excretion in humans (chap 8) -o level pure bio
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
what are some metabolic waste products
carbon dioxide
urea
mineral salts
water
what is excretion
the removal of metabolic waste products, toxic substances and substances in excess of the bodies requirements, so that harmful substances will not build up in the body to cause harm
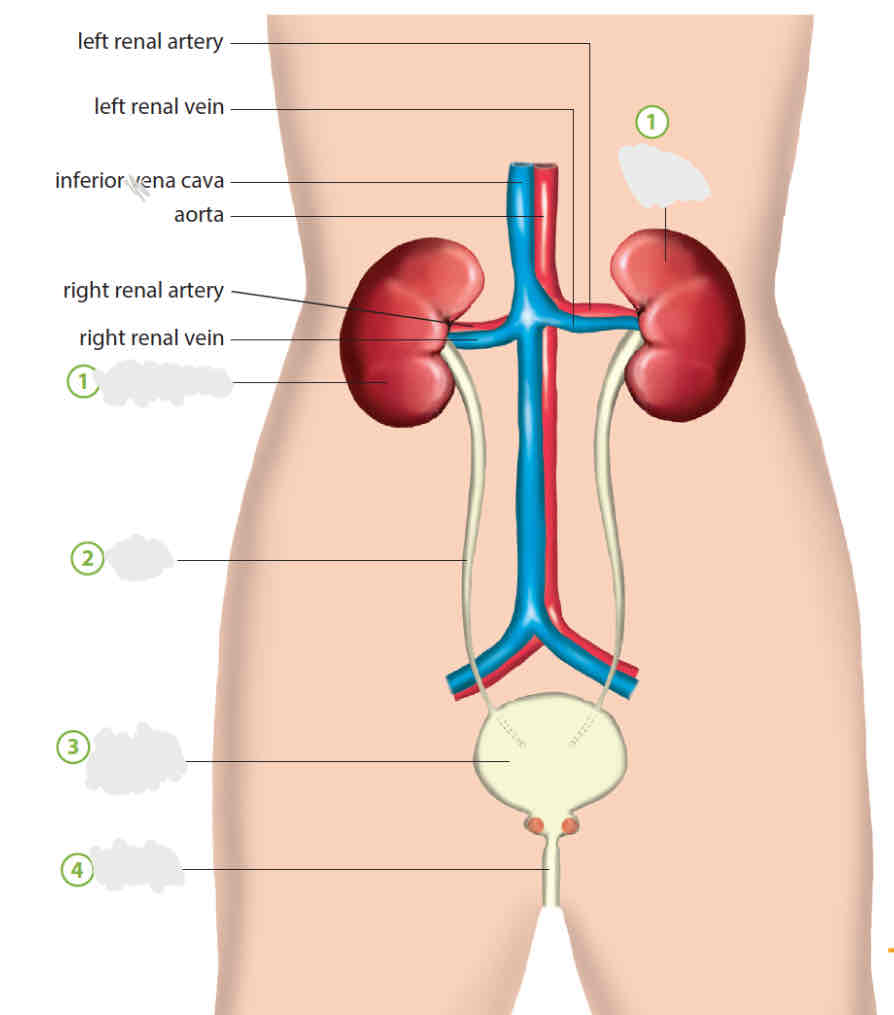
name them
left and right kidneys (reversed sides - same as heart)
ureter
urinary bladder
urethra
what is a nephron
basic functional units of the kidney
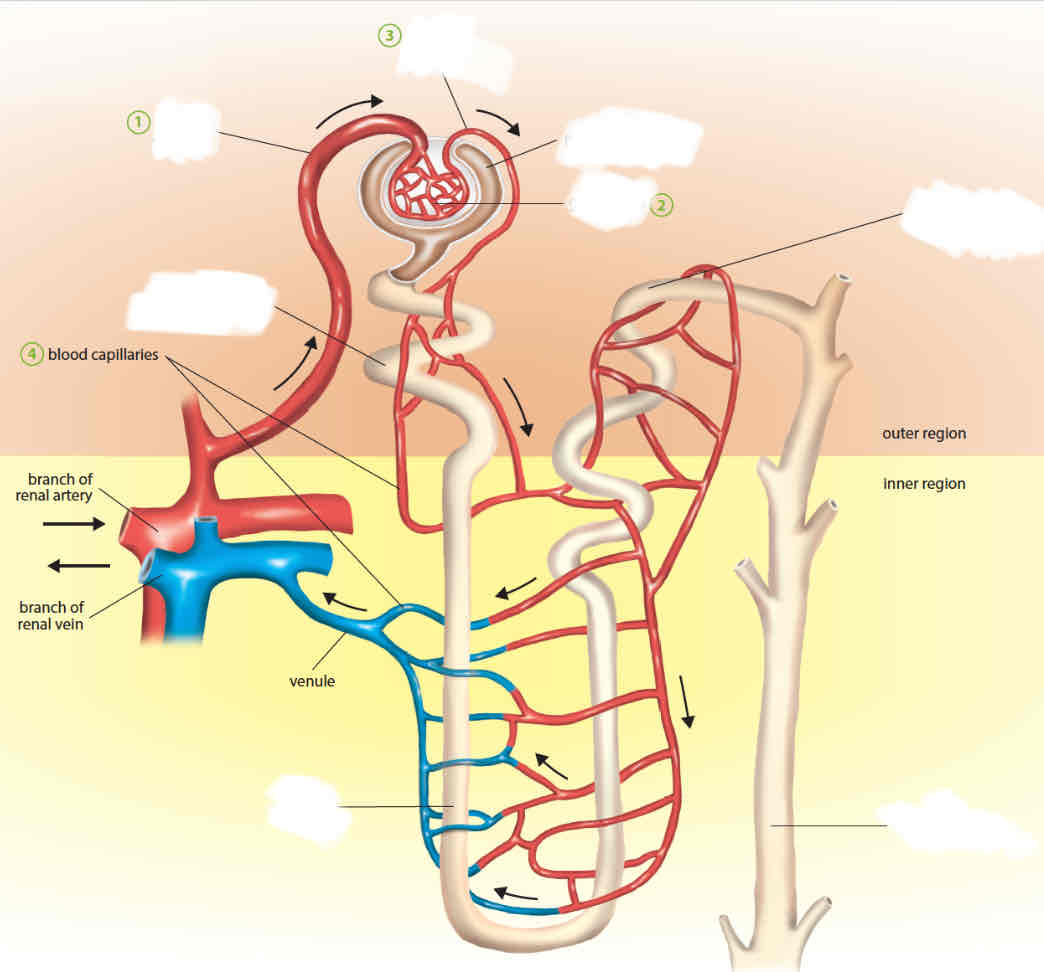
label
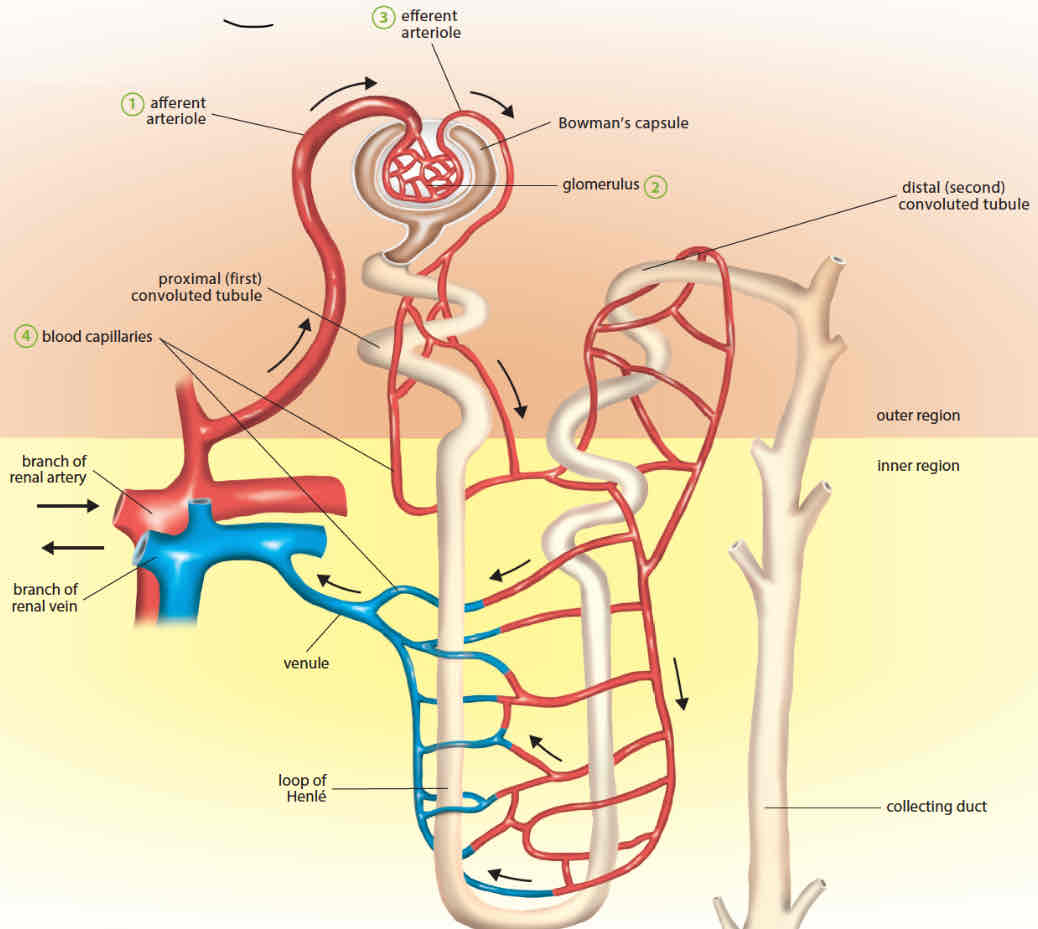
what is ultrafiltration
the first stage of urgent formation
process by which small molecules are filtered out of the blood by the glomerulus into the bowman’s capsule
how does ultrafiltration occur
the afferent arteriole is wider than the efferent arteriole, creating a high blood pressure in the glomerulus
blood plasma is forced out of the glomerular blood capillaries into the bowman’s capsule
filtered blood plasma is known as the glomerular filtrate
contains small soluble molecules such as salts, water, glucose, amino acids, and urea that is forced into the Bowman’s capsule
how is the glomerulus suited to urine formation
the glomerulus is a network of blood capillaries that provide a large surface area for the filtration process
the blood capillaries are one-cell thick
blood capillaries are covered by a thin partially permeable membrane - only allows very small soluble molecules to pass through
impermeable to blood cells, platelets and large molecules such as proteins
what is selective reabsorption
the process in which useful substances that the body needs is reabsorbed into the blood capillaries
how does selective reabsorption occur
proximal convoluted tubule:
most of the water is reabsorbed by osmosis
all of the glucose and amino acids is reabsorbed back by active transport
most mineral salts are reabsorbed by diffusion and active transport
loop of Henlé:
some water is reabsorbed by osmosis
some mineral salts are reabsorbed by active transport
distal convoluted tubule:
some water is reabsorbed by osmosis
some mineral salts are reabsorbed by active transport
collecting duct
reabsorbs some water by osmosis
what is osmoregulation
the control of water potential and solute concentration level in the blood to maintain a constant water potential in the body
why are kidneys important
the kidneys are excretory organs
they play an important role in excreting metabolic waste products
the kidneys are osmoregulators
they regulate the solute concentration and water potential in the blood to maintain a constant water potential in the blood
what are some causes of kidney failure
high blood pressure
diabetes
alcohol abuse
severe accidents
complications from major surgeries
how does a dialysis machine work
blood is drawn from the vein in the patients arm and is allowed to be pumped through the tubing in the dialysis machine
the tubing is bathed in a specially controlled dialysis fluid. the walls of the tubing in the dialysis machine are partially permeable
small molecules such as urea and metabolic waste products diffuse out of the tubing into the dialysis fluid. blood cells, platelets and large molecules such as proteins remain in the tubing
the filtered blood is then returned to a vein in the patients arm
what are the features of a dialysis machine
dialysis fluid contains the same concentration of glucose, amino acids and mineral salts as healthy blood
ensures that glucose, amino acids and mineral salts do not diffuse out of the blood and into the dialysis fluid.
if the patients blood lacks these essential substances, these substances will diffuse into the patients blood
dialysis fluid does not contain metabolic waste products
sets up a concentration gradient for waste products such as urea to diffuse into the dialysis fluid
tubing in the machine is narrow, long and coiled
increases surface area-to-volume ratio which helps to speed up the rate of exchange of substances between patients blood and the dialysis fluid
direction of blood flow is opposite to the flow of dialysis fluid
maintains concentration gradient for the removal of waste products
dialysis membrane is partially permeable