TAMU PBSI 107 Final Exam
1/349
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
350 Terms
Structuralism
Breaks down mental processes into their most basic components
Functionalism
Focuses on how mental processes help individuals adapt to their environment and meet their needs
Psychoanalytic Theory
Mental life occurs outside of conscious awareness
Psychoanalysis
Therapeutic approach to explore the unconscious
Gestalt Psychology
How we perceive and organize visual and sensory information as whole patterns rather than just separate components.
Behaviorism
Study of observable behaviors and how they're shaped by their environment
Humanism
Emphasizes the potential for good that is innate in all humans
Biopsychology
Explores how our biology influences our behavior;interdisciplinary (Sleep, drugs, reproductive behavior, sensory & motor systems, ingestive behaviors)
Developmental Psychology
The scientific study of development across al ifespan
Personality Psychology
Focuses on behaviors and thought patterns that are unique to each individual. How individuals interact and relate with others and how such interactions can affect behavior.
Biopsychosocial model
Focuses on how individual health is directly related or affected by biological, psychological, and sociocultural influences (Genes, pattern of behavior, relationships, psychological stress, and health)
Clinical Psychology
Focuses on diagnosis and treatment of psychological disorders and problematic patterns of behavior
Counseling Psychology
Focuses on emotional, social, vocational, and health-related outcomes in individuals who are considered psychologically healthy.
Sport Psychology
Study the psychological aspects of sport performance including motivation and performance anxiety, and the effects of sport on mental and emotional well being
Forensic Psychology
Branch of psychology dealing with justice system (Assess competency to stand trial, Asses state of mind of defendant, Act as consultants on child custody cases, Consult on sentencing and treatment recommendations, Advise on issues such as eyewitness & children testimony)
Industrial-Organizational Psychology
Branch that applies psychological theories, principles and research to industrial and organizational settings
Theory
A broad explanation of a phenomenon based on extensive evidence and testing
Hypothesis
A tentative and testable statement (prediction) about the relationship between two or more variables
Inductive Reasoning
Drawing general conclusions from specific examples (specific to general)
Deductive Reasoning
Using general premise(s) to reach a certain conclusion (general to specific)
Process of scientific research
Theory, hypothesis, data collection, analyze, report findings
Clinical or Case Studies
Research focused on one person or just a few individuals.• PROS: Allows for a lot of insight• CONS: Difficult to generalize to the larger population
Naturalistic Observation
Research based on observations of behavior in its natural setting• PROS:• Eliminates performance anxiety• Accurate and genuine behavior• CONS:• Observer bias*• Difficult to set up/control
Surveys
A list of questions to be answered by participants• PROS:• Gather data from a large sample• CONS:• Less depth of information• May not be accurate (misremembering, lying)• Sometimes gives objective value to a subjective experience
Archival Research
Using past records or data sets to answer various research questions, or to search for interesting patterns or relationships.• PROS:• Data already collected• Saves time• Saves money• CONS:• Lack of control• Incompleteness• May be outdated• Data integrity
Longitudinal Research
Research design in which data-gathering is administered over an extended period of time• PROS: Same participants• CONS: Time/money investment, attrition
Cross-Sectional Research
Research design that compares multiple segments of the population over time• PROS: cost-effective, no long-term com.• CONS: cohort effects, causality
Correlation
A measure that indicated whether two variables are related. When two variables are correlated, changes in one variable are associated with changes in the other.
Correlation coefficient (r)
A number from -1 to +1 that indicates the strength and direction of the relationship between variables.
Positive Correlation
The variables move together: If one variable goes up or down, the other does as well in the same direction.
Negative Correlation
The variables move in opposite direction: If one variable increases, the other decreases.
Cause-and-effect relationship
Whether changes in one variable cause changes in the other
Confounding variables
Unanticipated factors that may affect the variables of interest, make it difficult to determine the true relationship between the variables being studied
Illusory Correlation
False correlations; seeing a relationship between two things when in reality no such relationship exists
Independent Variable
The factor that is manipulated or changed by the researcher to observe its effect
Dependent Variable
The outcome or response that is measured to see if it is affected by the independent variable
Reliability
The ability to consistently produce a result• Inter-rater reliability• Internal consistency• Test-retest reliability
Validity
The extent to which a given instrument or tool accurately measures what its supposed to measure• Ecological validity• Construct validity• Face validity
Single-bind Study
Experiment in which the researcher knows which participants are in the experimental group and which are in the control group, but the participants do not
Double-bind Study
Experiment in which the researcher nor the participants know who is in the experimental group or control group (accounts for bias of the researcher)
Peripheral Nervous System
Connects the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body to relay information to and from the CNS (nerves)
Somatic Nervous System
Responsible for voluntary or conscious movement and sensory information• Motor Neurons = efferent fibers, Sensory Neurons = afferent fibers
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls involuntary bodily functions, operating automatically
Sympathetic Nervous System:
Prepares the body for stressful situations or emergencies (Dilates pupils, inhibits salivation, increases heart rate,dilates bronchi, inhibits digestion, inhibits contraction of bladder)
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Promotes relaxation and recovery (Constricts pupils, stimulates salivation, slows heart rate, constricts bronchi, stimulates digestion, causes bladder to contract)
Homeostasis
The process by which the body maintains stable internal conditions (balance, equilibrium)
Central Nervous System
The control center for processing and responding to information (Brain & Spinal Cord)
Brain
The central organ of the nervous system that controls sensory processing, bodily functions, and cognitive activities.
Cerebral cortex
The surface of the brain• Gyri (gyrus): Raised ridges, folds• Sulci (sulcus): Indentations in between, grooves
Longitudinal Fissure
The most prominent sulcus that separates the brain intro two hemispheres
Lateralization
The specialization of certain brain functions to one hemisphere• Left Hemisphere: Memory, selective attention, positive emotions• Right Hemisphere: Pitch perception, arousal, negative emotions
Frontal Lobe
Executive functions, decision-making, motor control (Motor Cortex: Planning and coordinating movement• Prefrontal Cortex: Higher-level cognitive function• Broca's Area: Language production)
Pariental Lobe
Sensory information and spatial awareness
Temporal Lobe
Auditory processing and memory (Wernicke's Area: Important for speech comprehension)
Occipital Lobe
Visual processing
Forebrain
Limbic System: Processing emotion and memory• Hippocampus: Learning and memory• Amygdala: Emotion and emotional meaning to memories• Hypothalamus: Homeostatic processes (body temp. appetite, etc.)
Hind Brain
Medulla: Controls automatic processes of the autonomic nervous system (breathing, blood pressure, etc.) Pons: Connects the hind brain to the rest of the brain and is involved in regulating brain activity during sleep Cerebellum: Receives messages from muscles, tendons, joints, and structures in our ear to control balance, coordination, movement and motor skills
Spinal Cord
A long, thin bundle of nerves that runs from the brain down to the lower back, transmitting signals between the brain and the body. Does not extend the full length of the spine
Neurons
Cells in the nervous system that transmit information through electrical and chemical signals• Primary cells responsible for communication within the nervous system• Transmit information through electrical and chemical signals
Glial cells (Glia)
Cells in the nervous system that support, protect, and nourish neurons• Play a supportive role to neurons• Provide support, nourishment, and protection to neurons• Maintain the environment around neurons
Soma
Cell body of a neuron that contains the nucleus
Cell membrane
The outer boundary of a cell that regulates what enters and exits the cell
Dendrites
Branch-like structures that receive signals from other neurons and send them to the soma
Axon
A long, thin fiber that carries the signals from the soma, enabling communication with other neurons
Axon terminal
The end part of an axon that releases signals to pass information to other cells
Neuron Structure
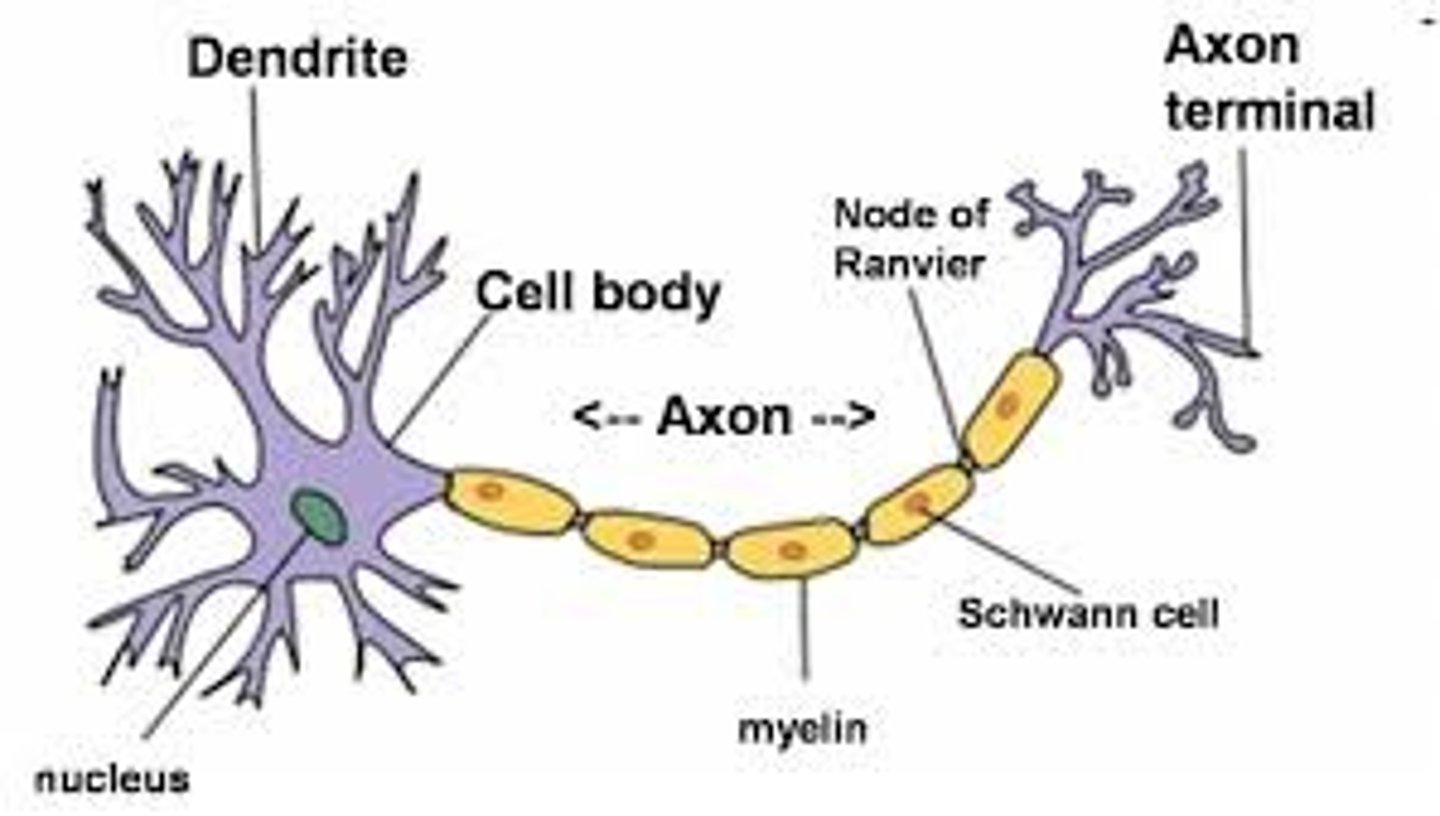
Myelin sheath
A fatty layer that wraps around and insulates the axon, speeding up the transmission of electrical signals
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath along the axon that help boost the speed of electrical signals as they travel down the axon• Saltatory conduction
Terminal buttons
The end part of an axon that releases signals to other cells
Synaptic vesicles
Small sacs in terminal buttons that store and release signals
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers of the nervous system
Synapse
The junction where communication occurs between two neurons
Synaptic Cleft
The gap between two neurons where signals are exchanged
Receptors
Sites on a cell's surface that receive and respond to these signals
Membrane potential
The difference in electrical charge between the extracellular and intracellular fluid
Resting potential
The membrane potential when the neuron is not actively sending a signal (-70 mV)
Ion channels
Gates in a cell membrane that allow specific ions to pass in and out of the cell
Action potential (all or nothing)
If the electrical charge reaches a certain level (threshold of excitation), the neuron becomes active, and the action potential begins
Reuptake
a neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron
Agonists
Chemicals that mimic a neurotransmitter at the receptor site• Ex. Treatment for Parkinson's (which involves an impairment to the dopamine system) includes dopamine agonists
Antagonists
Chemicals that block or impede the normal activity of a neurotransmitter at the receptor• Ex. Certain symptoms of Schizophrenia are associated with overactive dopamine. Therefore, treatment includes a dopamine antagonist
Reuptake inhibitors
Prevent unused neurotransmitter to be reabsorbed. Instead, it remains in the synaptic cleft for longer duration, increasing its effectiveness• Ex. Depression, which has been linked with reduced serotonin levels, is commonly treated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
Circadian rhythms
24-hour cycles that regulate physiological and behavioral patterns• Ex. Sleep-wake cycle, heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar, body temperature
Hypothalamus
Involved in homeostatic processes. In other words, homeostasis in biological system
Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
The brain's "clock mechanism," regulates circadian rhythms
Pineal gland
Small, pea-shaped gland located in the brain that produces melatonin
Melatonin
A hormone that fluctuates with light levels to help regulate sleep-wake cycle
Restoration and Memory Consolidation
Widely accepted
Energy conservation and predatory avoidance
Controversial
Gamma Waves, beta waves, alpha waves, theta waves, and delta waves
Highest to lowest frequency
Awake
Beta Waves
Stage 1 NREM
Begins Alpha, moves from Alpha to Theta
Stage 2 NREM
Sleep spindles, K complexes, theta brain waves
Stage 3 NREM
Delta waves
REM
Beta and Theta waves
Insomnia
A consistent difficulty in falling or staying asleep
Parasomnia
Abnormal behaviors, movements, emotions,perceptions, or dreams that occur during sleep or while falling asleep (Sleepwalking, REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD), Restless leg syndrom, Night terrors)
Sleepwalking (Somnambulism)
Sleeper engages in relatively complex behaviors ranging from wandering about to driving!
REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD)
Incomplete muscle paralysis, causing people to act out vivid and often violent dreams during REM
Restless leg syndrome
Uncontrollable urge to move the legs,often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations like itching,tingling, or aching