SME - Transverse & Longitudinal waves
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Define wavelength.
Wavelength (m) is the distance between a point on a wave and the same point on the next cycle of the wave, e.g. two crests, or two troughs
What is meant by the Amplitude of a wave?
Amplitude (m) is the magnitude of the maximum displacement reached by an oscillation in the wave.
What does the Period (T) represent in a wave?
Period T (s) is the time taken for one complete oscillation at one point on the wave
Define Frequency.
Frequency (Hz) is the number of complete wave cycles per second.
What is meant by the wave speed of a wave?
Wave speed (m s-^1) is the rate of movement of the wave.
Describe the relationship between wavelength & frequency in the wave equation.
Wave equation is v= fλ.
Wavelength Increases, frequency decreases.
Wavelength decreases, frequency increases.
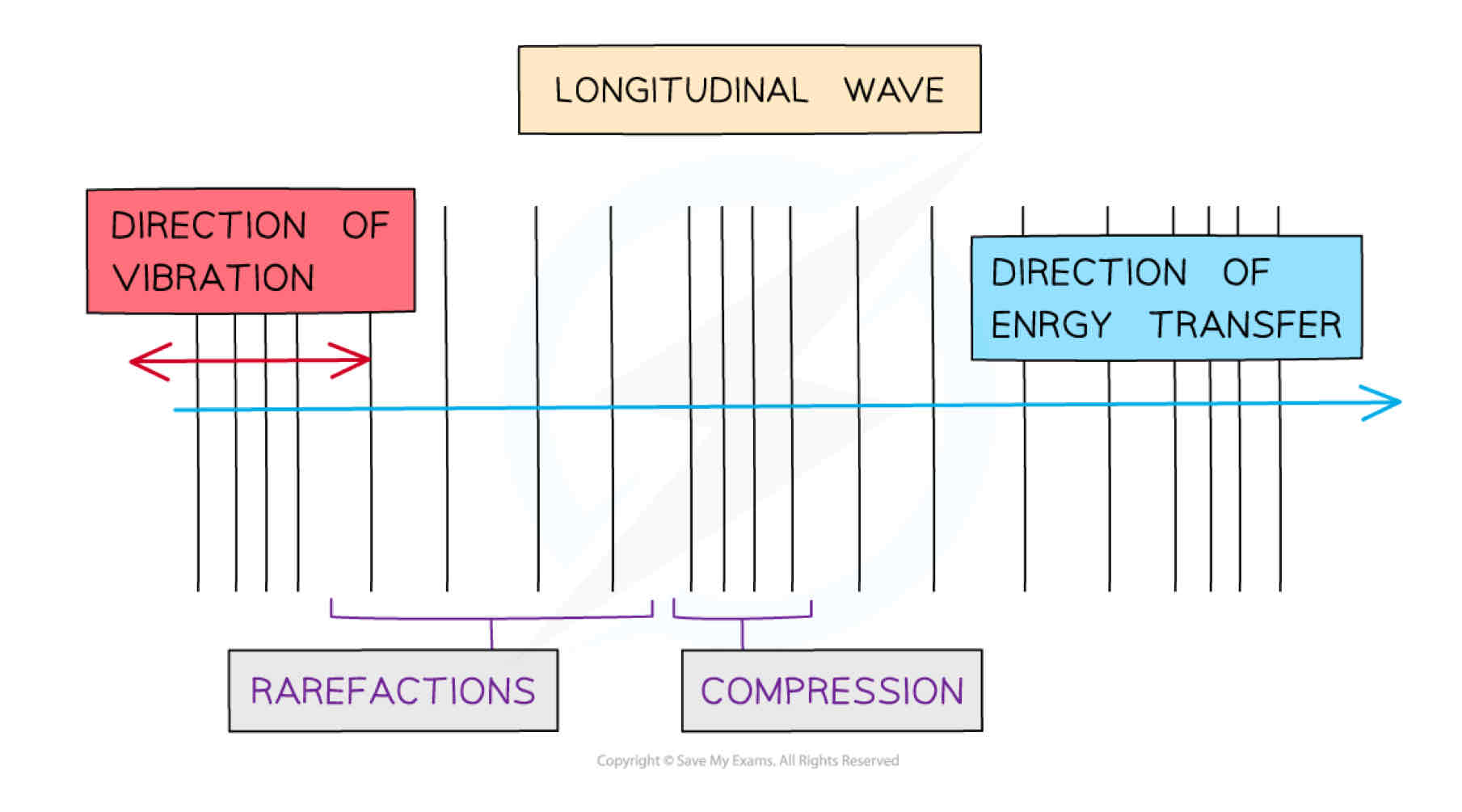
Define longitudinal waves.
Longitudinal wave is one where the particles oscillate parallel to the:
Propagation of the wave
Direction of energy transfer
What do longitudinal waves show?
Longitudinal waves show areas of:
High pressure, called compressions
Low pressure, called rarefactions
What is a transverse wave?
A transverse wave is one where the particles oscillate perpendicular to the direction of the:
Propagation of the wave
Direction of energy transfer
What do transverse waves show?
Transverse waves show areas of crests (peaks) and troughs.
Give examples of longitudinal waves.
Examples of longitudinal waves are:
Sound waves
Ultrasound waves
P-waves caused by earthquakes
Give examples of transverse waves.
Examples of transverse waves are:
Electromagnetic waves e.g. radio, visible light, UV
Vibrations on a guitar string
Waves on a rope or slinky
When do stationary waves occur?
When a wave is reflected with a 180° phase difference, creating a wave with a series of nodes and antinodes.