Mol Bio Exam 1 - D.J
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Semwal
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Define cell theory and key points
It is a fundamental theory of biology
1) All organisms consist of one or more cells
2) The cell is the basic unit of structure for all organisms
3) All cells arise from pre- existing cells
3 Main branches of biology and how they are connected to each other
1) Cytology - structure and function of plant cells
2) Genetics - the study of genes, genetic variation and heredity there of
3) Biochemistry - he chemical processes and substances that occur within living organisms
Cytology explores the cellular structures that house genetic material, while genetics examines how these materials dictate biochemical processes.
Cytology Tools
Microscopes (dyes, electron microscopy)
Immunohistochemistry
Biochemistry Tools
Centrifuges
Chromatography
Electrophoresis
Mass Spectrometry
Centrifuges
Biochemistry tool that spins around to separate by mass
solution based on size
Chromatography
Biochemistry tool used liquid or gas to separate by size/charge/or affinity
can be more specific
using liquid or gas to separate components
Electrophoresis
Biochemistry tool that uses electric current to separate DNA/RNA or proteins by size and charge
Genetrics Tools
Microarrays and Quantitative PCR to determine DNA sequencing
Robert Hooke
first described cells
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
Made lenses / first to observe cells
Robert brown
Identification of the nucleus
Matthias Schleiden
All PLANTS made of cells
Theodor Schwann
All ANIMALS made of cells
Anselme Payen and Louis Pasteur and Wilhelm Kuhne
Discovered first enzymes
Gregor Mendel
DNA is genetic material
Importance of carbon and properties
Carbon is the fundamental building block for all biological structures serving as the backbone of lipids, carbohydrates, DNA, and proteins
Needs 4 more electrons
Carbon is versatile and can interact easily with others
Can do single, double, or triple covalent bonds
Stable (hard to break)
Compatible with functional groups
Importance of water and properties
Water is a universal solvent, which is crucial in the transport of nutrients and chemicals in our body
Polar covalent
Electronegativity of oxygen
As a whole, neutral
nonpolar does not dissolve
Extensive H bonding (high surface tension/boiling point/specific heat/vaporization)
How would the properties of water change if the water molecule were linear rather than bent?
Water would be considered a non-polar molecule and will no longer be a universal solvent for polar and ionic molecules. As well as no hydrogen bond. It would also loose its high boiling point
Ways atoms interact
covalent, hydrogen, ionic, van der waals and hydrophobic interactions
Properties of cellular membrane
Semi-permeable
Amphipathic ( both hydrophilic + hydrophobic )
double layer of phospholipids
formed by hydrophobic interactions
Moves ions with transport proteins
Steps of Polymerization
1) Monomer activation uses ATP
2). Release of water (condensation reaction)
3) Repeat (further polymerization)
Self-Assembly
Process where molecules organize themselves into larger macromolecules that they were meant to be, sometimes with the help of chaperones. Mainly uses van der waal forces to form
Proteins types
enzymes (catalysts)
structural (hair)
motility (flagella)
regulatory '
transport (channels)
signaling (neurons)
receptor
defensive (antibodies)
storage
What can disrupt protein formation
Heat, pH, chemicals, and salt concentration
Primary structure
Linear amino acids linked with PEPTIDE bonds. determined by gene sequence and dictates higher levels
Secondary structure
local folding with HYDROGEN bonds
a-helix(spiral and one polypeptide)
beta sheet (strands and 1 or more polypeptides)
Helix or sheet?
Depends on amino acids
Tertiary Structure
INTERACTION with R group. and Ionic
3D folding of polypeptide
Goal is to be as stable as possible
fibrous and globular
Tools to know tertiary structure
Computer program and X-ray
Fibrous vs globular
Both tertiary proteins
Fibrous: long, coiled, extensible, insoluble in water (muscle and hair)
Globular: Compact, folded in on each other, random loops, soluble in water (hemoglobin)
Quaternary structure
Combinatinon of 2 or more polypeptides to form final protein
Uses chaperones
Many type of bonds (hydrogen, ionic, disulfide, hydrophobic, covalent)
Why protein folding?
To form a specific 3-D shape that is essential to complete its function
peptide vs polypeptide
polypeptide is a long peptide chain
Domain
Tertiary structure unit with a specific function
Motifs
Secondary Structure specific arangment of alpha helix and beta sheets
X ray crystallography
Used to determine 3D structure of proteins. Crystalize the molecule and shine x rays through to create a diffraction pattern
Nucleic acid types
DNA (storage) and RNA (expression)
Types of bonds in nucleic acid
Phosphodiester (phosphate to sugar)
also hydrogen
Components of a nucleotide
Sugar (deo/ribose)
DEO - DNA
Ribose - RNA
phosphate group
nitrogen base
Carbohydrates functions
energy storage, structure, cell signaling
Carbohydrate definition
long chains of sugar, can be branched
monosaccharides
glucose and fructose
disaccharides
sucrose (Gluc and fruc) and lactose
polysaccharides
cellulose - plant cell wall
chitin - insect cytoskeleton
peptide glycan - bacteria cell wall
Lipids properties
hydrophobic (some ampipathic)
high molecular weight
condensation synthesis
important in cell structure
NOT LINEAR POLYMERIZATION
Lipids exception to rule / differences
Not made with linear polymerization (there is no monomer that makes lipids, they just are lipids)
Hydrophobic (sometimes amphipathic)
Function of lipids
energy storage
membrane structure
signaling
Lipids similarities to other macromolecules
Made with condensation synthesis and important to life functions
6 classes of lipids
fatty acids
triacylglycerol
phospholipids
glycolipids
steroids
terpenes
Fatty acids
long unbranched hydrocarbons with a carboxyl on the end
amphipathic
Storage of energy when oxidized
Triacylglycerols
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids
Store energy
Insulation
Phospholipids
membranes
different R groups
Amphipathic
length and degree of saturation affects the fluidity of membrane
Glycolipids
Membrane bio recognition
Plant cells and nervous system
Amphipathic
Steroids
4 ring hydrocarbons
Nonpolar
sex hormones, glucocoticoids/ mineral corticoids
Types of light microscopy
Brightfield (stained or unstained)
Phase contrast
Differential interference contrast
Fluorescence
Confocal
electron microscopy
Brightfield microscopy
Light directly on specimen, can be dyed to add more contrast
Phase contrast
similar to brightfield but doesn’t need dye because it highlights contrast by amplifying variations in refractive index
Differential interference contrast
Like phase contrast but created a 3D surface of the specimen by detecting phase gradients
Fluorescence
Shows location of specific molecules in cell, can use dyes on the molecule
Confocal
uses lasers to illuminate a single plane within the specimen
Electron microscopy
extremley high resolution
2 types:
Scanning (surface of cell)
Transmission (internal view)
Why are cells small ?
surface area to volume ratio - as cells increase in size , their volume grows faster than their surface area
diffusion rate - allows for more efficient diffusion of nutrients , gases , and waste products in and put of the cell
efficient transport and communication - small cells can more effectively transport materials within the cells bc the distance are shorter
DNA and Protein synthesis limits
energy efficiency
cell division and growth control
adequate concentrations of reactants and catalysts
Ancestral cell
bacteria
archaea ( 1 st arrived on earth )
eukarya
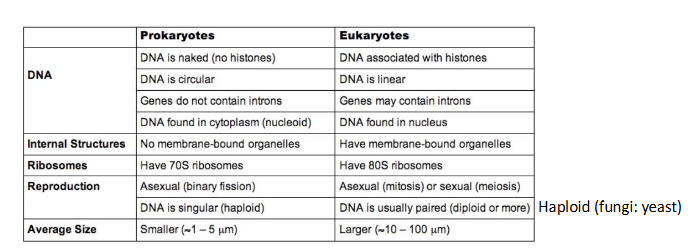
Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
pro : no nucleus, dna = circular , no membrane - bound organelle , smaller (1-10)
euk : nucleus , dna = linear , membrane - bound organelle , larger (10-100)
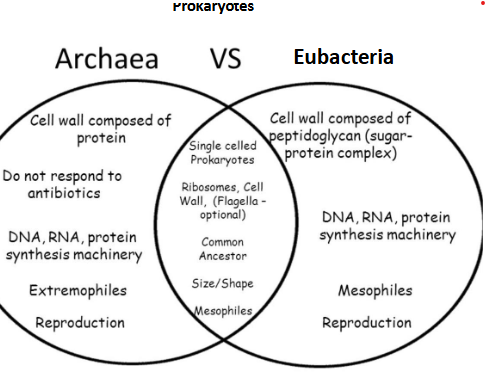
Archaea vs Eubacteria
a - cell wall is based on protein
e- cell wall is based on peptidoglycan ( sugar and protein)
Pili
hairs on the surface (cell-cell interaction, motility,
DNA uptake)
allows bacteria to stick to a surface
Mating: Can share information –
increases diversity
Flagella
motility
Cell attempts to solve 3 problems
1. Specificity problem
• Functional groups give specificity
• Atoms
2 Containment problem
• Bilipid layer (phospholipids)
• Gives rise to plasma membrane and organelles
3. Information problem
• Nucleic acids- DNA and RNA
• “storage” of data and is heritable
Differences between Cell types
1. Membrane-bound nucleus:
eukaryote→ (yes),
bacteria/archae → no
1. Organelles: internal, membrane-
bound with a specific function
• Exception: Caulobacter crescentus,
cyanobacteria
2. Exocytosis & endocytosis—
exchange material between
compartments in eukaryote
4. Organization of DNA: histones in euk, circular vs
Linear DNA
5. Segregation of DNA
• Binary fission (prok) vs. mitosis (euk)
6. Expression of DNA
• Prokaryotic: 1 mRNA→several proteins (operon)
• Eukaryotic: 1 mRNA→1 protein (usually)
Plant vs Animal differences
Plant - cell wall , central vacuole , chloroplasts
Animal - small or no vacuole , centrioles and centrosomes , flagella
Plants vs animals - similarities
ribosomes , endoplasmic reticulum , plasma membrane , golgi apparatus , mitochondria , nucleus
Where did cells come from?
Abiotic synthesis of simple compounds->Abiotic polymerization-
>encapsulated in lipid membranes
Plasma membrane
Lipid bilayer + proteins → fluid mosaic model.
Functions: selective permeability, structural support, signaling
A cell = p.m w membrane proteins = lipid bilayer with glycoprotein
Nucleus
Control center: DNA storage, transcription.
Components: nuclear envelope, chromatin, nucleolus (rRNA synthesis). Nuclear pores regulate transport.
Nuclear lamina = structural support
Mitochondria
Double membrane, dynamic movement in cells.
• Site of aerobic respiration:
o Glucose + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O + ATP.
• Own DNA (circular, maternally inherited).
• 70S ribosomes.
• Endosymbiont origin
Chloroplasts (plants)
Photosynthesis: solar energy + CO₂ → sugars + O₂.
• Double membrane, own DNA + 70S ribosomes.
• Endosymbiont origin
Endosymbiont Theory for Chloroplasts and Mitochondria
The endosymbiont theory proposes that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as
free-living prokaryotes that were engulfed by ancestral eukaryotic cells. Instead of being
digested, these prokaryotes formed a mutualistic relationship: the host cell provided
protection and nutrients, while the symbionts contributed energy production
(mitochondria: ATP via aerobic respiration; chloroplasts: sugars via photosynthesis).
Over time, most of their genes were transferred to the host nucleus, leaving them semi-
autonomous. Evidence includes their double membranes, circular DNA, 70S ribosomes,
maternal inheritance, and independent division similar to bacteria
Endomembrane system
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi apparatus
lysosomes
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Tubular membranes with
flattened sacs
• Outer membrane continuous
with nuclear envelope
• Rough: Associated with ribosomes to make
intermembrane proteins, secreted
proteins
• Smooth: Synthesis of lipid and steroids,
detoxification of drugs
Golgi Apparatus
Stacks of flattened vesicles
• Processing and packaging
secretory proteins
• Synthesizes complex
polysaccharides
• Vesicles
Lysosomes
stores enzymes to digest other molecules , autophagy
Peroxisomes
Several functions
• Generating/degrading H2O2
• Catalase
• Also degrade methanol,
ethanol, formate,
formaldehyde
• Breakdown of large fatty
acids
• High concentration in liver and kidney
Vacuole
• Animals
• Temporary storage and
transport
• Protozoa
• Feed by endocytosis, merge
with lysosome
• Plants
• Turgor pressure- maintains structure
Cytoskeleton
Highly structured (proteins)
• Dynamic
• Cell shape, movement, division,
moving organelles
cytoskeleton - 3 types
Microtubules (biggest)
• Intermediate filaments
• Microfilaments (actin, smallest)
Extracellular Matrix
Support outside plasma membrane.
• Animals: collagen-rich, flexible.
• Plants: rigid cellulose cell wall.
• Functions: support, adhesion, communication.