Lecture #1: Occupation, Health & Wellbeing
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is the definition of occupattion
everyday activities that people do as individuals, in families and with communities to occupy time and bring meaning and purpose to life
things people need/want and are expected to do
includes looking after self, enjoying life and contributing to social and economic fabric of their communities
matter fo health and wellbeing from individual to co.lective levels
can spark individual and societal change
occur in time,space and place
are assigned meanings informed by individuals and collective values
shaped in relation to contextual elements
the synthesis of doing, being, becoming and belonging that is central to everyday life and is necessayr for adaptation and survival
Why are occupations important?
occupation is a basic human need
has theraputic potential
Basic assumptions of occupation
occupations affect health and wellbeing
occupations organize time and bring structure to living
occupations bring meaning to life
occupations are idiosyncratic ( unique to each individual)
Are occupations always therapeutic or beneficial?
Not all occupations lead to health, well-being and justice, or have therapeutic value, even if they hold meaning, organize time, and bring structure to life. Occupations can be "maladaptive," even harmful, either to the individual or society
What three categories can we organize occupations into?
Self care
productivity
leisure
What is self care?
Activities of daily living
Basic ADLs: looking after self: eating, toileting, hygiene
Instrumental ADLs: more complex/independent living : transportation, finances, meal prep
What is productivity
activities that contribute to society:
school
work
volunteer
What is Leisure
Free time activities:
sports
hobbies
games
What is the taxonomic code of occupational performance
occupation
activity or set of activites that is oerformed with some consistency and regulairty that brings structure, and is given value and meaning by indivduals and a culture
Activity: A set of tasks with a specific end point/outcome that is greater than that of any constituent task
Task: A set of actions having an end point or a specific outcome
Action : Set of voluntary movements or mental processes that form a recognizeable and purposeful pattern such as grasping, holidng etc
Voluntary movement or mental processes: A simple voluntary muscle or mental activation - such as flexion, extension, adduction etc
What is the defintion of occupational therapy
the art and science of enabling engagement in everyday living, through occupation; of enabling people to perform the occupations that foster health and wellbeing; and of enabling a just and inclusive society so that all people may participate to their potential in the daily occupations of life”
occupational dysfunction
Refers to disruptions or difficulties in a person's ability to engage in meaningful daily activities
Components of Occupational Dysfunction include
occupational imbalance
occupational deprivation
occupational alienation
occupational marginalization
What is health
can be measured objectively and subjectively
can be a narrow or broad concept
a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity
According ot the WHO the determinants of health include:
the social and economic environment,
• the physical environment
• the person’s individual characteristics and behaviors
Basic Factors that determine health
Income
• Employment Status
• Social Status
• Education
• Physical Environment
• Personal Behavior and coping skills
• Social Support Networks
• Genetics
• Health Services
• Biological sex at birth
Upstream and down stream
"upstream" interventions focus on preventing health issues by addressing social determinants of health and root causes of inequality, like advocating for policy changes or improving community environments.
"Downstream" interventions, conversely, involve treating individual clients for immediate health needs, such as providing assistive devices or rehabilitation after an illness
what is the influence of occupations on health
Health promoting
health jeopardizing
depriving of health
Health Promoting Occupations
activities that support physical, emotional, cognitive, and social wellbeing.
They align with a person’s values, identity, and life goals.
ex excercising regularly, cooking nutriotious meals, volunteering
Builds resilience, reduces stress, enhances mood, improves physical health, and fosters a sense of purpose.
Health Jeopardizing occupations
activities that may be meaningful or habitual but carry risks to health (either physically, mentally, or socially
Ex: Overworking, substance use, excessive screen time
can lead to burnout, injury, addiction or social isolation
Health Depriving Occupations
the absence or restriction of meaningful activity (often due to external barriers like poverty, discrimination, incarceration, or disability).
ex Being unable to work due to injury, social exclusion, lack of access to education
Leads to occupational deprivation, loss of identity, depression, and diminished quality of life.
How is Wellbeing seen
a holistic state of physical, mental, and social health that emerges when individuals can participate in occupations that are personally meaningful, culturally relevant, and suited to their environment.
Key dimensions of wellbeing
Occupational enagement
balance
autonomy
environmental fit
identity and meaning
Quality of Life
A person’s perceived satisfaction with life, hope, self concept, socioeconomic factors, and overall health and functioning
In OT what is Quality of life about?
how well a person can engage in meaningful activities that reflect their values, identity, and goals. It’s not just about physical health or independence, but about living a life that feels purposeful and satisfying.
What are the factors impacting Quality of Life?
Physical health
• Strength, mobility, and energy to perform tasks.
Mental and emotional well-being
• Feeling capable, confident, and emotionally balanced.
Social participation
• Connecting with others and feeling included.
Environmental support
• Living in spaces that enable rather than restrict activity.
Occupational engagement
• Doing things that bring joy, meaning, and identity.
What is the difference between wellbeing and Quality of Life ?
Wellbeing
contributes to Quality of life: feeling physicall, emotionally and socially well enhances your overall life experience
like the weather - how you feel today, how balance and supported you are
Quality of Life:
Reflects wellbeing: A persons quality of life often includes measures of their wellbeing, like emotional stability, physical health, and social connectedness
Like the climate: Long term view of how satisfying and meaningful your life is overall
What three ways can occupation be measured?
occupational performance
occupational engagement
occupational participation
Occupational performance
ability to carry out specific tasks or activities in daily life
focus on skill execution and task completion
can be a sliding scale of success - being able to do 50% of an activity
Satisfaction with how well it is performed is NOT the focus
The enablement goal is to improve skills or adapt activities
Occupational Engagement
More than just how well you did - includes meaning and satisfaction
• Engagement includes motivation, emotional investment, and the sense of purpose behind doing something.
• The focus is on personal connection and meaningful participation
• Enablement Goal: Enhance meaning and motivation
Occupational Participation
Being involved in life situations and roles - at home, work school or in the community
about inclusion, access and social belonging
does not need to have a performance componenet
having access to occupational opportunities is key to participation
enablement goal: enable access, opportunity and inclusion
Occupational justice
The concept that every person has a right to access to occupations that satisfy health, societal, and personal needs •
Having access to and being able to participate in occupations that are meaningful
OT Models: PEO
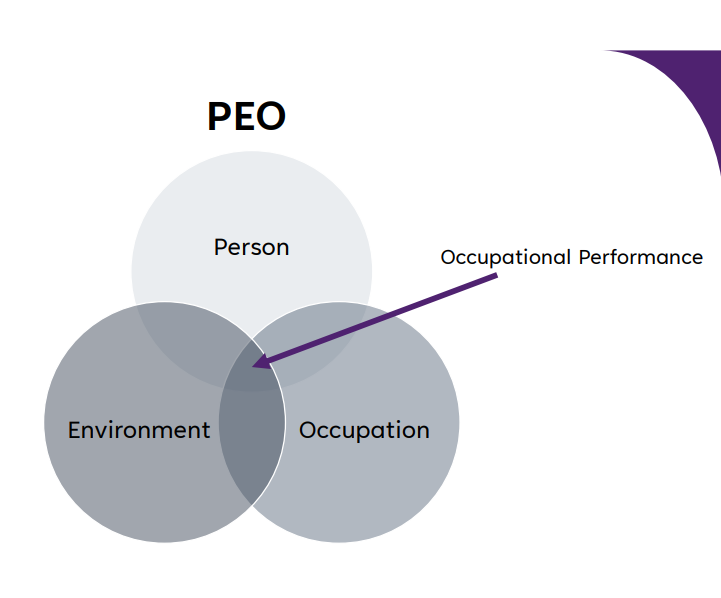
Occupational Performance as per the PEO
• The ability to choose, organize, and successfully perform meaningful occupations
• Occupational performance is the degree to which a person is able to successfully engage in an occupation within a given environment. It reflects how well the person can carry out tasks that are meaningful to them, considering both their capabilities and the supports or barriers in their surroundings
• Performance improves when there is greater congruence or "fit" between the person, environment, and occupation.
Barrier or faciliator
barrier
factors hindering access and effectiveness, such as limited funding, therapist shortages, patient cognitive limitations, or cultural differences
facilitators
factors that promote engagement and success, including effective screening mechanisms, interprofessional collaboration, patient-centered approaches, cultural awareness, and strong client-therapist relationships.
Basic PEO Questions
What are the demands of the occupation?
• Do the persons current personal abilities allow them to complete that occupation / activity?
• Are there any environmental factors that impact the occupation or the person (positively or negatively)?
Enabling Occupation
Promotes independance in occupations rather than doings things to or for someone
independace is variable and context dependant
CMCE stands for ?
Candadian model for client cented enablement
what are the key enablement skills of the Canadian model for client-centered enablement
Adapting - Modifying tasks, environments, or tools to support performance
Advocating - Promoting client rights and access to services or opportunities
Coaching - Guiding clients to build confidence and self-management skills
Collaborating - Working together to co-create solutions and goals
Consulting - Offering expert advice while respecting client autonomy
Coordinating - Organizing services and supports across systems
Designing / Building - Creating or modifying physical or social environments
Educating - Sharing knowledge to empower informed decision-making
Engaging - Fostering motivation and emotional investment in occupations
Specializing - Applying advanced clinical expertise when needed
what does the cmce model emphasize?
client centred practice
clients can be individuals, families, communites or populations
the relationship is intertwined meaning
It’s dynamic and evolving
It involves shared decision-making
• It respects the client’s right to take risks and make choices
What are the CMCE ethical foundations?
Respect
• Autonomy
• Empowerment
• Justice
• Holism
CMCE ethical foundations: Respect
in practice?
why it matters?
• Valuing the dignity, autonomy, and lived experience of every client.
• In Practice: Listening actively, honoring cultural and personal preferences, and avoiding assumptions or judgment.
Why It Matters: Respect builds trust and lays the groundwork for a collaborative therapeutic relationship
CMCE ethical foundations: Autonomy
in practice?
why it matters?
Supporting the clients right to make infomed choices about thier own life and care
In Practice: Providing options, encouraging decisionmaking, and respecting the client’s right to take risks.
• Why It Matters: Autonomy empowers clients to take ownership of their goals and outcomes.
CMCE ethical foundations: empowerment
in practice?
why it matters?
• Helping clients build confidence, skills, and control over their circumstances.
• In Practice: Using enablement skills like coaching, educating, and advocating to foster independence.
• Why It Matters: Empowered clients are more likely to engage meaningfully and sustain progress beyond therapy.
CMCE ethical foundations: Justice
in practice?
why it matters?
• Promoting fairness, equity, and access to meaningful occupation for all.
• In Practice: Challenging systemic barriers, advocating for inclusive environments, and addressing occupational injustice.
• Why It Matters: Justice ensures that therapy isn’t just about individual success, it’s about social change.
CMCE ethical foundations: Holism
in practice?
why it matters?
Viewing the client as a whole person (body, mind, spirit, and context) not just a diagnosis.
• In Practice: Considering emotional, social, cultural, and environmental factors in assessment and intervention.
• Why It Matters: Holistic care leads to more personalized, effective, and sustainable outcomes.