Motivational Theories
1/30
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is Motivation?
The intrinsic factors within an individual that arouse, maintain and channel behaviour towards a goal.
What are the Benefits of Motivated Staff?
Increased Productivity
Increased Quality
Reduced Staff Turnover
Improved Communication
Innovation
Job Satisfaction
Improved brand image
What was Taylor's Motivational Theory?
Employees are solely money motivated
Close Supervision
Piece-rate Pay
Specialised training for simple tasks
What are the Problems with Taylor's Theory?
Best way doesn't suit individual needs
Money isn't only motivator
High Labour Turnover
Piece rate only suitable for quantitative jobs
Taylor's Theory Usage
Leadership: Autocratic, Theory X Skill Level: Low & Money Motivated Financial Motivation Short Term
What was Mayo's Motivational Theory?
Social aspect of work is vital
Advocator of Team Working
Group Relationship/ Morale
How can Mayo's Theory be implemented?
Social/ sporting facilities provided
Work outings & trips
Team Working
Staff rooms/ Break Areas
What are the Problems with Mayo's Theory?
Assumes workers and managers have same goal
Increased knowledge through communication can cause problems
May lead to trade union power reduced
Mayo's Theory Useage
Leadership: Democratic, Theory Y Skill Level: High, Creative roles Non-financial Motivator Long Term solution
What was Maslow's Motivational Theory?
People have a hierarchy of needs and we wish to attain the highest level of the hierarchy however to meet this all below must be met first.
What is Maslow's hierarchy of needs?
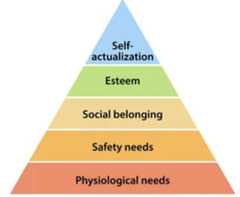
How can an Employer satisfy Physiological Needs?
Minimum Wage
Shelter
Water/ Food
Clothes
How can an Employer satisfy Safety Needs?
Job Security
Maternity/ Paternity Leave
Well-built premises
Fire Exits
How can an Employer meet Social Needs?
Teamwork
Social Events
Staff Rooms
How can an Employer satisfy Esteem Needs?
High/ Competitive Pay
Mutual Respect
Good Management
Bonuses
Promotion
Praise
How can an Employer satisfy Self-Actualisation?
Charity Work
Share of Responsibility
Empowerment
What are the Advantages of Maslow's Theory?
Practical Implications
Encourages utilisation of employers abilities
Identifies several solutions to motivation due to separate levels
What are the Disadvantages of Maslow's Theory?
Assumes once level is achieved, motivation stops
Some needs may be fulfilled outside of workplace
Difficult to assess and implement for each individual
What was Herzberg's Theory?
Two factors affect motivation, hygiene and motivational
Hygiene factors do not motivate but necessary
Both simultaneously
Aim for employees to have minimum dissatisfaction and maximum motivation
Herbert's Theory Uses
Leadership: Democratic, Theory Y Skill Level: Applied to any individual Both Financial and Non-Financial Long Term solution
What are Hygiene Factors?
Company Policies
Working Conditions
Fair Pay
Status
Job Security
What are Motivators?
Personal Achievement of goals/ targets
Recognition for achievement
Interest in work
Responsibility and more complex duties
Personal Growth and advancement
What are the Advantages of Herzberg's Theory?
Many factors considered
Useful/ practical methods
What are the Disadvantages of Herzberg's Theory?
Costly and time consuming
Pay could still contribute to motivation
What was Vroom's Theory?
Maximise happiness and minimise unhappiness
Performance based in individual factors
Positive correlation between efforts and performance
Favourable performance will result in desirable reward
Reward must satisfy and be worthwhile
What is Valence?
When a task is undertook because they believe the reward is worthwhile and has value.
What is Expectancy?
When employees expectations about their capability are in like with targets making them achievable in return oh a valent reward.
What is Instrumentality?
The employees perception of if rewards are actually going to be fulfilled by the manager
What was Porter and Lawler's Theory?
Rewards are intrinsic (internal) or extrinsic (external)
Intrinsic Rewards
Satisfaction, Enjoyment
Extrinsic Rewards
Pay Rise, Bonus, Time-off, Benefits