Materials Exam 2
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Dislocation motion results from what form(s) of stresses?
Shear Stresses
Which are properties of dislocations. Choose all that apply.
Dislocation motion in metals is generally easier in metals than ionically or covalently bonded materials
Dislocations interfere with each others motion through the lattice
Dislocations can multiply
Compressive and tensile stress fields exist around dislocations
What type of stress fields lies below a dislocation?
Tensile Stress Fields
What type of stress fields lies above a dislocation?
Compressive stress fields
If a compressive stress field is aligned with a tensile stress field, what is happening to the dislocations associated with each stress field?
The dislocations are being attracted to each other.
The slip system in a FCC crystal structure is
{111}<110>
Compare how the number of slip systems between different crystals relate
FCC=BCC>HCP
The criteria for tensile strength of metals based on crystal structures is evaluated by what 3 parameters?
Number of available slip systems
Density of slip planes/directions
Strength of bonds
In a FCC gold (Au) single crystal, a tensile stress of 210 MPa is applied along the [010] direction. Compute the resolved shear stress along the [111] direction on the (110) plane. The angles and are 54.7o and 45o. The critical resolved shear stress of this system is 118.36 MPa. From the options below, select what the resolved shear stress is and if it will result in slip (so select 2 of the 4 options below)
85 MPa
No, it will NOT slip
A single crystal metal is oriented such that the normal to the slip plane and the slip direction are at angles of 45oand 48o, respectively with the tensile axis. If the critically resolved shear stress is 890 psi what stress is necessary to initiate slip (in psi)?
1881
What are the 4 strengthening mechanisms common to all metals?
Work hardening
Second phase precipitation strengthening
Solid solution strengthening
Grain boundary strengthening (grain size reduction)
Grain boundaries hinder dislocation motion. If I want a strong steel rod, the best grain size would be…because it has the…
Highest grain boundary area
5 micrometers
What if the mechanism and effect of the recovery stage?
Mechanism: Reduction in lattice energy by removal of vacancies, interstitials and some dislocations by diffusion.
Effect: Mechanical properties are not drastically altered. Grains still have relatively high dislocation density and high internal strain
What is the mechanism and effect of recrystallization?
Mechanism: new dislocation free grains form at the old grain boundaries via atomic diffusion.
Effect: Strength & hardness decreases while ductile & toughness increases.
What is the mechanism and effect of grain growth?
Mechanism: Grain size increases, resulting in a decrease in lattice energy that comes from a high grain boundary surface area.
Effect: The microstructure is large, strain free grains. Strength & hardness decrease further; ductile & toughness increase
I have a steel ingot that has been beautifully cast. It has a homogeneous microstructure and nearly no internal defects. But, I need my grain structure to be as fine as possible. I want a higher strength!!! I am not worried about final shape. I just want good strength without a high dislocation density. Which of the following processes should I use?
Cold work > recovery > recrystallization
For hardening by second phase precipitates (and not by the precipitation harding mechanism) which situation probably offers a higher strength in a metal?
A microstructure whose 2nd phase is greatly out of alignment with the atomic planes of the matrix phase.
A superalloy fan disk from a jet engine undergoes a routine certification analysis and is found to contain a small void with a length of 7.7 mm and a crack tip radius of approximately 2 m. Determine the stress concentration factor expected for this defect.
89
True of False: The blunter the crack tip, the higher the magnified stress at said crack tip.
False
The total length of an internal crack is… while the total length of an external crack is…
2a
a
Brittle Material Failure characteristics
Almost no plastic deformation
Sharp, angular surfaces
Catastrophic failure
Ductile Material Failure Characteristics
Bending/yielding before failure
Rounded or blunted surfaces
Plastic deformation obvious before failure
The most common type of failure (in metals) is?
Fatigue
The WWII Liberty Troop transports failed mainly due to which mechanism?
Low temperature embrittlement
Which of the following statement(s) is/are true about plastic deformation in ductile metals?
It is the result of dislocation motion
It begins once the yield strength of the material is surpassed
It is permanent deformation
A dislocation moves best in a … and a …
Slip direction with high LPF
Slip plane with high PPF
During strain hardening…
dislocation motion becomes mpore difficult
dislocation stress field interactions increase
Dislocation density increases
Select all the factors, that if increased, will cause the magnified stress at the crack tip to also increase.
Applied stress
Crack length
Which of the following methods would NOT help engineer against creep?
Low stiffness
A structural component in the form of a wide plate is to be fabricated from a steel alloy that has a plane strain fracture toughness of 93 MPa-m1/2 and a yield strength of 864 MPa. If the design stress is one-half of the yield strength, what is the critical flaw length in mm? Assume Y = 1.13.
11.6
A flat metal plate has an internal crack with length 2.2 mm. What is the maximum tensile stress, in MPa, the plate can experience without failing? The plane strain fracture toughness of the metal is 42 MPa-m1/2. Assume a plane strain fracture geometry, mode I with Y = 1.0.
714
Higher carbon phase
Fe3C, Cementite
Lower Carbon Phase
Alpha Ferrite
Pearlite can be seen on cooling through the steel eutectoid. What is pearlite?
A microstructure composed of two phases
A hypoeutectoid steel, upon cooling to room temperature, will have what microstructure?
Grain of proeutectoid alpha ferrite, and grains of pearlite
A hypereutectoid steel, upon cooling to room temperature, will have what microstructure?
Grains of proeutectoid cementite, and grains of pearlite
A eutectoid steel, upon cooling to room temperature, will have what microstructure?
Grains of pearlite
A hypoeutectoid steel, upon cooling to room temperature, will have what phases present?
Ferrite and Cementite
Low Nucleation Rate, High Growth Rate
High Temperatures
Maximum overall transformation rate
Middling Temperatures
High Nucleation Rate, Low Growth Rate
Low Temperatures
What is the fraction of ferrite phase in a steel that has a 100% pearlitic microstructure (i.e. no pro-eutectic phases)
89%
What is the compositions of the ferrite phase in a hypereutectic steel that has a an overall composition of 1.3 wt% carbon.
0.022 wt%C
Spheroidite
"large" grains of cementite in a continuous ferrite matrix
Pearlite
layers of cementite and ferrite
Bainite
Needles of cementite in a continuous ferrite matrix
Martensite
a BCT phase of steel
Tempered Martensite
“tiny” grains of cementite in a continuous ferrite matrix
Toughness in steel is obtained by having a continuous ferrite matrix
True
Bainite Diffusion Dimension
1D
Pearlite Diffusion Dimension
2D
Spheroidite Diffusion Dimension
3D
Martenstite
No diffusion
Pearlite cooling rate
slow cooling
Tempered Martensite cooling rate
rapid quench followed by a reheat
Martensite cooling rate
rapid quench
Bainite cooling rate
Moderate cooling
Spheroidite cooling rate
verrrry slow cooling
What phases are typically present in tempered martensite?
cementite
ferrite
Martensite strength
Highest strength
tempered martensite strength
higher strength
Bainite strength
high strength
pearlite strength
average strength
spheroidite strength
lowest strength
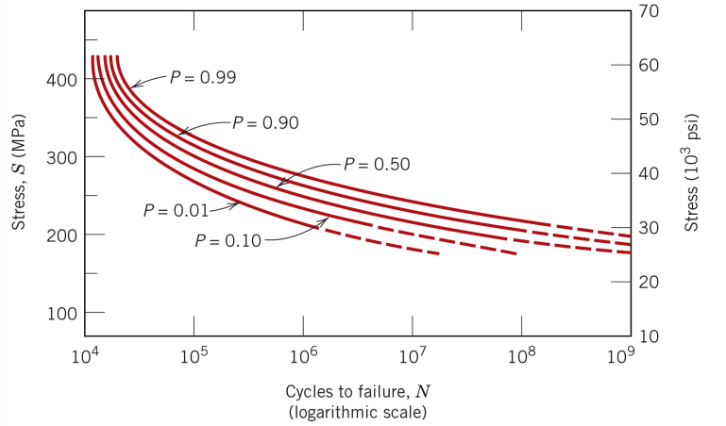
Metal components will be subjected to an environment where they will experience asymmetric cyclical with maximum tensile and compressive stresses of 400 and 100 MPa, respectively. Determine the anticipated number of cycles until failure for 90% of the components.
3×10^6 cycles
TTT Curves differ from phase diagrams, select which reason best explains why.
TTT Curves show what transformations occur when cooled at non-equilibrium rates, phase diagrams only show equilibrium transformations
Most cast irons contain C in the form of graphite.
True
Cast irons typically have compositions that contain…
more carbon than most steels
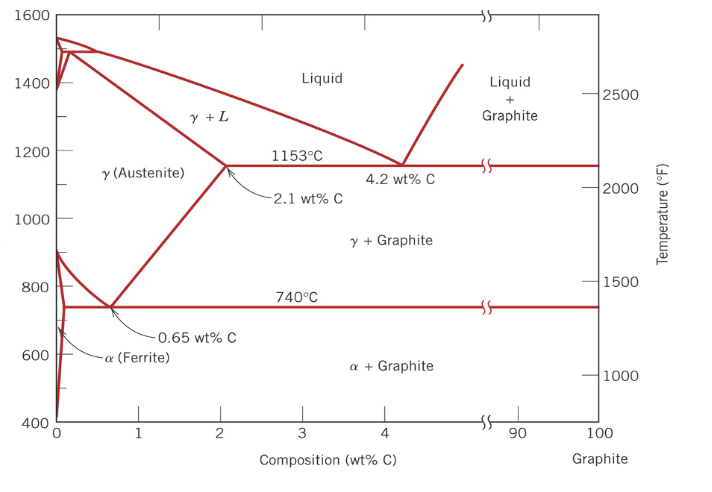
Cast irons all generally contain more than … wt% C.
2.1
An alloy system that can effectively be precipitation hardened must have both a … and a …
an appreciable maximum solubility of one component in the other
a steep solvus line
The most brittle steels are generally?
High carbon steels
Titanium is a strong yet ductile metal due to its HCP crystal structure
False
Titanium forms an incoherent oxide
False
Method of the “forming” category
Rolling
Extruding
Method of additive manufacturing
Power Bed Fusion
Direct Energy Deposition
Methods that involve pouring liquid metal
Lost Foam Casting
Sand Casting
Titanium is highly sought in manufacturing because…
Less dense than steel
Higher specific mechanical properties than steel
Titanium is exceptionally corrosion resistant
Element X assumes a diamond cubic crystal structure. If the atomic radius of X is 0.199 nm, what is the lattice parameter of its unit cell in nm?
0.92
As the ionic radius in an ionic compound increases, the coordination number?
increases
Ceramic materials typically have which of the following characteristics?
High compressive strength
Hard
Brittle
The radius of the atoms in a covalently bonded DC lattice ceramic material is 0.126 nm. Determine the lattice parameter of the unit cell in nm?
0.582
Determine the density (in g/cm3) of an AX ionic compound in which the ionic radii and atomic weights of the cation and anion are given below:
cation: radius = 0.100 nm A = 37.9 g/mol
anion: radius = 0.186 nm A = 41.6 g/mol
2.82
The radius ratios for the ions in an AX ceramic compound are given below. Determine the coordination number of the bonding.
0.502
Octahedral (6)
The radius ratios for the ions in an AX ceramic compound are given below. Determine the coordination number of the bonding.
0.800
Cubic (8)
The radius ratios for the ions in an AX ceramic compound are given below. Determine the coordination number of the bonding.
0.305
Tetrahedral (4)
The radius ratios for the ions in an AX ceramic compound are given below. Determine the coordination number of the bonding.
1.050
Dodecahedral (12)
For anions in an ionic crystal structure, which of the following properties are generally true?
negatively charged
gain valence electrons
typical larger than cation
Barium titanate is a piezoelectric material. Each unit cell of BaTiO3 has an electrical dipole associated with it because the center of cation positive charge in the unit cell is not coincident with the center of negative anion charge.
True
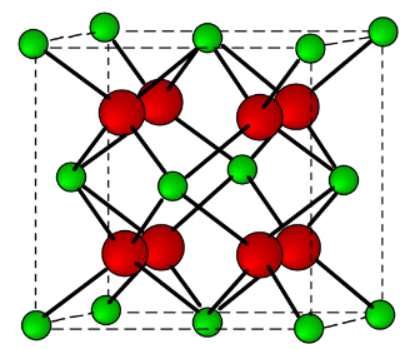
A ceramic material has the crystal structure depicted below. If the charge on the smaller, green cations is +4, what must the charge be on the larger, red anions for this structure to be electrically stable?
-2
Quartz, fused silica and cristobalite are silicates that all share ___ corner oxygen atoms between SiO4-4 tetrahedra?
4
Networks modifiers "break up" the SiO4-4 tetrahedral network in fused silica glasses. The common network modifiers are Na, Ca and B. Match these elements to the type of bond it forms in the silica glass?
B
Bridging bond between 3 tetrahdra
Networks modifiers "break up" the SiO4-4 tetrahedral network in fused silica glasses. The common network modifiers are Na, Ca and B. Match these elements to the type of bond it forms in the silica glass?
Na
Terminating bond
Networks modifiers "break up" the SiO4-4 tetrahedral network in fused silica glasses. The common network modifiers are Na, Ca and B. Match these elements to the type of bond it forms in the silica glass?
Ca
Bridging bond between 2 tetrahdra
Stainless steels all contain what other alloying element other than carbon?
chromium (Cr)
What is the most probable crystal structure of MnS assuming bonding in this material is mostly ionic in nature.
zinc-blende
Precipitation hardened alloys achieve strength by?
Introducing coherent, second phase particles that impost stress on the lattice
The precipitation hardening process proceeds in the following order
formation of solid solution
quenching
heating to allow controlled precipitation
When a precipitation hardened alloy is overaged, the results are?
formation of incoherent precipitate
decreased strength
Ceramic materials typically have which of the following characteristics?
High electrical resistivity
Brittle
High compressive strength
Hard
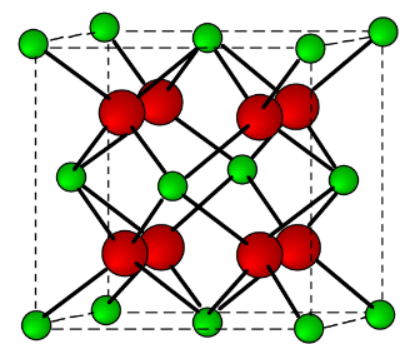
This is the fluorite structure. Based on the arrangement of anions, what is the Bravais lattice for this structure?
SC