PHARM 532 - Electrical Conductance Disorders (TEST 1)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
Sinoatrial (SA) Node Location
Located within the wall of the right atrium
2
New cards
Arioventricular (AV) Node Location
Located in the right atrial wall near autonomic parasympathetic ganglia
3
New cards
Bundle of His (Atrioventricular Bundle) Location
Interventricular septum
4
New cards
Purkinje Fibers location
Extend to apex (bottom) of heart and out to outer ventricular walls
5
New cards
Heart Pacemakers
- Sinoatrial (SA) node
- Atrioventricular (AV) node
- Bundle of His (Atrioventricular Bundle)
- Purkinje fibers
- Atrioventricular (AV) node
- Bundle of His (Atrioventricular Bundle)
- Purkinje fibers
6
New cards
What is the normal path of an electrical signal through the heart?
1) Sinoatrial (SA) node
2) Atrioventricular (AV) node
3) Bundle of His (Atrioventricular Bundle)
4) Purkinje fibers
2) Atrioventricular (AV) node
3) Bundle of His (Atrioventricular Bundle)
4) Purkinje fibers
7
New cards
What effect do sympathetic and parasympathetic activation have on the rate of depolarization and action potentials?
Sympathetic activation --> increased conduction velocity in AV node via increasing rate of depolarization of action potentials
Parasympathetic (vagal) activation --> decreased conduction velocity in AV node via decreasing slope of phase 0 of the nodal action potentials
Parasympathetic (vagal) activation --> decreased conduction velocity in AV node via decreasing slope of phase 0 of the nodal action potentials
8
New cards
What potential effect could an interrupted or abnormal signal at any point in the electrical pathway have on contraction of the atria and/or ventricles?
Arrhythmias
9
New cards
Which part of the cardiac action potential in non-pacemaker cells is denoted by which phase?
- Phase 0: rapid depolarization
- Phase 1: initial repolarization
- Phase 2: plateau phase
- Phase 3: repolarization
- Phase 4: resting membrane potential near equilibrium potential for K+
- Phase 1: initial repolarization
- Phase 2: plateau phase
- Phase 3: repolarization
- Phase 4: resting membrane potential near equilibrium potential for K+
10
New cards
Which ions and channels are responsible for each of the five (5) phases of the cardiac action potential in non-pacemaker cells?
- Phase 0: rapid depolarization involves Na+ and Ca2+
- Phase 1: initial repolarization involves K+ and Ca2+
- Phase 2: plateau phase involves Ca2+
- Phase 3: repolarization involves K+
- Phase 4: resting membrane potential near equilibrium potential for K+ involves K+, Na+, and Ca2+
- Phase 1: initial repolarization involves K+ and Ca2+
- Phase 2: plateau phase involves Ca2+
- Phase 3: repolarization involves K+
- Phase 4: resting membrane potential near equilibrium potential for K+ involves K+, Na+, and Ca2+
11
New cards
What are the differences in shape of the action potentials in pacemaker vs non-pacemaker cells?
Non-pacemaker has rapid depolarization ("fast response")
Pacemaker has spontaneous, slower depolarization ("slow response")
Pacemaker has spontaneous, slower depolarization ("slow response")
12
New cards
What are the differences in duration and shape of the atrial and ventricular action potentials compared to action potentials seen in skeletal muscle cells and neurons?
- Nerve cell: ~1 ms
- Skeletal muscle cell: ~2-5 ms
- Cardiac muscle cell: 200-400 ms
- Skeletal muscle cell: ~2-5 ms
- Cardiac muscle cell: 200-400 ms
13
New cards
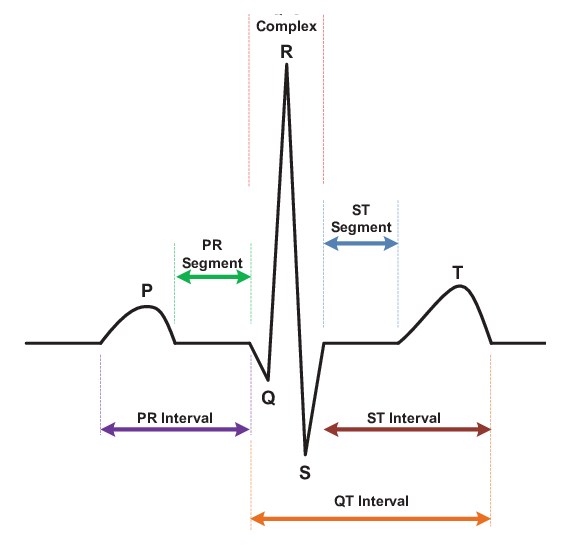
ECG Components
- P wave
- QRS complex
- T wave
- PR interval
- ST segment
- QT interval
- QRS complex
- T wave
- PR interval
- ST segment
- QT interval
14
New cards
P wave
Atrial depolarization
15
New cards
QRS Complex
Ventricular depolarization
16
New cards
T Wave
Ventricular repolarization
17
New cards
PR Interval
Atrial depolarization + AV nodal delay
18
New cards
ST Segment
Isoelectric period of depolarized ventricles
19
New cards
QT Interval
Duration of depolarization + repolarization - corresponds to action potential durations throughout ventricles
20
New cards
Sinus Rhythm
Rhythm of the heart
21
New cards
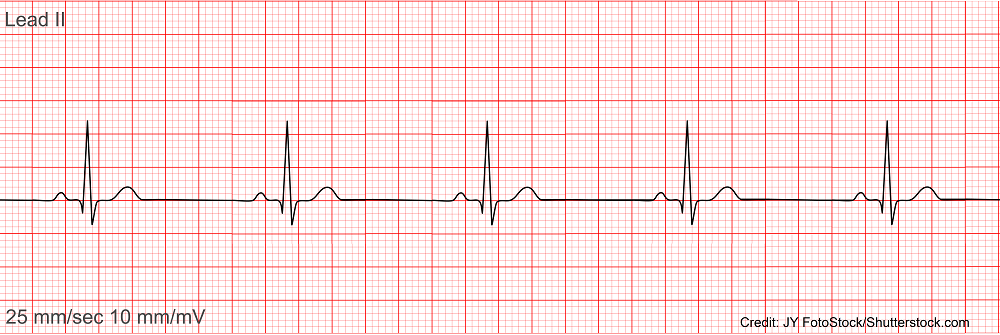
Sinus Bradycardia
HR < 60 bpm
22
New cards
Sinus Bradycardia Treatment
Pacemaker
23
New cards
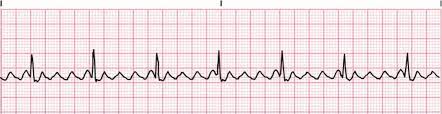
Atrial Flutter
- Supraventricular arrhythmia
- Depolarization currents arise from SA but atrial rate too high for all impulses to be conducted through the AV node
- Depolarization currents arise from SA but atrial rate too high for all impulses to be conducted through the AV node
24
New cards
Atrial Flutter Treatment
- Ventricular rate control
- Electrical or pharmacological cardioversion
- Catheter-based radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
- Anti-coagulant medication
- Antiarrhythmic meds
- Electrical or pharmacological cardioversion
- Catheter-based radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
- Anti-coagulant medication
- Antiarrhythmic meds
25
New cards
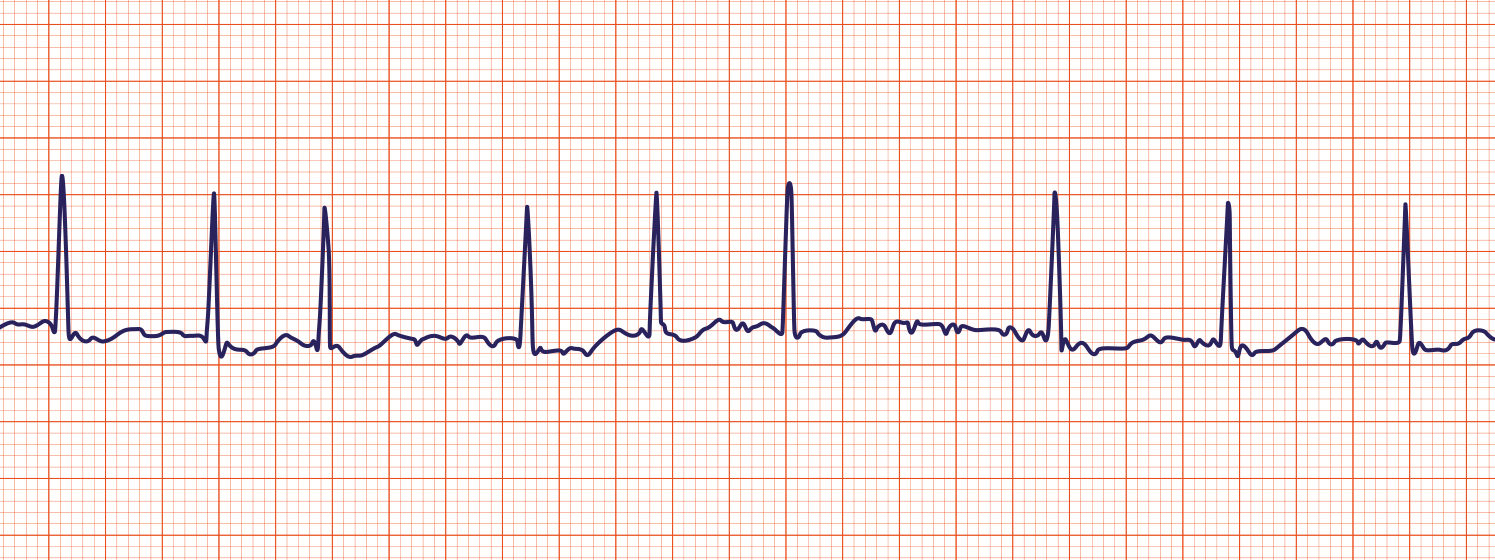
Atrial Fibrillation
- Supraventricular arrhythmia
-Depolarization currents arise from non-SA node sites throughout the atria
-Depolarization currents arise from non-SA node sites throughout the atria
26
New cards
Atrial Fibrillation Treatment
- Cardioversion
- Anti-coagulant medication
- Anti-coagulant medication
27
New cards
Atrioventricular Block
Heart block
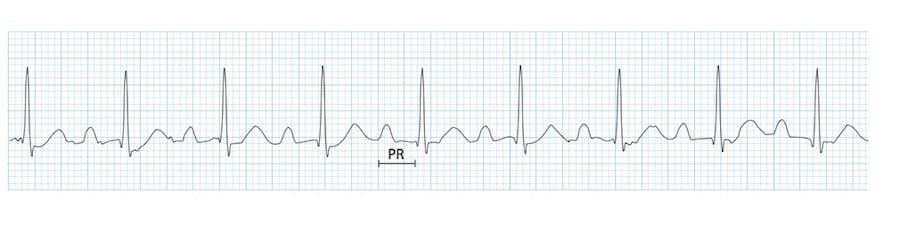
28
New cards
Atrioventricular Block Treatment
Pacemaker
29
New cards
Ectopic foci (premature ventricular complex)
- Can occur within the atria or ventricles
- Premature and bizarrely shaped QRS complexes
- Premature and bizarrely shaped QRS complexes
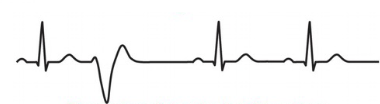
30
New cards
Ectopic Foci (Premature Ventricular Complex) Treatment
- Oxygen if hypoxic
- Antiarrhythmic meds
- Beta-blockers
- Electrolytes
- Ca2+ channel blockers
- Antiarrhythmic meds
- Beta-blockers
- Electrolytes
- Ca2+ channel blockers
31
New cards
Ventricular Tachycardia
- HR 100-280 bpm
- Can be sustained or non-sustained (paroxysmal)
- Can be sustained or non-sustained (paroxysmal)

32
New cards
Ventricular Tachycardia Treatment
- Cardioversion
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
- Catheter-based radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
- Catheter-based radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
33
New cards
Ventricular Fibrillation
Uncoordinated ventricular depolarizations

34
New cards
Ventricular Fibrillation Treatment
- Immediate defibrillation
- Catheter-based radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
- Catheter-based radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
35
New cards
What are the most common arrhythmias in the US?
- Atrial flutter
- Atrial fibrillation
- Atrial fibrillation
36
New cards
Less Serious General Symptoms of Arrythmia
•Palpitations
•Slow heartbeat
•Irregular heartbeat
•Feeling pauses between heartbeats
•Slow heartbeat
•Irregular heartbeat
•Feeling pauses between heartbeats
37
New cards
More Serious General Symptoms of Arrythmia
•Anxiety
•Dyspnea
•Syncope
•Dizziness
•Fatigue
•Sweating
•Chest pain
•Dyspnea
•Syncope
•Dizziness
•Fatigue
•Sweating
•Chest pain
38
New cards
What techniques are typically used to diagnose arrhythmias?
• Electrocardiogram (ECG) to evaluate the electrical activity of the heart
• Holter monitoring (24 hour portable ECG recording)
• Echocardiogram
• Exercise stress test
• Tilt table test
• Holter monitoring (24 hour portable ECG recording)
• Echocardiogram
• Exercise stress test
• Tilt table test
39
New cards
What are some common risk factors for development of arrhythmia?
• Age
• Gender (F
• Gender (F
40
New cards
What are some common causes of arrhythmia?
- Coronary artery disease
- Altered impulse formation
- Altered impulse conduction
- Altered impulse formation
- Altered impulse conduction
41
New cards
Afterpolarization
Abnormal depolarizations that interrupt phase 2, phase 3, or phase 4 of the cardiac action potential
42
New cards
Afterpolarization Types
Early afterdepolarization (EAD) and Delayed afterdepolarization (DAD)
43
New cards
Early Afterdepolarization (EAD) Cause
Can be caused by anti-arrhythmia drugs such as quinidine, dofetilide, ibutilide
44
New cards
Delayed Afterdepolarization (DAD)
Caused by abnormal Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and digoxin