?
gravitational forces are always attractive, charges can both attract and repel
What is gravity?
a force of attraction between objects due to their masses
what is G
The universal Gravitational constant 6.67 x 10^--11
What can field lines tell you about a field?
The direction of the field and the strength of the field depending on the density of the field lines.
what is g?
the force per unit mass in a uniform field.
in a radial field, the magnitude of g is the proportionality constant at that point between force and mass.
What is gravitational potential?
The potential energy per kilogram, at any point in the field. 0 potential is defined at infinity, hence at a point close to a mass the potential of an object would be negative.
what is the work done by moving a mass in a field?
Mass x change in potential
what is the gravitational potential difference?
Gravitational potential difference is the difference in the gravitational potentials of two points in a gravitational field.
what is an equipotential surface?
A surface in which every point on the surface has the same potential
how much work is done when you move 1km in any direction on a equipotential?
no work is done as the potential is the same at each point
Why is gravitational potential negative?
Because you have to do work against the gravitational field to move an object out of it. as outside is defined as 0 then inside must be negative.
How is the orbital period related to the radius of a circular orbit?
T^2 is directly proportional to R^3
Compare the PE and KE of a lower orbit to a higher one.
a lower orbit has less potential and more kinetic than a higher one
what is the period of a geosynchronous orbit?
Geosynchronous orbits have a period of one day.
what symbol represents the permittivity of free space?
ε0
when calculating the force between 2 particles what can air be treated as?
a vacuum
for charged spheres, the charge can be assumed to be at what part of the sphere?
the centre
what is stronger? the gravitational force or the electrostatic?
electrostatic
electric field lines always go from______________ to ____________
positive to negative
what is electric field strength?
The force per unit charge acting at a point in an electric field.
what is the magnitude of electric field strength in a uniform field?
constant for all points
what is the trajectory of a particle entering a uniform field at right angles?
its parabolic (curved, u-shaped)
how is electric potential related to electric field strength?
E = V/r
how is capacitance calculated?
C = Q/V
what is relative permittivity?
The ratio of charge stored with the dielectric to the charge stored without the dielectric. the greater the permittivity, the greater the capacitance.
what does the area under the graph of charge against p.d represent?
the energy stored in the capacitor.descibe
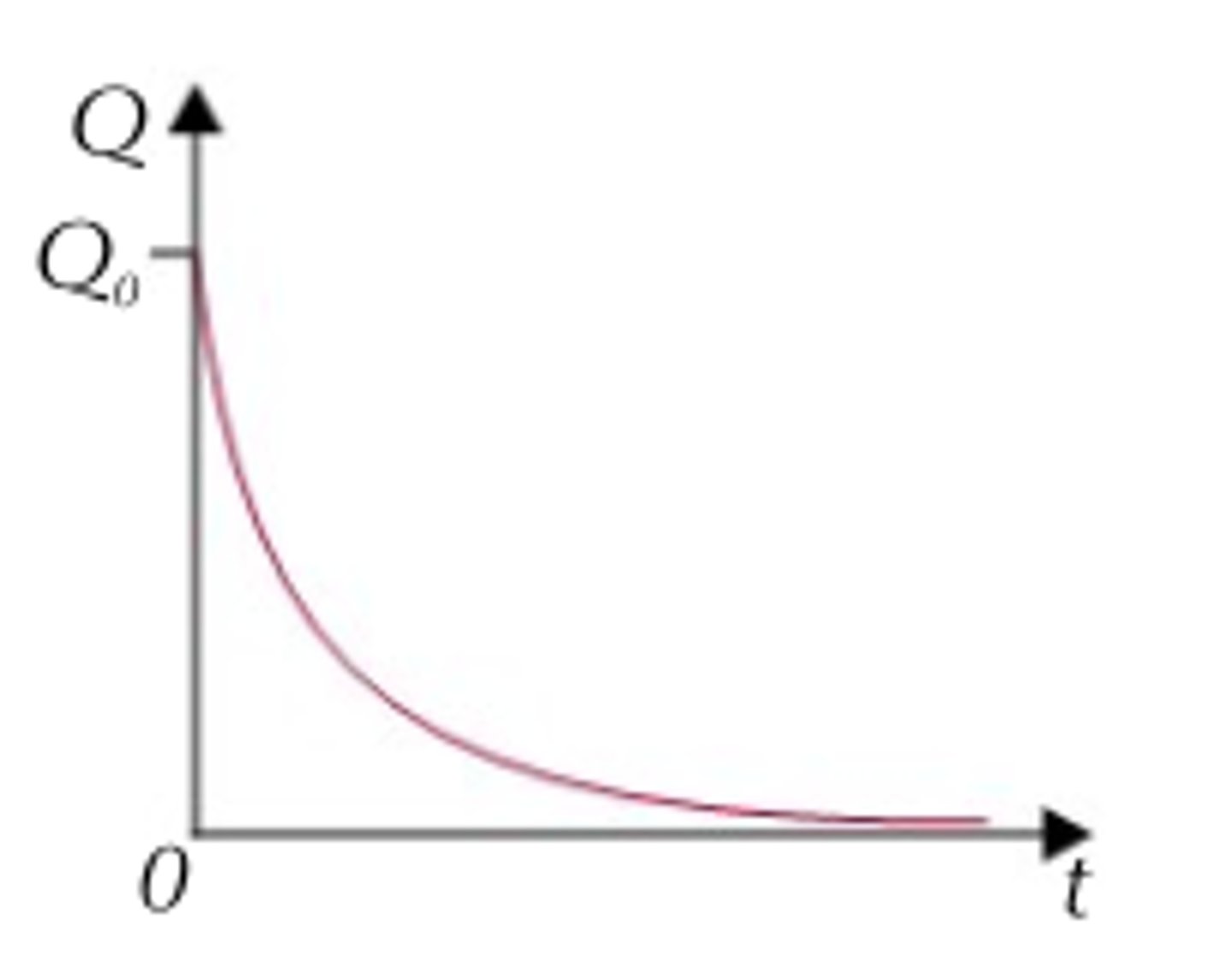
Describe the Q against t graph for the discharging of a capacitor through a resistor.
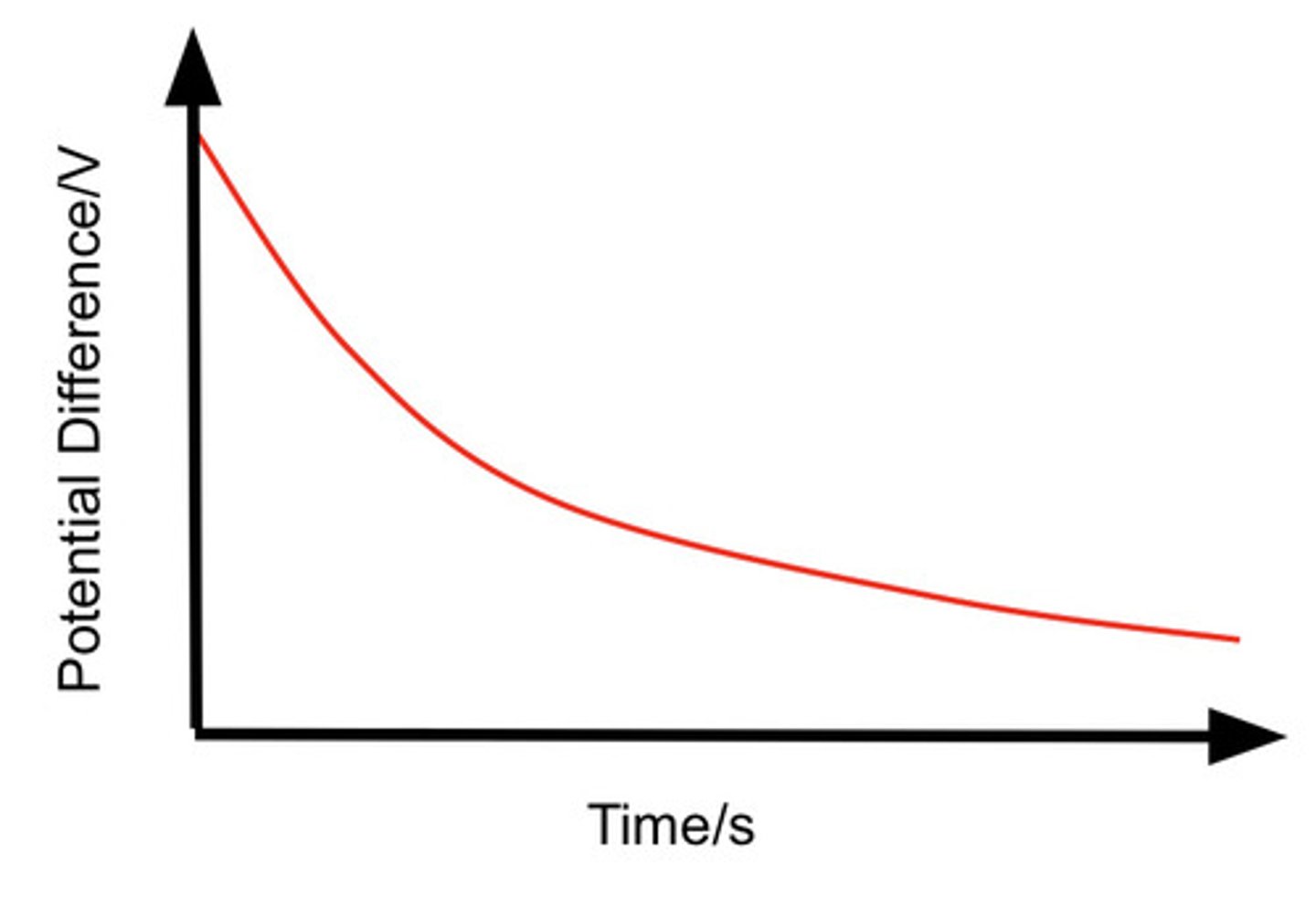
Describe the V against t graph for the discharging of a capacitor through a resistor.
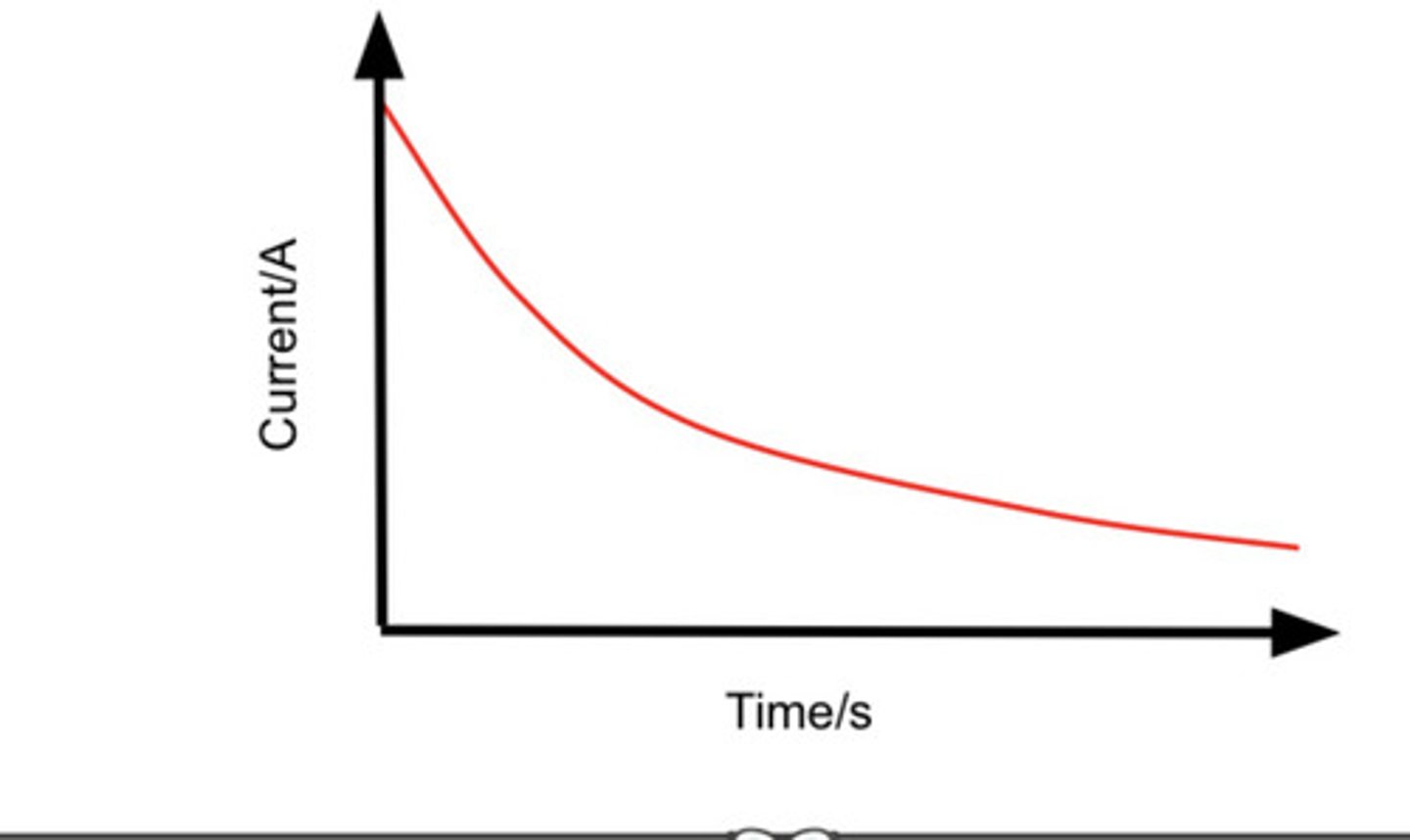
Describe the I against t graph for the discharging of a capacitor through a resistor.
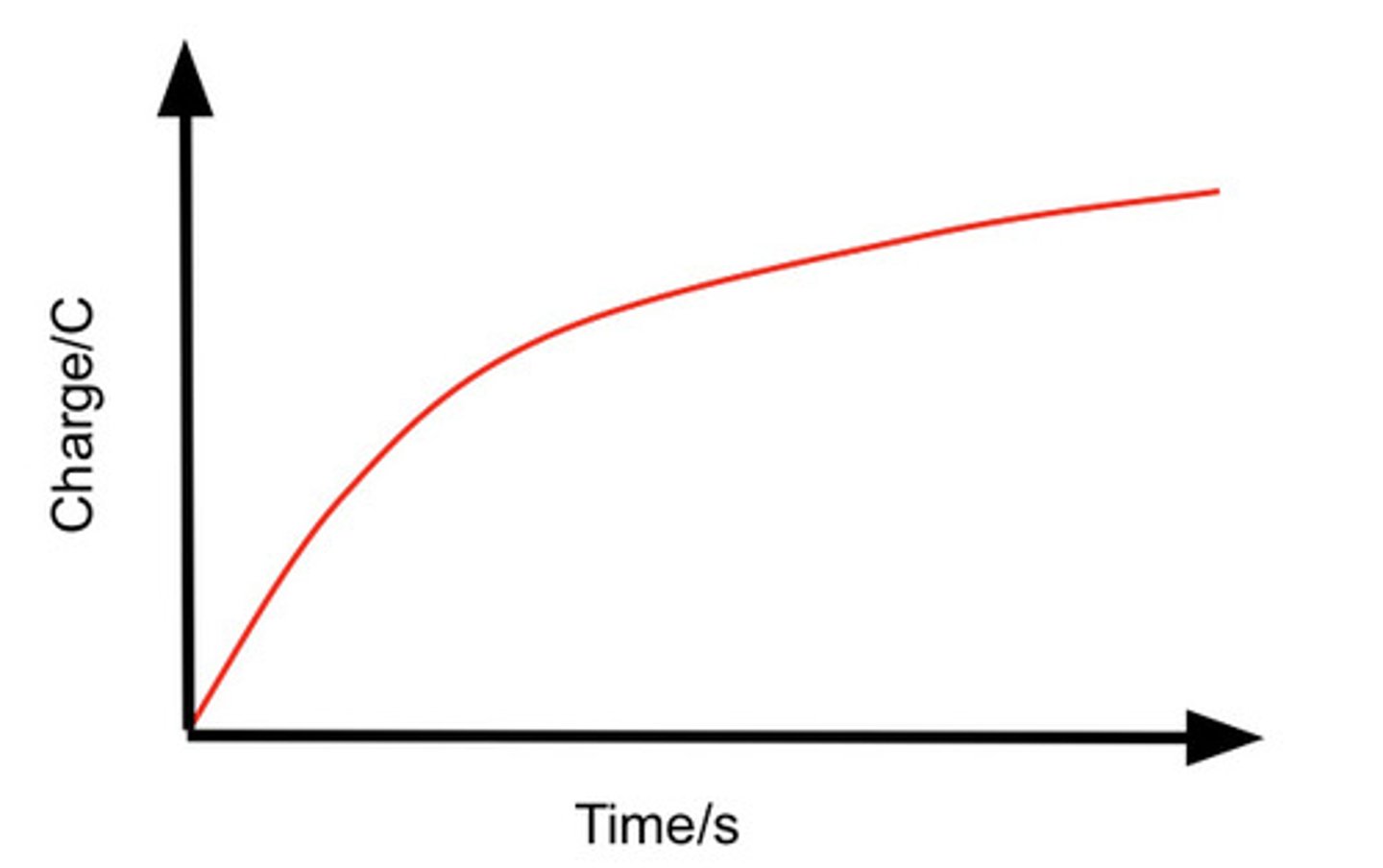
Describe the Q against t graph for the charging of a capacitor through a fixed resistor.
Describe the V against t graph for the charging of a capacitor through a resistor.
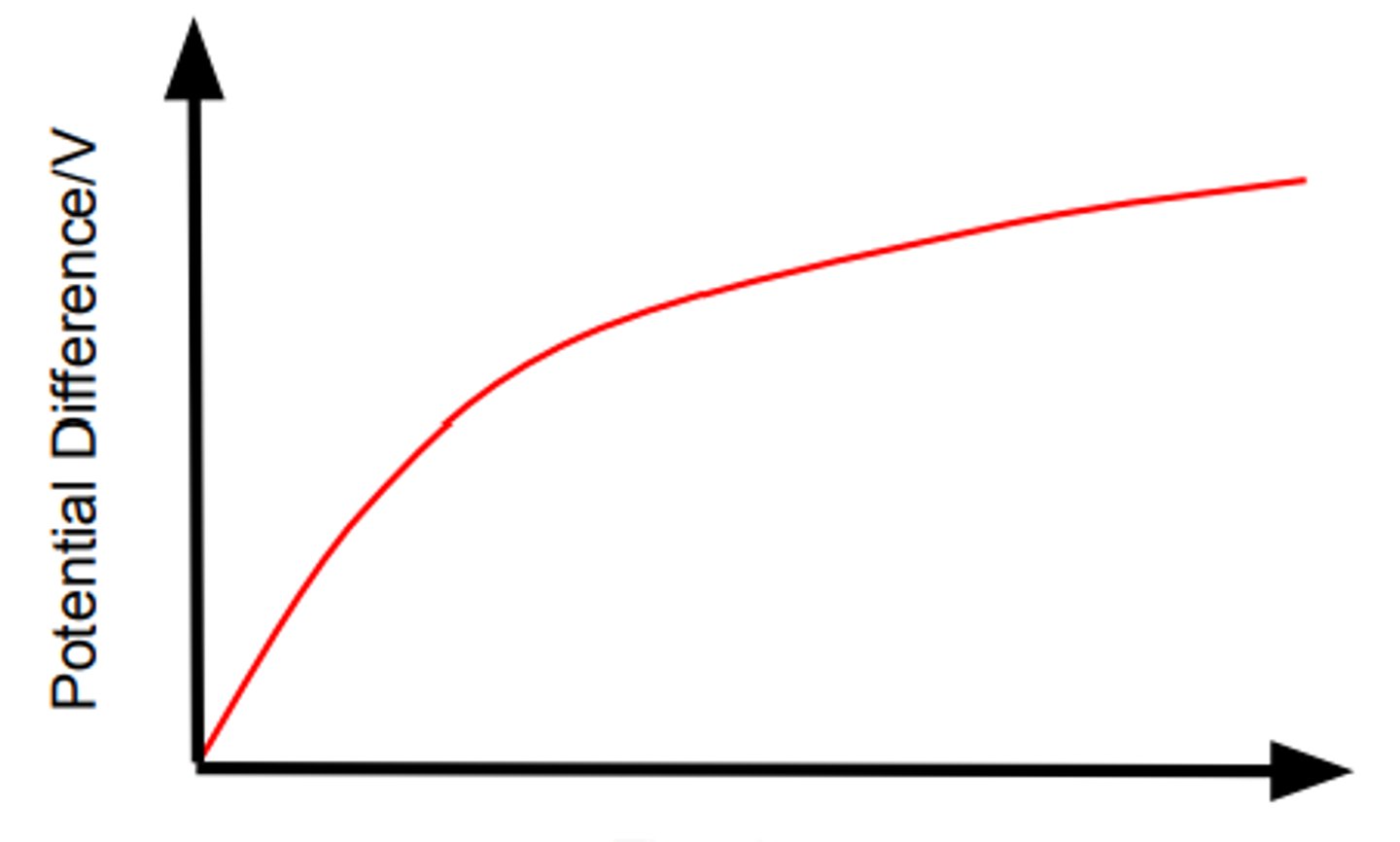
What is the time constant?
The time taken for a capacitor to discharge to 37% its peak voltage/charge to 63% its peak voltage
How was 37% derived when using the time constant?
● Start with the formula Q = Q0 e -t/RC
● When t = RC (after 1 time constant), the formula becomes Q = Q0 e -1
● e-1 ≈ 0.37, which is where 37% came from.
What is the half time of a capacitor?
T½ = 0.69RC
What equations do we require for charging a capacitor?
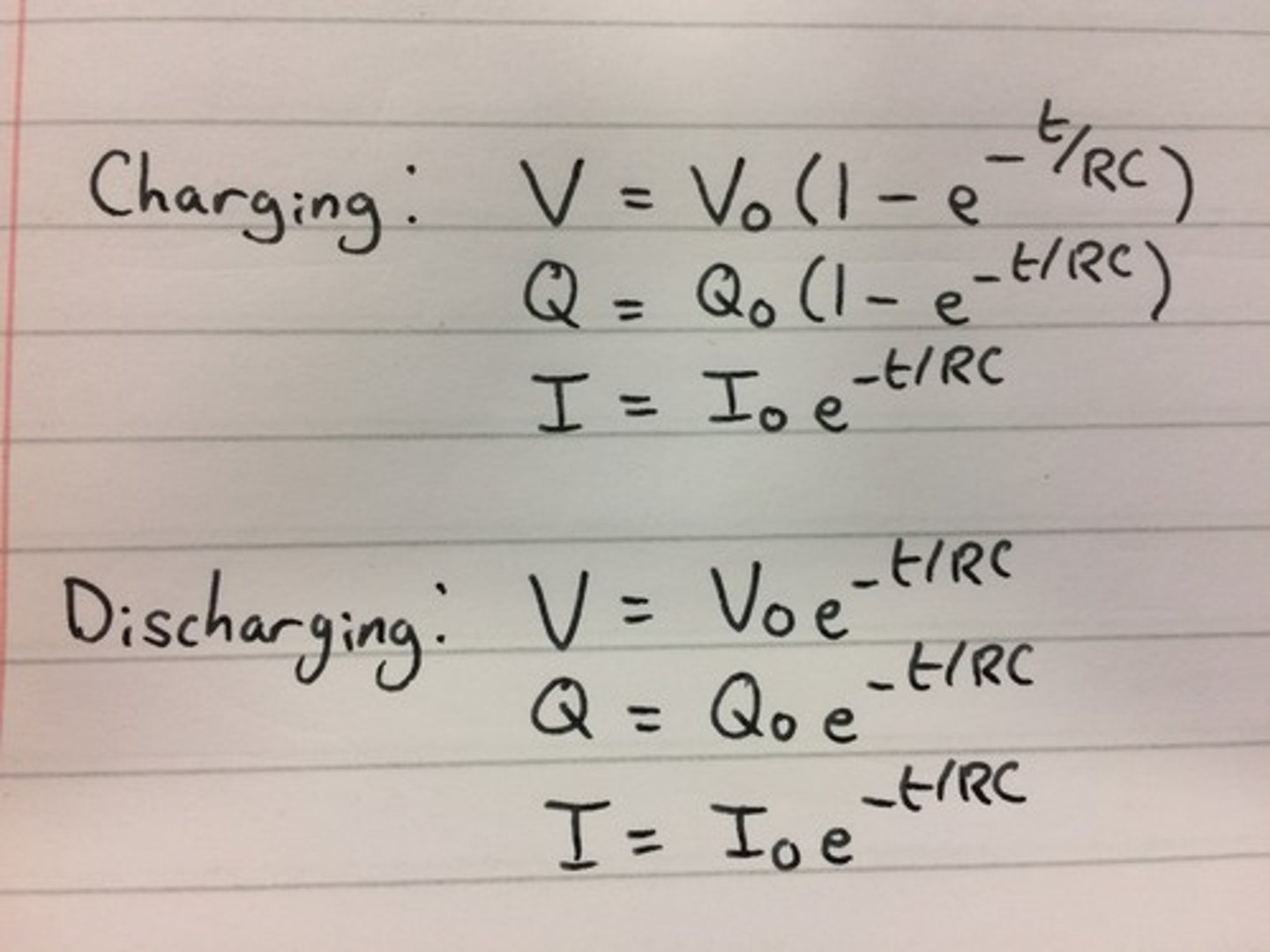
how does a capacitor charge up?
1. Electrons move from negative to positive around the circuit.
2. The electrons are deposited on plate A, making it negatively charged.
3. Electrons travel from plate B to the positive terminal of the battery, giving the plate a positive charge.
4. Electrons build up on plate A and an equal amount of electrons are removed from plate B, creating a potential difference across the plates.
5. When the p.d across plates = source p.d., the capacitor is fully charged and current stops flowing.
describe and explain in terms of thee movement of the electrons how the p.d across a capacitor changes when it discharges across a resistor.
electrons move in opposite direction than when the capacitor was charging up.
charge on plate A decreases as it loses electrons and plate B gains electrons neutralising them.
p.d decreases exponentially across the plates.
State the 3 expressions for the energy stored by a capacitor.
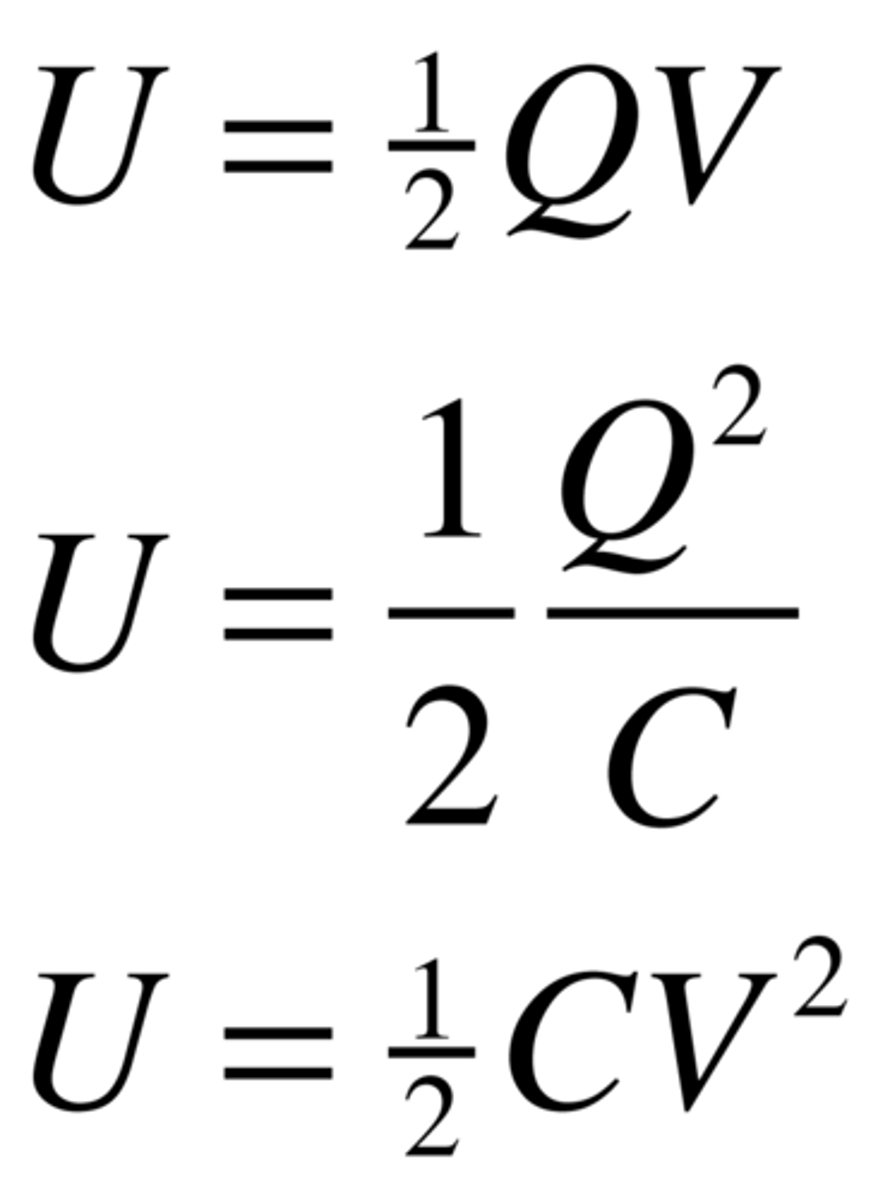
what 2 factors affect the time taken for a capacitor to charge or discharge?
the capacitance - affects the amount of charge that can be stored
resistance - affects the current in the circuit and how quickly it flows, hence how quickly it charges/discharges.
When a magnetic field is perpendicular to a current-carrying wire, does the wire feel a force?
yes
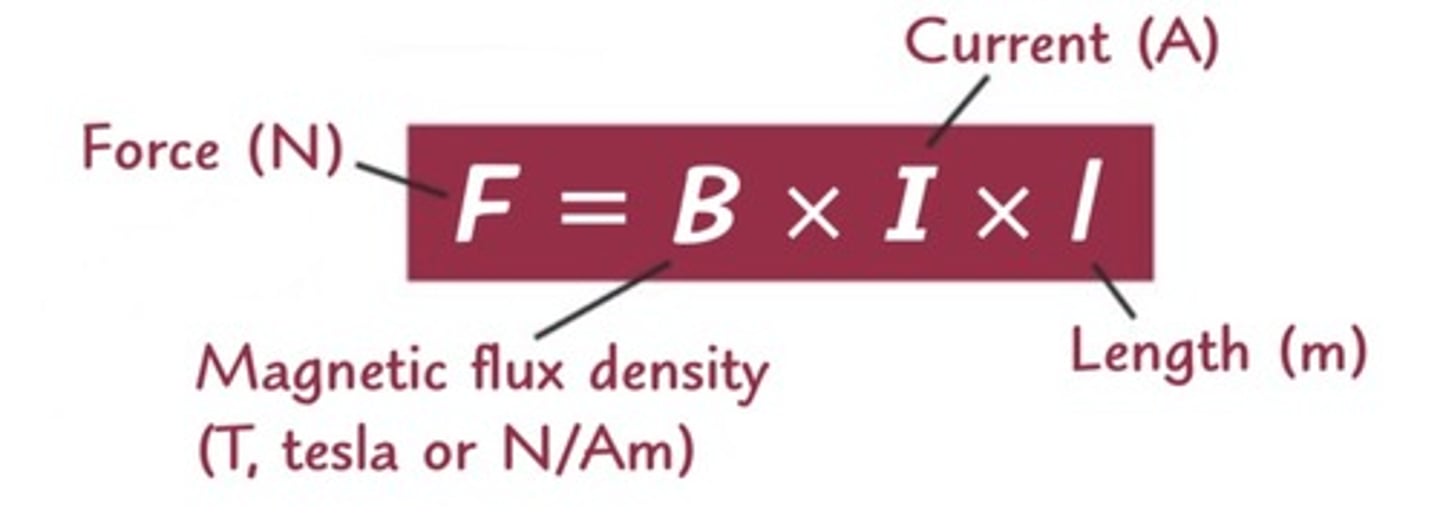
flemmings left hand rule for motors represents what properties on what fingers?
thumb - force
first finger - field
second finger - current
what is magnetic flux density?
Flux density measured in Tesla (T) or Webers/meters² (Wb/m²), is the flux per metre².
a charged particle moving through a field feels a force when it is travelling along the field lines or perpendicular to them?
perpendicular to them
what is the equation for the force felt by the moving charge in a magnetic field?
F = BQV
Is the force applied to the particles applied perpendicular to the particles motion or in one direction?
perpendicular to its motion, causing it to move in a circular motion.
which fields to cyclotrons use?
electric and magnetic
How does a Cyclotron work and what's the electric and magnetic fields purpose in a cyclotron?
it is made up of 2 semicircular electrodes called dees with a magnetic field applied perpendicular and alternating p.d applied between them. each dee is a metal electrode with opposite charges creating an electric field in the gap. this accelerates the particles. the magnetic field causes the particles to move in a circular motion, which allows it to gain speed whilst minimise space. as they speed up the radius of their motion increases, until it breaks free tangential to one of the dees.
what is magnetic flux?
number of turns cutting the flux at one time
What is the flux linkage of a rectangular coil rotating through a magnetic field?
BAN cos
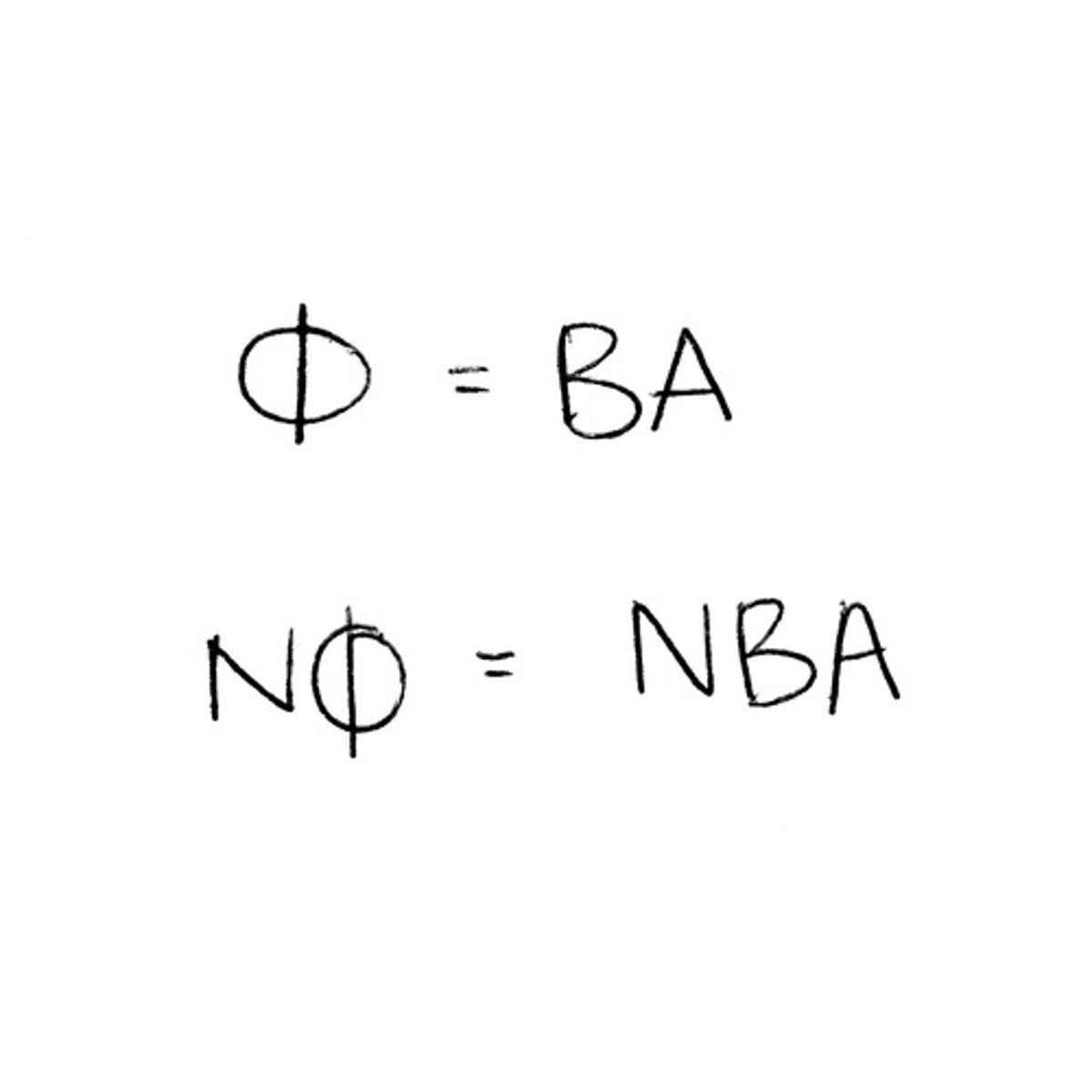
What is Faraday's Law?
The induced emf is directly proportional to the rate of change of flux linkage
What is Lenz's law?
The induced e.m.f is always in such a direction as to oppose the change that caused it.
what happens when you move a straight conductor through a magnetic field?
the electrons experience a force pushing them to one end of the conductor creating an emf across the conductor. the rod obeys faradays law. it is changing flux as it moves through the field hence the emf is induced.
what would the emf produced be when rotating a coil at a constant rate in a magnetic field?

how do you use an oscilloscope?
1. find suitable time base
2. count how many waves until line hits projection on x axis
3. count squares to that point
4. work out 1 wave
5. multiply by time base
6. this gives the time and to work out frequency= 1/T
how does a transformer work?
When an alternating current travels in the primary coil a fluctuating magnetic field is created which continually cuts the secondary coil inducing a voltage
what kind of current is produced in a transformer and why?
alternating as the emf is induced by a changing magnetic field hence the emf induced is alternating.
Why are transformers used?
By changing the number of coils, the transformers can be used to increase the voltage and reduce current when transporting power, with minimal energy loses. The voltage is then dropped again locally to ensure safe usage in households.
what equation links the number of coils in a transformer with their voltages?
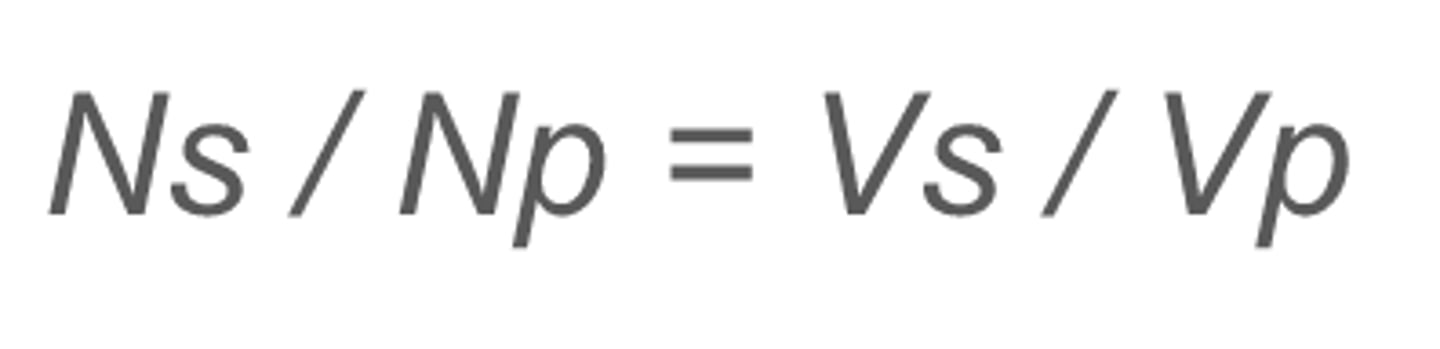
what is transformer efficiency?
The ratio of output power in the transformer to input power.
= IsVs / IpVp
in a step up transformer does the secondary coil or the primary coil have more turns?
secondary because the pd needs to be larger as it increases the voltage
What is an eddy current?
As the primary coils magnetic field induces emf in the secondary coil, it also induces emf and hence mini currents within the iron core.These are known as eddy currents.
Why are eddy currents a problem?
By Lenz's law the emf created and its field opposes that of the primary coil. This causes energy loss via resistive heating of the iron core by the eddy currents, which reduces efficiency.
how can you reduce eddy current losses?
Use a laminated iron core. Thin sheets of iron with an electrical insulator in between, which reduces the eddy currents circuit.