MARKETING FINAL
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
Production orientation?
A business approach that focuses on the efficient production of goods, emphasizing high production efficiency and low costs.
This strategy assumes that if products are available, consumers will buy them.
demand > supply
Product orientation ?
A business approach that prioritizes the quality and features of a product over consumer demand or market trends, believing that a great product will sell itself at a fair price.
Sales orientation?
A business strategy that focuses on selling and promoting products rather than on creating products that meet customer needs. This approach emphasizes aggressive sales techniques to achieve high sales volume. It is possible to sell a product to someone who has no need for it.
Marketing orientation?
A business approach that prioritizes understanding and meeting the needs and wants of customers, integrating market research and customer feedback into product development and marketing strategies. And the value that products and services create for consumers
What is providing value?
Value = Benefits - cost
Step 1 : Understand the consumer
Step 2 : Value creation, accomplished when a compagny proposes a solution to a consumer’s needs : resulting in a gain.
How do we understand a consumer in the value proposition matrix?
We look at 3 things
1- Job-to-be-done : what the consumer is trying to accomplish
2- Pain they are trying to avoid : what goes wrong while doing the job-to-be-done
3- The gains they are seeking : what they gain when accomplising the job-to-be-done.
What is the value proposition matrix?
Process by which a compagny provides value to consumer by creating pain/ alleviating pain.
Exchange?
Process where an organization exchanges benefits for consumer resources such as money, time, or effort.
What is a need
A state of lacking something
ex: hungry, lonely, thirsty or in need of safety or belonging.
What is a want?
Way of meeting your need
ex: going to Mcdo, drinking orange juice, high quality product to signal something for esteem
Customer lifetime value?
Sum of all profits that can be made from a customer over their lifetime.
Favorable because the cost of obtaining a new customer is much higher than retaining an old customer.
2 aspects of customer loyalty?
Customer retention: how long has that customer been buying from your brand?
Customer share : proportion of a customer’s relevant purchases that come from your brand
ex: % of cereal purchases that come from your brand
Easiest way to obtain is with customer satisfaction
Market share?
The compagny’s share of demand
= compagny demand/ market demand
Actual demand?
Compagn’y actual sales at a specific point in time
Potential demand?
The estimated level of sales that a company could achieve under optimal conditions, reflecting the maximum possible demand for its products or services.
Demand projection
Based on consumers who might be receptive to the product
What might demand be in the futur.
What are the types of markets?
Consumer goods market : sell directly to consumers
Distribution intermediaries market : sell to distributor , they will sell to consumers
Business Market (B2B) : sell to another organization
Government Market (B2G): sell to government
International market.
Why is marketing important for a compagny?
To identify and understand the consumers, adapt to their needs
Will contribute to reach growth, sales and objectives
Should align with business mission, reason of existence
Marketing objectives should relate to the business’s objectives
Who is in charge of Ethics?
American Marketing Association Code of Conduct
What are the main principles of Ethics in marketing?
Product must be fair
Price must be fair
Promotion must be truthful
Customer service quality must be consistent.
What is a marketing plan?
An analytical framework marketing objectives (SMART), target audience, strategies, and tactics to achieve business goals. Action program, situational analysis and ressource allocation are also included.
What is the marketing strategy?
Choosing who to market to
Target consumers that will get the most value from our product
Enacting the marketing plan?
The implementation of the Marketing Mix
What? specific statement of each of the 4P’s
Who? Who is/ the team responsible for each goals of the 4P’s
When? create a schedule, calendar for each goal
Control and contingency planning?
Control : How we measure progress towards achieving the marketing objectives.
“ Are my marketing actions having the intended effects?”
Contingency planning: Possible solutions to deal with unforeseen circumstances.
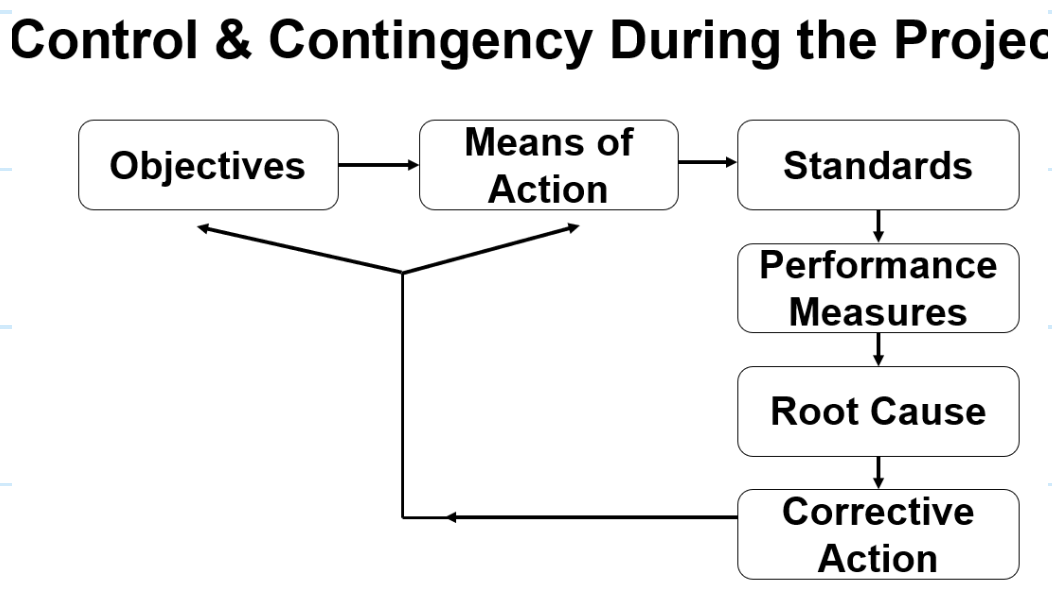
Marketing Audits?
The compagny will try to comprehensively, systematically and critically examines their entire marketing plan
An analysis of how well the plan is currently being enacted and what is likely coming in the futur
→ Ends with suggestions
Marketing information system?
Set of ressources and procedures for collecting and analyzing data from the organization’s internal and external environment
→ The system will then transfer this data into useful infromation to inform decision making
help with decisions related to : targeting, positioning, control and contingency
What are the 2 types of data?
Primary
Secondary
What is primary data?
Information collected firsthand for a specific research purpose, such as surveys or interviews or focus groups, experiements.
To answer a specific question
What is secondary data?
Information collected by someone other than the user. Pre-existing data
What are the 3 types of research?
Exploratory research :used to gather preliminary information that will help define problems and suggest hypotheses. Flexible, unstructuresed research approaches.
Descriptive research: used to describe characteristics of a population or phenomenon, often using surveys. More structured forms of data collection.
Causal research: used to identify cause-and-effect relationships. Looking at specific effects on one things on another
How to know if primary data is good?
Is it relevant? Is it reliable? Is it valid?
How to know is secondary data is good?
Who collected the data? Is it good? Is it consistenet across various sources? Is it up to date? How was it generated?
Internal environment?
Combination of the strenghts and weaknesses of a compagny which can influence its ability to succeed in the market.
Ressources and core competencies?
internal environment :
internal capabilities that contribute to competitive superiority, but are not easily duplicated
Come from a compagny’s resources
Human ressources
Financial
Informational resources
Purchasing resources
Current offer?
internal envir.
What do you currently offer and is it working?
Is what we are offering consistent with mission?
Could some producst be changes or developed further?
Past performance?
The history of a company's achievements and failures that provide insights.
What worked what didn’t?
Relations with business partners?
Distributors and parteners = good relation = strenght= could be sure your product will is showed
What is the value chain? (primary activities)
5 Primary activities
inbound logistics : can you procure, receive, and store materials affordably and quickly
operations : can you producer a high-quality product quick & affordably
outbound logistics : can you efficiently get products to consumers
marketing and sales : segmentation, targeting and positioning
After-sale service : installation, repair, return
What is support activities to the value chain
All activities that ensure that other activities are executes as efficiently as possible.
Infrastructure : management, financial and legal systems in place to manage resources and make decisions?
Human Ressources : systems in place to recruit, train and keep excellent employees
Technological Development : can you innovate technologically to gain advantage on the primary activities
Purchasing and Procurement : can you get materials affordably and quickly
Benchmarking?
A process of comparing business processes and performance metrics to industry bests or best practices from other companies.
This helps organizations identify areas for improvement and enhance their operational efficiency.
External environement (micro), and the 2 strategies?
Refers to the factors outside of a company that can impact its operations and performance, including competitors, customers, suppliers, and market trends.
Semi controllable
The organization can adopt 2 strategies :
Pro-active: Track ans react
Passive : react to the market changes as they occur
Industry competitors in Porter’s 5 forces?
3 components
Growth rate of the industry : These components help assess the intensity of competition within an industry and influence pricing and profitability.
Number of competitors : concentrated markets = more competition
Differentiation among competitors :switching cots are low = not much differentiation.
Transfer costs : time, money, psychological
Substitutes in Porter’s 5 forces?
High risk when transfer costs are cheaper
Products that satisfy the same needs as your product but may be more efficient or affordable.
Macro environment
All factors of external envrionment that can’t be controlled and will affect supply and demand
PESTEL :
Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors
SWOT : Weakness + Strenght
Internal environment
Weakness : areas where the organization lacks resources or capabilities compared to competitors.
Strength : attributes that give the organization an advantage over others in the industry.
SWOT : Threat & Opportunity
External envrionment
Threat : factors that could harm the organization or its competitive position.
conditions that can lead to advantageous situations for the organization.
Opportunity : factors that could benefit the organization if leveraged effectively.
What is consumer behaviour?
Set of processes that individuals use when selecting, securing, using or disposing of products, to satisfy their needs
What is involvement in a consumer decision?
How important is the situation to the consumer?
Based on their needs/interest/values,product, brand
What is processing efforts in a consumer decision?
How much thought consumers put into a decision
ex: buying a house vs buying shoes
What is brand laziness in a consumer decision?
Involvement and processing effort = LOW
habitual purchases made on the bases of convinience
What is brand loyalty in a consumer decision? 2 ways it’s measured?
Commitment to a brand based on the benfits and values it provides to a consumer
Quality, Emotions
Measure in 2 ways :
Really positive attitude toward the brand
+
Consistently buying from the brand
What is variety seeking in a consumer decision?
Consumers are invested in the category but have not set preferences
and choose among brands for the sake of novelty or change.
What is problem solving in a consumer decision?
involves unfamiliar expensive products , not purchased frequently
Consumers collect as much info as they can and carefully examine each alternatives
What is a cognitive decision?
Meet utilitarian need
Process a lot of information → high effort
What is an emotional decision?
Products that need a “pleasant sensation” → fashion, dessert
HEDONIC need
experiential products, → music movies
What are the steps of the decision lifecycle
Need Recognition,
Information Search,
Evaluation of Alternatives,
Purchase/ Choice,
Post-Purchase Evaluation.
way less intense for low-involvement decisions.
2 types of information search?
Internal search : retrieving information from memory and experiences
External search : gathering information from outside sources such as reviews, friends, or advertisements.
What is enduring involvement in influences?
A long-term interest in a product or category, leading to persistent engagement and deeper knowledge over time.
e.g.: sneakerheads
What is situational involvement in influences?
A temporary interest in a product or category, driven by specific circumstances or immediate needs, which can lead to heightened attention and decision-making during that period. Don’t bother keeping up to date in this category after the purchase.
What are the types of risks with a purchase?
Monetary risk : related to cost or ownership
Social risk : related to affiliation, group and status
Physical risk : physical integrity, health and welness
Functional risk : related to the performance of a product and it’s ability to meet the need
psychological risk: related to self-esteem and self-confidence
What is consideration set?
Group of brands or products that a consumer evaluates when making a purchasing decision.
What is the non-compensatory model ?
consumers evaluate options based on a specific criteria, where the failure to meet any one criterion eliminates that option from consideration.
What is the compensatory model ?
A decision-making approach where consumers evaluate options by considering the overall value, allowing positive attributes to compensate for negative ones.
variety of attributes → filters
Internal influences on purchase decisions?
Central Psychological processes
Psychographic variables
what are the central Psychological processes
Motivation : the internal state of internal stimulation that provided the energy required to satisfy a need. Determines the level of effort that a consumer is willing to dedicate to the decision
Perception : the process by which consumers interpret information and form an understanding of the world around them. (5 senses)
Exposure : the process whereby a consumer comes into contact with a stimulus
Attention : the focusing of mental resources on stimulus.
Interpretation : The action of assigning a meaning to a sensory stimulus
Inferences : conclusions drawn by consumers based on their perceptions and experiences, filling in gaps in information.
Mental categorization : consumers organize knowledge based on similarities
Attitude : en eduring evaluation of a perso, objectif or subject
Hedonic and symbolic needs?
Hedonic needs are driven by the desire for pleasure the self-concept, while symbolic needs relate to self-esteem and social status, fulfilling emotional and social connections.
Utilitarian needs?
Utilitarian needs refer to practical, functional requirements that consumers seek to fulfill, focusing on the functionality and utility of products rather than emotional or social aspects.
Psychographic variables (internal influences)
Identity and self-concept : the way individuals perceive themselves
Values : Abstract, lasting beliefs about what is good or bad, acceptable or unacceptable and preferable or not
Lifestyle : the way individuals live, including their activities and pastimes, the way they dedicate their spare time
Contextual influences?
Mood : a temporary emotional state which may be positive of negative
Time available : time to make a decision.
Physical & Social Environment :
Types of Reference groups (external influences)
Real or imaginary group that influence a person’s decisions
Informational : valuable sources of information, play a role in the information search for the product
Normative :groups that set standards for behavior and attitudes, influencing individuals to conform to their expectations.
Comparative : Procure a comparison point to evaluate it’s own performance or conduct
Subculture (external influences)
Group whose members share beliefs
Differentiate themselves from other groups
ex: generations, ethnic groups, regional, social classes
Culture (external influences)
The culture of a poeple or social group is essential factor that shapes consumer behaviors
What are the 4 parts of the marketing strategy in order?
Segmentation : group them into categories
Targeting : choose a segment based on profatibility
Positioning : figure out what appeals to them and position your brand
Differentiation: differentiate products from other brands with similar offerings
What is Segmentation?
grouping consumers based on their buying behaviour, needs and expectations, response to marketing.
Name all the segmentation variables?
Sociodemographic
Geographic
Psychographic
Behavioral
Volume and Profitability
Lifestyle
What is a behavioral variable?
Concerns customer needs, expectations and behaviour
The benefits sought.
may lead to segmentation based on a situation
Psychographic variable?
Mindset, values, opinions, interest in various activities and attitudes towards life
Sociodemographic variable?
Demographic, economic and social caracteristics
ex: income, age, education , gender, religion, ethnic origin, language and family size.
Lifestyles variable?
Combination of psychographic, geographic and sociodemographic variables
What variables are not used for Business market segmentation?
Psychographic and lifestyle
Instead → organizational culture and procurement policy,
ex : purchasing process, types of relationships with suppliers
Socidemographic
Instead → economic variables
business customer’s size
industry
financial solvency
growth
What makes a segment profitable?
Size : large sale volume
Growth : strong growth potential
Accessibility : economical way of reaching the target through distribution and promotion
Competitive situation : # and strenght of competitors
Adaptation costs
What are the 4 types of targeting?
Mass
Sgemented
Niche
Personalized
Mass marketing?
A marketing strategy that targets the whole market with the same marketing mix aiming for a large volume of sales by appealing to common needs and preferences.
Prices
Segmented marketing?
target one, few, or all segments
Marketing mix components are adapted to each fo te segment
Niche marketing?
Single marketing mix tailored to a specific, well-defined segment of the market, focusing on unique needs and preferences.
1 single small segment
< 10% of the market
Personalized marketing?
Adapting a compagny’s offering to each of the customers that it plans to win over
extreme = every customer is a segment
common in B2B
If consumer’s aren’t aware of the brand? what type of postioning?
Desired positioning, all brands have it
NO actual postitionins
If consumers think of the brand differently than the brand would prefer?
Gap between the desired and actual brand positioning
What is a desired positioning?
The identity, image and personality of a brand/business
The place that the business wished to occupy in the customers heart and mind
Need to be consistent with the desired positioning
How is the desired positioning defined?
Market study of customers and of the positioning of existing brands
What makes a sucessful postioning
Consistent with the target
Clear and unambiguous (brand must represent something specific and relevant for the targets set)
Represent value for the consumer (tangible or symbolic)
Why differentiation?
To provide target customers with a reason to choose the brand
Must be significant for the customers, an aspect that counts for the customer
It can adres any or all marketing mix components
Points of Parity?
Attributes or benefits that are not unique to a brand but are shared with other brands in the same category.
They help establish a brand's relevance and credibility in the market.
Points of Differentiation
Attributes or benefits that make a brand stand out from its competitors, providing unique value that appeals to target customers.
What is the structure of the statement of positioning
For [Target], [Brand], is a [concept] that [distinguising characteristics/differentition], and it’s [justification or comparative advantage]
Do a positioning statement for St-Hubert resto-barrs
For Young people who want to meet and spend time together, St-Hubert restos bars, is a full menu with beer and wine, that offers good music and relaxed ambience whether you want to unwind or watch a hockey game and it has several restaurants across Québec.
What is a product?
a group of benefits offered to consumers
Fulfills a customer’s job-to-be-done
what are the 3 dimensions of a product?
Benefits : motive that drives the consumer’s consumption, drive the value the consumer’s get from the product
Core Product : what is offered to consumers to provide the benefit they seek
quater-inch drill = core product
quater-inch hole = benefit
Related services: anything that enhances the core product and adds value to the consumer's experience. ex: delivery
What is the Design dimension of a core product?
Functional attributes : to be useful for the consumer
Form : the way the product looks
→ tension between the two
What is the Brand dimension of a core product?
Signs that allow a product/ business to differentiate itself from the competition
ex: name, sign, logo