carina market failure
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
market failure definition
the failure of the market to allocate resoucres efficiently. market failure results in allocative inefficiency - where too much or too little of a good/service are produced or consumed from the view of society
externality definition
when the actions of producers or consumers give rise to negative or positive side effects on those not involved in that action
Marginal Private Cost (MPC) definition
the costs to producers for producing one more unit of a good
Marginal Social Cost (MSC) definition
the cost to society for producing one more unit of a good
Marginal Private Benefit (MPB) definition
the benefits to consumers for consuming one more unit of a good
Marginal Social Benefit (MSB) definition
the benefits to society for consuming one more unit of a good
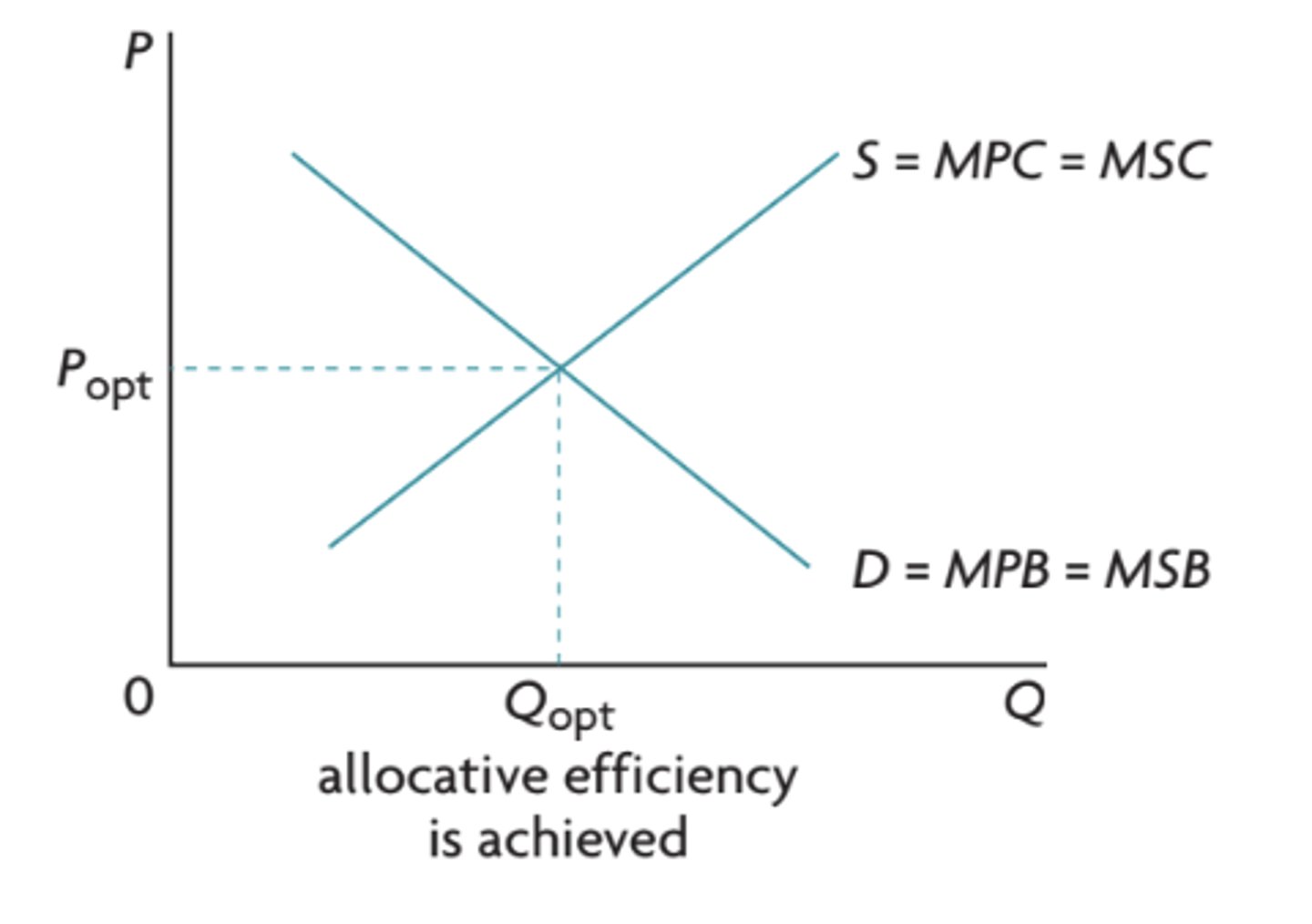
when is allocative efficiency achieved?
MSB=MSC
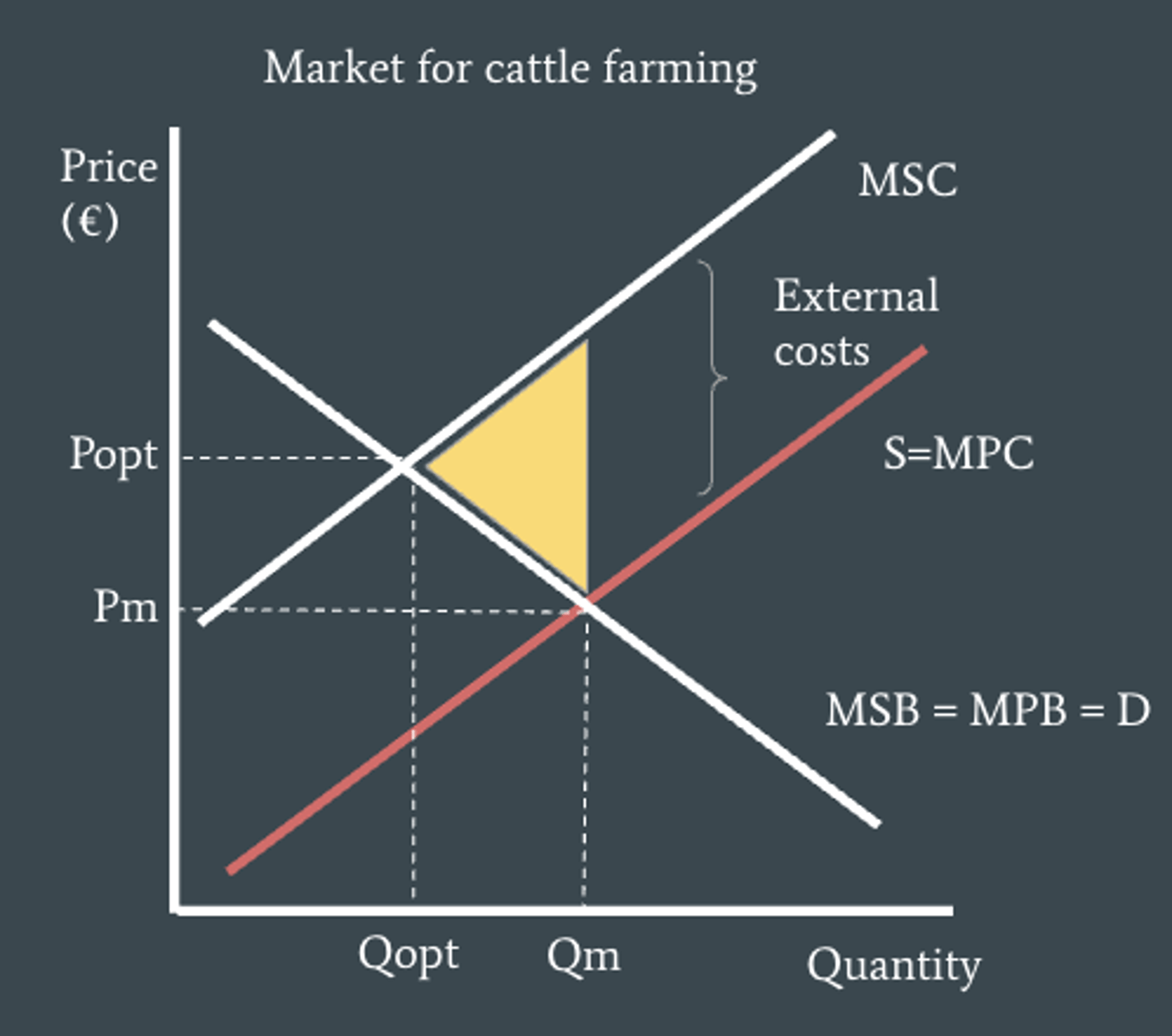
Negative externalities of production definition
the external costs created by producers
what does a negative externality of production diagram look like?
has two supply curves - one MSC (at the top) and one S=MPC
has one demand curve (D=MSB=MPB)
Popt is when MSC meets MSB
Pm is when S=MPC meets D=MPB=MSB
tradable permits definition
a market based policy in which a governmental body sets an amount of permits that can be bought and sold by polluters
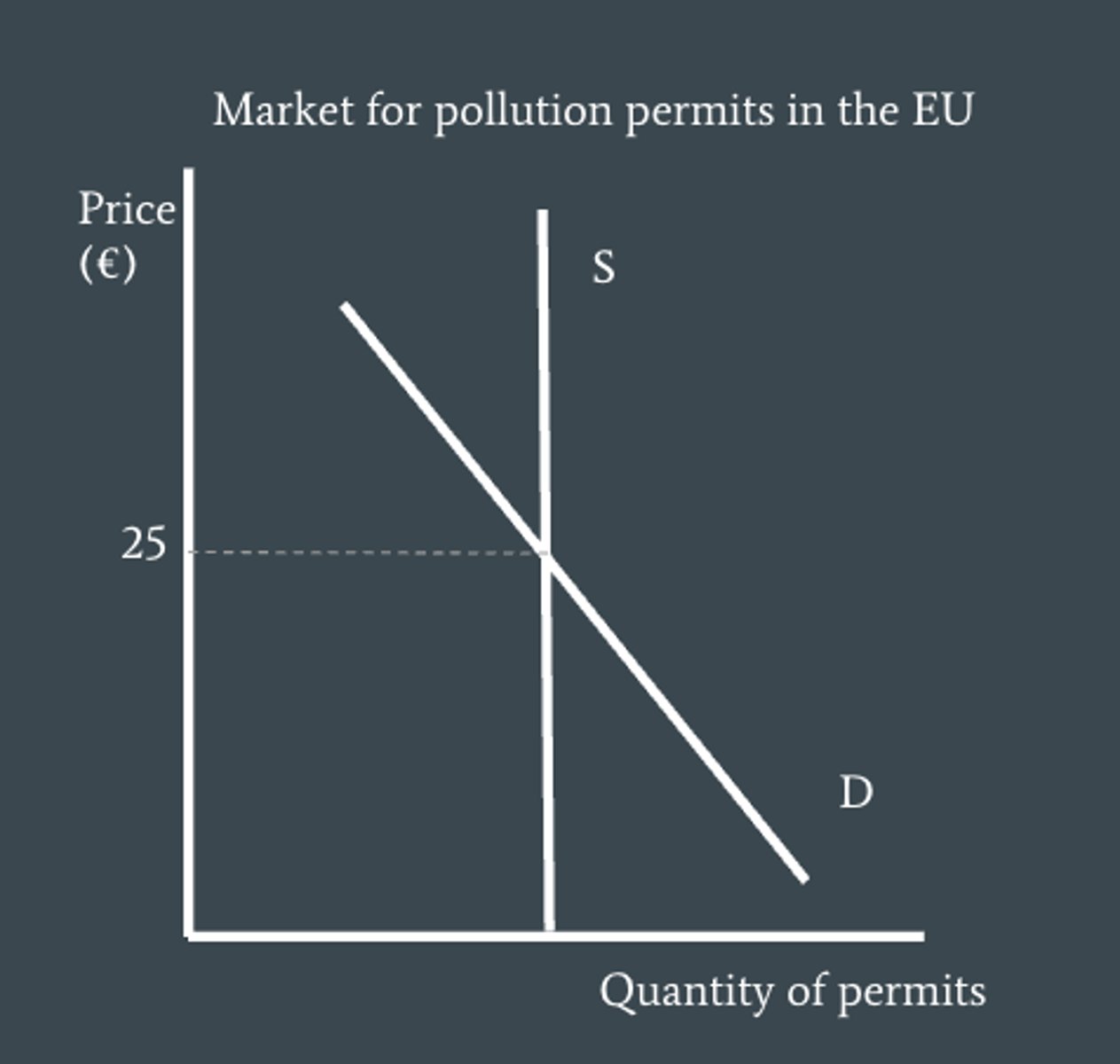
what are the additional costs of the permits intended to account for?
for the external costs created by the firms of pollution
what happens if polluters use fewer than they permits they need?
they have the ability to sell them off to firms who need more
what is the intention of the governmental body in regards to tradable permits?
that they reduce the amount of tradable permits on the market from year to year which should increase the price of each permit, ceteris paribus
regulation definition
rule on the production or consumption of a good/service. regulations do not allow for the externality to be internalized.
negative externalities of consumption definition
the external costs created by consumers
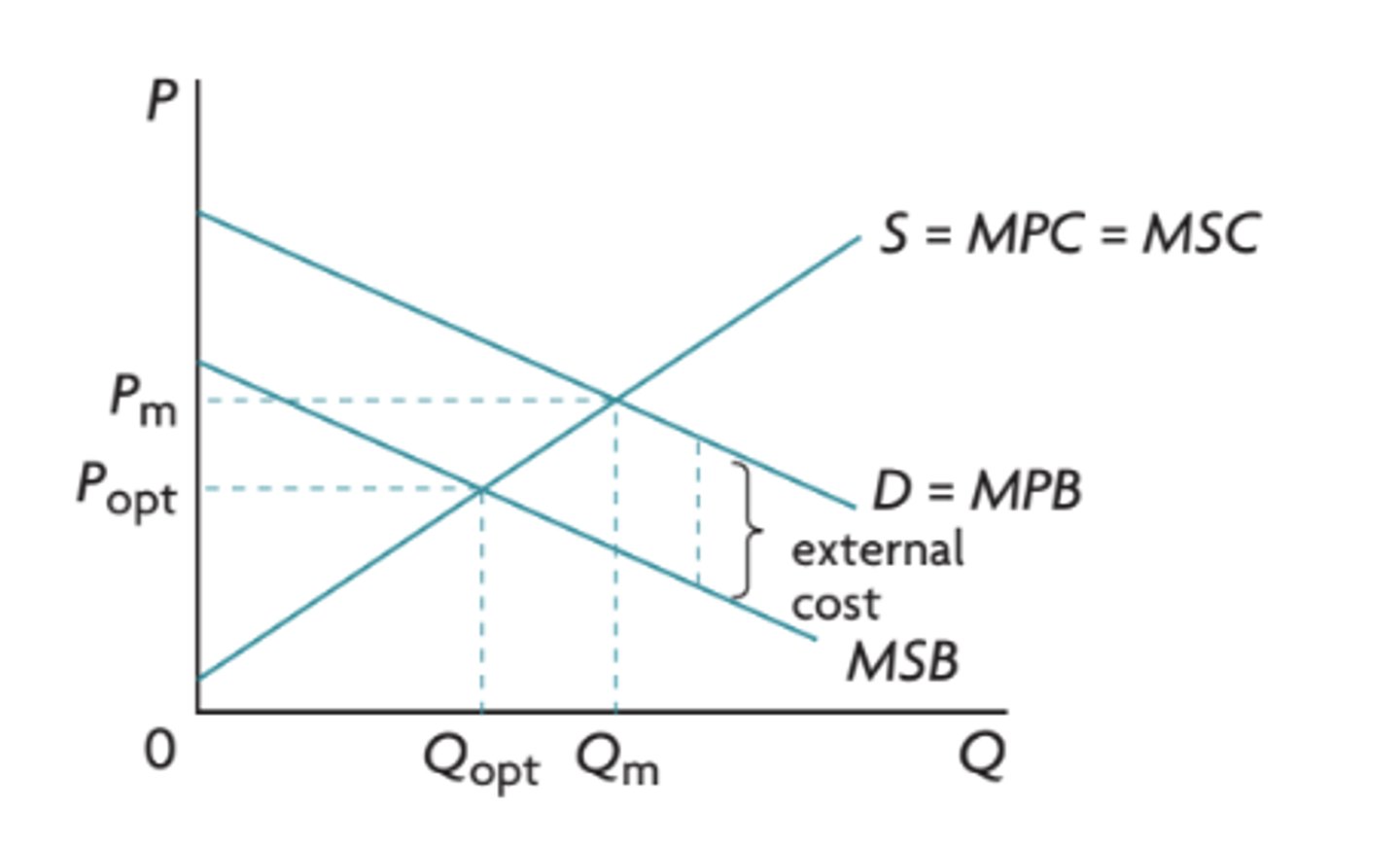
example of negative externality of consumption
when people smoke cigarettes the second-hand smoke can lead to others getting sick and if the smokers themselves get sick they create additional costs for the healthcare system.
what causes the market demand to be greater than what would be optimal for society?
the personal benefit that smokers receive from enjoying their habit is greater than the benefit society receives
what could be the reason behind the overconsumption of cigarrettes?
due to consumers being ignorant about the negative side effects
Demerit goods definition
Goods that have harmful effects on the consumer and create spillover costs for society. All demerit goods create negative externalities of consumptions but not all negative externalities of consumption are demerit goods.
positive externalities of production e
positive externalities of production definition
the external benefits created by producers
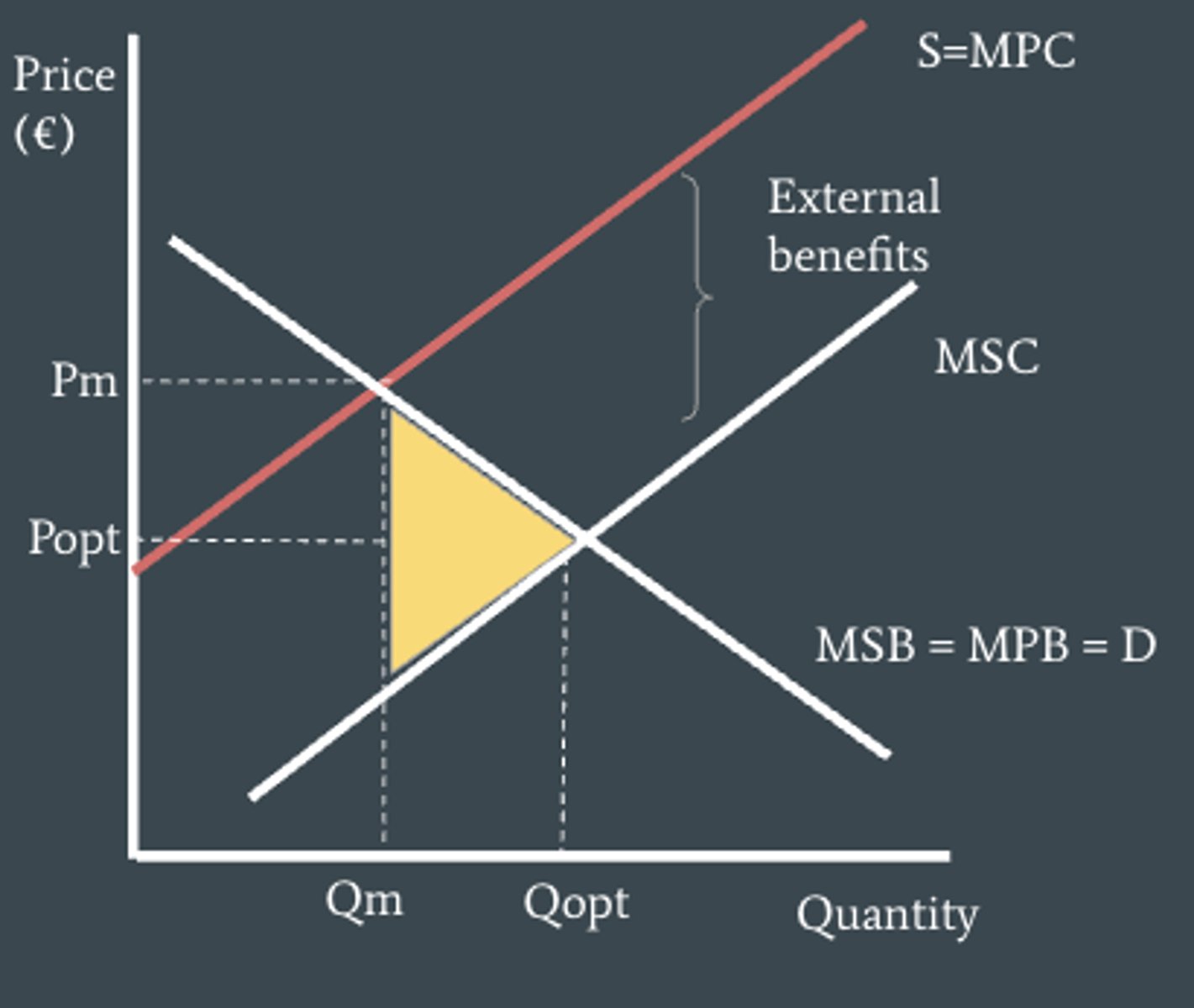
example of a positive production externality
if a firm were to engage in research and development and developed and new technology that spread to other parts of the economy this would create positive spillover benefits
positive externality of consumption definition
external benefits that are created by consumers
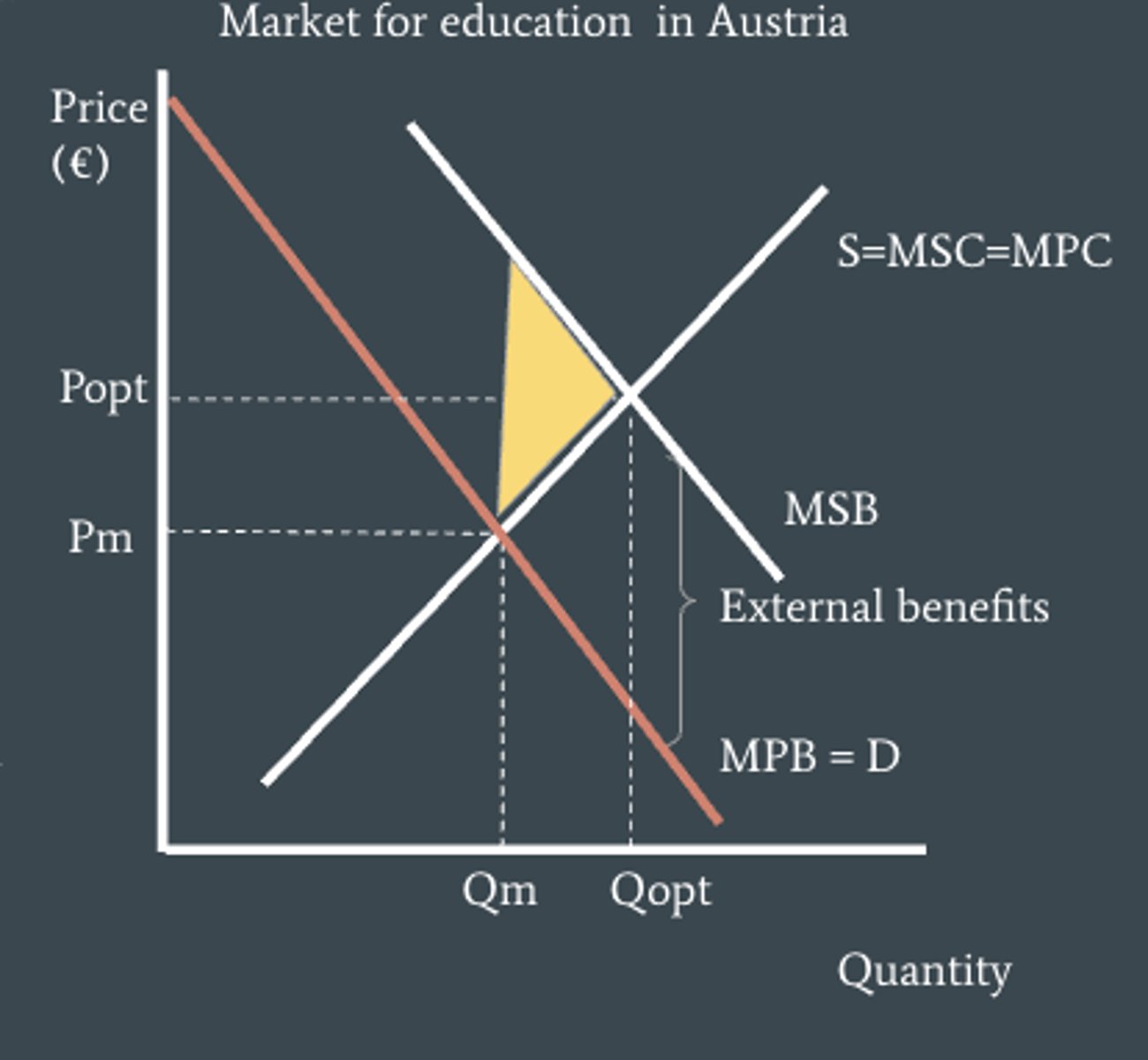
example of a positive consumption externality
getting an education create external benefits for society. A more educated society is likely to be more productive, have higher paying jobs and pay more in taxes as a result.
why would there be an underconsumption of education?
due to consumer ignorance of the positive benefits or from the inability for consumers to afford the good, despite its positive benefits
merit goods definition
goods/services that are beneficial for consumers and create spillover effects for society
pubic good definition
are subject to the free rider problem
which two requirements must a public good meet?
1 - non-rivalrous: the consumption by one person does not reduce consumption by someone else
2 - non-excludable: it is not possible to exclude someone from using the good
what is the free rider problem?
when people can enjoy the good/service without paying for it
goods that are excludable and rivalrous are___?
private goods - example= computers, phones, gasoline
goods that are excludable and non-rivalrous are ___?
quasi public goods - examples= museums, cable TV and public transportation
goods that are non-excludable and rivalrous are ___?
common pool resources - examples = rivers, lakes, fish in the ocean
goods that are non-excludable and non-rivalrous are ___?
public goods - examples= national defense, street lights, lighthouses
direct government provision definition
when the government fully funds public goods (that create positive externalities)
contracting out definition
when the government allows private firms to carry out an activity that they might have previously done themselves. This is paid for with public funds and has its own dis/advantages