Bio Midterm 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
1
New cards
What do paramecium have?
Self awareness; conscious choice
2
New cards
Invaginations
Indents in cells
3
New cards
Symbiosis
Two things living together; can be good or bad in biology
4
New cards
Endosymbiosis
Something taking another thing into its body (i.e. bacteria being engulfed by other cells and turned into organelles)
5
New cards
What does symbiogenesis mean?
Sym = same, bio = life, genesis = creation
* Same meaning as endosymbiosis
* Same meaning as endosymbiosis
6
New cards
Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic:
* older
* simpler, smaller
* no membrane-bound organelles
* flagella/fimbriae
* nucleiod region (no nucleus)
Eukaryotic:
* animal cells
* larger, more complex
* membrane-bound organelles
* nucleus
* older
* simpler, smaller
* no membrane-bound organelles
* flagella/fimbriae
* nucleiod region (no nucleus)
Eukaryotic:
* animal cells
* larger, more complex
* membrane-bound organelles
* nucleus
7
New cards
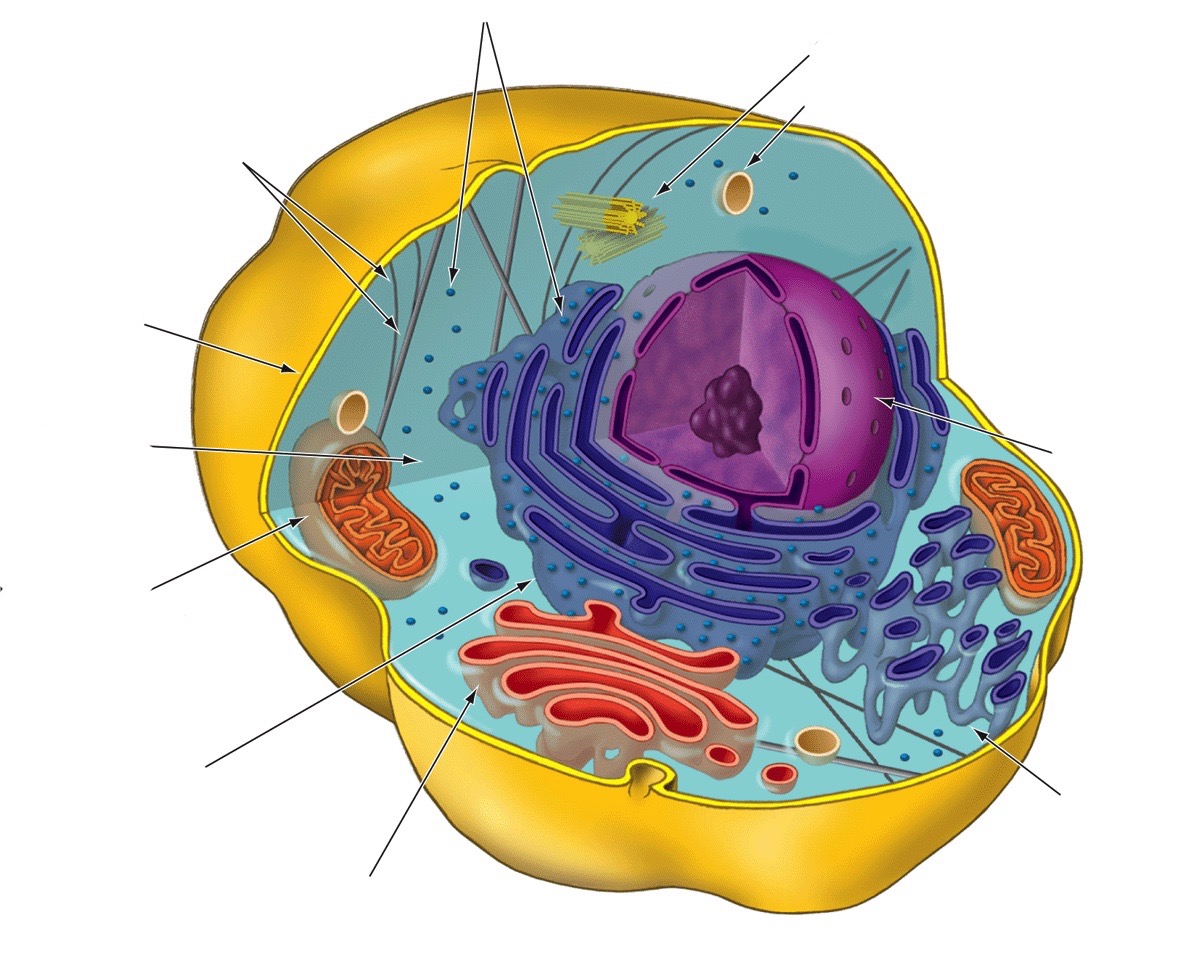
Ribosomes
Function: protein synthesis
8
New cards
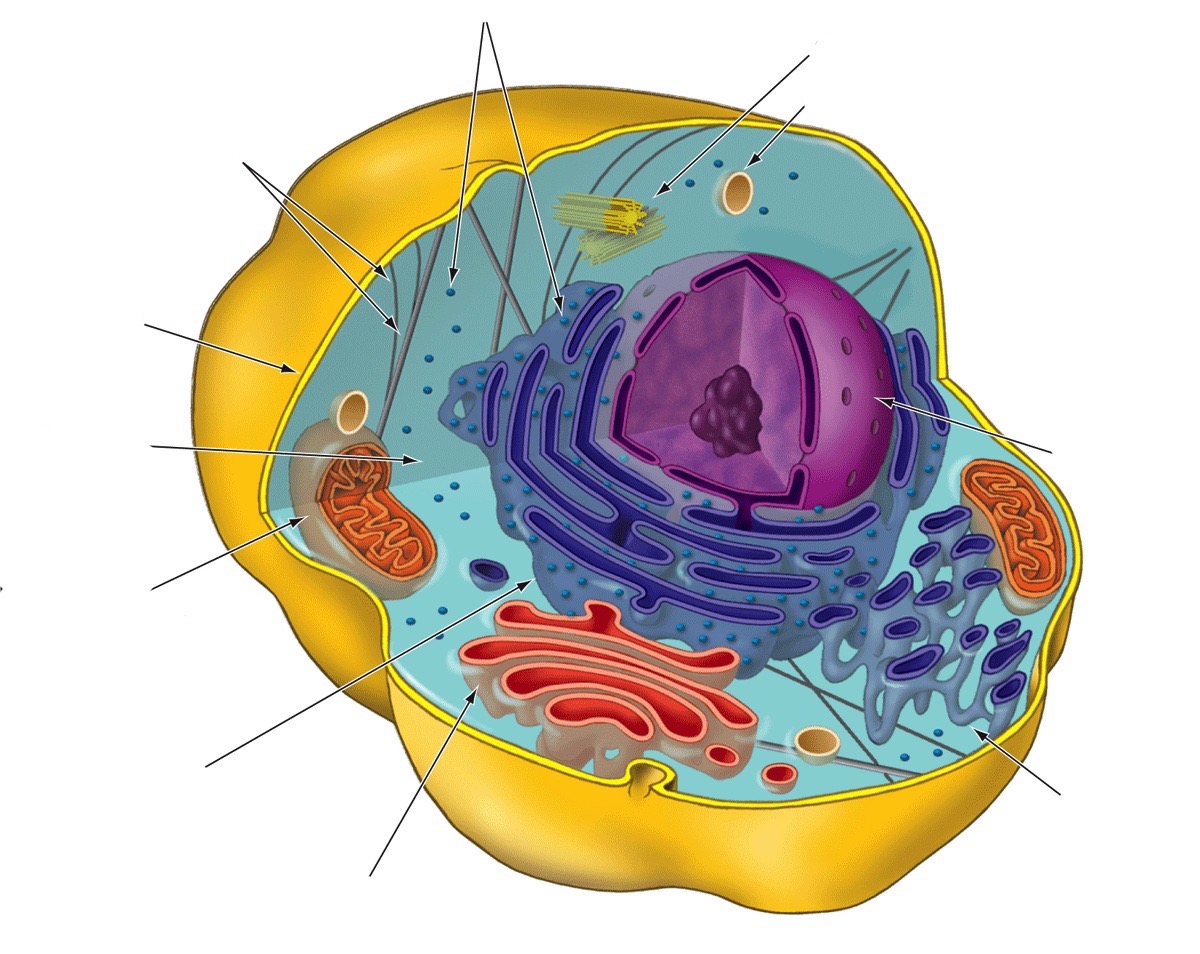
Cytoskeleton
Provides shape and structure
9
New cards
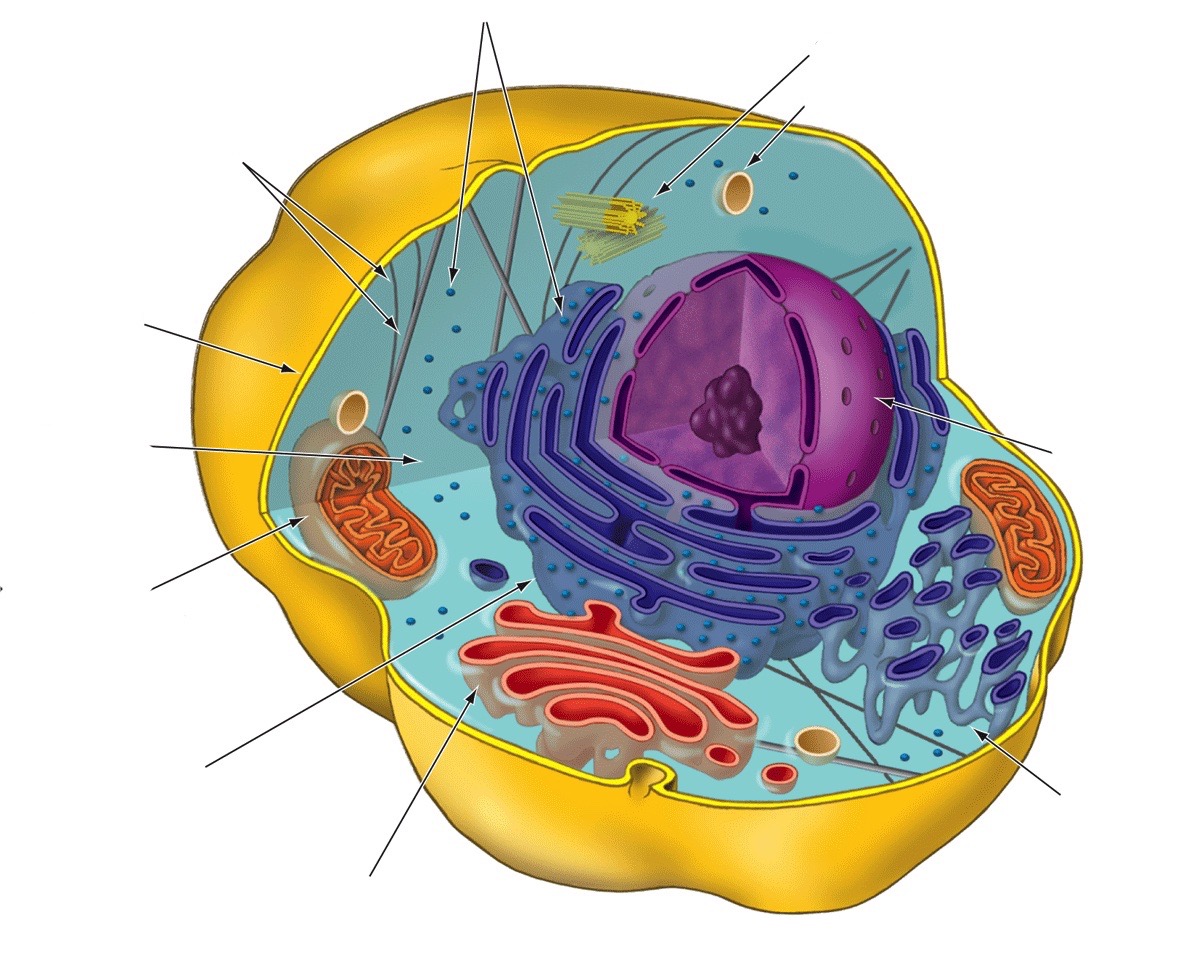
Plasma membrane
Thin film surrounding cells; border guard that regulates flow of materials into and out of the cell
10
New cards
Plasma membrane’s structure
Phospholipid bilayer: contains phospholipids with a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail (tails connect while the heads are inside and outside of the cell) with proteins embedded in it
11
New cards
Hydrophilic
Polar (likes water)
12
New cards
Hydrophobic
Non-polar (doesn’t like water)
13
New cards
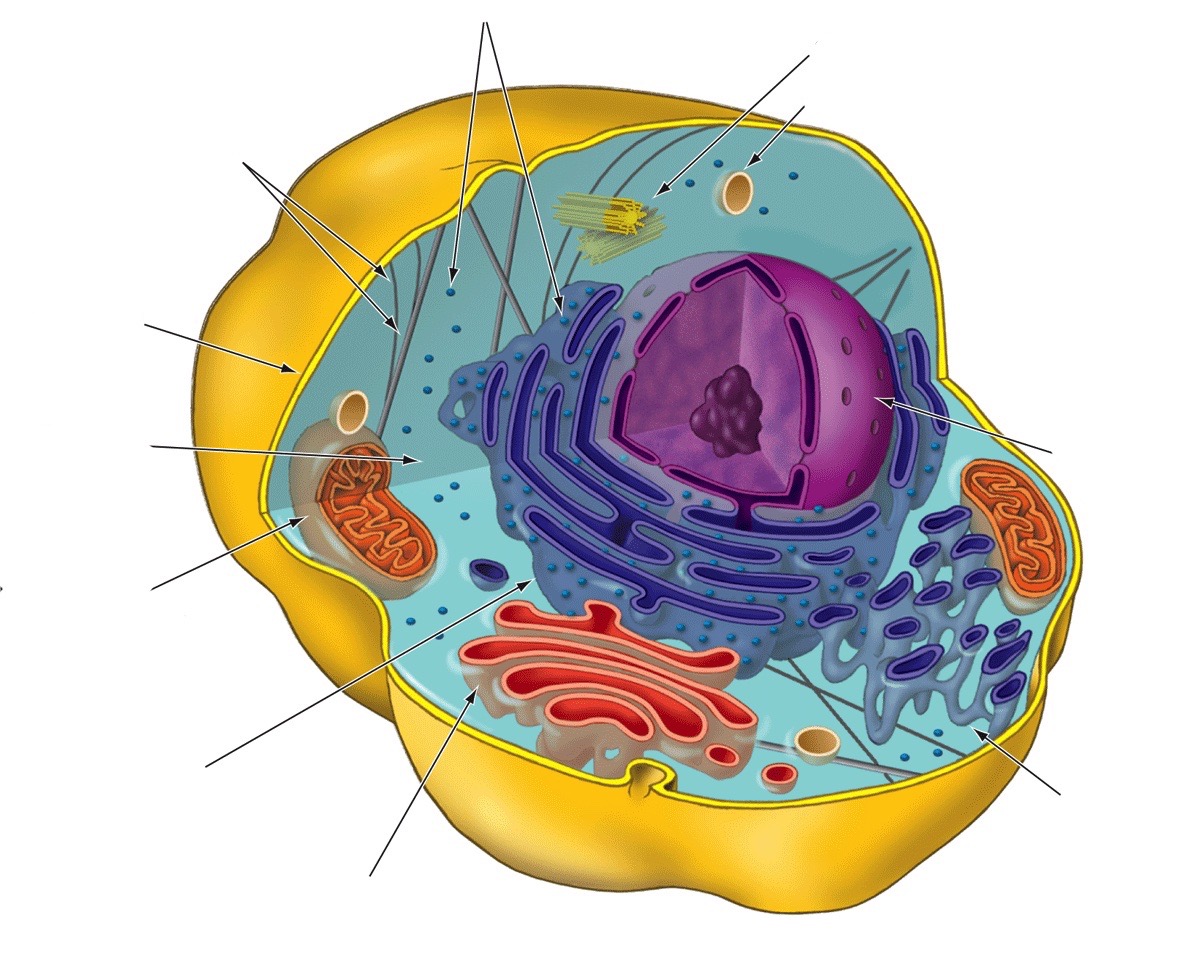
Cytoplasm
Gel-like fluid inside the cell
14
New cards
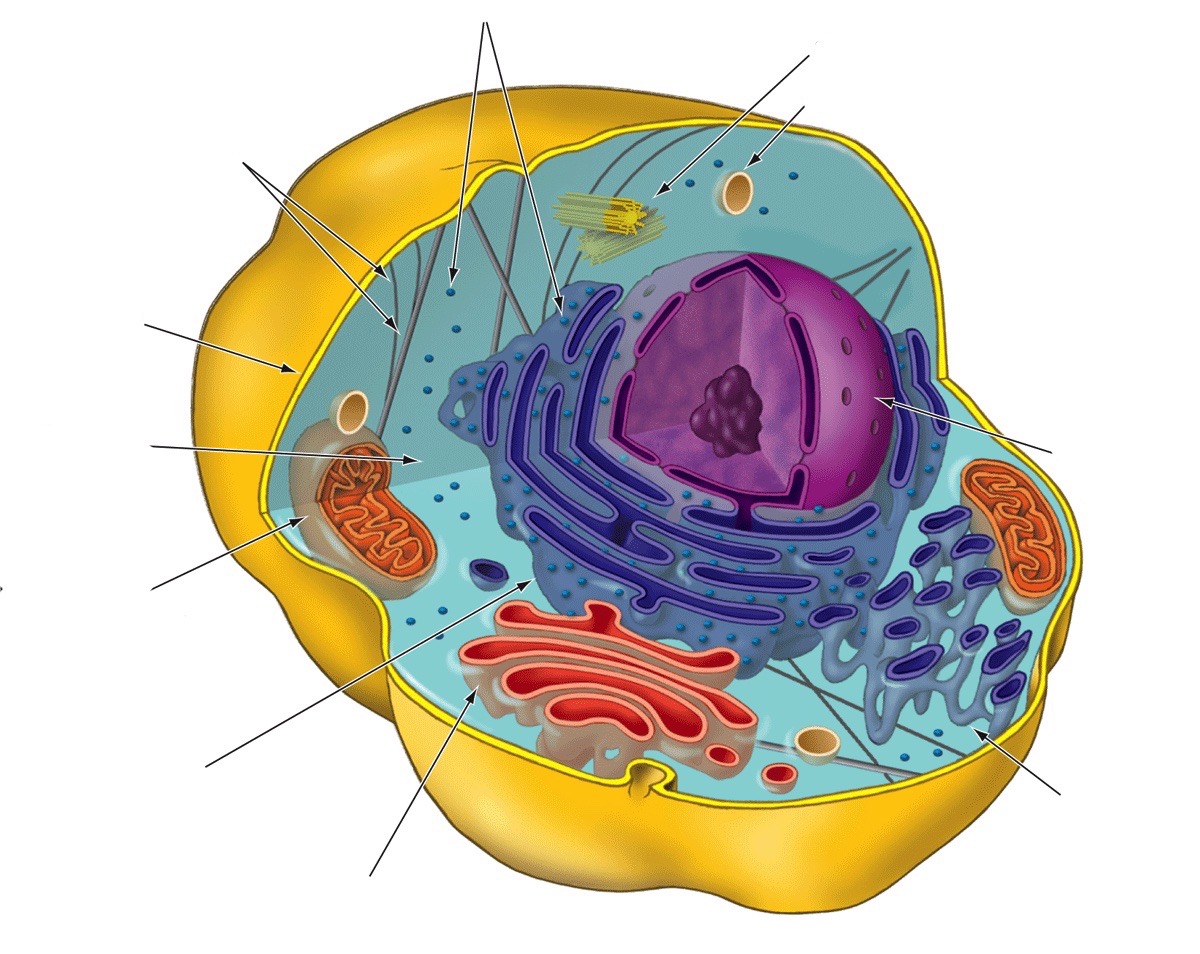
Mitochondria
Cellular respiration; generates chemical energy needed to fuel the cell’s biochemical reactions
* inner/outer membrane
* Cristae
* Matrix
* inner/outer membrane
* Cristae
* Matrix
15
New cards
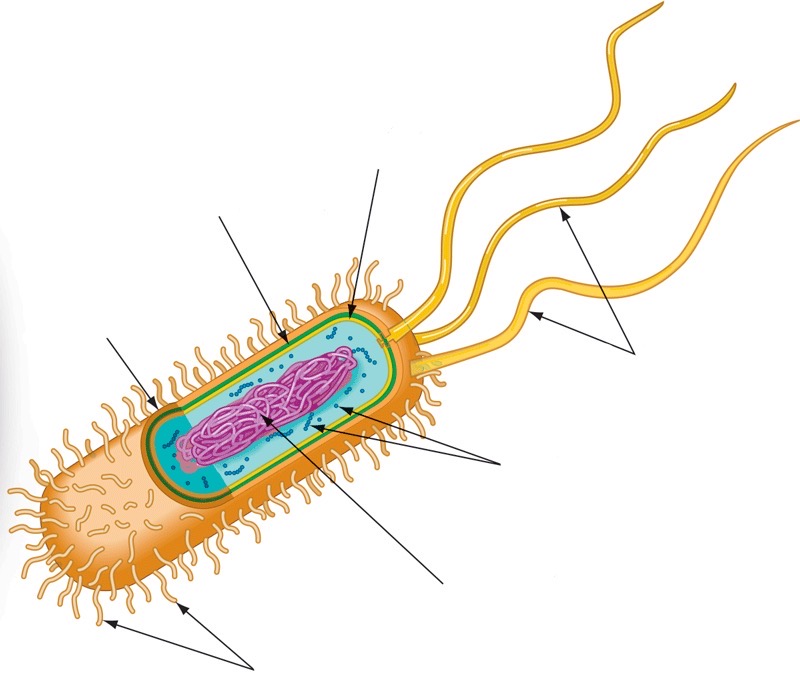
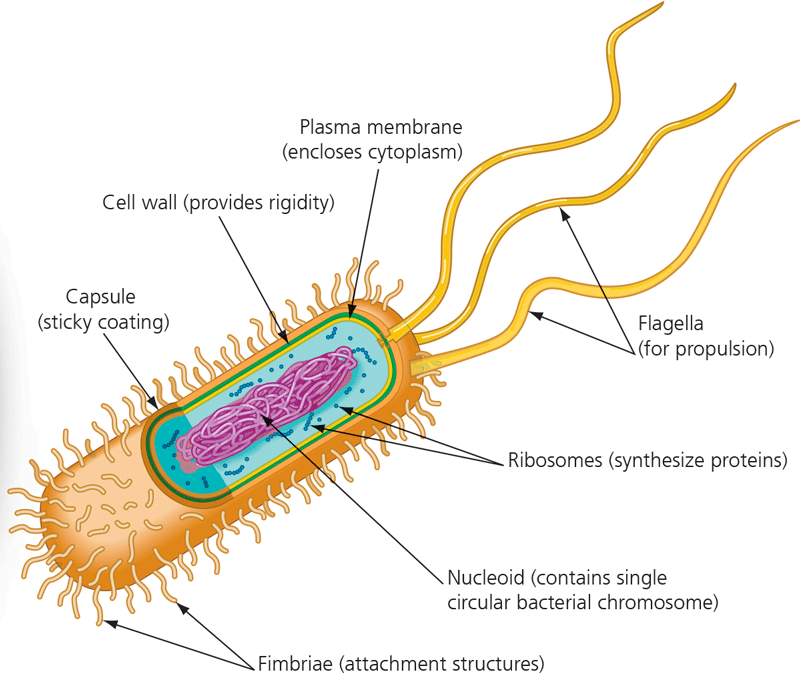
Prokaryotic cell wall
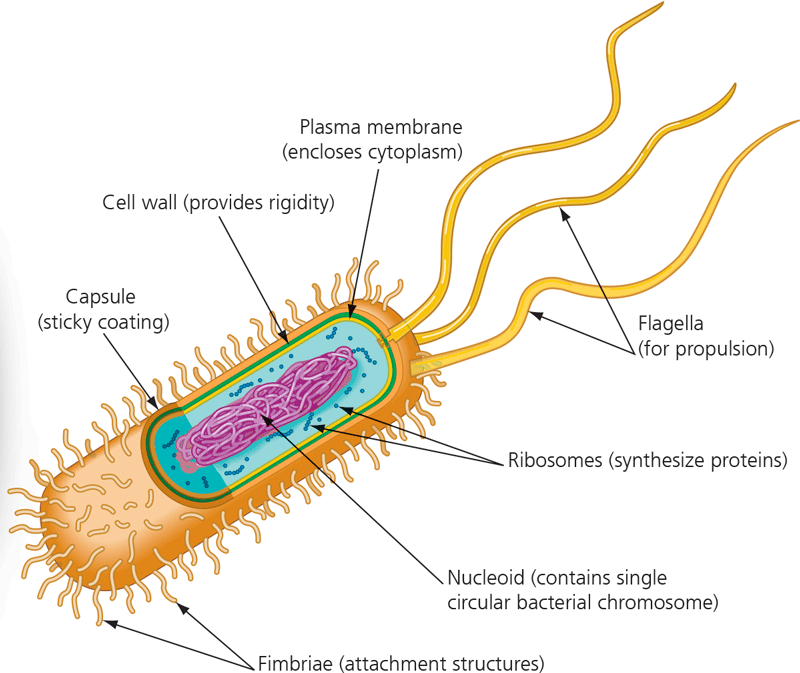
16
New cards
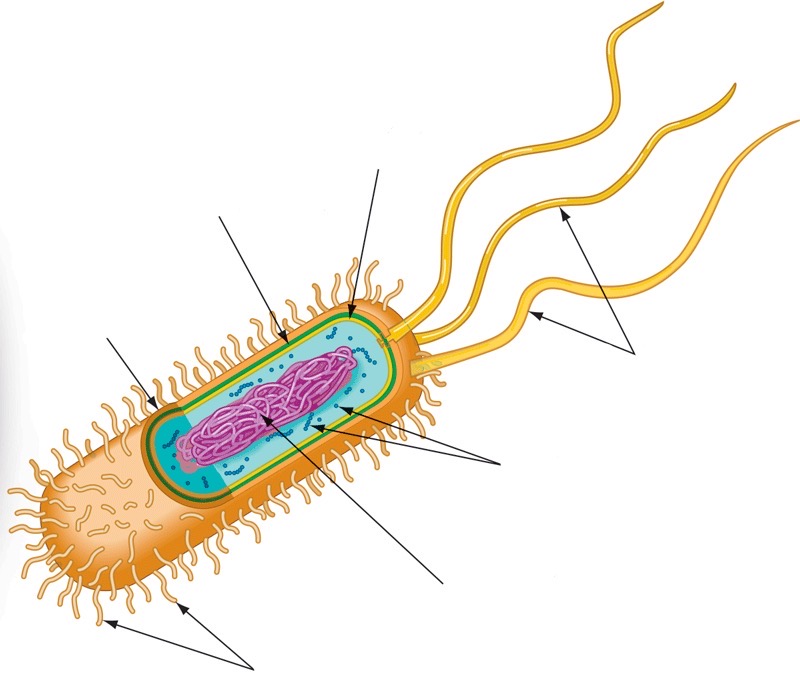
Capsule
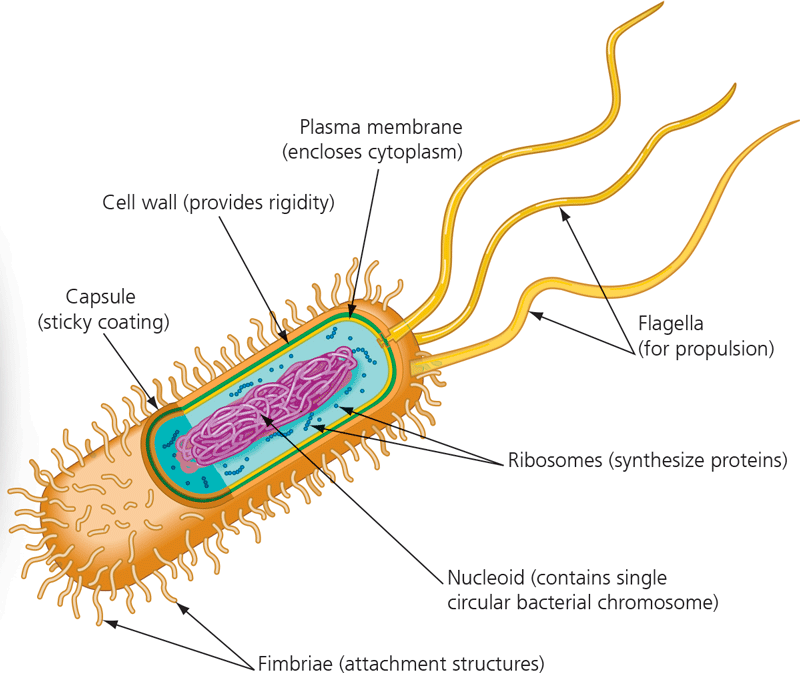
17
New cards
Fimbriae
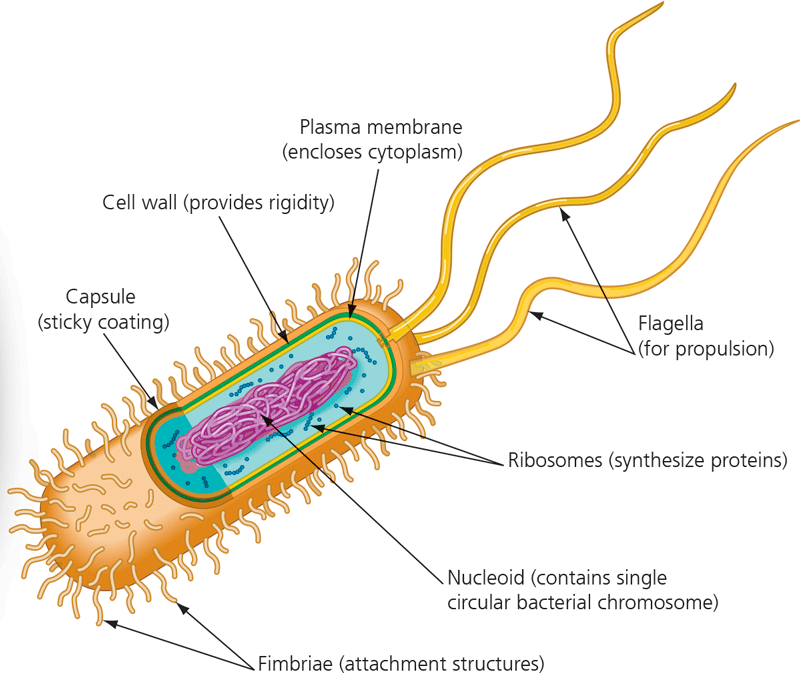
18
New cards
Nucleoid
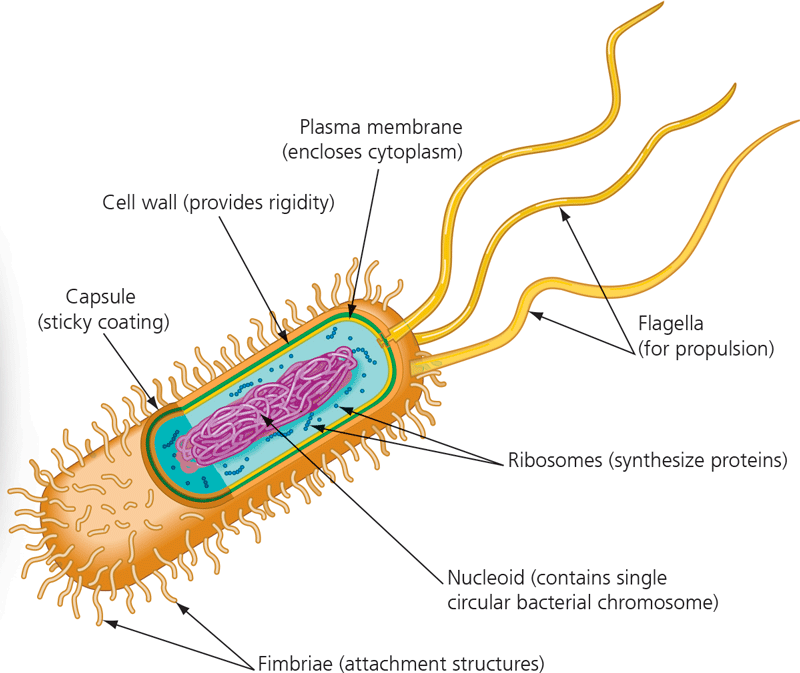
19
New cards
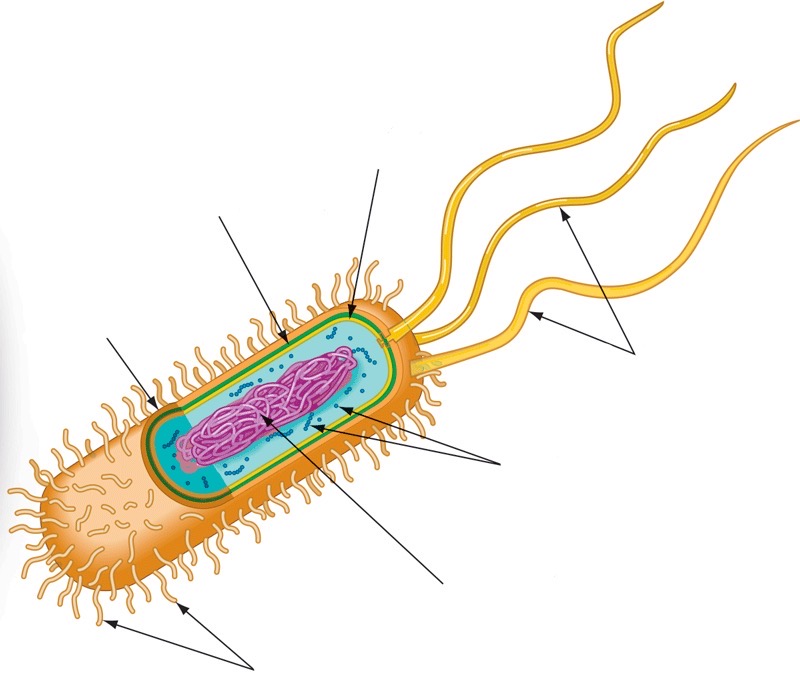
Ribosomes
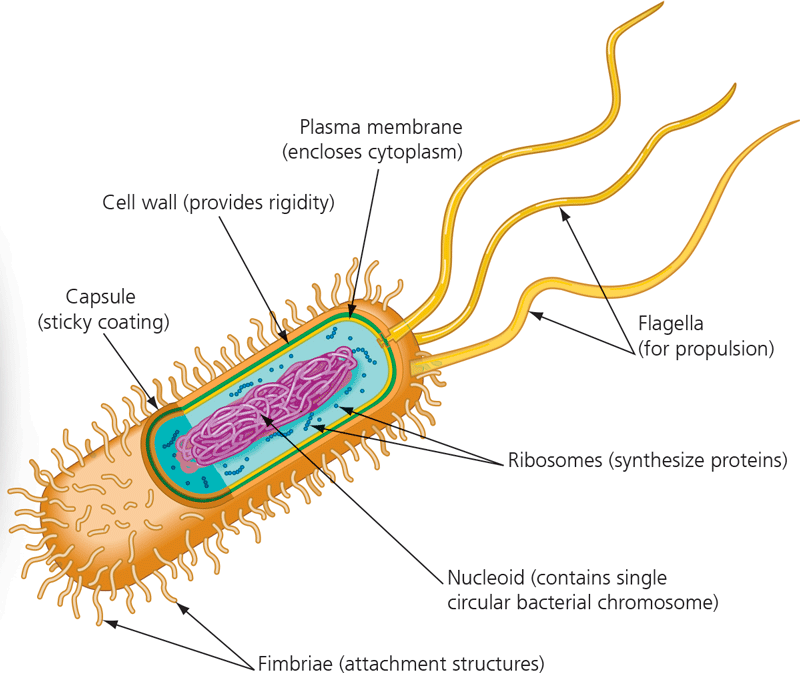
20
New cards
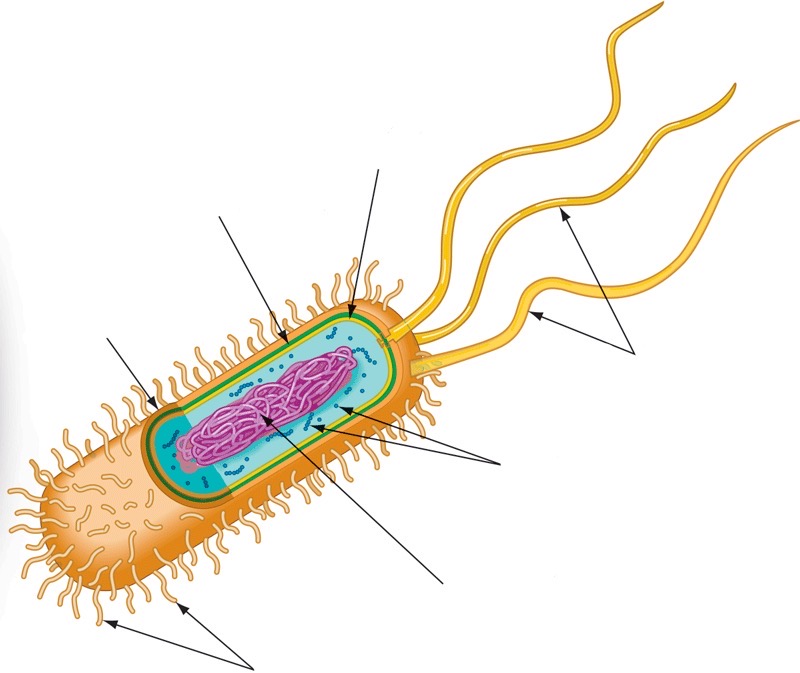
Flagella
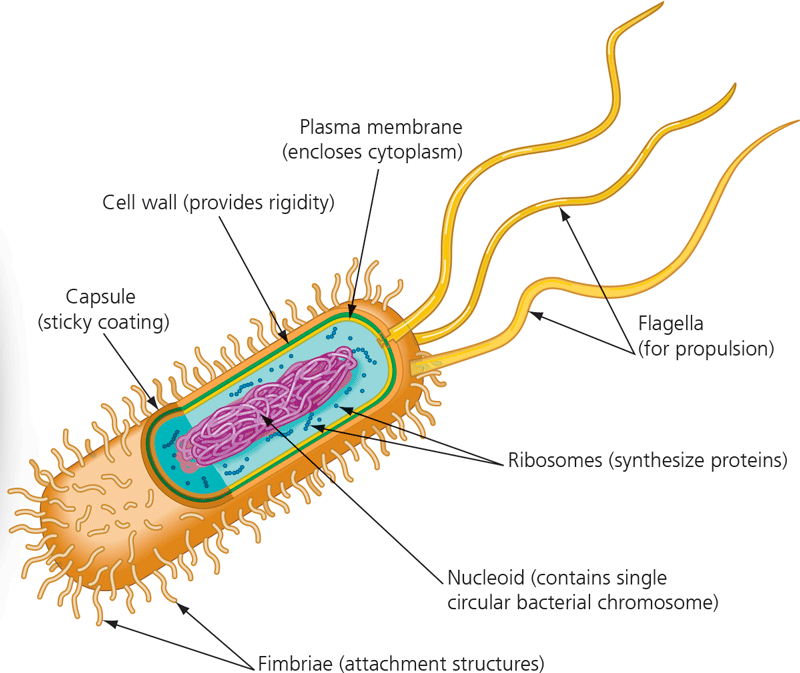
21
New cards
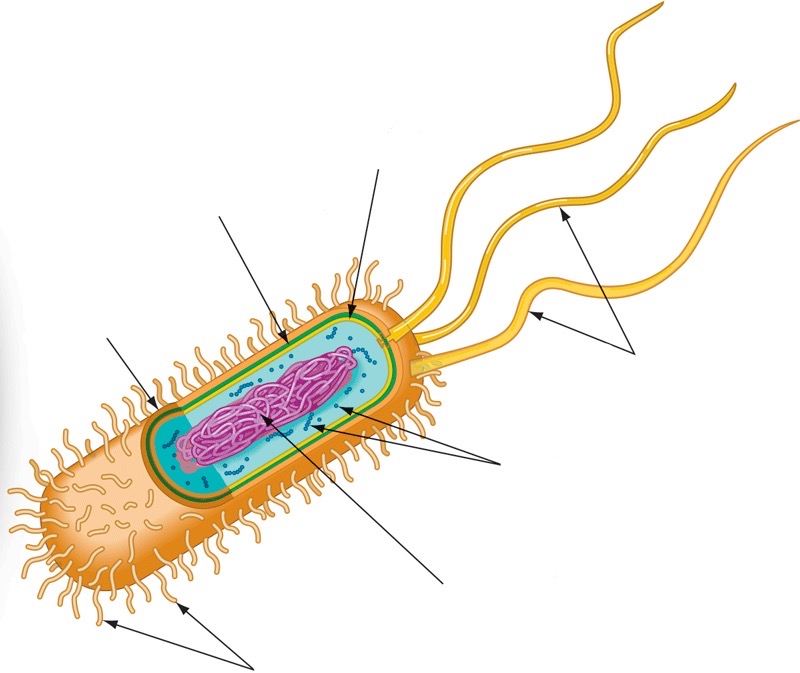
Plasma membrane
22
New cards
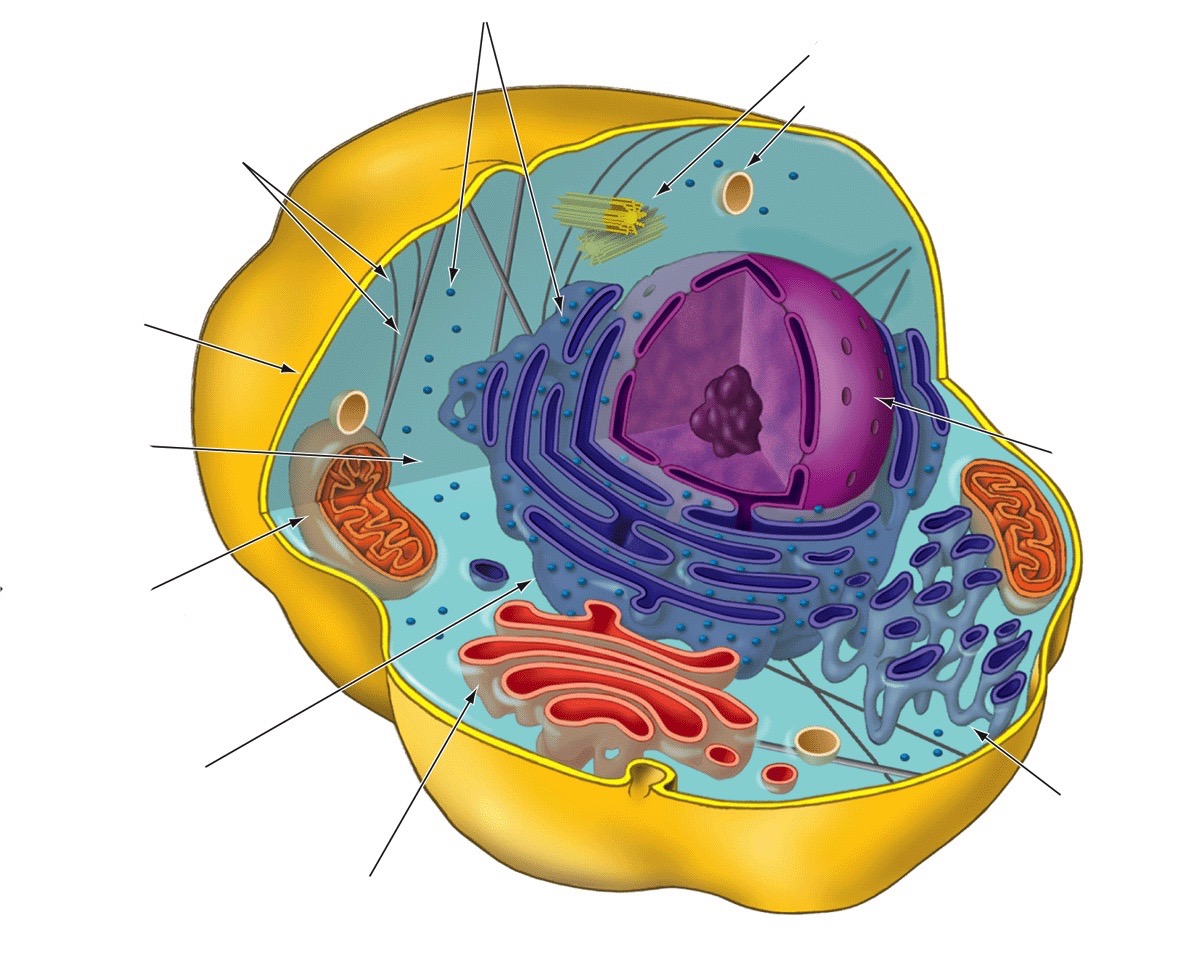
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Makes phospholipids that are inserted into the ER membrane; the attached ribosomes produce proteins
23
New cards
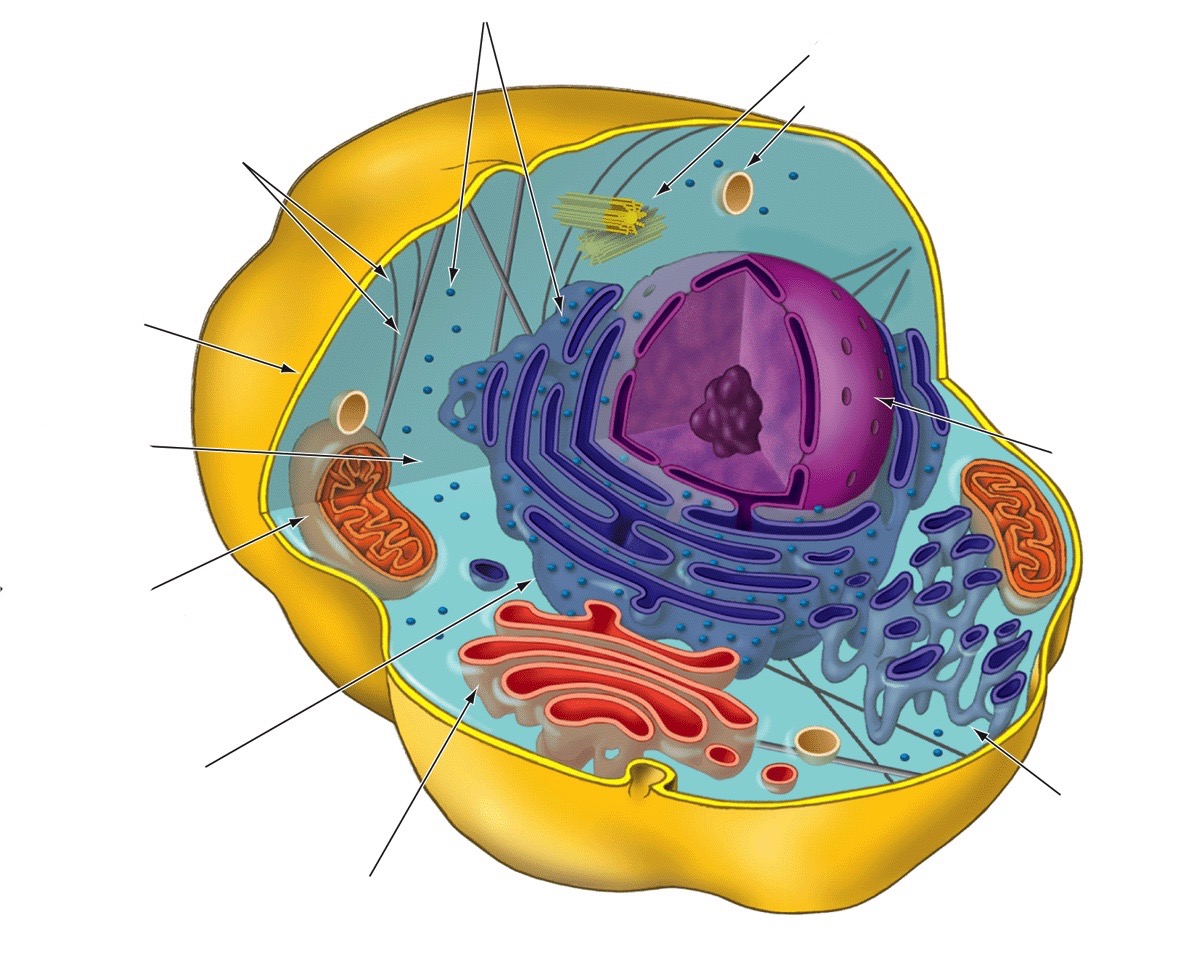
Golgi apparatus
Receives, refines, stores, and distributes chemical products of the cell (factory)
24
New cards
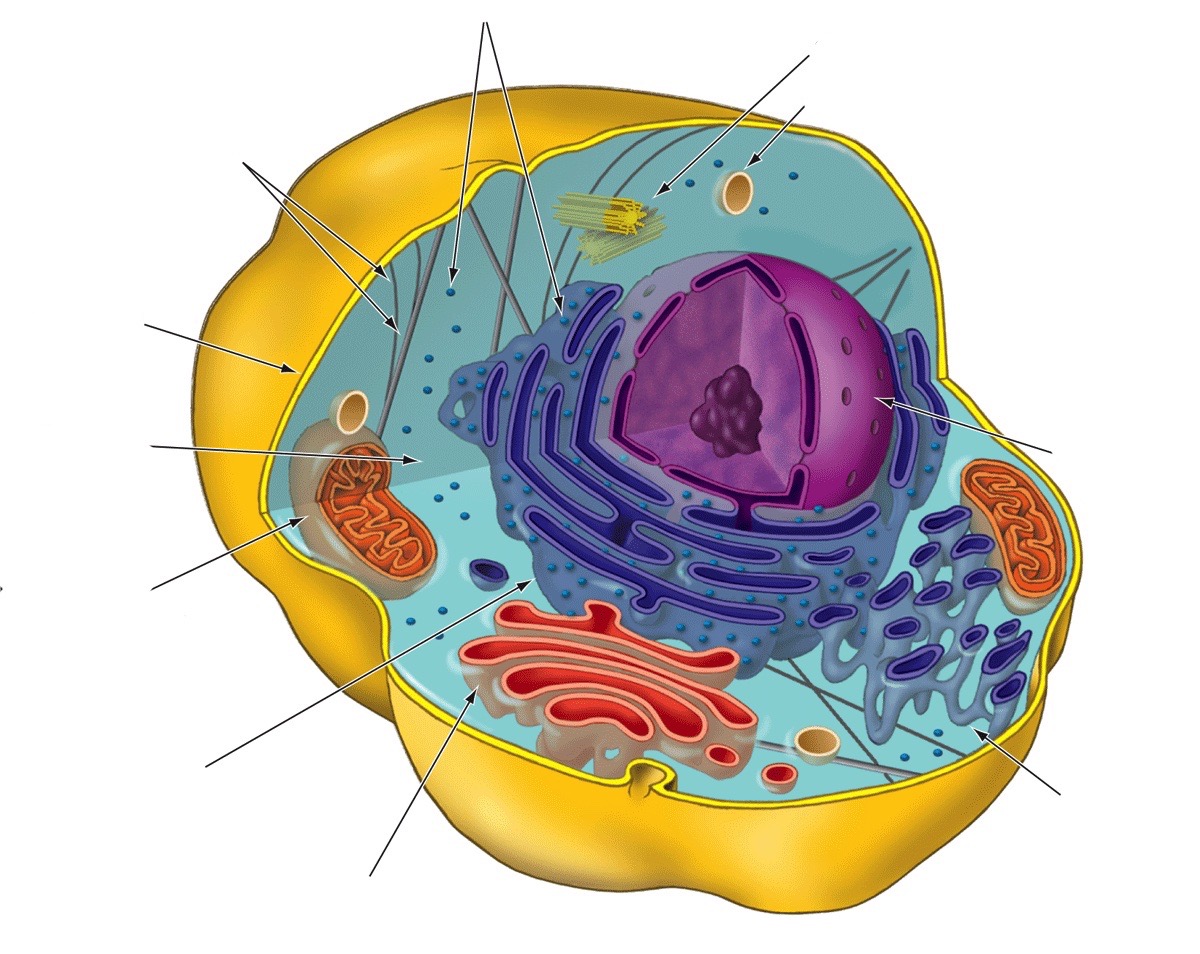
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Synthesis of lipids
25
New cards
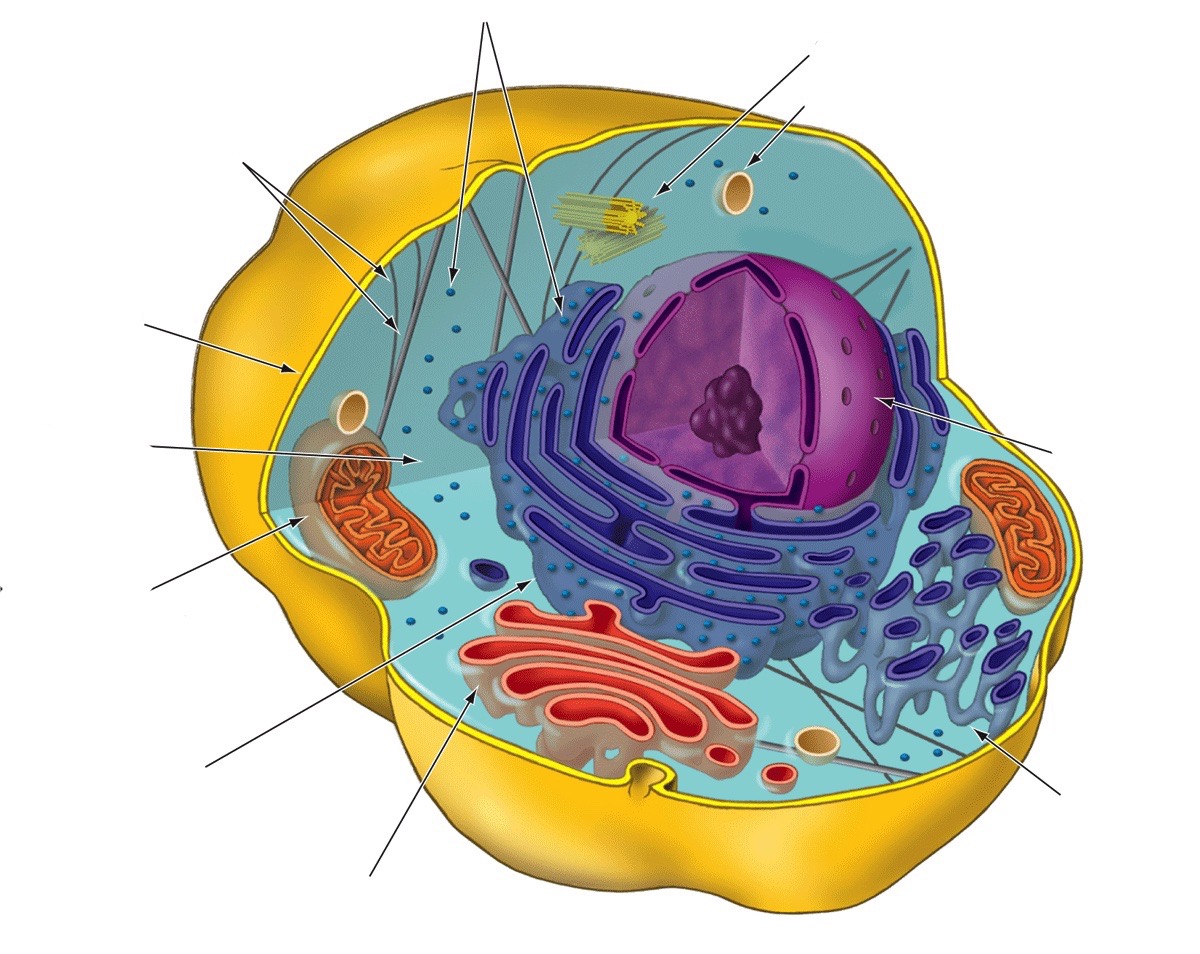
Nucleus
Stores genetic information
26
New cards
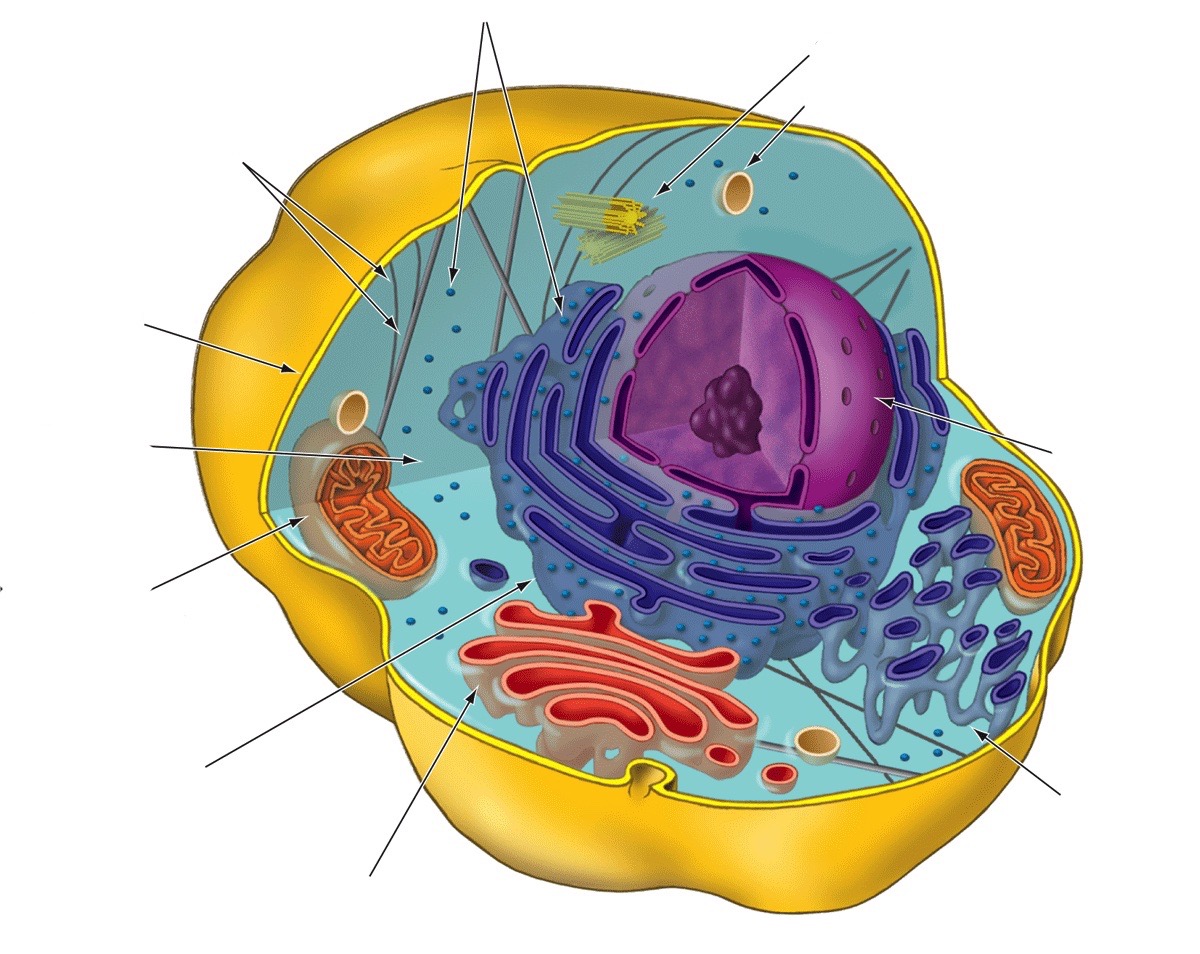
Lysosome
Breaks down stuff
27
New cards
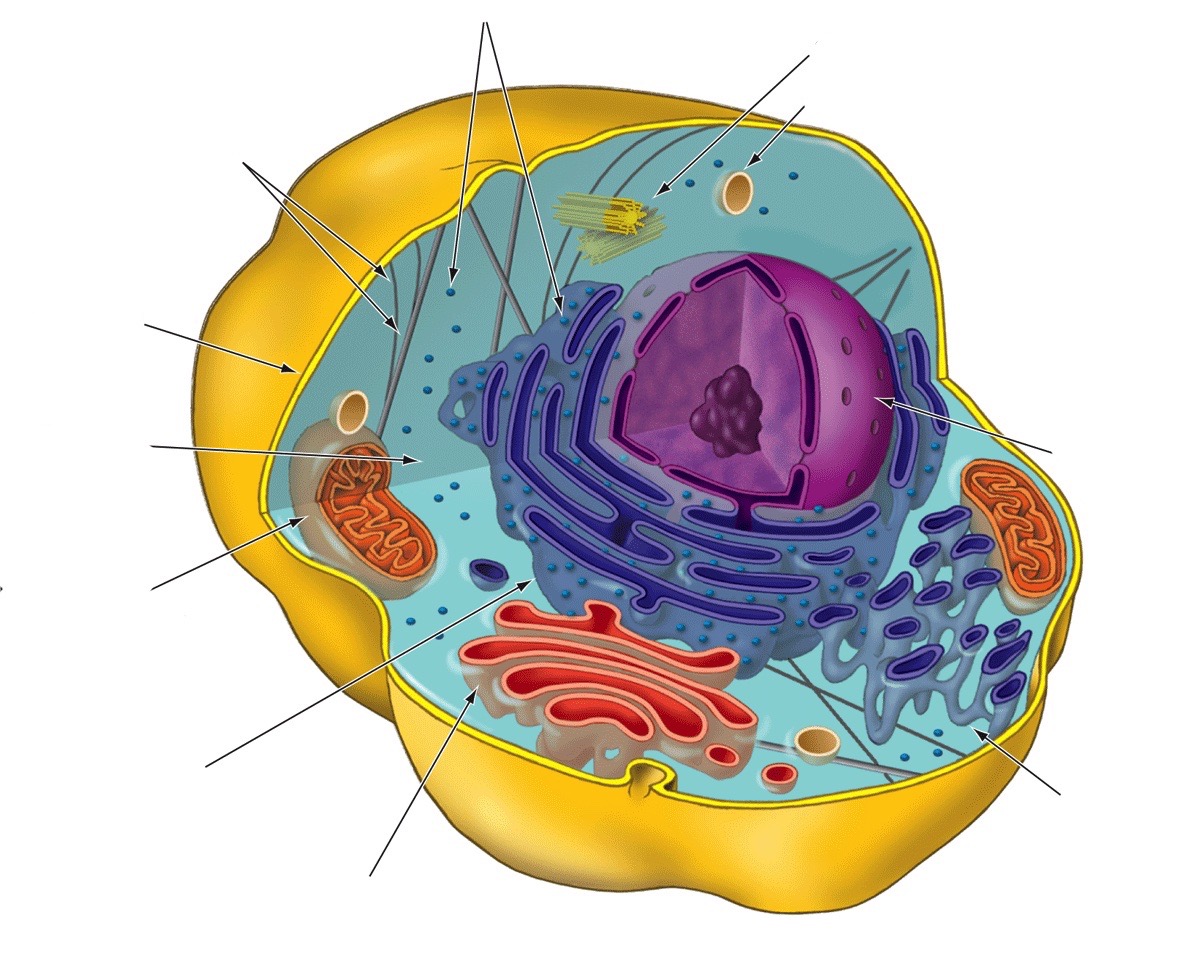
Centrosome
Provides structure and organizes microtubules
28
New cards
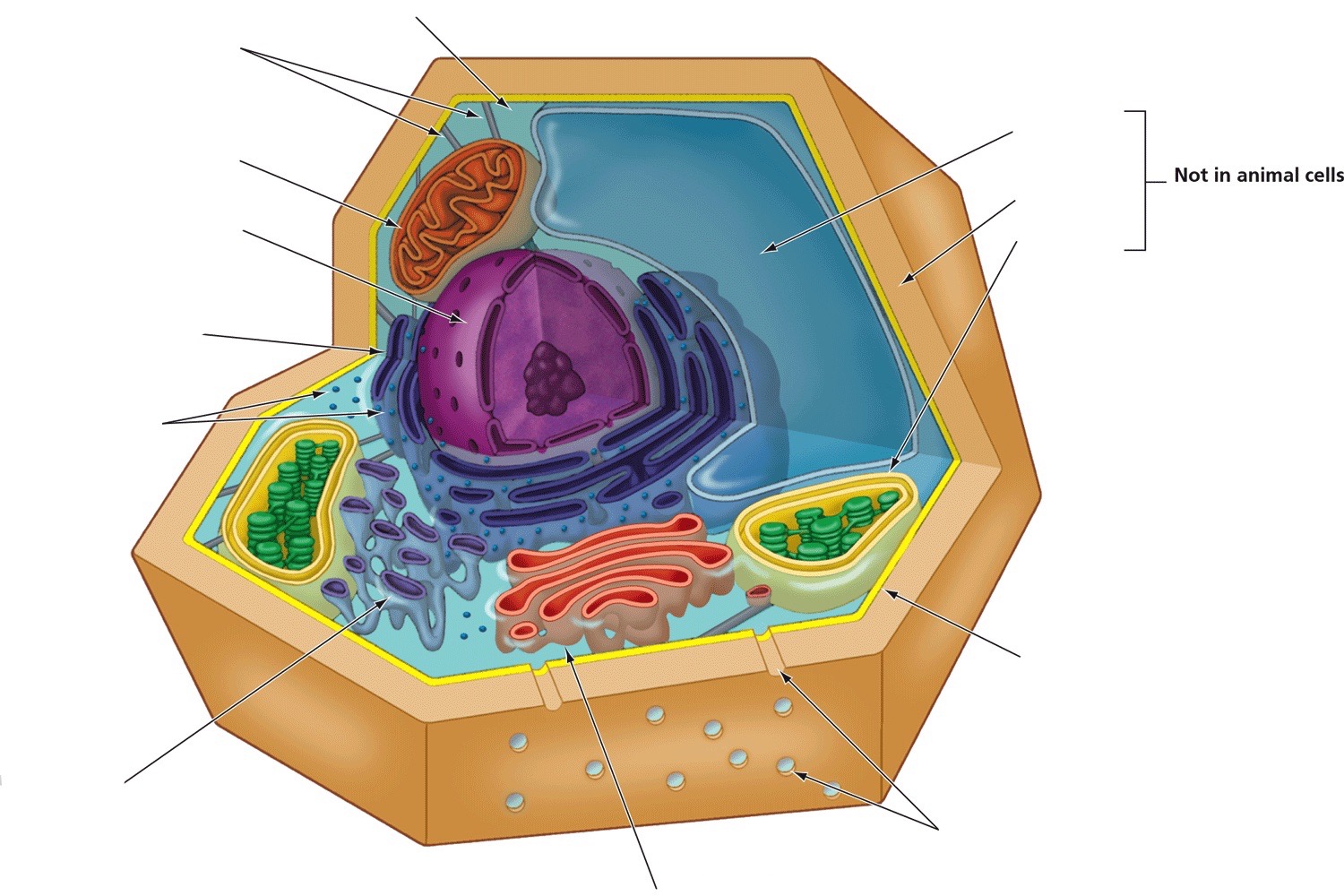
Central vacuole
Storage
29
New cards
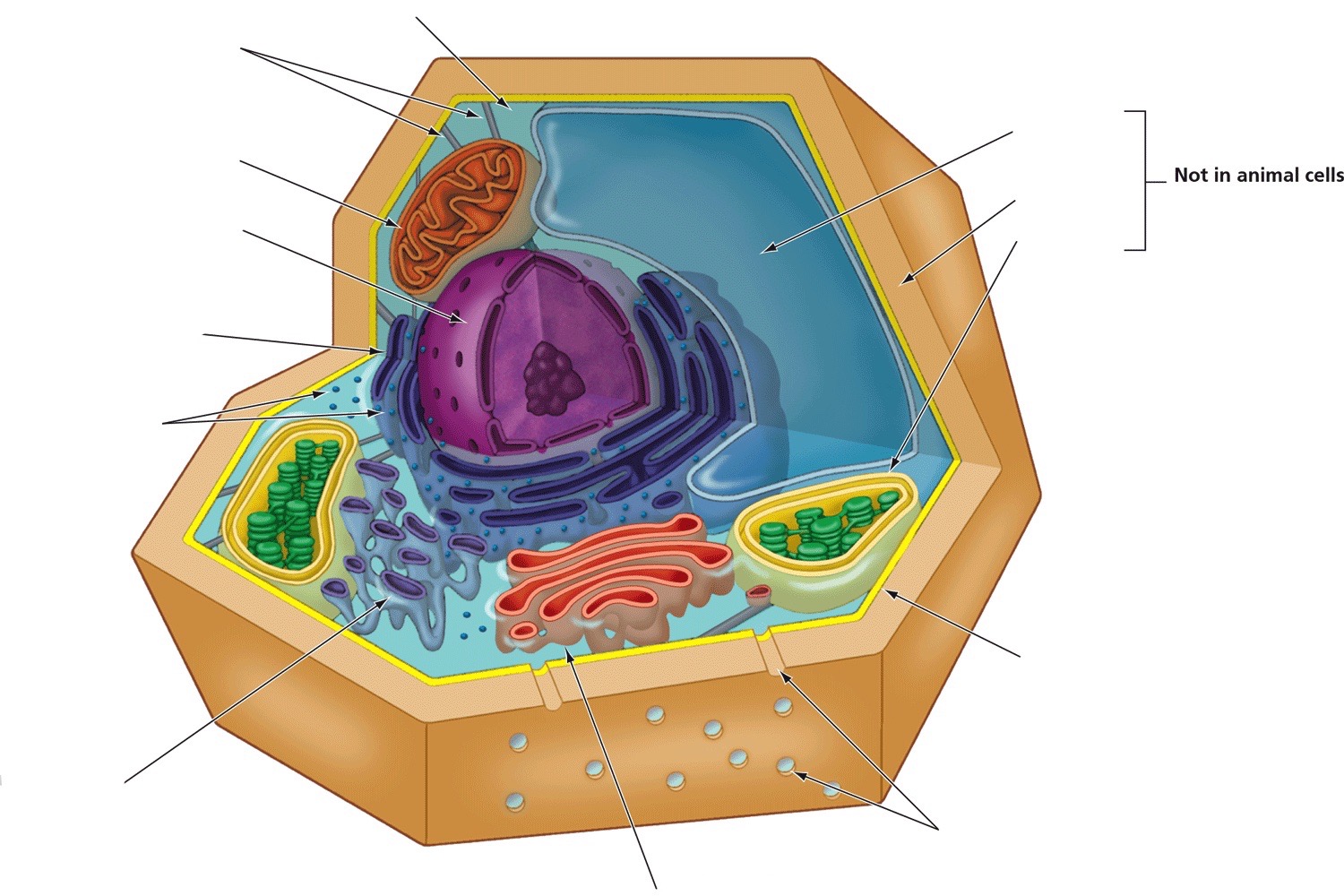
Cell wall
Provides structure, support, and protection
30
New cards
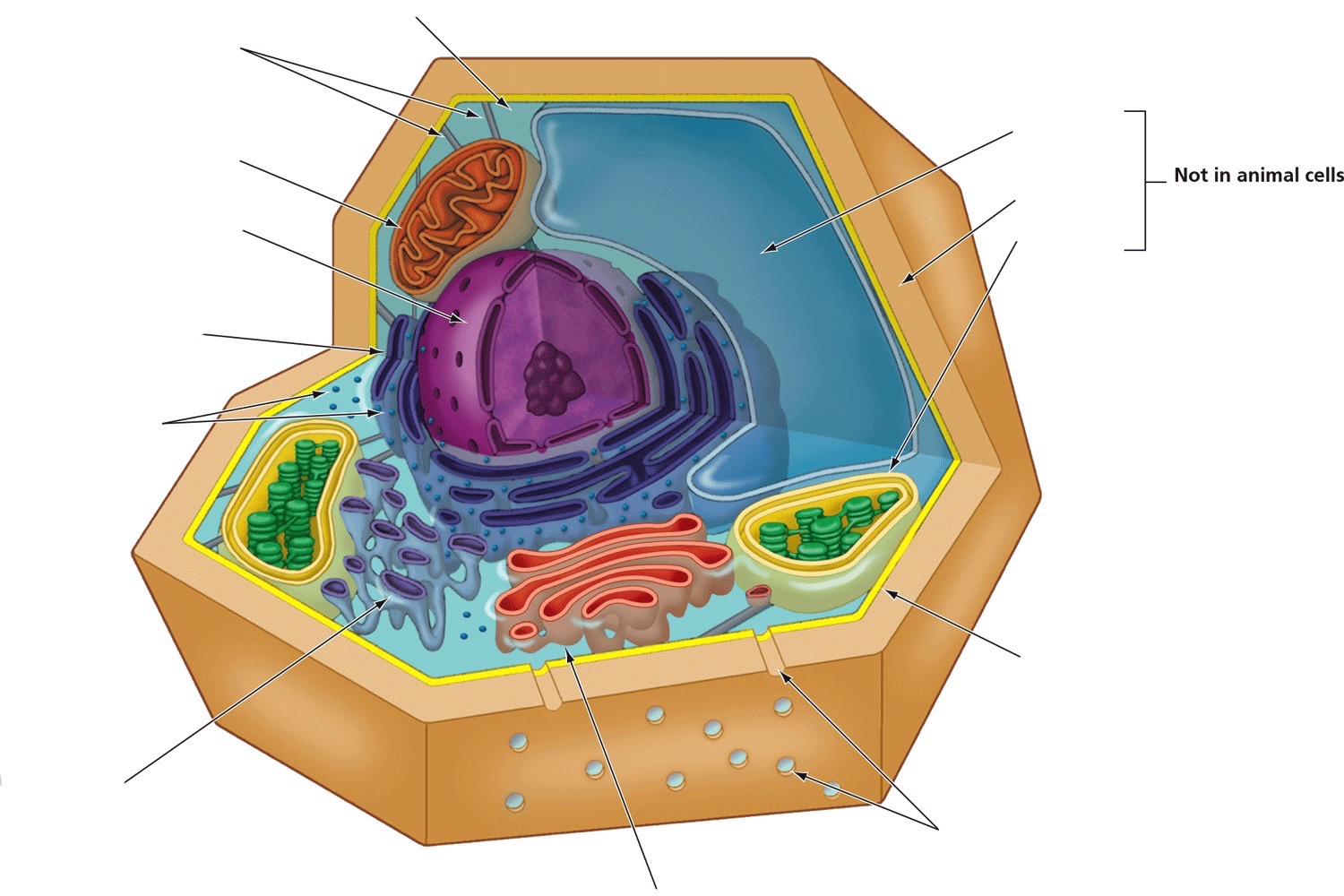
Chloroplasts
Produce energy through photosynthesis
31
New cards
Do individuals “stand alone?”
No
32
New cards
How many bacteria are there for 1 cell?
10
33
New cards
Why “get big?”
* Less chance of dying
* Able to do more
* Can’t be swallowed as easily
* Able to do more
* Can’t be swallowed as easily
34
New cards
Takeaway from the Pando Aspen Grove story
The trees are all one organism, they’re connected
35
New cards
What does “pando” mean
“I spread”
36
New cards
What are we here for?
“To learn to enjoy more, and to increase in knowledge and experience.” -Brigham Young
37
New cards
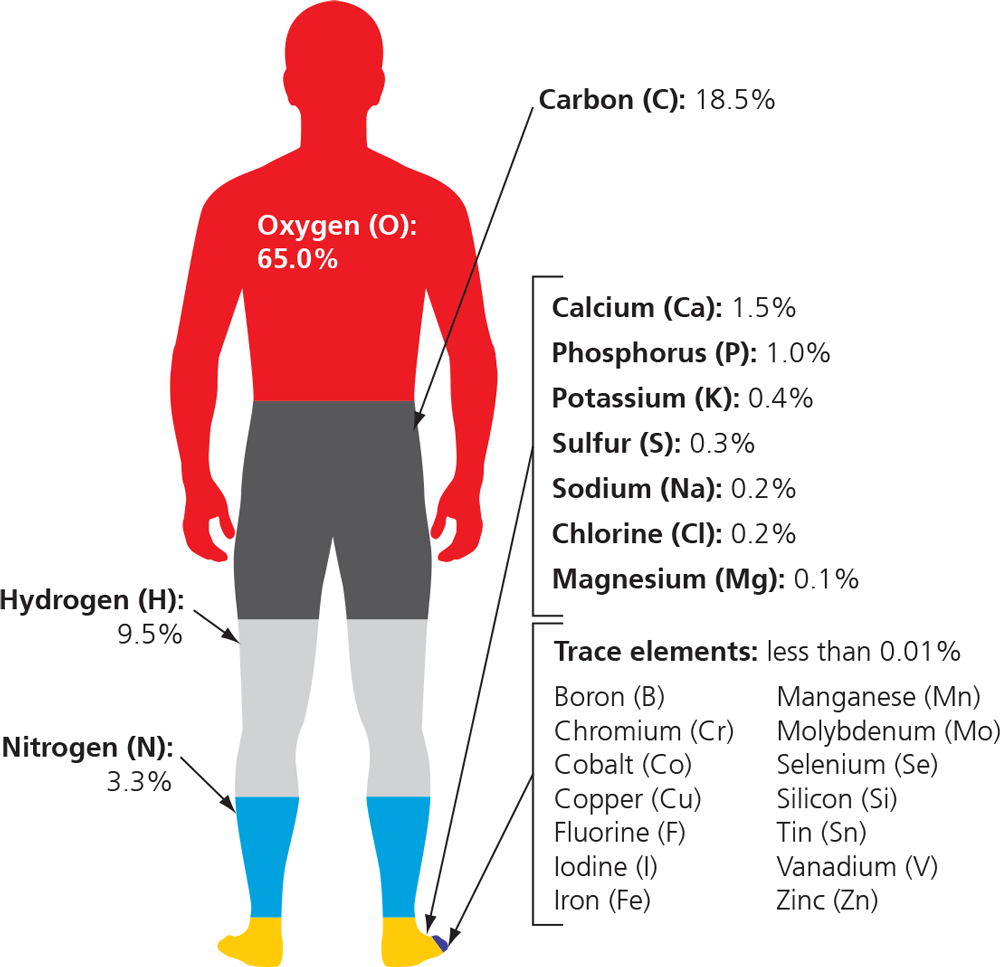
What are our bodies made of at the atomic level?
CHNOPS (carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfer)
38
New cards
Functions of carbohydrates
Store energy (short term and long term) and provide structural integrity
39
New cards
Cellulose
Long carbohydrate chain found in plants
40
New cards
Structure of lipids
Simple chain of carbons having a carboxyl functional group at one end
41
New cards
Lipids…
Do not dissolve in water
42
New cards
Functions of lipids
1. Long term storage; bonds are harder to break down than carbohydrates so it stores energy better
2. Structure: membranes (**separates the water within from the water without**)
3. Messengers: hormones
43
New cards
Fat has…
Twice as much kcal per gram than carbohydrates and proteins
44
New cards
Properties of lipids (fats, oils, and waxes)
* Have carboxyl functional group at one end
* Do not dissolve in water
* C, H, O, P
* Do not dissolve in water
* C, H, O, P
45
New cards
“Apparently so close in overall composition, but those ‘minor’ differences make female and male.”
Hormones: estrogen and testosterone
* similar molecules
* similar molecules
46
New cards
Function of proteins
Structure (give things shape) and machinery (enzymes)
47
New cards
What can come from proteins
An infinite possibility of molecular forms from 20 or so simpler units
48
New cards
Two main types of proteins
1. Structural proteins (keratin, hair, collagen)
2. Enzymes
49
New cards
If one amino acid is changed…
The protein either stops working, works better, or stays the same
50
New cards
Proteins are a long chain of
Amino acids
51
New cards
Amino acids have…
An amino group and a carboxyl group with a side chain that varies
52
New cards
Alpha helix shape
Spiral shape (slinky)
53
New cards
Secondary structure
Beads that coil and make sheets
54
New cards
Tertiary structure
Random shape (balled up slinky)
55
New cards
Quaternary structure
Multiple balled up slinky’s
56
New cards
Enzymes
* Catalyze reactions in a controlled way
* We’d burn up if all the energy from reactions was released at the same time
* Enzymes = machinery
* We’d burn up if all the energy from reactions was released at the same time
* Enzymes = machinery
57
New cards
Function of DNA
Store genetic information
58
New cards
4 nucleotides in DNA
A, T, C, G
59
New cards
4 nucleotides in RNA
A, U, C, G
60
New cards
What causes the double helix shape?
Charges
61
New cards
The central dogma of molecular biology
“DNA makes RNA makes protein”
62
New cards
“I believe a leaf of grass is no less than the journey-work of the stars.”
Walt Whitman
63
New cards
How many bonds can C, H, N, and O make?
Carbon: 4
Hydrogen: 1
Nitrogen: 3
Oxygen: 2
Hydrogen: 1
Nitrogen: 3
Oxygen: 2
64
New cards
Two types of carbohydrates:
1. Simple sugars: monosaccharides (glucose)
2. Complex carbohydrates: polysaccharides (long chain)
65
New cards
What are the polysaccharides talked about in class?
1. Cellulose
2. Starch
3. Glycogen
4. Chitin
66
New cards
Cellulose
Long carbohydrate chain found in plants (wood)
67
New cards
Starch
Carbohydrate found in plants (potatoes)
68
New cards
Glycogen
The equivalent of starch but for our bodies; for energy storage
69
New cards
Chitin
* Carbohydrate found in only a few types of animals
* “The crunch that satisfies” (stepping on a cockroach)
* “The crunch that satisfies” (stepping on a cockroach)
70
New cards
Functional groups of carbon bonds
Hydroxyl, carbonyl, amino, carboxyl
71
New cards
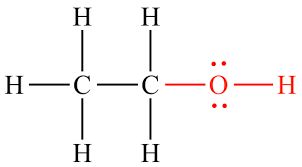
Hydroxyl group
Carbon bonded to one oxygen
* C-OH
* Found in alcohols and sugars
* C-OH
* Found in alcohols and sugars
72
New cards
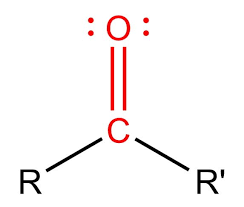
Carbonyl
Carbon double bonded to oxygen
* C=O
* Found in sugars
* C=O
* Found in sugars
73
New cards
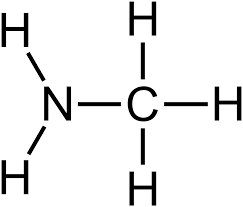
Amino group
Nitrogen bonded to carbon and two hydrogens
* C-N-H-H
* Found in amino acids and urea in urine from protein breakdown
* C-N-H-H
* Found in amino acids and urea in urine from protein breakdown
74
New cards
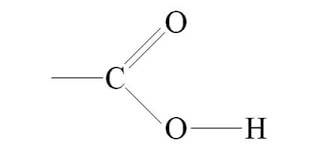
Carboxyl group
Combination of carbonyl and hydroxyl groups
* OH-C=O
* Found in amino acids, fatty acids, and some vitamins
* OH-C=O
* Found in amino acids, fatty acids, and some vitamins
75
New cards
What does the emergent property tell us?
We can’t predict what’s going to happen when we take things apart and put them back together in a different way
76
New cards
Ionic bond
Bonding of two ions of opposite charges (second strongest bond)
77
New cards
Covalent bond
Sharing of electrons between atoms (strongest bond on living level)
78
New cards
Hydrogen bond
Weak attractions between partially charged atoms (weakest bonds)
79
New cards
Why is water wonderful?
* Polarity: H is positive, O is negative
* Thermal buffer: takes a lot of energy for water to change phases
* Cohesion: surface tension
* Solvent: water can dissolve
* Ice floats
* Thermal buffer: takes a lot of energy for water to change phases
* Cohesion: surface tension
* Solvent: water can dissolve
* Ice floats
80
New cards
How many bonds can carbon make?
4
81
New cards
Parsimony
Simpler is better
82
New cards
Eukaryotic cells
Plant and animal cells (has nucleus)
83
New cards
Prokaryotic cells
No nucleus
84
New cards
4 macromolecules of life
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids/nucleotides
85
New cards
5 tools of discovery
1. Faith
2. Force
3. Consensus
4. Art
5. Science
86
New cards
What method did Doubting Thomas use to know that Jesus was resurrected?
Empiricism
87
New cards
Science differs from other discovery tools because…
It’s based on materialism, which can be good or bad
88
New cards
Science is…
Self-correcting, it has a way to detect when it’s being fooled, and ideas could be thrown out if new information provided more explanatory power
89
New cards
Age of the universe
13\.8 billion years
90
New cards
Age of the earth
4\.6 billion years
91
New cards
Age of earliest life on earth
3\.5 billion years
92
New cards
Age of earliest Homo sapiens
200,000 years
93
New cards
Characters vs character states
Characters are things like eye color, height, leaf shape, and character states are the specifics of those characteristics like blue, short, medium, needle-like, etc.
94
New cards
Linnaeus’s system
Taxon = classification unit to which organisms are assigned
* Mammalia is a taxon at the class level
* Mammalia is a taxon at the class level
95
New cards
Which direction does time travel on cladograms
From left to right because things diversify through time so things are older on the left and younger on the right
96
New cards
Sister species share a
Node
97
New cards
Why are there so many kinds of things? (DNA level)
A, T, C, and G can code for infinite different proteins
98
New cards
Why are there so many kinds of things? (atomic scale)
Carbon can make 4 sharing bonds
99
New cards
Why are there so many kinds of things? (cellular level)
Cells can be put together in lots of different ways
100
New cards
Why are there so many kinds of things? (carbohydrates)
Used for energy storage, structure, and protection