enthalpy & thermochemical equations (u1, ch9.1)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
thermodynamics
study of energy transfer and energy changes
thermochemistry
- Study of energy changes involved in physical changes (change in state, solutions) and chemical changes (combustion, decomposition, formation, etc.)
Law of Conservation of Energy
- Energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed from one form to another
system
- the particles/objects under observation. (ex. solution)
- If a _______ loses energy, the surroundings gain the exact same amount of energy, and vice versa.
surroundings
- everything with which the system can exchange energy.
- everything else in the universe (outside the system)
kinetic energy
- energy of motion (energy of particles moving or thermal energy)
- more KE = higher temp
potential energy
- stored energy (energy stored in chemical bonds)
ex. ionic bonds, covalent bonds (intramolecular forces)
transfer of heat
Heat, "Q," refers to the transfer of energy between objects of different temperatures.
- Heat can be measured in Joules (J) or kilojoules (kJ)
2nd law of thermodynamics
- energy goes from hot to cold
- Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe.
- hot -> more energy
- cold -> less energy
ex. when you touch ice, you are not cold due to the coolness of the ice. instead, YOUR heat is lost and transferred to the ice.
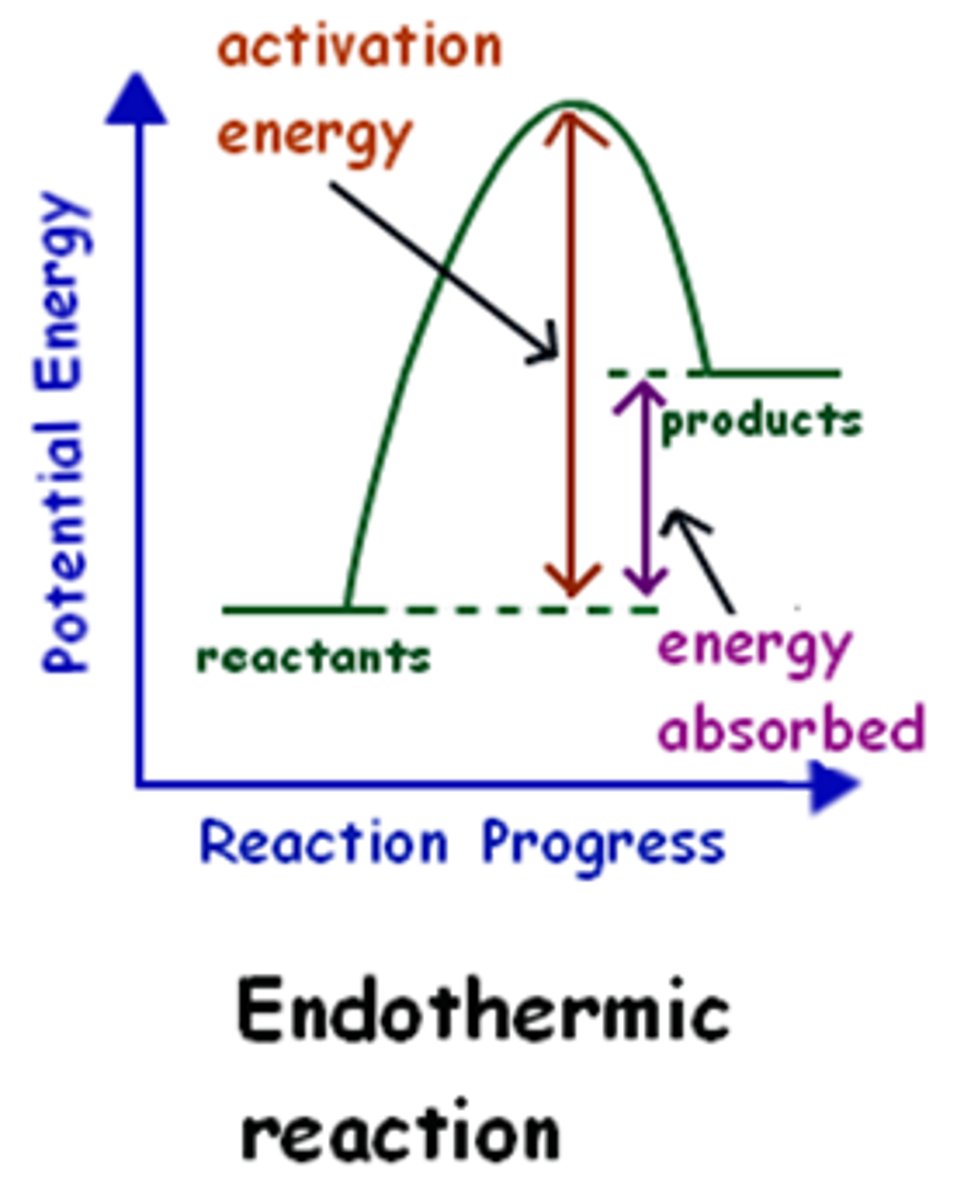
Endothermic
- energy is absorbed by the system
- surroundings lose heat
- DECREASE IN TEMPERATURE
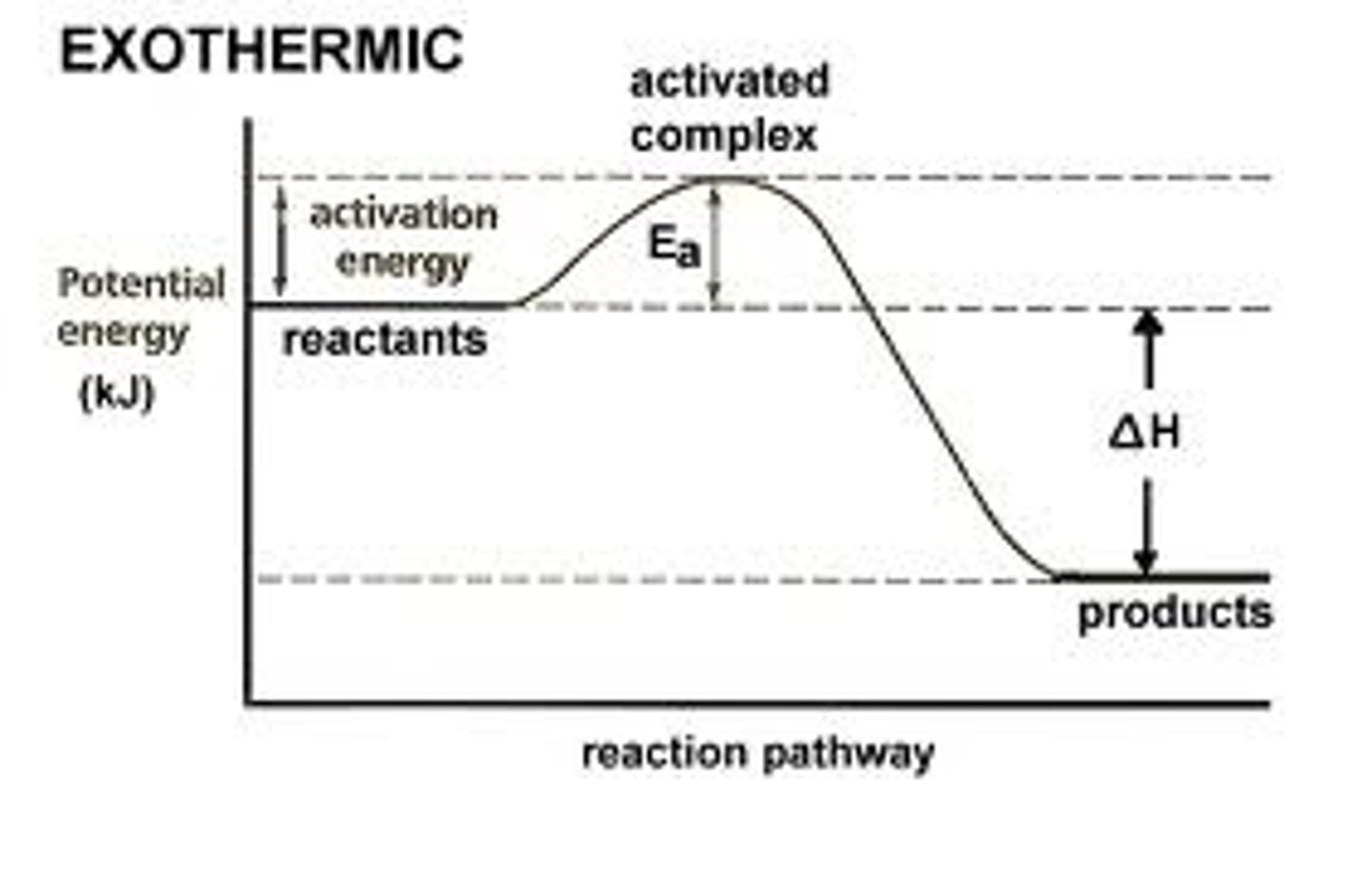
exothermic
- energy is released by the system
- temperature of surroundings gain heat
- INCREASE IN TEMPERATURE
change in energy
energy of products - energy of reactants
energy of bonds broken - energy of bonds formed
form
the amount of energy used to ______ bonds is EXOTHERMIC
break
the amount of energy used to ______ bonds is ENDOTHERMIC
greater than
when..
Energy absorbed to break bonds is ________________ energy released when bonds form
--> the reaction is ENDOTHERMIC
less than
when..
Energy absorbed to break bonds is ________________ energy released when bonds form
--> the reaction is EXOOTHERMIC
energy and enthalpy
- Enthalpy, "H," is the total internal energy of a system.
- it cannot be directly measured since it is difficult to determine the amount of stored (potential) energy within a substance
- differences in enthalpy can be calculated!
- enthalpy change, △H, communicates the difference between the enthalpy of the products and the enthalpy of the reactants
- H products = H reactants
or
- △H = Hp - Hr
one mole
molar enthalpy is the enthalpy change of ____ ______ of substance in the process
notation
△rH = enthalpy of reaction
△rH° = standard enthalpy of reaction ("°" denotes SATP conditions)
ex. CH₄O(g) + 2O₂(g) --> CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(g)
△rH = -802.5kJ (energy is released, evident due to the NEGATIVE SIGN "-", exothermic)
thermochemical equation
representing enthalpy change
- balanced chemical equation including enthalpy for reaction
ex. CH₄O(g) + 2O₂(g) --> CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(g) + 802.5kJ
H notation
- △__ __________
enthalpy is written separately from the chemical equation
ex.
CH₄O(g) + 2O₂(g) --> CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(g) + 802.5kJ
△H = -802.5kJ