Module 6 Population size and competition
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
what is limiting factor
environmental resource or constraint that limits pop growth
what are abiotic factors
temp, light, pH, water/oxygen availability, humidity
what are biotic factors
predators, disease, competition, food
what is carrying capacity
max pop size an env can support (earth capacity is 2-40bn
what are the two types of migration
immigration, emmigration
what is immigration
movement of individual organisms into a particular area, increases pop size
what is emigration
movement of individual organisms away from a particular area, decreases pop size
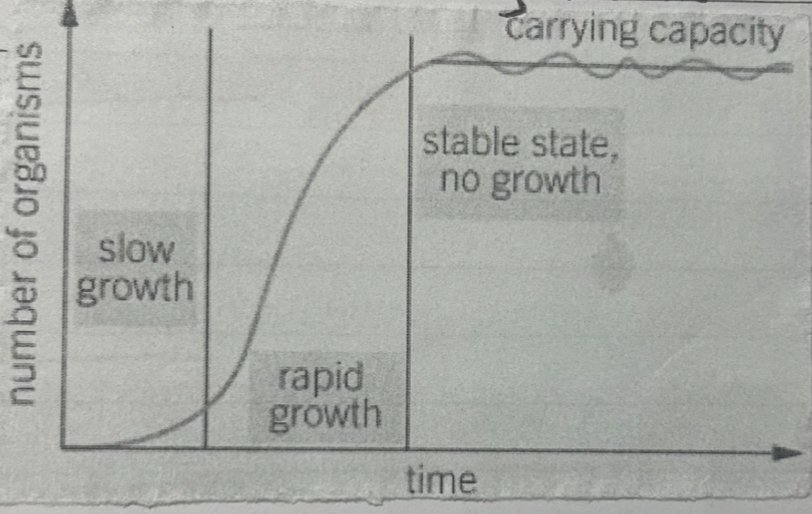
what does this growth show
pop growth with no limiting factors
what are density independent factors
factors that affect whole pop regardless of its size, can change pop size and remove pop e.g. earthquakes, fires, volcanic eruptions, storms
what is competitive exclusion principle
1 specie better adapted so out compete other causing pop decline of weaker specie
what is interspecific competition
competition between different species for same resources
what is intraspecific competition
competition between members of same species
what is an example of intraspecific competition
red vs grey squirrel, grey squirrel has more varied diet and are larger so less resources for red squirrels
what happens when members of the same species compete for same resources
the availability of the resources determines the pop size so fluctuations of pop number
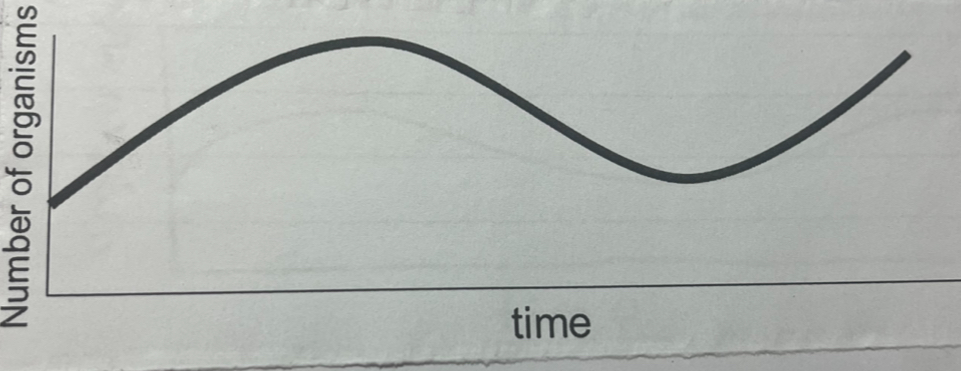
what does this graph show
number of organisms fluctuating due to availability of resources
how are predators evolved to be efficient at capturing prey
bursts of speed, stealth, fast reactions
how are prey evolved to avoid capture
camouflage, mimicry, defence mechanisms
how are predator and prey interlinked
as pop size of one changes it causes change in the other
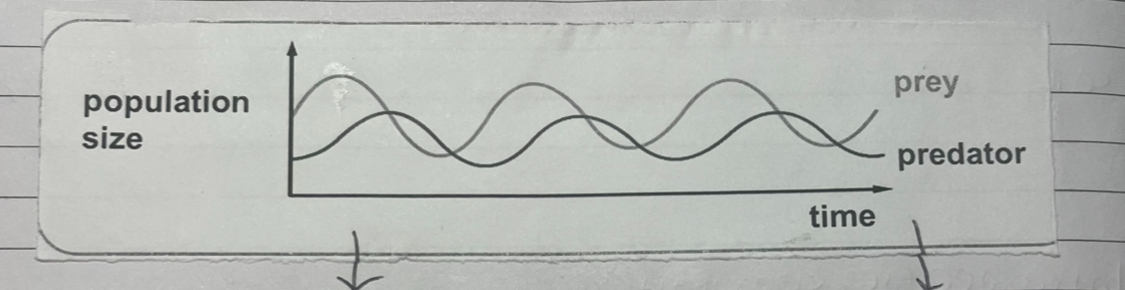
what does the graph show
lag time for predators to respond to increase in prey and reproduce