17-8 : B- oxidation pathway in saturated fatty acids
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Step 1
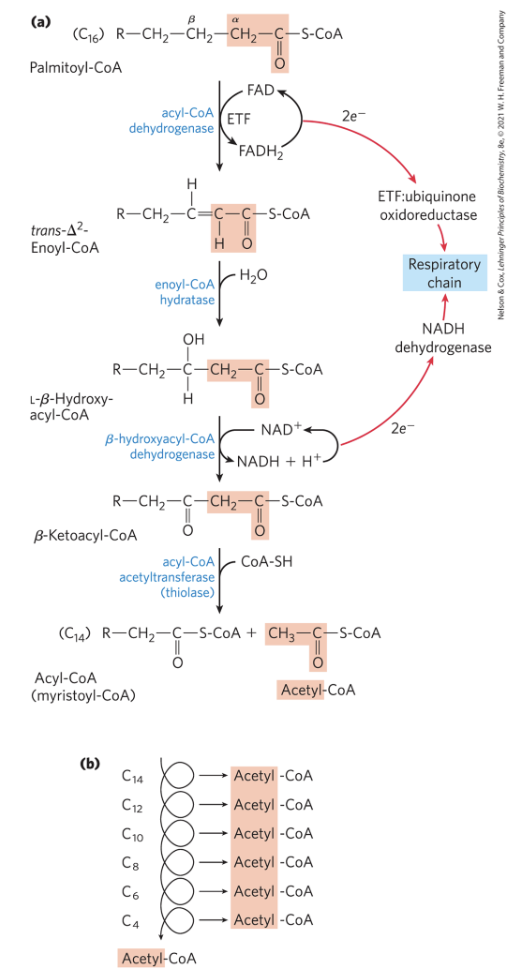
Dehydrogenation of fatty acyl-CoA forms a trans double bond between the 2nd and 3rd carbons, creating trans-Δ²-enoyl-CoA. Three enzymes handle this step based on chain length: VLCAD (12–18 carbons), MCAD (4–14 carbons), and SCAD (4–8 carbons). These enzymes use FAD to transfer electrons.
Step 2
H20 added across double-bond of trans-delta2-Enoyl-CoA >>> L-Beta-hydroxyacyl-CoA (3-hydroxyacyl-CoA)
Catalyzed by enoyl-CoA hydratase
Step 3
Dehydrogenation of L-Beta-hydroxyacyl-CoA >>> Beta-ketoacyl-CoA
Catalyzed by Beta-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (specific for L stereoisomer)
Electron flow:
NADH formed in reaction (2 e-) >>>> NADH dehydrogenase >>> respiratory chain
ATP >>> ADP as e- pass to O2
Step 4
. Thiolysis reaction: Beta-ketoacyl-CoA is cleaved by the reaction with the thiol group of Coenzyme A >>> Acetyl-CoA + Acyl-CoA (Myristoyl-CoA)
Catalyzed by acyl-CoA acetyltransferase (thiolase)
How are the last three steps catalyzed ?
12 or more fatty acyl chains : trifunctional (TFP)
12 or less fatty acyl chains : catalyzed by 4 soulube wnzymes in matrix