Physics Paper 2
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms

Waves
Transfer energy without transferring matter

Longitudinal wave
Vibrations are parallel to the direction of the wave
Consist of compression & rarefractions
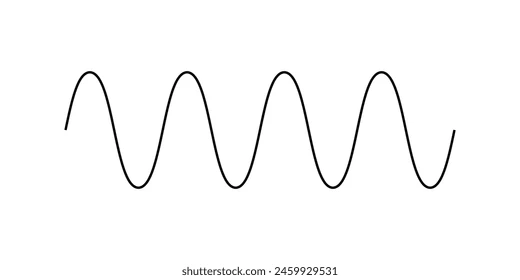
Transverse wave
Vibrations are at right angles (perpendicular) to the direction of the wave
Frequency =
1 / time period
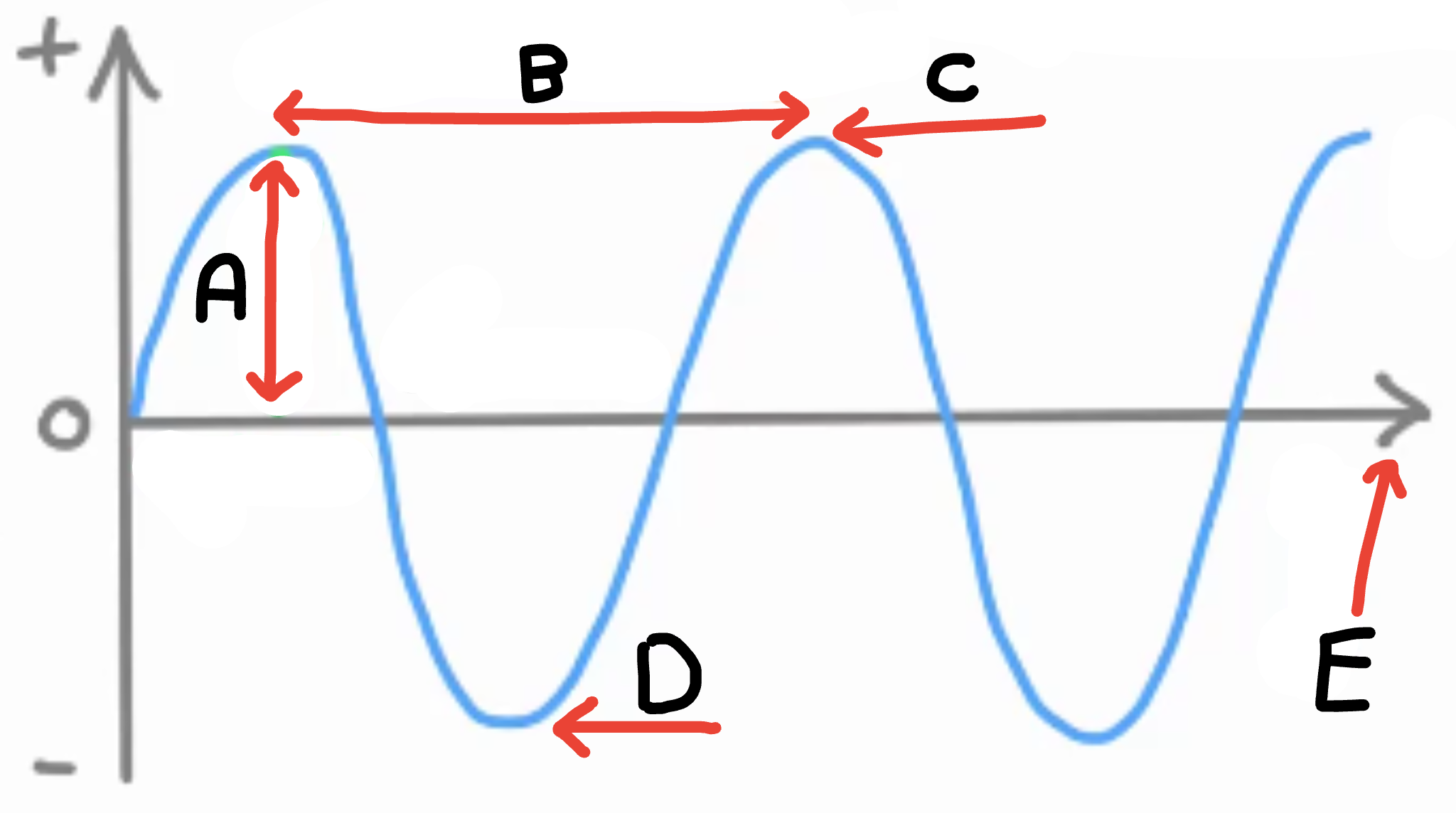
What is A
Amplitude
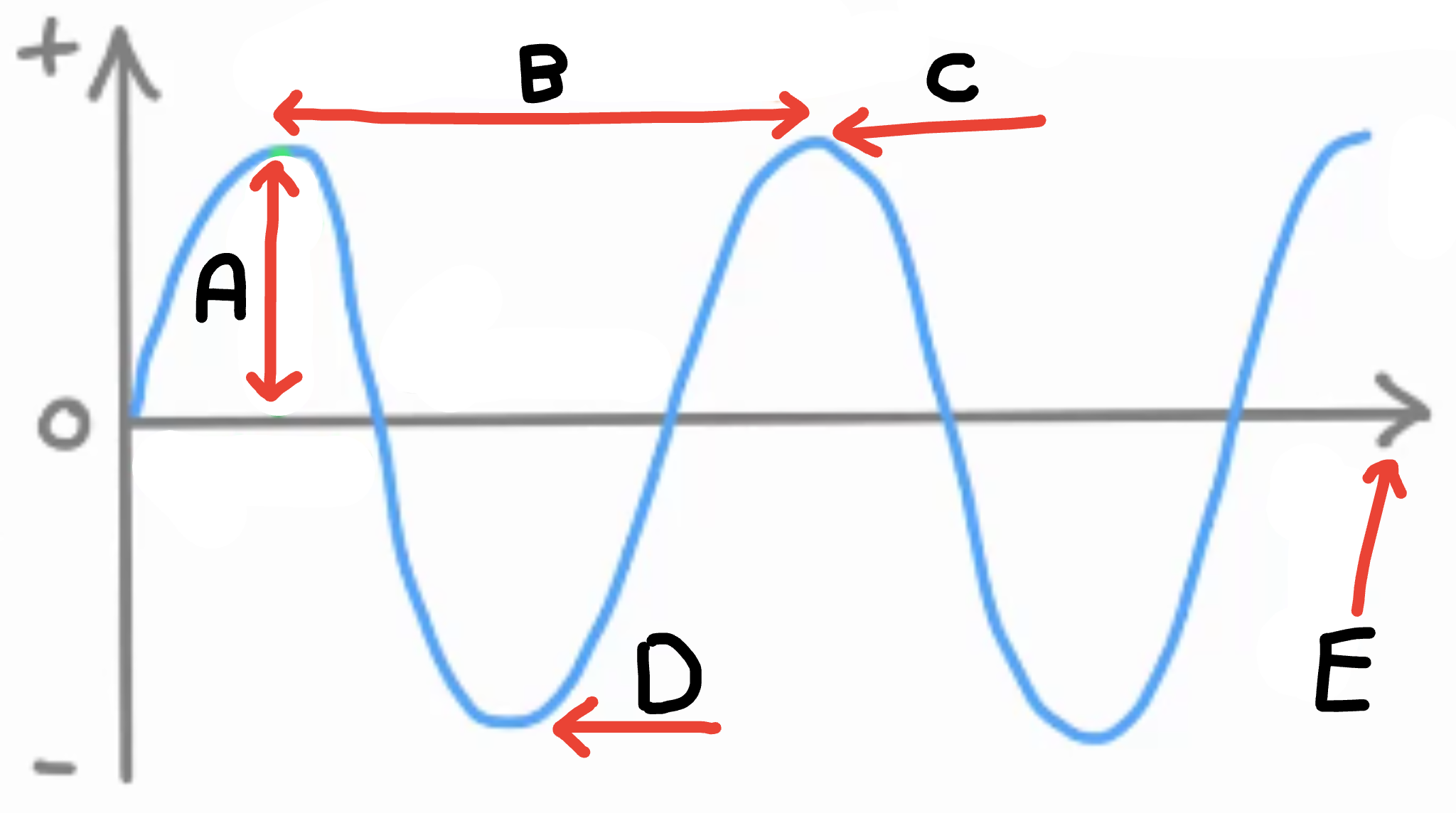
What is B
Wave length
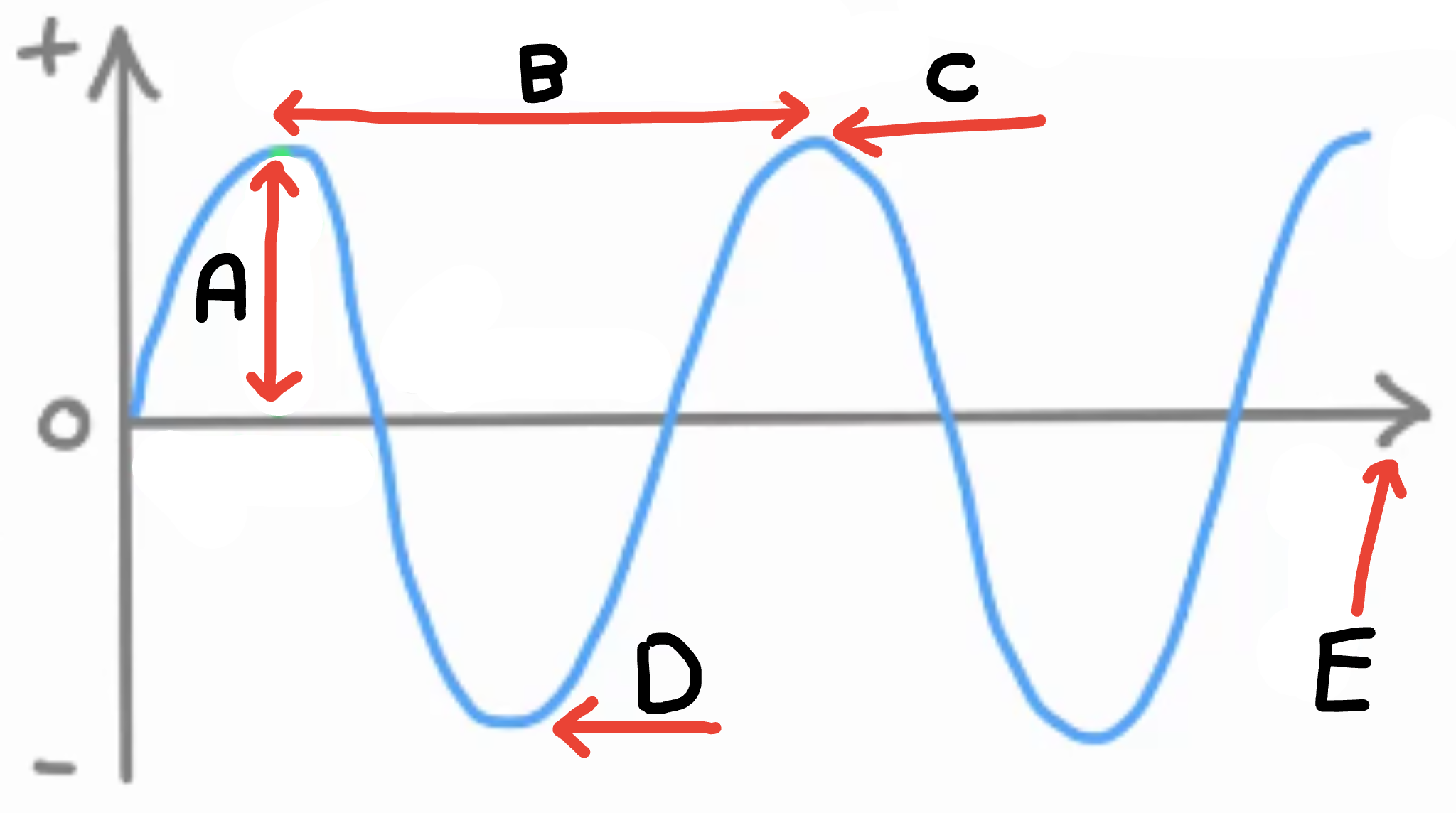
What is C
Peak/crest
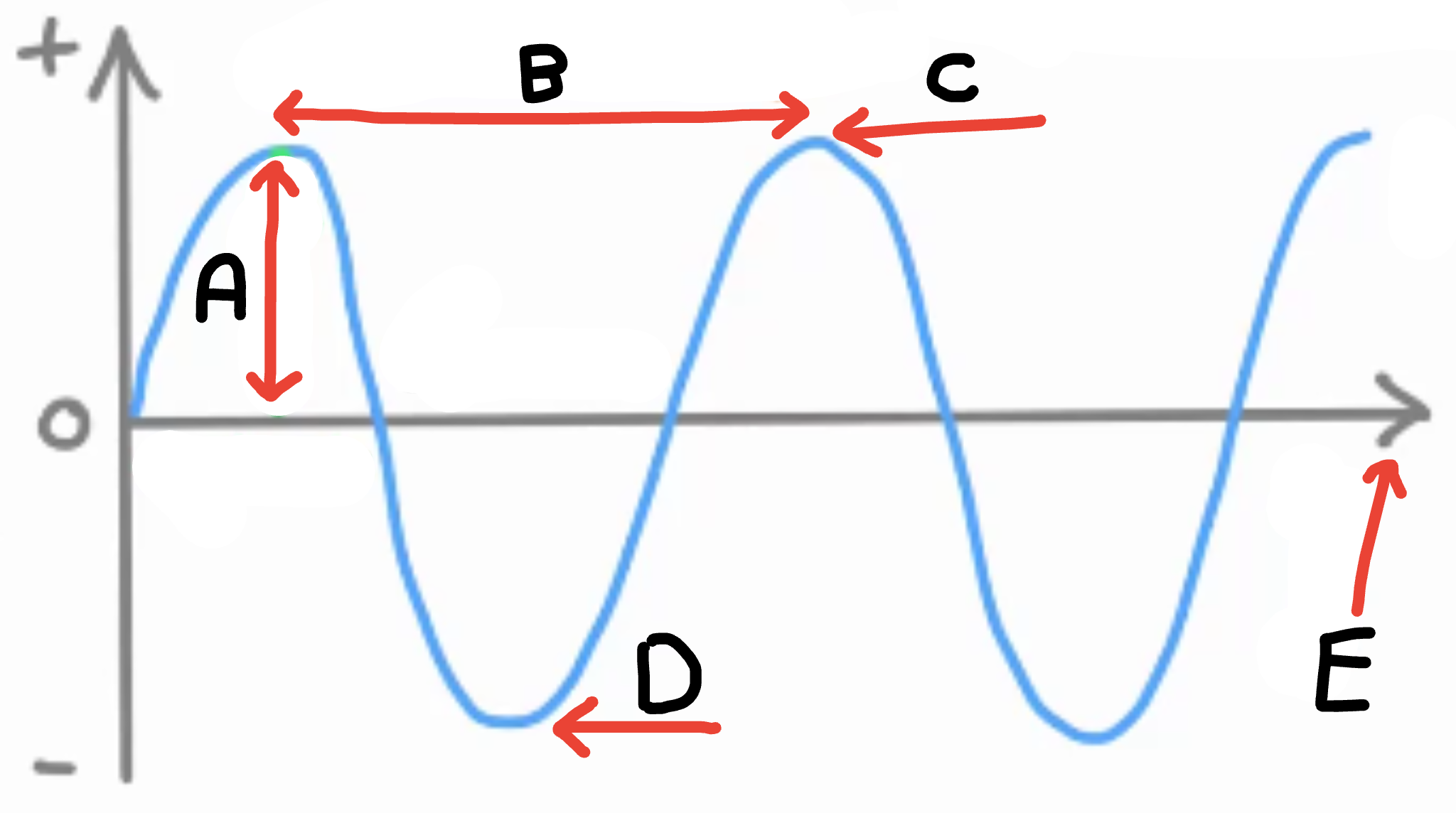
What is D
Trough
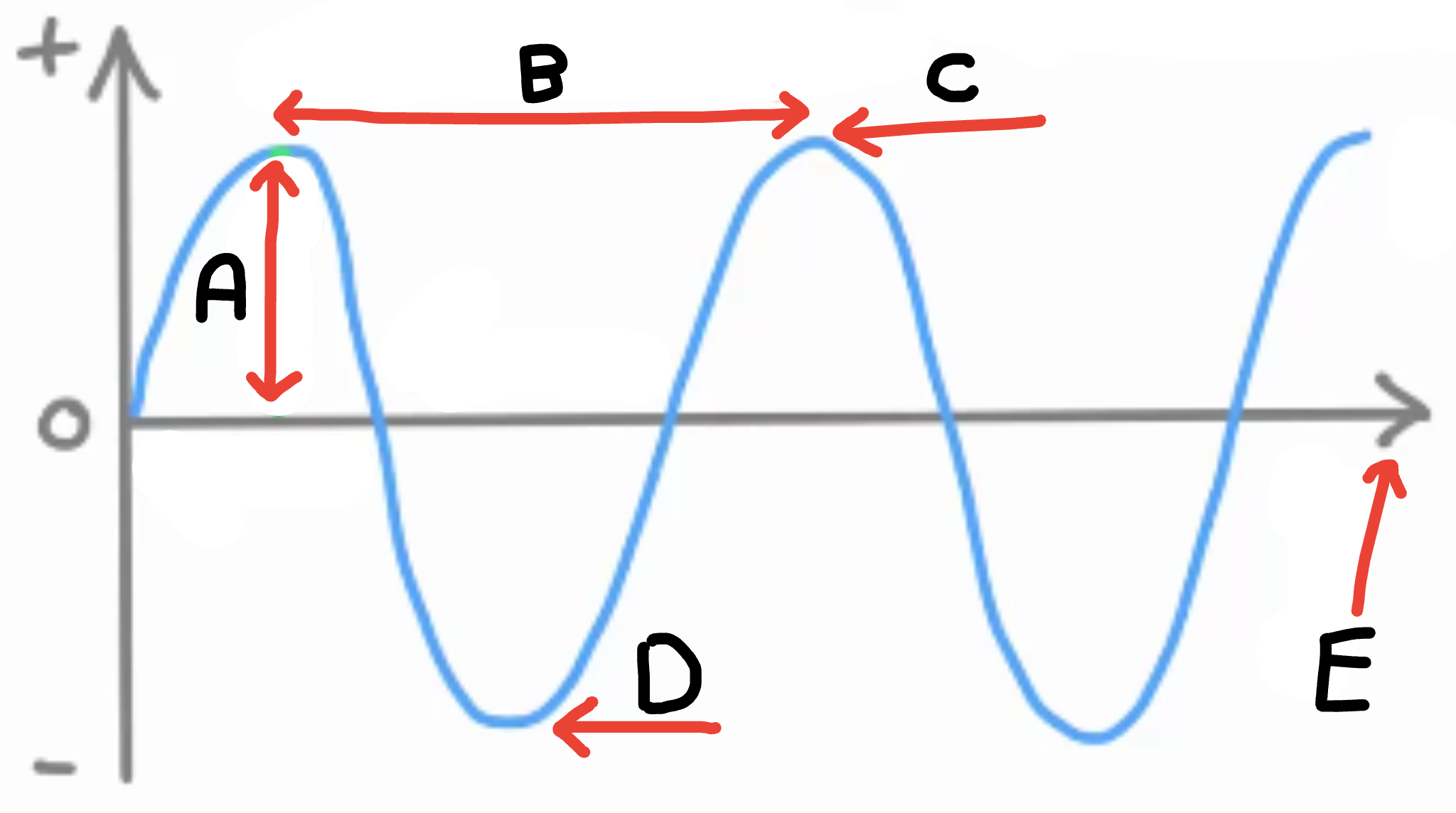
What is E
Energy transfer

How does a human hear?
Sound waves cause your eardrum to vibrate, which sends a signal to your brain.
Human hearing range
20Hz to 20kHz
frequency above 20kHz is called ultrasound

How does sonar work?
When sound meets a boundary between two mediums (materials), some sound is TRANSMITTED (passes through), while some is REFLECTED
The resulting echoes can be timed to build up a image of what's out of view e.g. a baby in a womb, or ocean floor underneath a boat.
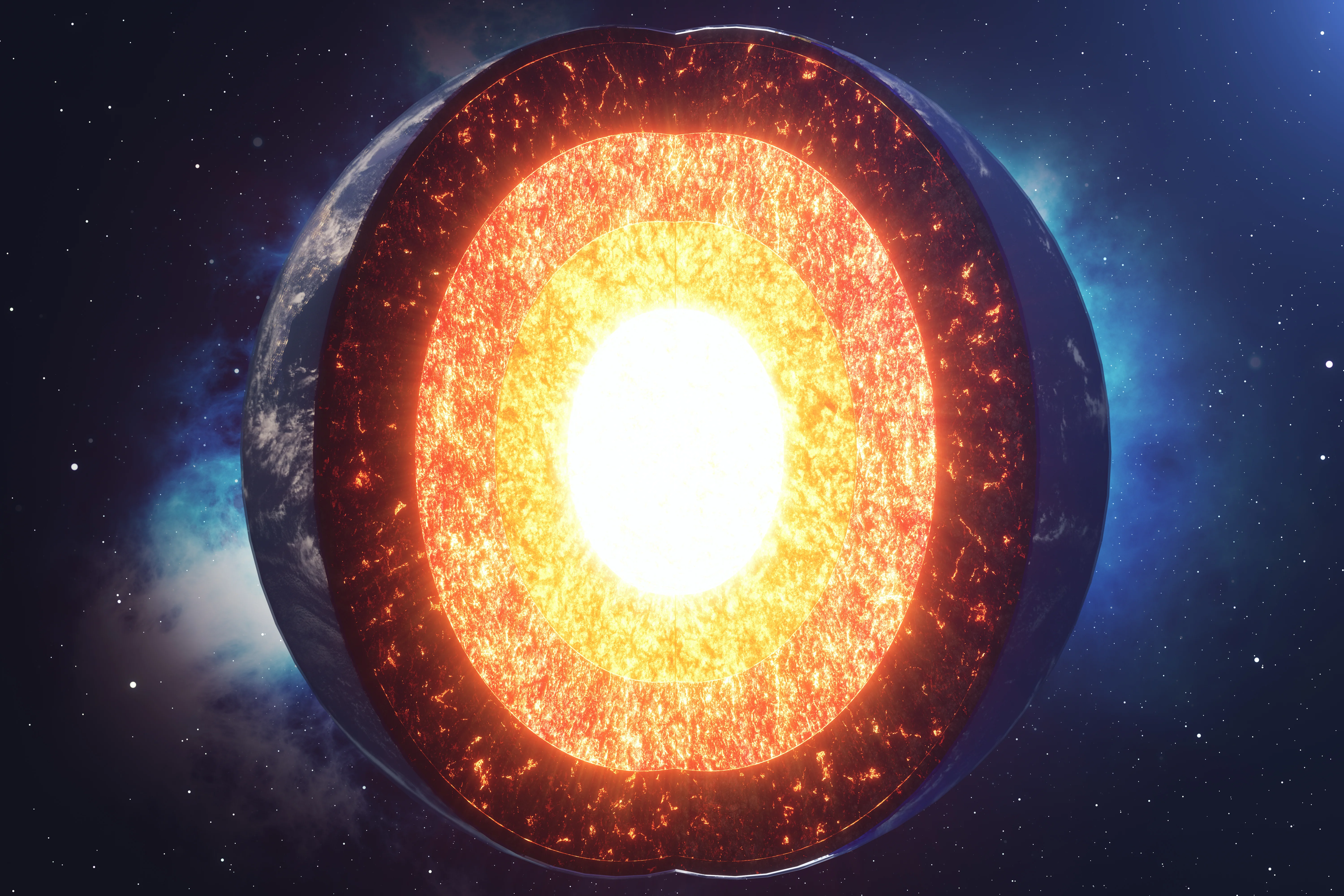

How do we know the earth has a molten (liquid) core?
The fact that seismic P-waves (longitudinal) pass through the centre of the Earth while S-waves (transverse) do not
P wave
are faster, longitudinal waves that can travel through solids and liquids
S wave
are slower, transverse waves that can only travel through solids
Specular reflection
Smooth surfaces (mirror) reflect light in a single clear direction.
Angle of incidence = angle of reflection, both measured from the normal.
Diffuse reflection
Rough surfaces scatter light in many directions because the surface is uneven.
No clear reflected image.
EM(electromagnetic) waves
Special since they dont need a medium to travel through
Only wave that can travel through a vacuum in space
Produced when an electron loses energy(gamma is emitted by nuclei)
Can be absorbed by an electron
EM wave spectrum (Lowest to highest frequency)
Radio waves
Micro waves
Infrared
Visible light
Ultra violet
X-rays
Gamma rays
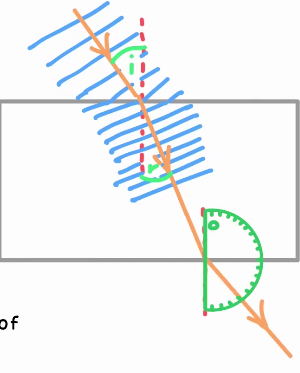
Refraction
When waves enter a new medium (material), their speed changes, as does their angle
If speed decreases wavelength also does, while frequency stays constant
If wave slows down it bends towards the normal
When light exits it speeds up again and bends away from the normal