Adaptations to environment
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
habitat
the place in which an organism, a community or a population lives
refers to the geographical location, the type of ecosystem and physical location
adaptations to abiotic environment
all organisms are adapted to their abiotic environment, seen clearly in plants that live in extreme habits e.g sand dunes and mangrove swamps
grass & sand dunes
has rhizomes (underground stems) that grow deep into the dune to obtain water
trees & mangrove swamps
swamps are flooded w/ seawater at high tide
as a result, trees have salt glands on leaves to secrete excess salt
cable roots grow close to the soil surface, where there is the most oxygen
species distribution and abiotic factors
distribution of a species (where it lives) can be limited by abiotic factors
factors affecting plant distribution:
temperature
availability of mineral nutrients
soil pH
factors affecting animal distribution
water availability
temperature
adaptations of a species give it ranges of tolerance
measuring ranges of tolerance of abiotic factors
if a species is unable to grow in an area because the level of a variable is outside the range of tolerance, that variable is a limiting factor
to measure this, transects are used:
measure the abiotic variable
using electronic sensors or data loggers
measure species distribution
number of individuals touching the transect are recorded
formation of coral reef
coral reefs can only develop where conditions are suitable for hard corals,
depth
less than 50 m, so light penetrates for zooxanthellae photosynthesis
pH
alkaline, so CaCO3 can be deposited in skeleton
salinity
between 32-42 parts per thousand of dissolved ions
clarity
clear water to allow light penetration
temperature
23-29 C so coral and zooxanthellae remain healthy
terrestrial biome distribution
with given combinations of abiotic factors (usually temp and rainfall), a particular time of ecosystem is likely to develop
all ecosystems of a specific type are biomes
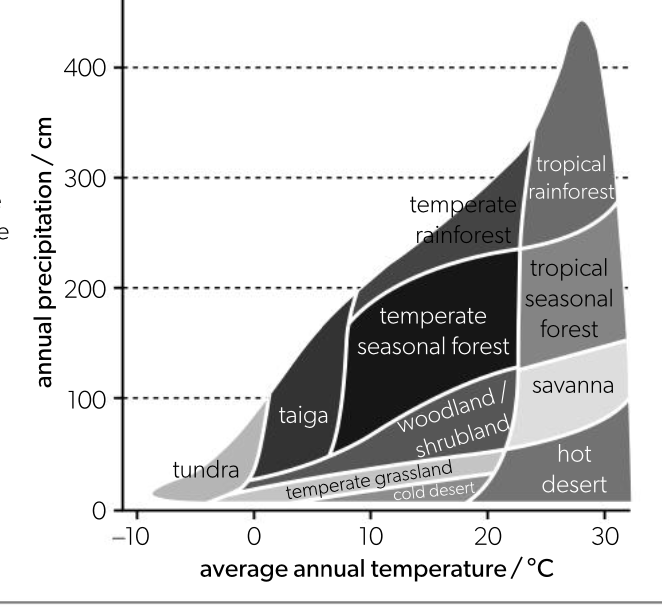
biomes
groups of ecosystems that resemble each other, due to similar communities because of similar abiotic conditions and convergent evolution
major biomes:
temperate forest
temperature moderate with cold winters and warm summers, medium rainfall
grassland
medium/high temp in summer, cold in water, moderate rainfall w/ a dry season
taiga (boreal forest)
low temps with short summers, medium/high rainfall
tundra
very low temps with very short summers, more snow than rainfall
adaptations to life in hot desert
hot desert
very high daytime temp and colder nights
little rainfall, long droughts,
very little soil development
adapted species: fennec fox
nocturnal so avoids high daytime temps
long thick hair for insulation in cold nights and hot days
pale coloured cot that reflects sunlight
longer loop of henle to reabsorb more water
adaptations to life in tropical rainforest
tropical rainforests have:
high light intensity
high temps
much rainfall
adapted species: yellow meranti tree
grows over 100 m tall to avoid competition for light
smooth trunk to shed rainwater rapidly
trunk thickened at base to support against shallow soil