IQ #4
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Chapter 7
Revenue and Collection Cycle
basic activities in revenue and collection cycle
(1) receiving and processing customer orders, including credit approval
(2) delivering goods/services to customers
(3) billing customers and accounting for AR
(4) collecting and depositing cash received from customers
(1.) receiving and processing customer orders;
If these controls fail,
orders might process for fictitious customers
Credit might be approved for bad credit risks
Shipping docs might be created for goods that DNE in inventory
(2.) delivering goods and services to customers
Physical custody of inv goods start in warehouse
Custody is transferred to shipping order that permits inv clerk to release goods to the shipping department
bill of lading
form that the carrier signs to verify that the goods are shipped.
packing slip
describes the goods being shipped, and the quantity of goods shipped, is often included with the shipment.
(3.) billing customers and accounting for AR
When delivery is complete the transaction is completed by filing a shipment record and preparing final invoice
Sales invoice is the bill sent to the customer that indicates the amount due and the payment terms.
when auditing the revenue and collection cycle, auditors normally select balances to confirm from
accounts receivable listing
using the audit risk model
(1.) Set audit risk at desired levels (normally, low).
(2.) Assess risk of material misstatement
2a) Inherent Risk? Note that AS 2110 indicates that the auditor should [presume that there is a fraud risk involving improper revenue recognition.
2b.) control risk?
(3.) Set detection risk at the significant account and assertion level based on the level of audit risk and risk of material misstatement.
audit risk is manifested when
material misstatement enters the financial reporting process (inherent risk)
that the client's internal controls do not prevent or detect (control risk) and
that auditors substantive procedures do not detect
(detection risk)
test of operating effectiveness of internal control
if a control is missing or ineffective, RMM increases but an error or fraud is by no means certain
internal controls are designed to
reduce RMM by preventing or detecting errors and fraud
types of risk in the revenue cycle
Improper revenue recognition
Fictitious sales
Returns and allowances
Collectability of receivables
Revenue Recognition must be
1. earned and 2. realized or realizable
revenues are normally earned when
the company has substantially accomplished what it must to be entitled to the benefits
SEC guidance (SAB 104)
-Persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists
-Delivery has occurred or services have been rendered
-The seller's price to the buyer is fixed or determinable
-Collectibility is reasonably assured
ASC 606 5-step process
1. identify the contract with customer
2. identify the performance obligations
3. determine the transaction price
4. allocate the transaction price to POs
5. recognize revenue when the entity satisfies a PO
As we have more POs then
this increases inherent risk
Revenue and its relevant assertions
Occurrence
Completeness
Cutoff
Revenue and Occurrence
WCGW?
- overstate sales by adding fictitious transactions or inflating actual sales
INTERNAL CONTROL ACTIVITY
- invoice are supported by bill of lading
TEST OF CONTROL
- vouch sales to invoices, supporting shipping docs
Revenue and completeness
WCGW?
- not all sales recorded
INTERNAL CONTROL ACTIVITY
- invoice, shipping docs, orders are prenumbered and checked
TEST OF CONTROL
- scan docs and trace shipping do to recording in sales detail file
Revenue and Cutoff
WCGW?
- sales recorded in incorrect period
INTERNAL CONTROL ACTIVITY
- date of shipping doc is compared to invoice date
TEST OF CONTROL
- trace shipping date to sales invoice date and FOB item
key control procedures of the revenue and collection cycle
SEPERATION OF DUTITES
Recording, authorization, custody
Recording
- adequate documents and records
bill of lading, invoices
- Independent checks on performance
monthly stmt to customer
Authorization
authorization of transactions
- write offs
- EDI transactions
- perform credit checks
- pricing
Custody
access to assets
- shipping department
- lock box
internal control activities and design evaluation
The question an auditor should ask is, "Has the audit client designed and implemented a control that, if operating effectively, would mitigate the identified risk of material misstatement? Would it prevent or detect the material misstatement?" TOP DOWN PROCESS
three way match
1. customer actually places the order (invoice)
- reduces the risk of fictitious sales
2. company has shipped the goods (agree to shipping docs)
- ensures revenue is earned
3. customer has been billed properly (agree to purchase order)
- supports accuracy and completeness
Dual direction of a test sample
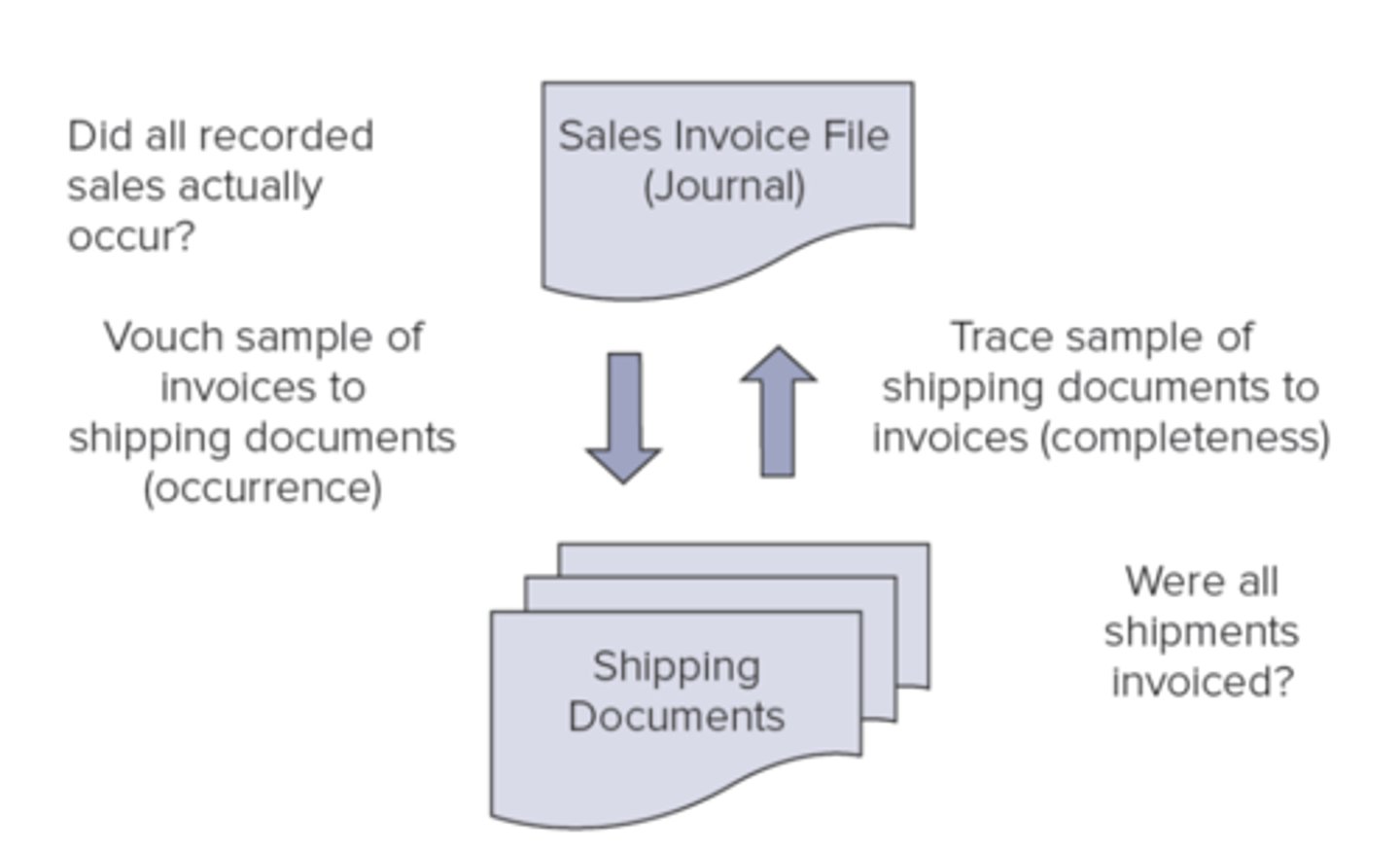
substantive procedures
audit tests that directly evaluate the accuracy and completeness of fin stmt balances, help auditors detect material misstatements, either error or fraud.
substantive procedures include
tests of details
- directly examining documents, evidence, confirmations
substantive analytical procedures
- studying relationships among data
Auditing Accounts Receivable
- test reconciliations
- perform substantive analytical procedures
- send confirmations
- test sales cut-off
- analyze the ADA
- fill our presentation and disclosure checklists
Accounts Receivable and their relevant assertions
Existence
Completeness
Valuation
AR Existence
- start at the general ledger -- test reconciliation
- select from A/R listing -- send confirmations
- evaluate confirmation replies
- perform alternate tests for no-replies
using confirmations
-Primarily for verifying EXISTENCE.
Factors likely to affect the reliability of confirmations
-Previous audit experience
-Intended recipient of the confirmation
-Type of information being confirmed
-->The auditor may confirm entire BALANCES or individual TRANSACTIONS.
-Type of confirmation being sent
Types of confirmations
- Positive Confirmations
- Negative Confirmations
- Blank Confirmations
positive confirmation
request indicating balance is correct or not
negative confrimations
- requests response only if something is wrong
blank confirmations
confirmation does not contain balance, customer use fill it in themselves
- dont tell counterparty amount, they tell you: valuation
circumstances that could justify the omission of the confirmation of a client's accounts receivable
- not material to fin stmt
- if RMM is low
- may be inefficient
- expected to be ineffective (based on previous years
other matters related to confirmations
- confirmations returned by the post office as non-deliverable MUST be investigated
- auditors should follow up on electronic responses
Non-response to Positive/blank confirmation requests
follow up 2nd or 3rd time
alternative procedures
follow-up on all exceptions
alternative procedures to non response
- vouch cash collections
- examine shipping documents
- examine client- generated supporting documents
- invoices
- inspect correspondence files
exception testing
designed to identify a violation of a particular control activity through the use of an automated test procedure designed to test all items in a population
uncollectible accounts
•Inspect customer files for collectability
•Recalculate allowance and bad debt expense
•Verify reasonableness of allowance and bad debt expense
•Inspect documentation for appropriateness of accounts written off
-Inspect documentation for additional collection procedures
-Inspect documentation for appropriate authorization
valuation -- presented at collectible amounts
- obtain, examine ages trial balance
- evaluate significantly past due items
- consider confirmation replies/disputes/exceptions
- analyze write-off trends/ turnover
analytical procedures for sales revenue
-Comparisons with previous periods
-Comparisons with industry
analytical procedures for allowance for doubtful accounts, bad debt expense
- compare bad debt exp as percentage of sales to previous periods
- compare ADA as percentage to gross receivables to previous periods
BEST substantive evidence, because last years estimates
analytical procedures for accounts receivable
compare AR turnover to previous periods
Sales cutoff procedures
1. Used to verify whether Revenues are recorded in the CORRECT ACCOUNTING PERIOD.
--"Holding the books open" (could be legit or not: can finish finalizing sales from end of DEC vs holding open til they get the sales they need)
2. Examine SALES INVOICES and SHIPPING DOCUMENTS shortly prior to and after year-end.
3. Examine returns after year-end.
Revenue -- detail tests of cutoff
control procedure “credit sales approved by credit department” is related which assertion
Accuracy; Credit approval helps ensure that the sale will be collectible
An unexplained decrease in ratio of gross profit to sales may suggest
unrecorded sales;
Which of the following responses to an accounts receivable confirmation at December 31 would cause an audit team the most concern
“These goods were returned for credit on November 15.”
Audit documentation often includes a client-prepared, aged trial balance of accounts receivable as of the balance sheet date. The audit team uses this aging primarily to
Estimate credit losses.
In the audit of accounts receivable, the most important emphasis should be on the
Existence assertion.
Chapter 8
Acquisition and Expenditure Cycle
three ways to recognize expenses
1. when they can be matched with related revenues and those revenues are recognized
- cogs with sales
2. in the period they are incurred
- utility bills
3. when they are allocated to future periods benefited by a "systematic and rational" process (depreciation)
- machinery
Typical activities of acquisition and expenditure cycle
1. purchase goods and services
2. receiving the goods or services
3. recording the asset or exp and related liability
? paying the invoice through the cash disbursement process
1. purchase goods and services
- requests items by sending purchase requisition
- department requesting purchase of items prepares a Purchase Order
- tiered authorization
2. receiving the goods or services
- when goods arrive, supplier will have bill of lading
- After vendor approval, goods are received by company and evidenced by preparing a RECEIVING REPORT
3. Recording the Asset or Expense and Related Liability
- AP is recorded when purchaser received goods
- AP department attached a voucher
- vendor bills company for goods using vendor's invoice
voucher
package of documents that contains supporting documents for a transaction
example is purchase voucher
contains
- purchase requisition
- purchase order
- receiving report
- vendor invoice
- negotiable check
"think folder or binder"
liabilities are not recorded until
receiving reports have been matched to purchase, orders, and invoices
- when there's a problem, liability is delayed or not recorded --> overstating profits, understates costs
recognition of rebates, refunds, and price agreements
GAAP requires allocation over the period of benefit
using audit risk model
(1.) Set audit risk at desired levels (normally, low).
(2.) Assess RMM
(3.) inherent risk?
- unrecorded liabilities
- capitalizing expenses (R&D)
- transactions with related parties
(3.) Set detection risk at the significant account and assertion level based on the level of audit risk and risk of material
LOW AR = HIGH IR HIGH CR LOW DR
Relative assertions risks to expenditures
- existence/occurrence
MODERATE RISK both
- completeness and cutoff
HIGH RISK both
- valuation and accuracy
MODERATE liab, HIGH exp
- presentation and disclosure
HIGH exp
overstated expenses can relate to
over-accruals and embezzlements
understated liabilities often associated with
earnings management and debt covenants
control procedures for separation of duties
1. authorization of purchase is done by purchasing department
2. custody of inventory is help by receiving department
3. transactions recorded by general acct and accounts payable department
4. reconcile liabilities to customer stmts and general ledger
audit evidence in management reports and data files
- open purchase orders
- unmatched receiving reports
- unmatched vendor invoices
exhibit 8.7 dual direction of tests
add image
the completeness assertion
search for unrecorded liabilities
- inquire about procedures for identifying and recording liabilities
- scan open purchase order file
- examine
- unmatched vendor stmts or invoices
- unmatched receiving reports
- trace unpaid vouchers in AP ledger
- confirm AP with normal suppliers
- review cash disbursements
auditing PPE
- small number of transactions --> high dollar transactions
- authorization of acquisitions and disposals (board of directors)
- less concern for access to assets
- unrecorded disposals
auditing PPE: depreciation expense
- recalculate and evaluate reasonableness of useful life, salvage value, cost, and method
- depreciation has to be consistent with company policy and across years
auditing cost and expense accounts
- analytical procedures
- agree to related balance sheet account
- substantive tests of transactions
- vouch detail
accrued liabilities
Major differences between accrued liabilities and accounts payable (Examples include interest, property taxes, wages, and income taxes payable. These payables are not normally invoiced or evidenced by the receipt of goods (LACK OF INVOICE)).
- These differences may make it more difficult to detect unrecorded accruals.
auditing accrued liabilities and prepaid expenses
- agree balances to prior year work papers
- verify payments
- examine underlying agreements
- recalculate amounts
- search for unrecorded accruals
- analytical procedures
12 MONTHS AND ONLY 12 MONTHS RECORDED
income taxes payable
complex area; requires tax specialist
- vouch payments
- examine correspondence with gov agencies
- follow stnds for auditing estimates
- usually finalized towards very end of audit
Fraud in Accounts Payable
•Inspect invoices in files for photocopies
•Inspect vendor's invoices submitted in numerical order
•Inspect vendor's invoices that are always in round numbers
•Scan vendor's invoices for invoices that are always slightly lower than a review threshold
•Scan vendor invoices for vendors with only post office box addresses
•Scan vendor invoices for invoices with no listed telephone number
•Match vendor and employee address and telephone numbers
•Scan multiple vendors at the same address and telephone number
•Vouch a sample of vendor invoices to the approved vendor list
•Review invoices for addresses of the local mail drops
purchase cutoffs
- verify cut offs for purchases
- examine receiving reports and vendor sales invoices occurring around year-end to ensure inventory received is included in the appropriate period
An audit team would most likely examine the detail support for charges to which of the following accounts?
Legal advice; The auditor examines the specific charges to determine potential litigation.
When auditing account balances of liabilities, auditors are most concerned with management’s assertion about
Completeness; The hiding of
liabilities is a primary concern for all auditors in the liability and expense areas.
Supplies expense is generally audited in connection with supplies inventory.
Which of the following tests of details most likely would help an auditor determine whether accounts payable have been misstated?
Examining vendor statements for amounts not reported as purchases.