Chapter 13 Soils GEOL 215
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Soils definition
Unconsolidated surficial deposits produced indirectly or directly by weathering processes and capable of supporting plant life
Residual soils
direct weathering of bedrock
Transported soils
erosion and redeposition
Humus
Partially decayed organic matter
Loam
soils that contain equal proportional parts of sand and silt and low amounts of clay
Soil formation factors
Geology (bedrock)
Climate (T and Moisture)
Organisms (topsoil, aeration, structure, nutrient)
Relief (controls thickness)
Time
Time
C horizon decreases as weathered away, organic matter increases, B horizon increases as C decreases
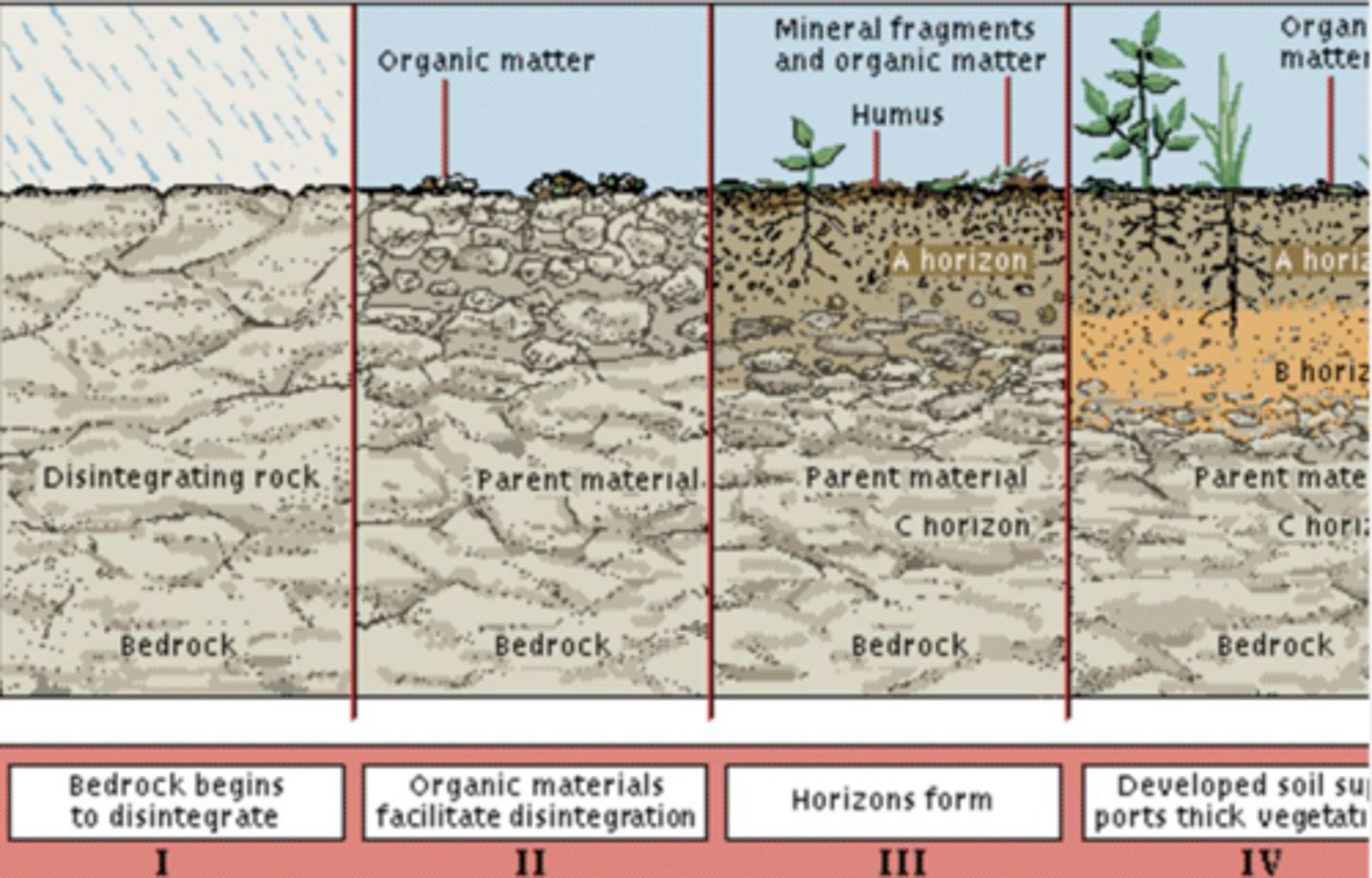
Weathering factors in soils
Jointing
Climate (precip, T, freeze-thaw)
Sun exposure
Vegetation (breakup)
Disaggregation
breaking of rock with no chemical alterations
Disintegration
decomposition of primary minerals comprising the rock forming secondary minerals more stable at surface
Pedon
Hexagonal column profile of soil from soil to bedrock. polypedon, multiple
O-horizon
Very top layer; darkly colored, humus, organic, plant material
A-horizon
2nd layer but technically first, top soil; Mineral material, zone of leaching where dissolution, cation exchange, and fluid percolation occurs that removes ions
E-horizon
3rd layer; Lightly colored, Zone of leaching, leaching of Fe, rich in resistant minerals like quartz, zone of eluviation
Leaching
Removal of dissolved substances
Eluviation
removal of both dissolved and suspended materials like clay and iron oxides and nutrients
illuviation
Where Salts, Fe, clay, minerals are percolated and deposited
B-horizon
4th layer; Reddish in color, Zone of accumulation, enriched from constituents leached from A-horizon, illuviation, carbon precipitation common in arid env
B-horizon precipitates
Carbon in arid env
Silcrete and gypsum common
C-horizon
5th layer; Soil mantle, bedrock, regolith, moderately, minimally weathered materials, not significantly enriched
Horizon development ideal conditions
presence of vegetation
precipitation
absence of erosion
No disturbances
Soil taxonomy classification properties
Soil horizons
Nutrient chemicals
Distribution of organic materials
Soil color
Overall climate
Oxisols
Where: S. America and S. Africa
Color: Reddish (iron) and Yellowish (Al Oxides)
Characteristics: Low CEC and Fertility b/c eluviation of material
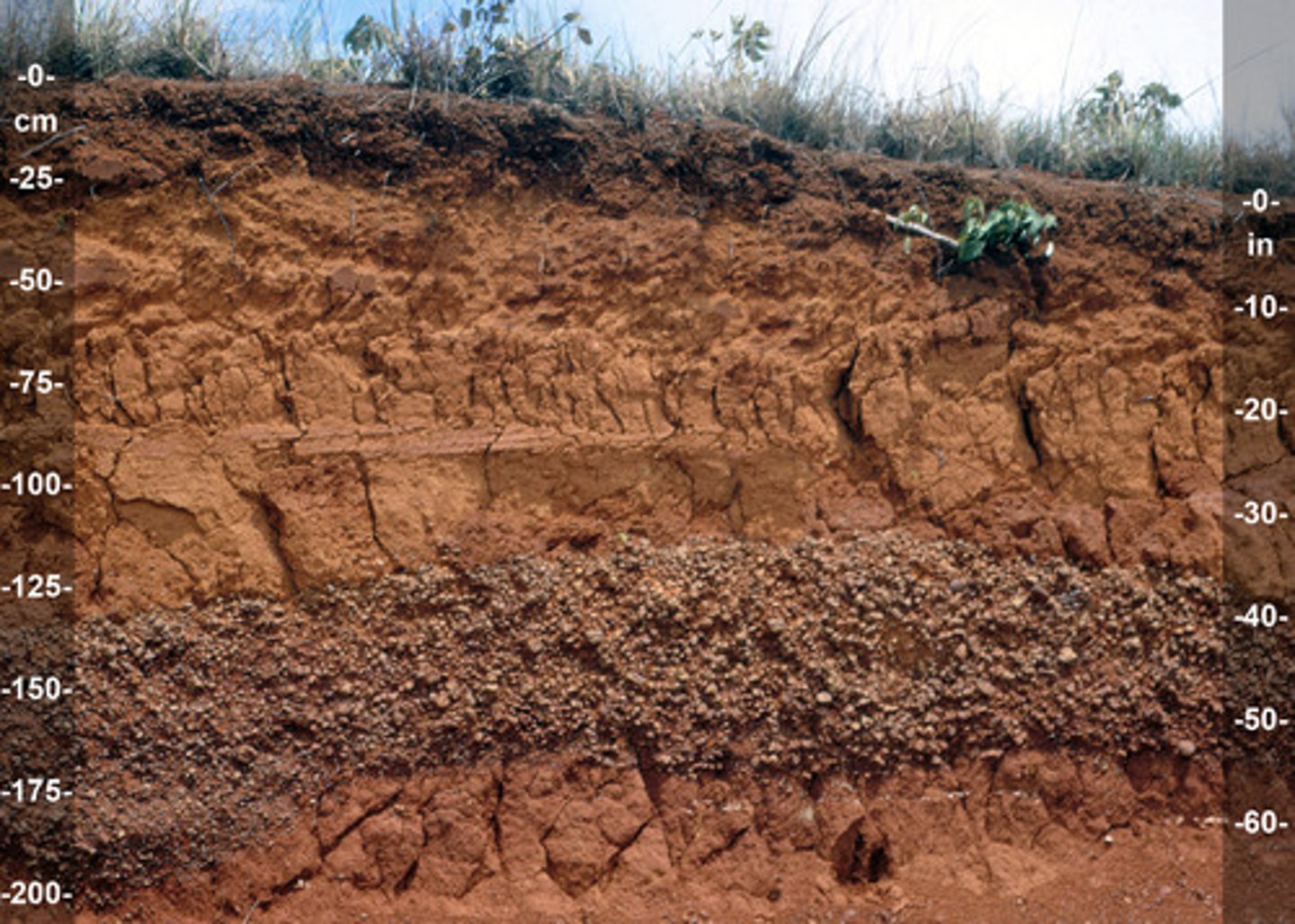

Aridisols
Where: W. Americas and Australia. Arid
Characteristics: shallow horizons, lacks O, salinization high POTET, Calcification
Mollisols
Where: Middle U.S. (great plains) and Middle Eurasia ("fertile triangle" of Russia-ukraine region)
Characteristics: Grasslands, dark organic later, high CEC, high fertility
Alfisols
Where: Widespread, SE Australia, Europe
Color: Grayish brown to reddish
Characteristics: CEC adequate, fertile with enough moisture and T, mostly under forests and mixed vegetation
Engineering Grain size
DIFFERENT than Wentworth-Udden (WU) scale that we use, dependent on mechanical properties, are a bit larger than WU
Strong soils
Resistant to stress, excellent for building
Weak soils
subject to compression, collapse, flow when stressed
Soil sensitivity
measure of tendency of soils to change
Atterberg limits
measure of Effect of water. It's shrinkage limit, plastic limit, liquid limit. 4 classes
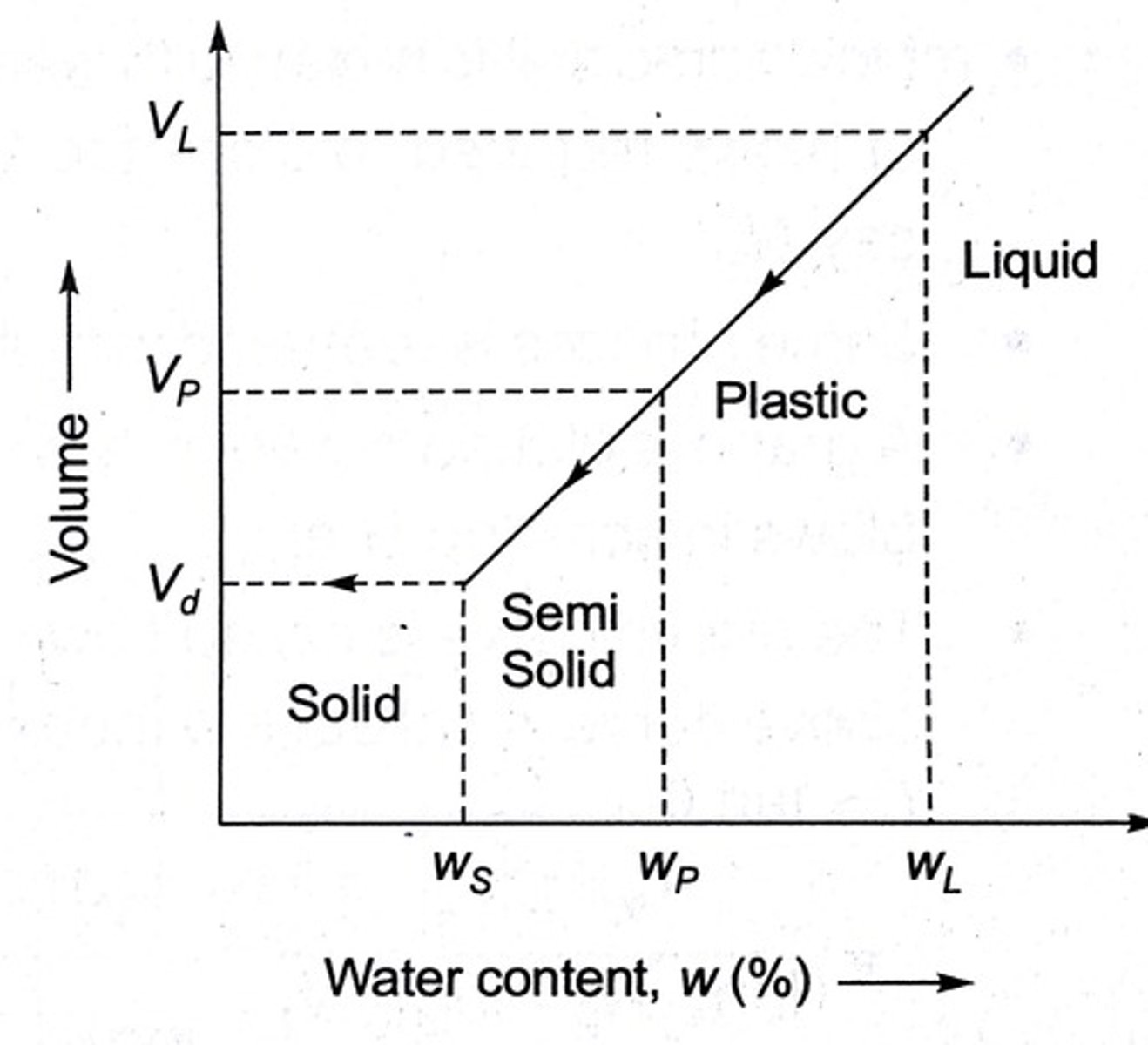
Shrinkage limit (SL)
boundary btw brittle solids and semi-solids. Below SL, soils don't shrink bc no moisture
Plastic Limit (PL)
Boundary that separates semi-solid and plastic soils. Plasticity is Measure of cohesiveness
Liquid Limit (LL)
Separates plastic soils from liquid soils. Water content makes soil lose shear strength, liquefaction
Plasticity Index (PI)
Range of water contents over which the soil behaves as a plastic substance, is the difference between LL and PL
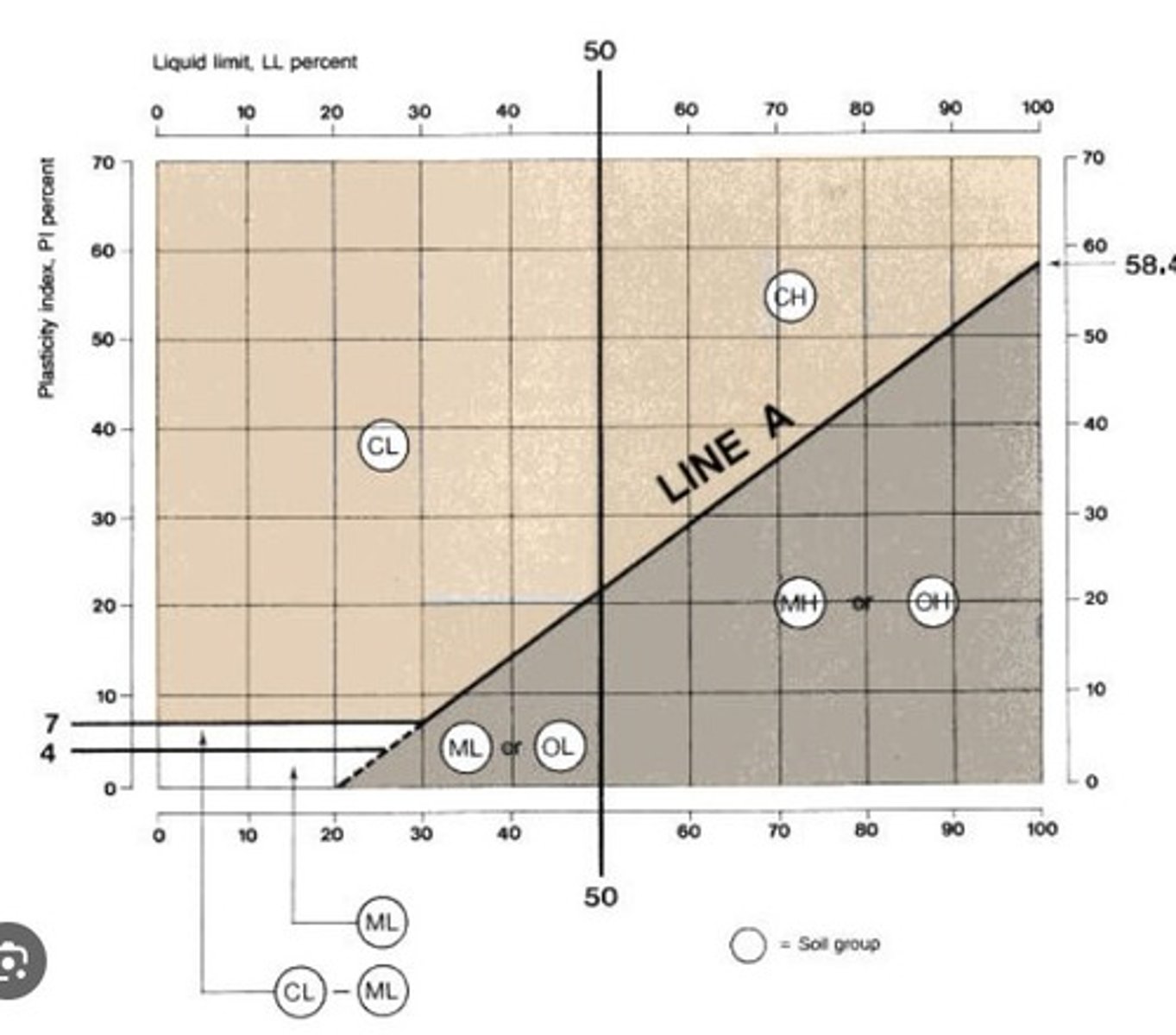
Casagrande diagrams
Plasticity vs LL.
Silt-rich: low plasticity, low LL
illite/smectite: very high plasticity and LL
Compressibility
tendency of soils to consolidate and lose volume. Only a problem when differential compaction occurs
Paleosols
Old soils. May be altered during diagenesis or truncated by erosion. Alteration may remove O, oxidize Fe, Dehydrate limonite to hematite