Nanotech (18-20)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
3 kinds of cancers
Carcinomas: in epithelial tissues, so skin membrane
Sarcomas: in connective tissue
Leukemias: in blood cells
Nanotech description
Create stuff on nano scale, so between 10^-9 and -6 meters (nanometer and um)
Nano medicine is offshoot of nanotech, specific for treatment of
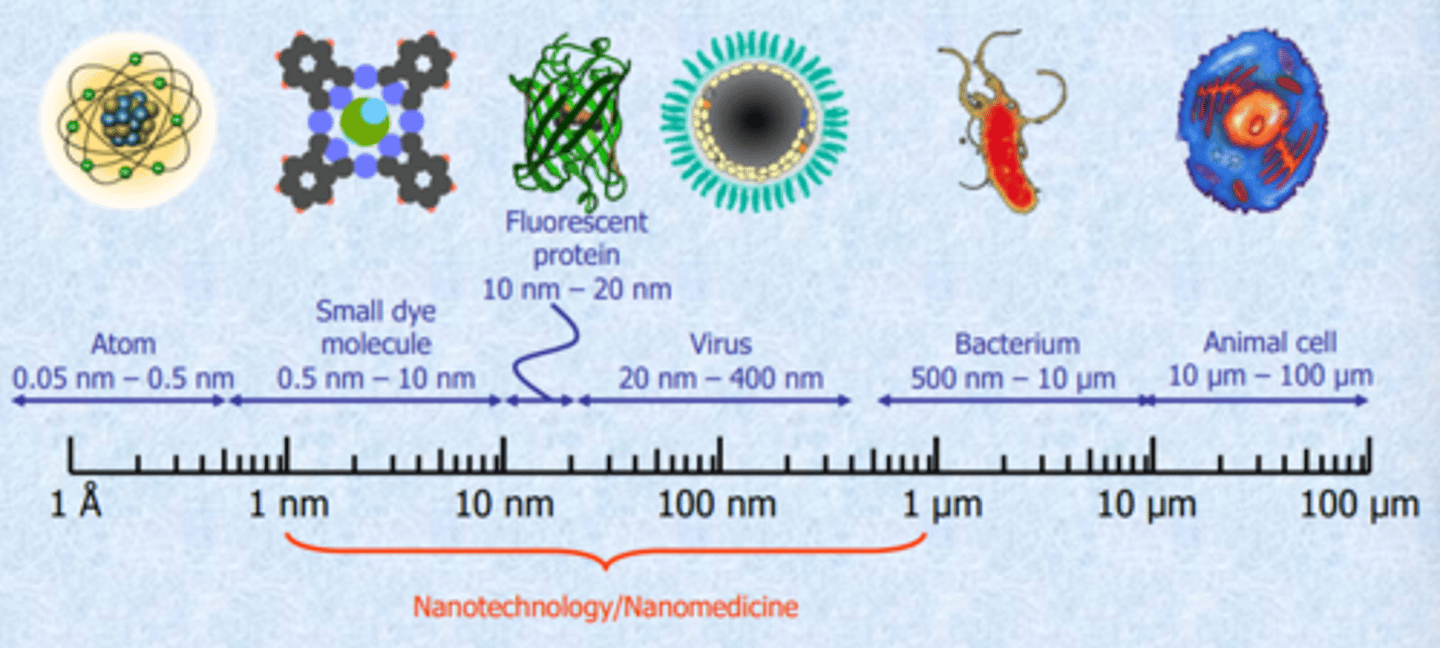
Nanotech scale
1nm-1um is important, there can easily penetrate.
Polymeric nanoparticle advantage (3/disadvantages
Polymersome, dendrimer, polymer micelle, nanosphere
Advantage: precise control of particle, payload flexibility and easy surface modification
Disadvantage: Possible aggregation and toxicity
Inorganic nanoparticles Advantages (3) and disadvantages
Silica, quantum dot, iron oxide, and gold nanoparticles
Advantage: unique electrical, magnetic and optical properties. Can vary in size shape and geometry, best for theragnostic application
Can have toxicity and soluble limitations
Lipidbased nanoparticle advantages (3) and disadvantages
Liposome, lipid nanoparticle, emulsion
Advantages: Easy formulation, high F, payload flexibility
disadvantage: Limited encapsulation efficiency
3 Dispersed systems
Molecular dispersion <1nm (can't see in electron microscope and pass through stuff easily)
Colloidal dispersion: 1nm-0.5 um (can see in electron, can't pass through semipermeable membrane and diffuse slow)
Coarse dispersion: >0.5um (visible, do not pass through anything)
Liposome description
Encapsulates region on aq solution (core) inside a hydrophobic membrane. Inside core are hydrophilic drugs that can not easily pass though lipids
Hydrophobic drugs can be dissolved into the membrane of liposomes
Liposome drug release mechanism (3)
Can have diffusion through a pH change
Membrane fusion
Or endocytosis
ASO therapy
used to block synthesis of protein by binding to mRNA, complementary to chosen sequence. Can be RNA or DNA
ASO mechanism (3 things)
ASO bind to mRNA to prevent synthesis of protein
Degrade mRNA portion of duplex, releases ASO for further binding
Release of ASO into blood stream and then excretion
RNAi
Double stranded RNA inhibit gene products on posttranscriptional level (block mRNA to protein), can be induced artificially.
Co-suppression
dsRNA can inhibit gene expression. Suppress expression of gene and introduced gene.
Found when people tried making flower more purple, but instead turned it white.
siRNA proccess
Dicer enzymes cut up dsRNA into small RNA fragments called small interfering RNA/siRNA. They bind to RNA induced silencing complex/RISC (when siRNA unwinds and bind to mRNA), using antisense RNA
RISC has enzyme called slicer to cleave bound mRNA and cause gene suppression
4 Advantages of antisense/siRNA therapy
Extremely high specificity
Selective knockout of single critical target
Potential for increased efficacy
Reduced likelihood of side effects
4 Challenges with siRNA
Low stability: siRNA easily go through hydrolysis
Chemically stabilized siRNA is maintained for 30 mins while unmodified siRNA duplex is degraded in 1 min
Rapid elimination: Small size of siRNA lead to quick elimination (half life of < 5 mins)
Poor cellular internalization: delivery of siRNA across membrane is limited by negative charged siRNA by the like charged cell membrane
Dendrimer description and 3 properties
Branched molecule that resembles branch of a tree
Dendrimer can be water soluble if end group is hydrophilic group like carboxyl
Can design water soluble dendrimer with internal hydrophobicity
Volume of dendrimer increases when it has a positive charge
Highest dendrimer generation used and what 3 properties increase with each generation?
MW, diameter and surface groups (double each time) increase
4th generation is the max used.
For Poly amidoamine dendrimers (PAMAM)
Traditional vs Modified dendrimers
Traditional: has external positive charge for siRNA binding, leading to nanofiber shaped structures seen since they are not internalized
Modified: acetylated surface, internal positive charge for siRNA binding leading to internalization and well condensed spheroidal nanoparticle seen in microscope
QPAMAM-NHAc description
Is a 4th generation dendrimer with modified surface, has reduced cyto and genotoxicity, leading to good internalization.
Quantum Dots
Small semiconductor particles, only several nanometers in size. Emit frequency if energy applied and can turn frequencies by changing size and shape and stuff.
Colloidal quantum dots emit different color light.
Quantum dot nanocrystal sstructure
have a core (quantum dot), shell, polymer coating, and then biomolecule.
Superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) Nanoparticles description and application (2)
Used as contrast agents for MRI, allow targeting of vectors to desired locations through magnetic fields
Can act as miniature heaters that can kill cancer cells.
CD44 antigen
Cell surface glycoprotein used for interaction, adhesion and migration, important marker for cancer stem cells.
Cancer stem cells/Initiating cells description
Responsible for initiation, extensive proliferation of primary tumor and spreading of metastases.
Can self renew
Non targeted vs LHRH targeted dendrimer affect
Non targeted, still the dendrimers localized everywhere, but for LHRH receptor targeted dendrimers, see them pretty much only in the tumors.
CD44 suppression effect
Suppression of CD44 in cancer stem cells ENHANCE antitumor effect of anticancer drug, limiting tumor growth and preventing adverse side effects of chemotherapy
Suppression of P-gp effect
Lead to increased drug accumulation inside cancer cells and suppresses drug resistance.
Personalized Medicine Definition
Right treatment for right patient at right time. Understand genetic make up to understand biology of tumor.
3 Steps to create personalized medicine
1: Analyze patient individual profile
2: Anticipate patient reaction to certain drugs
3: Overcome potential complications or adverse side effects
5 Limitations of systemic lung delivery
Enzymatic Degradation in Gi Tract and Liver
Short half life and degradation of drugs in blood stream
Low accumulation and retention of drugs in lungs
Low efficacy of treatment
possible adverse side effects on other organs and tissues
3 Advantages of local inhalation drug delivery directly to the lungs
Enhanced accumulation and retention of drugs in lungs
Prevention/limitation of penetration of drugs into blood stream and accumulation in other healthy organs
High efficacy of treatment
Main challenge of lung delivery
Most free dugs can not be delivered into drugs by inhalation so need special delivery system
Nanotech drugs (4) and where in nLC
Anticancer, anti inflammatory, antioxidants, PGe2, on the inside of NLC
Nanotech nucleic acids and where in NLC
SiRNA, ASO.
Choose from lots of factors, is on the inside of NLC
Nanotech targeting agents and where in NLC
LHRH on the outside of NLC.
Nano tech DSPE-PEG-Polyethylene glycol
Molecules introduced to NLC (nanostructure lipid carrier) to stabilize against aggregation
DOTAP for nanotech and where in NLC
NLC prepared through incorporation of DOTaP into naoparticle structure
Inhalation delivery of lipid nanoparticle leads to?
Preferential accumulation in the lungs mainly. IV can go anywhere but inhalation is lungs.
Virus like particle vaccines, example and when first introduced
HPV use this
1986 first introduced for HepB
Nucleic acid vaccine, example and first introduced
SARS-Cov-2 use this
introduced in 2020
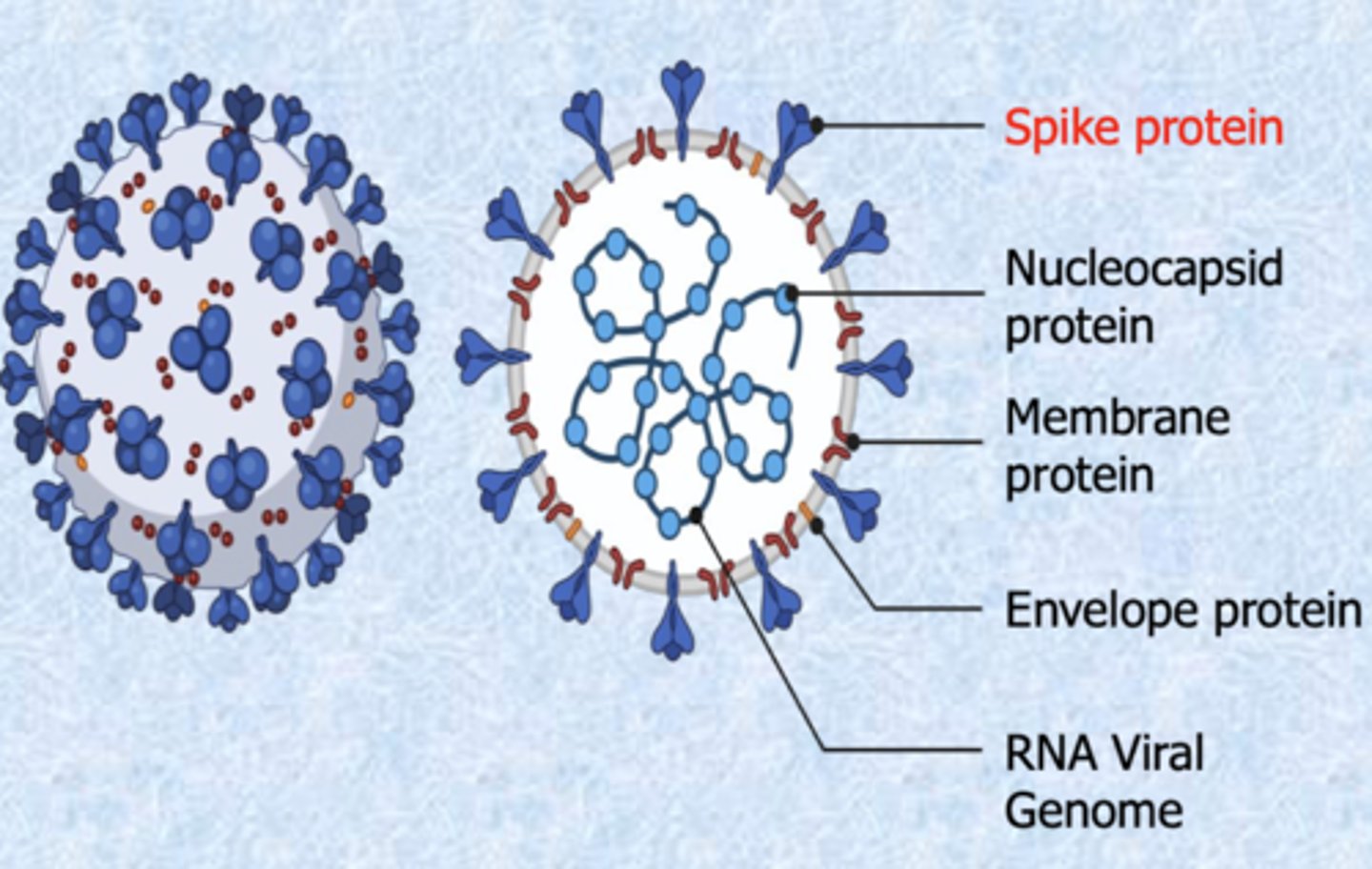
Human Coronavirus structure
Has single strand positive sense RNA surrounded by membrane. Envelope has glycoprotein.
Coronavirus replication 9 Steps
1: Bind and viral entry through receptor mediated endocytosis
2: Release of viral genome
3: translation
4: RNA replication
5: Subgenomic/nested transcription
6: translation of viral structure protein(N,S,E,M) (S=Spike,m=membrane,e=envelope, n=nucleocapsid), SEM go to ER.
7: S, E and M protein combine with nucleocapsid (S=Spike,m=membrane,e=envelope, n=nucleocapsid)
forms ERGIC
8: formation of mature virion inside a golgi vesicle formed from the SEM bound to the ER.
9: exocytosis
How does coronavirus replication start?
Have a host cell to attach to through the spike glycoprotein binding to the angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor protein on the host cell and invade.
2 approaches for therapeutic treatment
Prevent virus entry into host cell (Target ACE2 receptor)
Suppress various steps in virus replication inside cells (Target RBD of spike protein)
Acute immune response to corona
Activation of ACE2 activates inflammatory factors to kill, and kills lung epithelial cells
Acute response provides immediate protection, but in the long run adaptive long term immune response should be initiated not acute anymore.
2 Types of COVID vaccines
mRNA encoding SARS-COV2 Spike protein or
Adenovirus vector encoding S protein.
Basically help differentiate naive T cells to recognize the S protein and train them to kill SARS COV2.
mRNA based COVID 19 Vaccines description
Lipid nanoparticle encapsulated mRNA
Lipid nanoparticles done through rapid mixing with microfluidic devices. Formed by merging smaller lipid vesicles.
3 Main strategies for RNA type and delivery system
mRNA, sa(Self amplifying), RNA
LIPID nanoparticles (CNE)
Cationic Nano emulsions (CNE)