Topic 7 - Rate of reaction & Energy changes
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
How do you calculate rate of reaction?
Amount of reactant used up OR product formed / time.
What units could be used for rate of reaction?
g/s, cm cubed/s, mol/s.
How can you measure the rate of reaction when a gas is given off?
Gas syringe can measure volume of gas produced in a given time. More gas produced in a set time, the faster the reaction.
During a reaction, a gas is produced so mass decreases. We can measure the mass using a mass balance and workout the change of mass in a given time. The faster the reading the drops, the faster rate of reaction.
How can you measure the rate of reaction when a precipitate is formed?
Put a black cross below a beaker containing reactants.
Time how long it takes for cross to disappear after second reactant is added. This is when the precipitate clouds the solution.
Why is using the precipitation method to investigate rate of reaction not very accurate?
It’s subjective so people are likely to disagree over the exact point at which the cross is no longer visible.
Define: Activation Energy
The minimum amount of energy required for a reaction between two reacting particles.
What must happen for a reaction to occur?
Particles must collide with sufficient energy.
Which two things does rate of reaction depend on?
Energy transfer and frequency of collisions.
Marble chips react with hydrochloric acid to produce calcium chloride, water and carbon dioxide. How can the rate of this rate of reaction?
Increase the surface area of marble chips by making them smaller.
Increase concentration of acid.
Increase temperature.
What are successful collisions?
When reacting particles collide with enough energy.
What are unsuccessful collisions?
When reacting particles don’t collide with enough energy.
Which factors does rate of reaction depend on?
Temperature, Concentration, Pressure, Surface Area, Catalysts.
Explain how temperature affects the rate of reaction.
Increasing temperature increases the rate of reaction.
This is because the reactants have more energy so more particles have energy above the activation energy meaning more collisions will be successful.
Collisions also occur more frequently because the particles have more kinetic energy.
Explain how surface area affects the rate of reaction.
Increasing the surface area of reactants increases the rate of reaction.
This is because a greater surface area means there are more exposed particles so more frequent successful collisions.
Explain how an catalyst affects the rate of reaction.
A catalyst increases the rate of reaction without being sued up.
This is because it provides an alternate reaction pathway with a lower activation energy.
More particles will have sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy and react so more successful collisions occur in the same time.
Explain how concentration affects the rate of reaction.
Increasing concentration increases the rate of reaction.
This is because there are more reacting particles in the same volume so there are more frequent successful collisions.
Explain how pressure affects the rate of reaction.
Increasing the pressure of a gaseous reaction increases the rate of reaction.
This is because there are more reacting particles in the same volume of gas (or the same number of particles in a smaller volume) so more frequent successful collisions occur.
What is the job of a catalyst?
Increases rate of reaction without being used up or chemically changed.
How does a catalyst speed up rate of reaction?
It provides an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy.
What are enzyme?
Biological catalysts that increase rate of reactions in living cells.
What enzyme is used to produce ethanol from glucose?
Yeast.
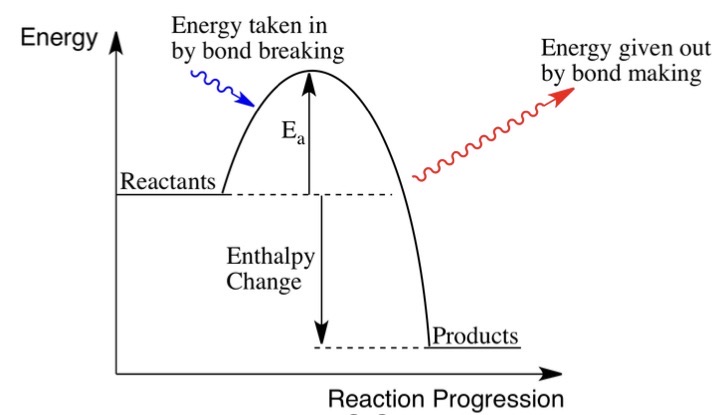
What is meant by an exothermic reaction?
A reaction that gives out energy to the surroundings.
Which type of reaction gives out energy to the surroundings?
Exothermic reaction.
What is meant by an endothermic reaction?
A reaction that takes in heat energy from the surroundings.
Which type of reaction takes in heat energy from the surroundings?
Endothermic reaction.
Are neutralisation reactions endothermic or exothermic?
Exothermic.
Are displacement reaction endothermic or exothermic?
Either.
Is salt dissolving in water exothermic or endothermic?
Either.
Are precipitation reactions endothermic or exothermic?
Exothermic.
Name three types of reaction that exothermic.
Combustion, Neutralisation, Preciptation.
Give two examples of endothermic reactions.
Photosynthesis, Thermal Decomposition.
How could you measure the temperature change of a neutralisation reaction?
Measure initial temperature of the solutions.
Mix both reactants in a polystyrene cup.
Record highest temperature reached.
Calculate the temperature change.
How can heat loss be minimised during an experiment looking a changes in temeperature?
Use a polystyrene cup.
Place reaction cup in a beaker full of wool for extra insulation.
Lid on the reaction cup.
Describe the bonds during an exothermic reaction.
Energy released when forming new bonds is greater than the energy used to break old ones so it releases energy.
Describe the bonds during an endothermic reaction.
Energy used to break old bonds is greater than energy released when new bonds are formed, so the reaction absorbs energy.
Energy released when forming new bonds is greater than the energy used to break old ones. Is this an exothermic or endothermic reaction?
Exothermic.
Energy used to break old bonds is greater than energy released when new bonds are formed. Is this an endothermic or exothermic reaction?
Endothermic.
How can the energy change of a reaction be calculated from bond energies?
Total energy of bonds broken - Total energy of bonds made.
Energy taken in - Energy given out.
If the energy change of a reaction is negative, is the reaction exothermic or endothermic?
Exothermic as energy has been lost to surroundings.
If the energy change of a reaction is positive, is the reaction exothermic or endothermic?
Endothermic as energy has been take in from the surroundings.
Drawn an endothermic reaction profile.
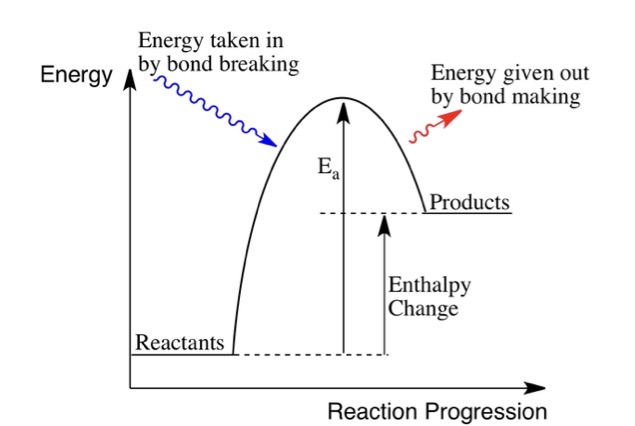
Drawn an exothermic reaction profile.