Unit 5: Economic Performance and Challenges
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Merged flashcards from several presentations of Unit 5 in an Economics class.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
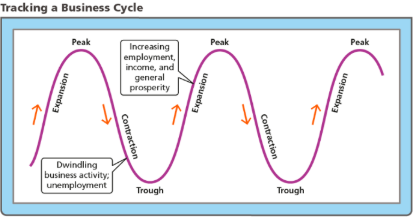
Business cycle
The alternation between economic downturns, known as recessions, and economic upturns, known as expansions
Often affected by specific economic variables that bring about the next phase; however, forecasting is difficult

Business investment
Factor in the business cycle where businesses spend more money, increasing GDP and economic expansion
Office buildings are one manifestation of this

Credit cost
Factor in the business cycle describing the cost of borrowing money
Higher levels of this may result in decreased consumer spending or business investment

External shocks
Factor in the business cycle describing those outside of a business’s control that positively or negatively affect growth
Wars and global pandemics are examples of this

Consumer expectations
Factor in the business cycle describing predictions made by consumers about the future that affect present spending
Recessions
Periods of economic downturn when output and employment are falling with dwindling business activity
Defined as 2 consecutive quarters of falling real GDP
Usually lasts from 6 to 18 months with 6 to 10 percent unemployment

Depressions
Deep and prolonged downturns
No precise definition; usually defined as a recession with high unemployment and low economic output
Stagflation
A decline in real GDP (output) combined with a rise in the price level (inflation)
Expansions
Periods of economic upturn when output and employment are rising with general prosperity
Measured by a rise in real GDP
Peak
The time when real GDP stops rising and the economy has reached the height of an economic expansion
Unemployment and inflation are low
Contraction
The time after a peak marked by a decline in falling real GDP and higher unemployment
Trough
The time after a contraction when the economy has “bottomed out” as real GDP stops falling and expansion begins
Growth
Factor in the economy that allows for more and better goods over time, improving the standard of living
Most commonly measured by the change in real GDP over time
Real GDP
Measurement of GDP accounting for inflation
Must grow as fast as the population does for definite growth; shown in the measurement of this per capita
Can exclude other factors in life quality, such as stress, wealth distribution, or environmental state

Productivity
The engine for economic growth and rising real GDP
Allows for greater output per worker with better skills, capital, or technology
Capital deepening
Increasing the capital-to-worker ratio to allow for more productivity per worker; can be seen through investments in human and physical capital
Human capital
Capital that includes education, training, and experience for people
Physical capital
Capital that includes tools, machines, and equipment for people
Savings
Money set aside for later
Allows for greater capital deepening as financial intermediaries support investments in facilities and equipment
Promoted by many nations to raise GDP and standards of living
Capital formation
The saving and investment cycle that creates more money within the economy as loans are made

Taxation
Power a government has to influence capital formation
Higher levels on individuals lead to less disposable income and lower savings rates
Using this for infrastructure allows for greater growth over time, though
Infrastructure
Public goods that a government invests in with tax money for increased trade or productivity
Technological progress
A driver of economic growth that allows for greater efficiency without increasing the number of inputs used; driven through:
Research and innovation patents
Innovation incentives
Education and experience adoption
Resource scarcity for better methods
Can be measured through growth not attributable to capital or labor
Scientific research
Research that generates new or improved production techniques, improved physical capital, and better goods and services

Innovation
Activity that leads to higher output, boosted GDP, and greater business profits
Often requires research; this can be enabled by government-sanctioned monopolies
Unemployment
The state of not being employed; can be both an individual and nationwide issue
Tracked by economists to aid economic reccovery or growth
A zero percent rate is impossible due to the three types of this having at least some people

Structural unemployment
Unemployment created or depleted by changes in the economy, such as those in the telecommunications or healthcare sector
Results from industrial reorganization or technological change
Skills, location, or wage demands typically mismatch the requirements of the job
Job training
A way to address structural unemployment, allowing workers to gain skills in response to structural changes
However, this takes time and does not ensure high-wage jobs
Collective bargaining
Union activity that negotiates on behalf of all workers
Labor strike
Union activity that results in a collective refusal to work

Labor union
Organization within a place of employment that can raise wages or benefits
While this is good for workers, it can also cause structural unemployment as higher wages create surpluses

Frictional unemployment
Unemployment created by the constant changes in the workforce
Measured as the time workers spend searching for work — always exists with searches for a first or better job
Is typically brief in periods of low unemployment

Cyclical unemployment
Unemployment that relates to the trends in growth and production that occur within the business cycle
Minimized during business peaks as output is maximized
May grow during recessions where workers are laid off
Natural rate of unemployment
The rate of employment that arises from the effects of frictional and structural unemployment
Is inevitable as the minimum rate that the actual rate fluctuates around
Is never zero
Full employment
The rate of unemployment when cyclical unemployment does not exist, ignoring the natural rate of unemployment

Seasonal unemployment
Unemployment that occurs when industries slow or shut down for seasonal shifts in production schedules, such as in harvesting industries or holiday seasons
Typical part of a healthy economy
Labor force
The total amount of people who are employed and unemployed but looking for a job in a country

Unemployment rate
The percentage of people in the labor force who are unemployed
Determined by the Bureau of Labor Statistics through a monthly household survey of 60,000 families
Adjusted for seasonal unemployment for more accurate comparisons across months, but can vary across different demographic groups
Rises during recessions and falls during expansions
Discouraged workers
Workers who could work but have given up seeking employment due to the state of the job market
Not counted in the unemployment rate; this may lead to an understatement in the amount of people who want to work but are unable to find jobs

Marginally attached workers
Workers who would like to be employed and have looked for a job in the past but are not currently looking for work
Underemployed workers
People who would like to work more hours than they do or are overqualified for their jobs
Inflation
The rate at which the value of a currency is falling and, consequently, the general level of prices for goods and services is rising
Leads to a decline of the purchasing power of a given currency over time
Deflation
The general decline of the price level of goods and services
Associated with a contraction in the supply of money and credit, but prices can also fall due to increased productivity and technological improvements

Aggregate price level
A measure of the overall level of prices in an economy

Consumption bundle
A typical group of goods and services purchased by customers
Market basket
A hypothetical consumption bundle used to measure changes in the overall price level
Revised approximately every decade to reflect shifts in consumer purchasing behavior
Price index
A way of measuring how the average price of a standard group of goods changes over time
Helps consumers and businesses make economic decisions
Aids governments in making policy decisions, such as in setting interest rates to ease inflation
Base year
A year arbitrarily chosen for comparison when calculating a price index, which compares the price of the market basket of goods in a given year to its price in this
Inflation rate
Calculated as the annual percentage change in an official price index
Can lead to workers or pensioners losing money if income does not keep up with this

Consumer price index (CPI)
Measures the cost of a market basket of a typical urban American family
Calculated by the Bureau of Labor Statistics by surveying 23,000 retail outlets in 87 cities, tabulating over 80,000 prices per month for an overall weighted average
Used to evaluate changes in the cost of living as well as the rate of inflation or deflation; is thus used to index the price of certain goods or payments like Social Security
However, it can ignore technological improvements or households moving away from a good due to price increases
Producer price index (PPI)
Measures the cost of a typical basket of goods and services purchased by producers
Usually moves in tandem with other measures of inflation
Money supply
One of the factors of inflation describing a rise in the supply of a currency without a matching rise in the production of goods and services
Prices thus rise due to heightened demand for a limited supply of products, reducing purchasing power
Quantity theory of money
Believes that the value of money and resulting inflation are caused by the supply and demand of the currency
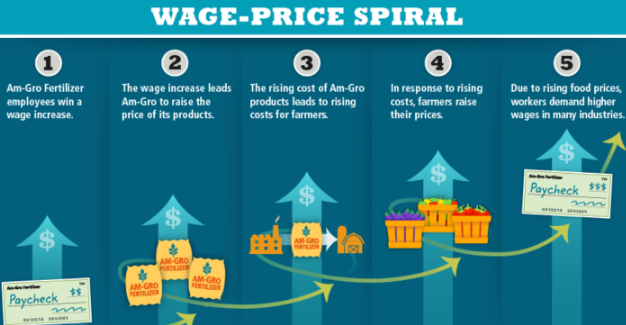
Wage-price spiral
Phenomenon that states that employers providing higher wages lead to higher costs, leading to higher overall prices and thus a need for even higher wages
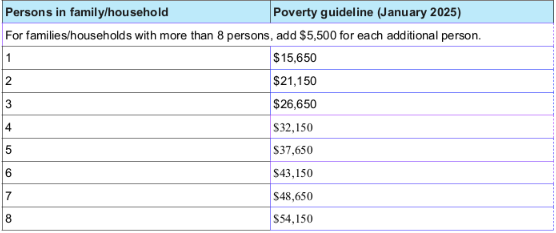
Poverty threshold
The income below which income is insufficient to support a family or household
This measurement was developed in the mid-1960s, derived from the cost of a minimum nutritional food diet for temporary or emergency use multiplied by three
Varies with the size of the family; applies to each person if counted
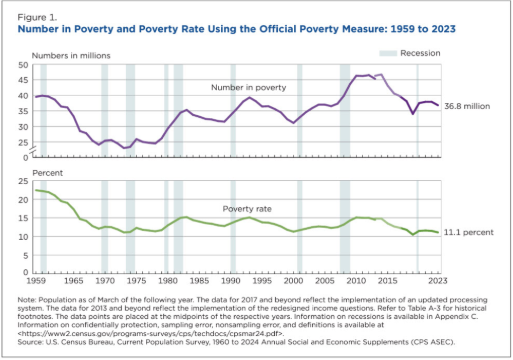
Poverty rate
The percentage of people who live in households with income below the official poverty threshold
Differs sharply by group, with minorities, children, residents in inner cities, and women being the largest groups in poverty

Working poor
People who have a job but also have low wages or a limited work schedule
Poverty causes
Includes:
Unemployment or underemployment
Family structure shifts
Geographical location (more common in inner cities, rural areas)
Unequal treatment or opportunity
Globalization and relocation of jobs
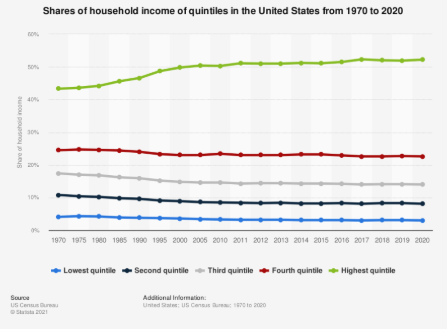
Income distribution
The way income is distributed throughout a country
In the United States, most growth and income is skewed to the top 5 to 20%, leading to a shrinking middle class and greater skill, inheritance, and field differences
Measures of this, however, can ignore tax and transfer program impacts
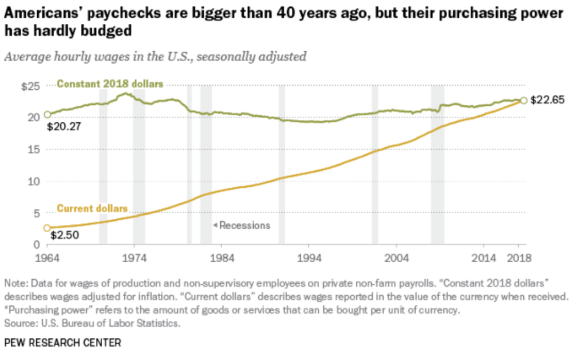
Wage increases
Limited in the United States due to inflation and rising benefit costs
Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
Refundable federal tax credit aimed at supporting low and moderate-income families with children
Allows recipients with earned income to recieve a payment even if they owe no income tax, boosting earnings and reducing poverty
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF)
Means-tested, time-limited cash assistance program for very low-income families with children
Funded by a federal grant and run by the states, providing short-term help, job preparation, and familial stability
Federal lifetime limit of 60 months with work participation often required for funds
Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)
Program that offers monthly grocery benefits to low income individuals and families, provided via an EBT card accepted at most supermarkets and numerous farmers’ markets
Eligibility determined based on household income and size, with certain provisions allowing certain non-citizens and students to qualify under particular conditions
Amounts are calculated to supply enough funds to afford nutrient-rich foods and beverages