Gene-Modifying Methods in Neurobiology
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
Knock Out (KO)
Ablation of a gene within the genome
Knock In (KI)
Insertion of a gene at a targeted location in the genome (usually used to insert a mutation or a reporter gene)
Knock Down
Reduction of a gene expression (through siRNA (silencing RNA) inserted mutation, expression of Dominant-Negative forms or modification of promoter sequences)
What are some Knock Down Methods
siRNA inserted mutation
Expression of Dominant-Negative forms
Modification of promoter sequence
Transgenic
Random insertion of a foreign gene (from another species)
Is the location in the genome of a transgenic gene modification controlled?
No
Coding Sequences
Sequences that record information for protein synthesis
Fluorescent Proteins
Proteins that emit light upon excitation, used for visualization
Dominant-Negative Proteins
Modified proteins that interfere with the function of the wild-type protein
Cannot sustain the same function as the endogenous
Beta-Galactosidase (LacZ)
An enzyme used as a reporter that reveals its presence through colorimetric assays
Colorimetric Assays
Analytical technique that detects the presence or concentration of a substance by measuring the change in color that results from a chemical reaction
Exogenous Proteins
Proteins that are not normally present in the cell, introduced from outside
Exogenous proteins allow…
Registration of the neuronal activity
Modification of neuronal activity
Induction of neuronal death
Tracing of synaptic connections
GCamP
Fluorescent Ca2+ sensor
Fluorescence in the presence of high concentrations of Ca2+
Optogenetics
A technique to control neuronal activity using light
DREADD
Designer Receptor Exclusively Activated by Designer Drug
DREADD
Used to modify neuronal activity pharmacologically
Provides a ligand to modify the activity
Either increases or decreases the activity of the neuron
DTA toxin
A toxin used to induce neuronal death
System for co-expression via Fusion protein
Fusion of the protein of interest and a Tag (ex: GFP, HA)
Multiple proteins simultaneously expressed in same cells at same temporal pattern
We know that since they are fused, when one is present, the other is too
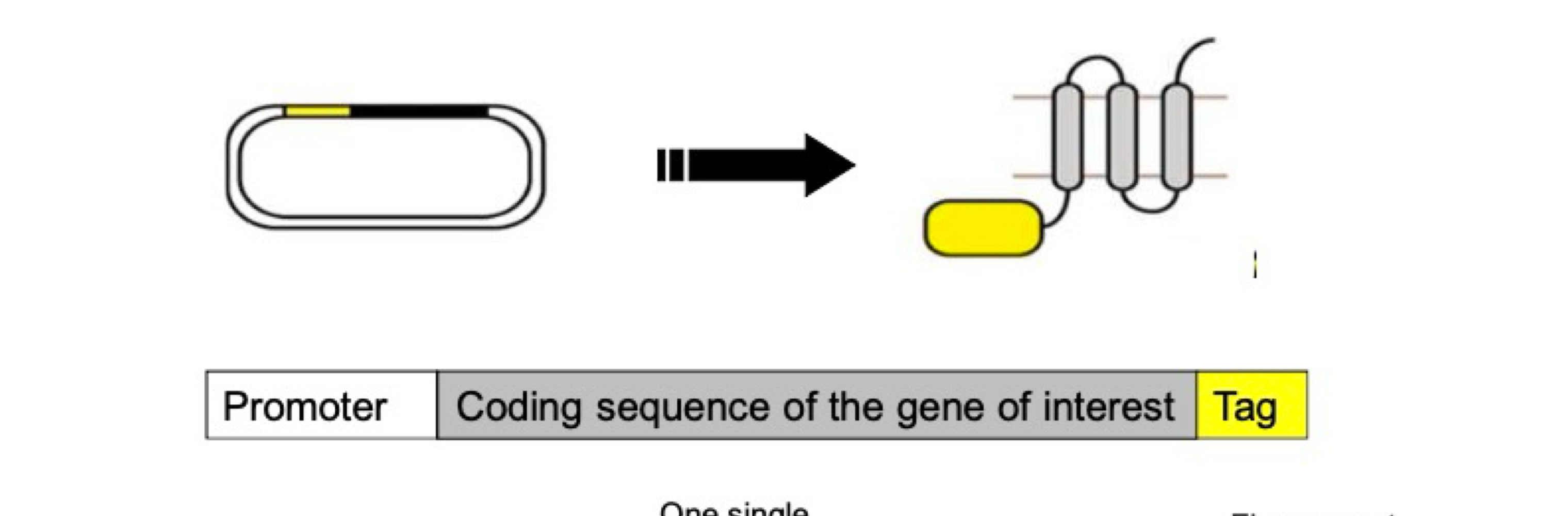
What process is displayed?
System for co-expression : fusion of protein of interest (POI) and a tag
Limitation of co-expression via Fusion protein/Tag
Shape/space (3-D organization) is altered
Fused might be bigger and not addressed properly in the cell
Coexpression with a fusion protein starts with one single mRNA and results in ___.
One single protein
IRES
Internal Ribosome Entry Site
Coexpression of a protein of interest and reporter through IRES starts with one single mRNA and results in ___
2 independent proteins
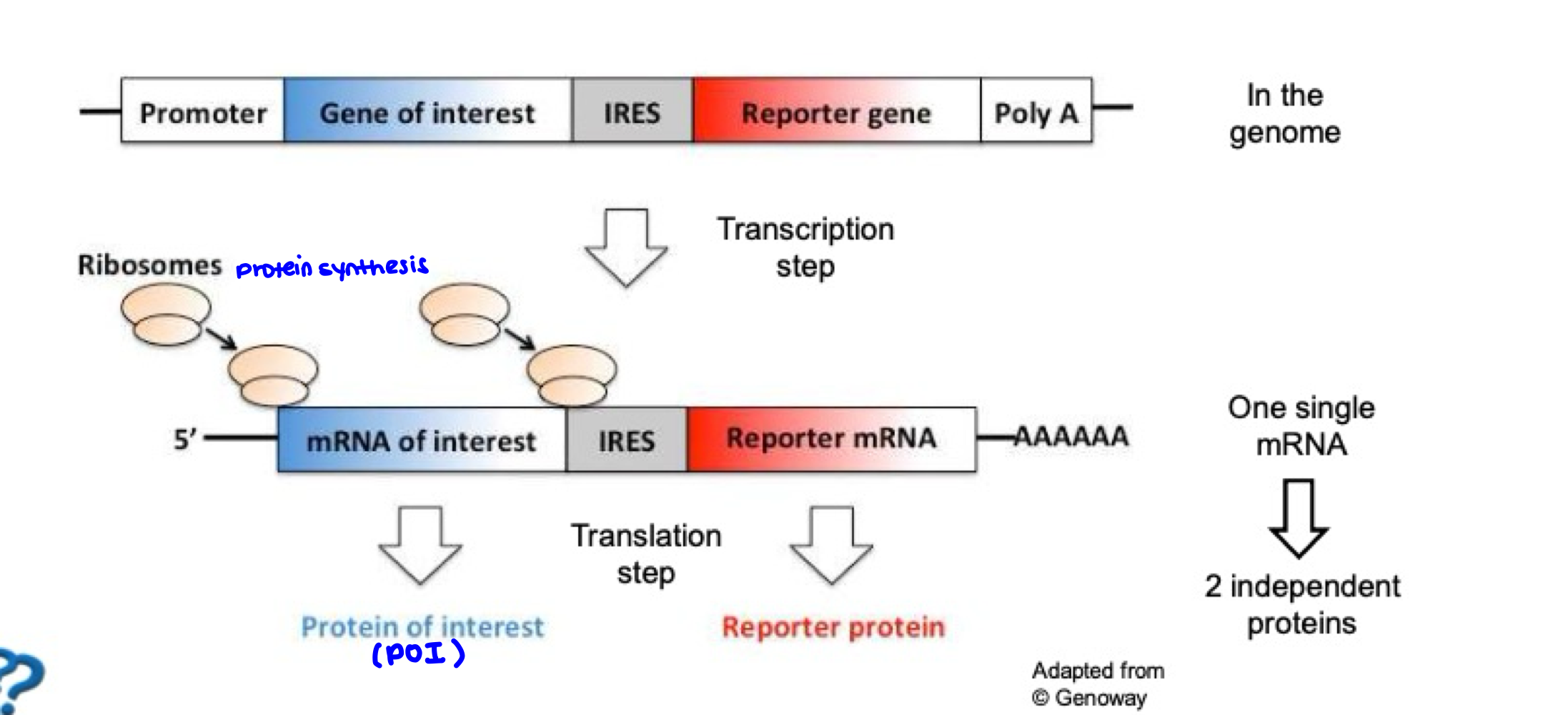
What process is displayed?
Coexpression via IRES
The location (inside cell) of the reporter protein is ___ of that of the POI.
Independent
→Both are within the same cell, but precise sub-cellular location of both might differ
Limitation of IRES
Level of expression of POI is higher than reporter protein (imbalance)
Advantage of IRES over Fusion Protein
Since the genes are not fused, there are no potential issues related to altered protein function or conformational change
Advantage of Fusion Protein over IRES
Often expressed more efficiently because their entire construct is treated as a single gene, and translation of both proteins is driven by a single promoter
→Eliminates the need for 2 independent translation events
RNAi
Interference RNA, a method to inhibit target gene expression by degrading mRNA
siRNA
short interfering RNA
2 Strands of siRNA
Guide and Passenger strand
siRNA Guide Strand
Directs silencing - binds to complementary mRNA molecule
siRNA Passenger Strand
Degraded during RNAi process
shRNA
short hairpin RNA
Sequence Carrier
Can be a plasmid or virus
Determined by the length of the sequence of interest to be expressed
Determines the entry path and the duration of the expression in the cell
Which carrier type will be used if the sequence is long?
Plasmid
Why plasmids for long sequences?
Limited space in the genome of a virus
Plasmid stays in cytoplasm → cell will eventually get rid of it
Transfection
Entry of one or several plasmids into cells using chemical compounds to make the cell permeable
RNAi Principle
Induces the degradation of the target mRNA and thereby blocks the synthesis of the protein
→No more protein = No more protein expression
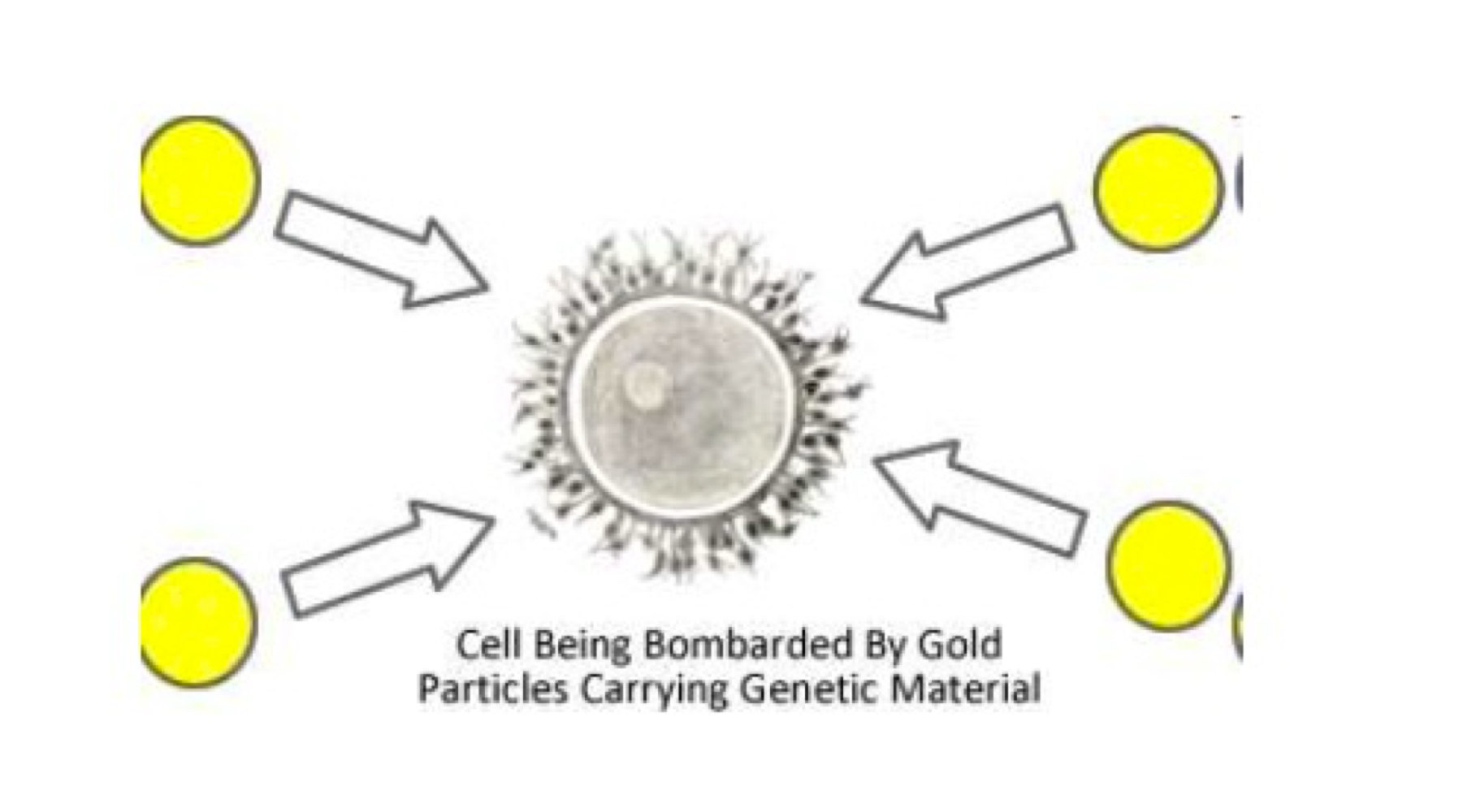
Gene Gun Method
Entry of plasmids by bombarding cells with particles coated in plasmids
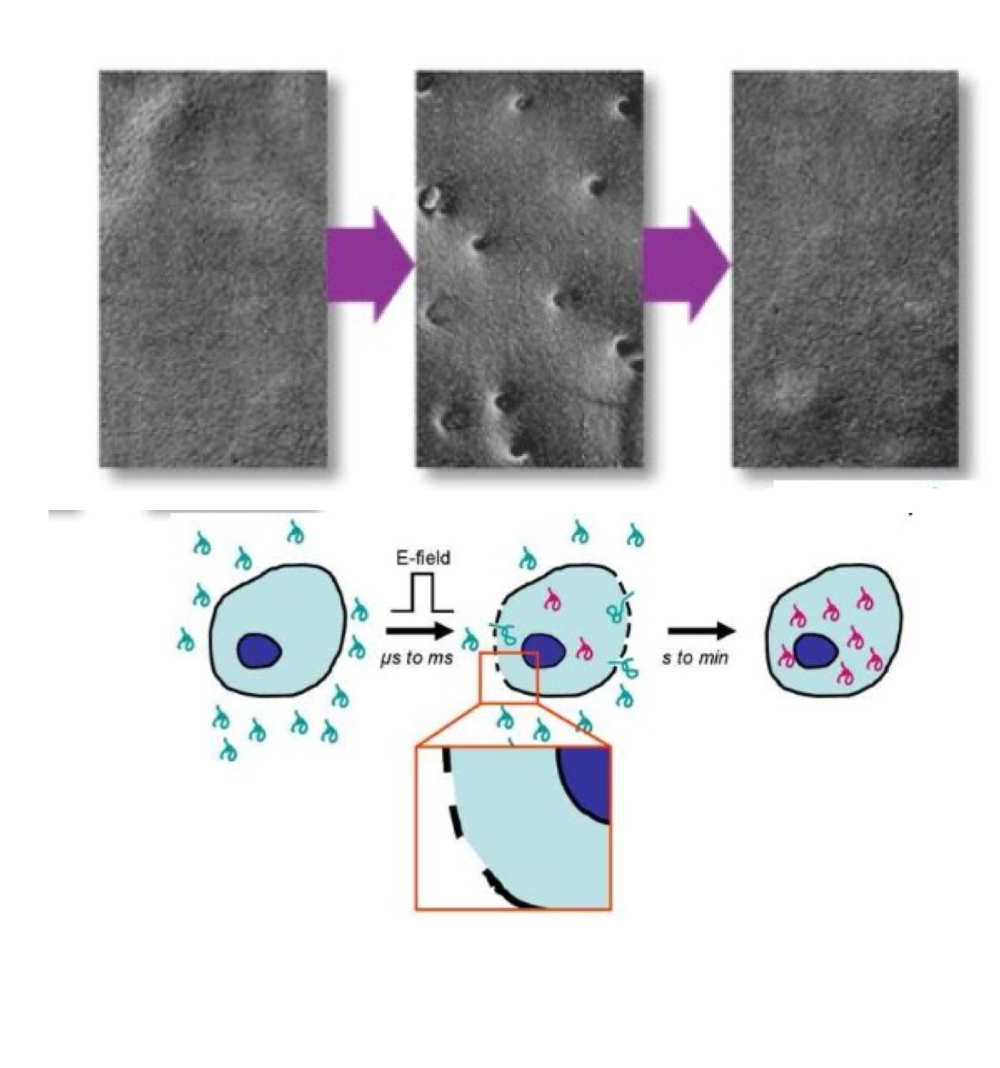
Electroporation
Entry of plasmids into cells through the application of an electric shock
Viral Transduction
Entry of genes into cells via viruses, which can integrate into the host genome
Spatial Specificity
Control over which cell type expresses a gene by choosing appropriate promoters
Temporal Specificity
Control over the timing of gene expression during development
Inducible Promoter
A promoter whose activity can be experimentally triggered at a specific time
Recombination
Change the arrangement of DNA inside the genome using enzymes
Cre-recombinase
An enzyme that recognizes LoxP sites for targeted recombination
Flippase-recombinase
An enzyme that recognizes FRT sites for targeted recombination
CrispR/Cas9
A genome editing technique that makes a cut at a targeted site in the genome
Guide RNA
RNA that directs the Cas9 protein to the specific site in the genome
Homology Directed Repair
A repair process that replaces the endogenous sequence with a donor template
Donor Template
A homologous sequence used to control what is inserted during genome editing
Reporter Proteins
Lab-engineered genes that light up (report) when they bind to a specific chemical (like a neurotransmitter).
Entry Path
Route for genetic material into cells.
Carrier
Plasmid or virus used for gene delivery.
Transitory Expression
Temporary gene expression in cells.
Permanent Expression
Long-lasting gene expression via integration.
Plasmid
Circular DNA that remains in cytoplasm.
Virus
Pathogen that can integrate into host genome.
Transfection
Introduction of one or several plasmids after application of chemical compounds that make the cells permeable (in vitro)
What are the methods of transfection?
Electroporation
Transfection
Gene Fun
Gene Gun Method
Plasmid delivery via particle (coated in plasmids) bombardment.
Gene Gun Uses
in vitro slice for nervous system
Injection of fluorescent dyes
Electroporation
Electric shock creates pores for plasmid entry.
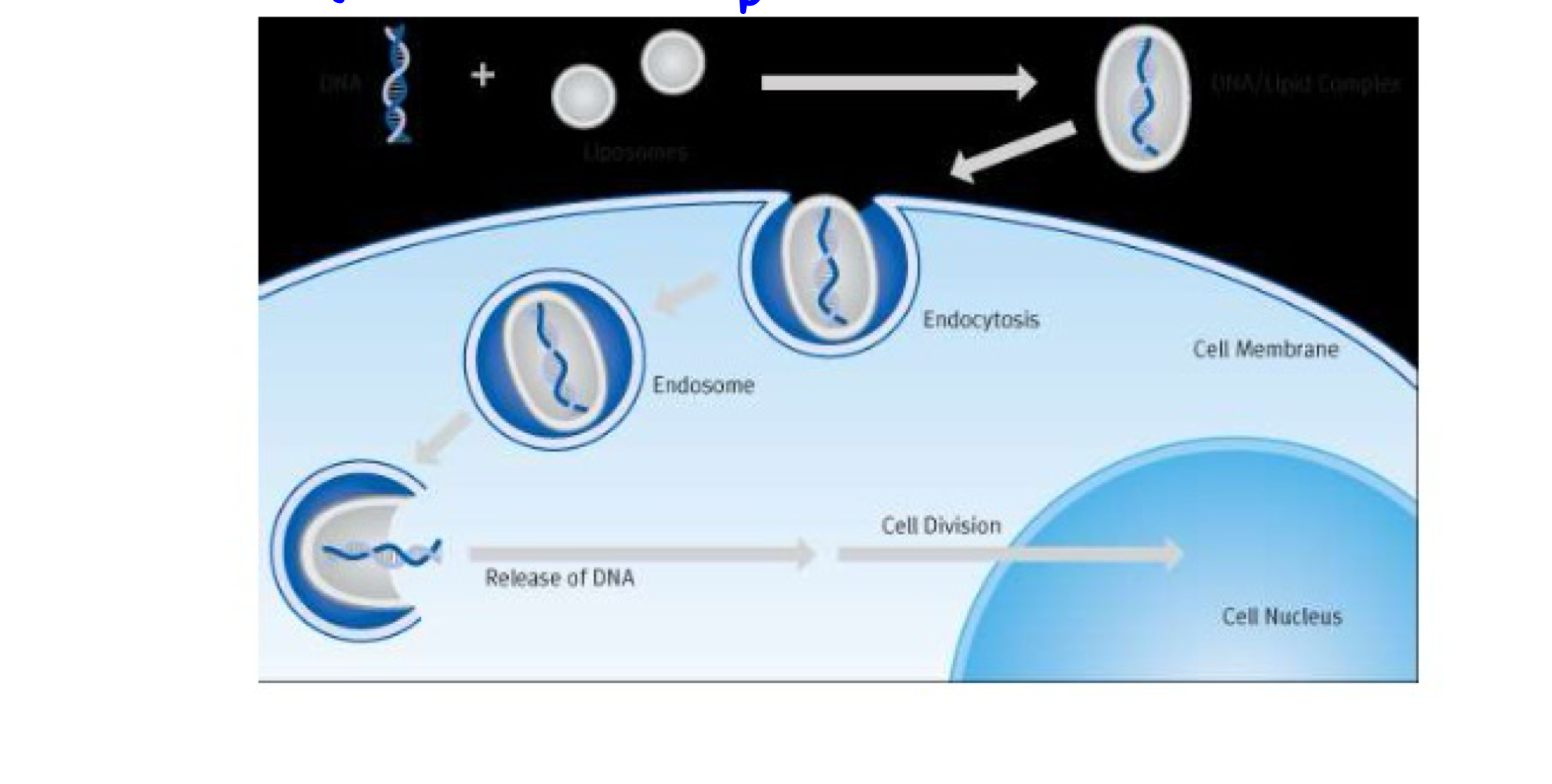
What is this image displaying?
Transfection
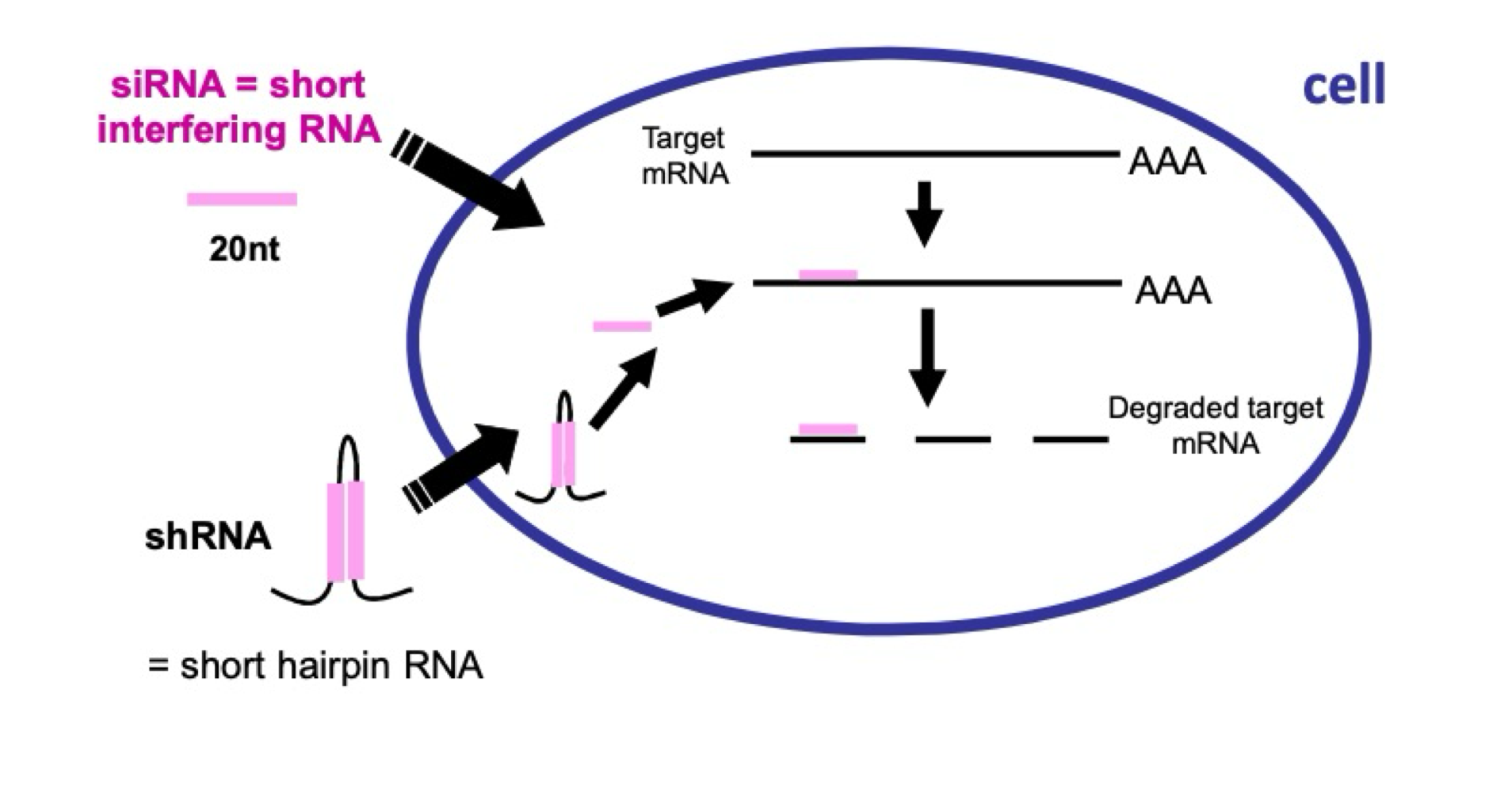
What is this image displaying?
RNAi
What is this image displaying?
Gene Gun Method
What is this image displaying?
Electroporation
In Vitro
Experiments conducted in controlled environments outside living organisms.
In Vivo
Experiments performed within a living organism.
Calcium Phosphate
Chemical used to facilitate plasmid entry.
Liposomes
Lipid-based carriers for plasmid delivery.
Transduction
Gene delivery using viral vectors.
Cell Tropism
Virus's preference for infecting specific cell types.
Lentivirus
Virus that integrates into host genome. Integrated genetic material for long-term gene expression
Adenovirus
Virus that does not integrate into host genome.
Can infect a wide range of cells, but do not integrate into genome → transient expression
AAV (Adeno-Associated Virus)
Rarely integrates into genome (very restrictive in transgene size they can carry)
GFP
Green fluorescent protein used as a marker.
Trans-synaptic Propagation
Virus spreads across synapses in nervous system.
Soft-skill Phase
Period for postnatal needle applications.
Spatial Specificity
Determines which cell type expresses a gene
Chooses the promoter that allows expression
Ubiquitous Promoters
Promoters expressed in all cell types.
Not Specific
Allows strong expression levels of sequences
Ex: CMV, PGK, SV40, CAGG
Neuron-Specific Promoters
Promoters active only in neuronal cells.
Even if it gets into a different cell, it won't be expressed
Ex: Β-Tubulin, CamKlla, NSE
Neuronal Subtype Specific Promoters
Promoters for specific neuronal subtypes.
More Specific
Ex: TH, VGluT, VGAT
What is an inconvenience of more specific promoters?
Trigger lower expression levels compared to ubiquitous
Temporal Specificity
Expression control at specific maturation stages.
Ex: Nestin, DCX
Inducible Promoter
Promoter activated experimentally at a chosen time.
Most common
Promoter usually off, but you can trigger it when you want
Examples of Inducible Promoters
Tet System (promoter TRE); HSP System; Operon Lactose System (IPTG)
Tet Inducible System
Tetracycline-controlled transcriptional activation system.
The Tet System controls ___ specificity
Temporal
tTA
Tet TransActivator (Tet-OFF)
Spontaneously Active
→Contains tetracycline repressor (TetR) and transcriptional activation domain
rtTA
Reverse Tet TransActivator (Tet-ON)
Spontaneously inactive
tTA is active in the ___ of Doxycycline (Dox).
Absence
rtTA is active in the ___ of Doxycycline (Dox).
Presence
In the Tet-OFF (tTA) system, the presence of Dox causes the ___ of gene expression.
Repression
In the Tet-ON (rtTA) system, the presence of Dox causes the ___ of gene expression.
Activation
tTA has a(n) ___ relationship with doxycycline.
inverse (+Dox → NO expression)
rtTA has a(n) ___ relationship with doxycycline.
direct/proportional (+Dox → Expression)