Groundwater: Soil, Porosity, Aquifers, and Weathering
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
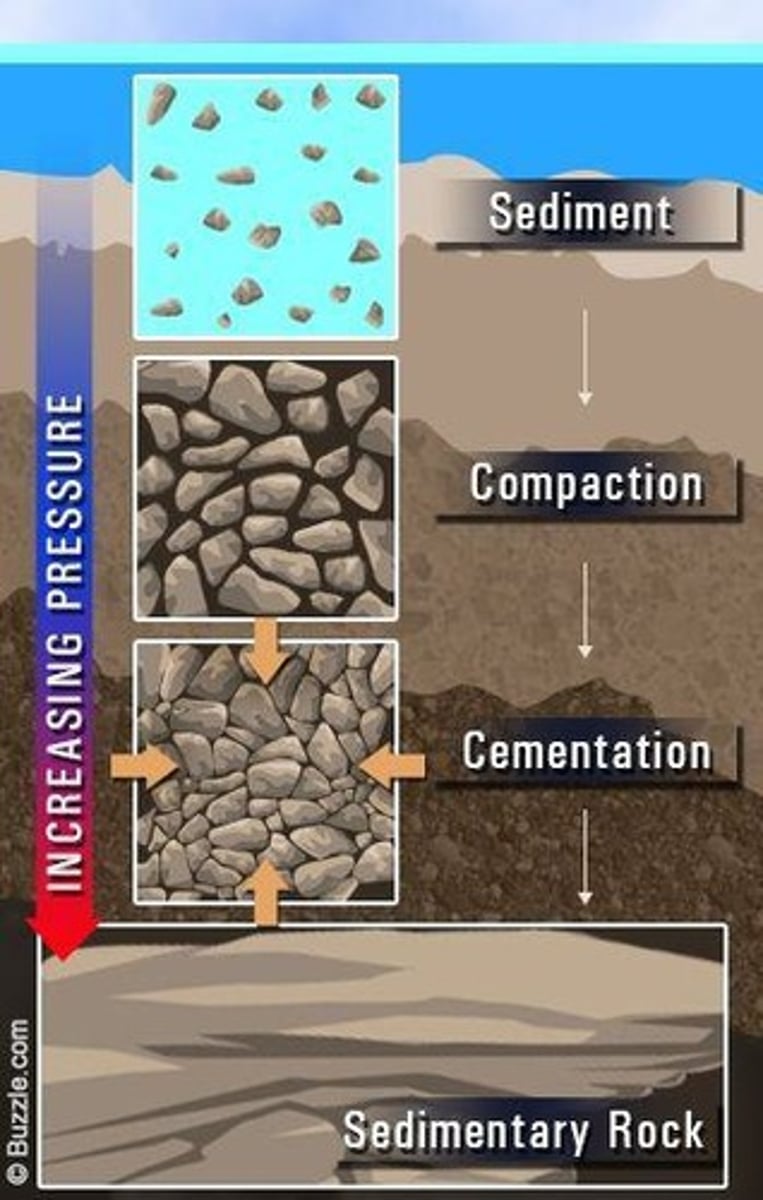
Sediment
Material that forms from the weathering and erosion of rocks.
Water Table
The uppermost part of the zone of saturation.
Zones of Aeration
The zone above the water table where soil pores can be filled with a mixture of air and water (but < 100% water).
Zones of Saturation
The zone below the water table where soil pores are 100% filled with water.
Soil Texture
The classification of soil based on the proportions of sand, silt, and clay.
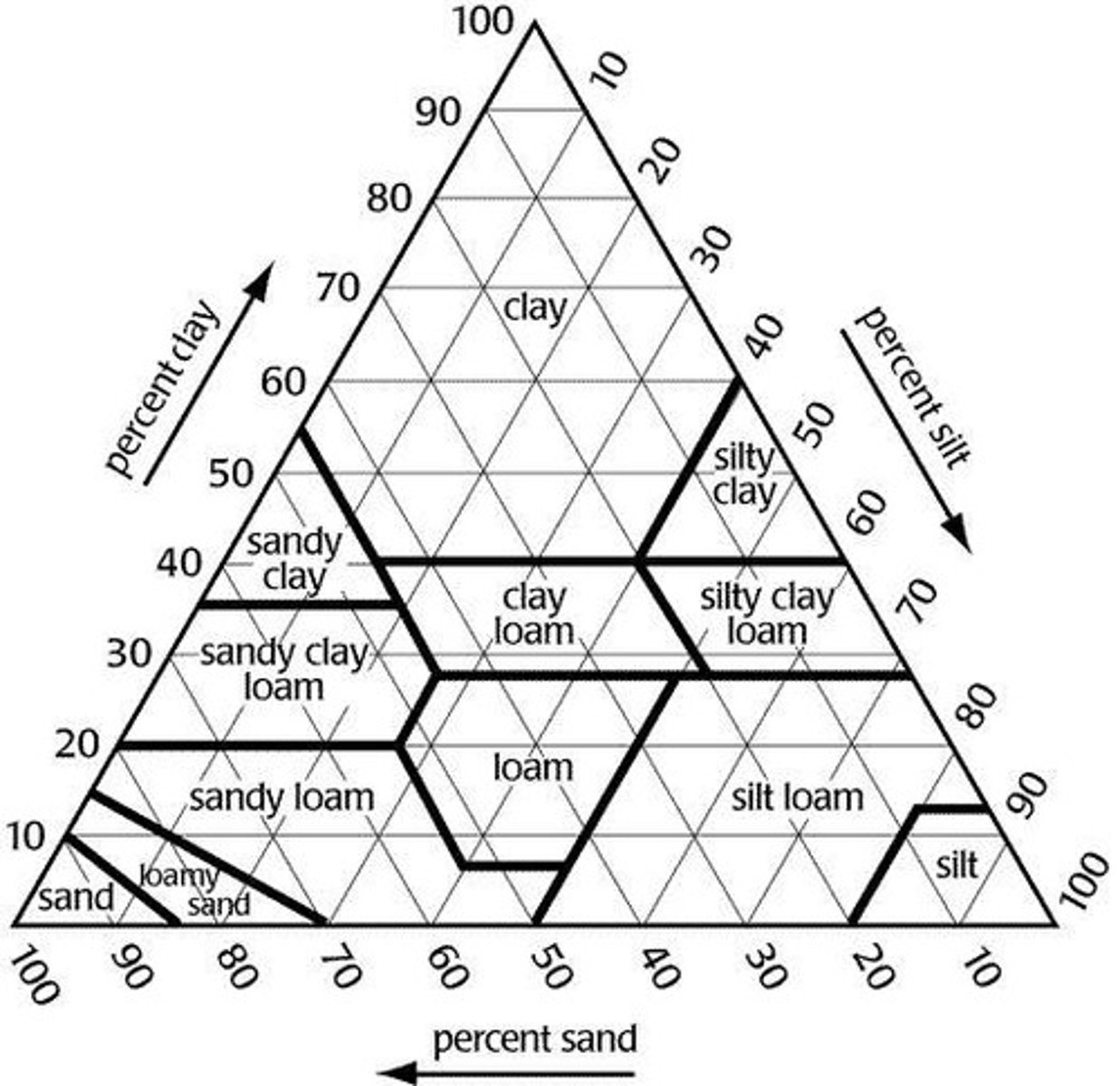
Textural Triangle
A tool used to determine the textural classification of soil based on its sand, silt, and clay content.
Porosity
The measure of the void spaces in a material, indicating how much water it can hold.
High Porosity Material
Materials that have a large number of pore spaces, allowing them to hold more water.
Low Porosity Material
Materials that have few pore spaces, limiting their ability to hold water.
Permeability
The ability of a material to allow fluids to pass through it.
Soil Texture Classification Example 1
Soil with 40% sand, 40% silt, and 20% clay.
Soil Texture Classification Example 2
Soil with 50% sand, 25% silt, and 25% clay.
Soil Texture Classification Example 3
Soil with 25% sand, 20% silt, and 55% clay.
Soil Texture Classification Example 4
Soil with 10% sand, 55% silt, and 35% clay.
Soil Texture Classification Example 5
Soil with 10% sand, 65% silt, and unknown clay content.
Capillary Fringe
The area located above the water table where water wicks up towards the surface due to adhesion and cohesion properties.
Adhesion
The property of water that causes it to stick to solid surfaces.
Cohesion
The property of water that causes it to stick to itself.
Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks
Types of rocks that are usually solid and have little to no pore spaces, thus exhibiting low porosity.
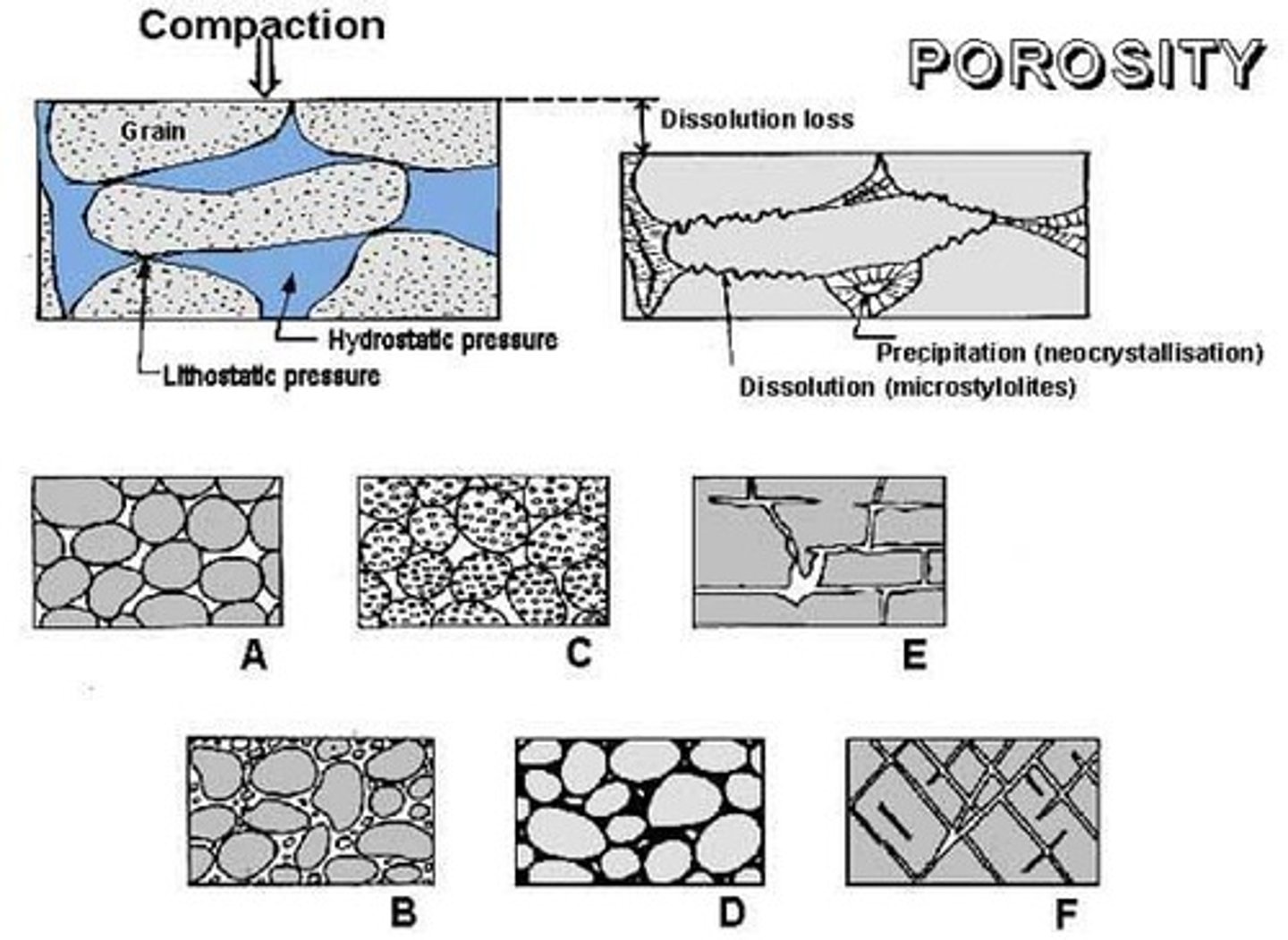
Sedimentary Rocks
Rocks made of compacted weathered and eroded rock particles that have empty spaces between grains, thus exhibiting porosity.
Mechanical Weathering
The process of physically breaking down rocks, such as through frost wedging.
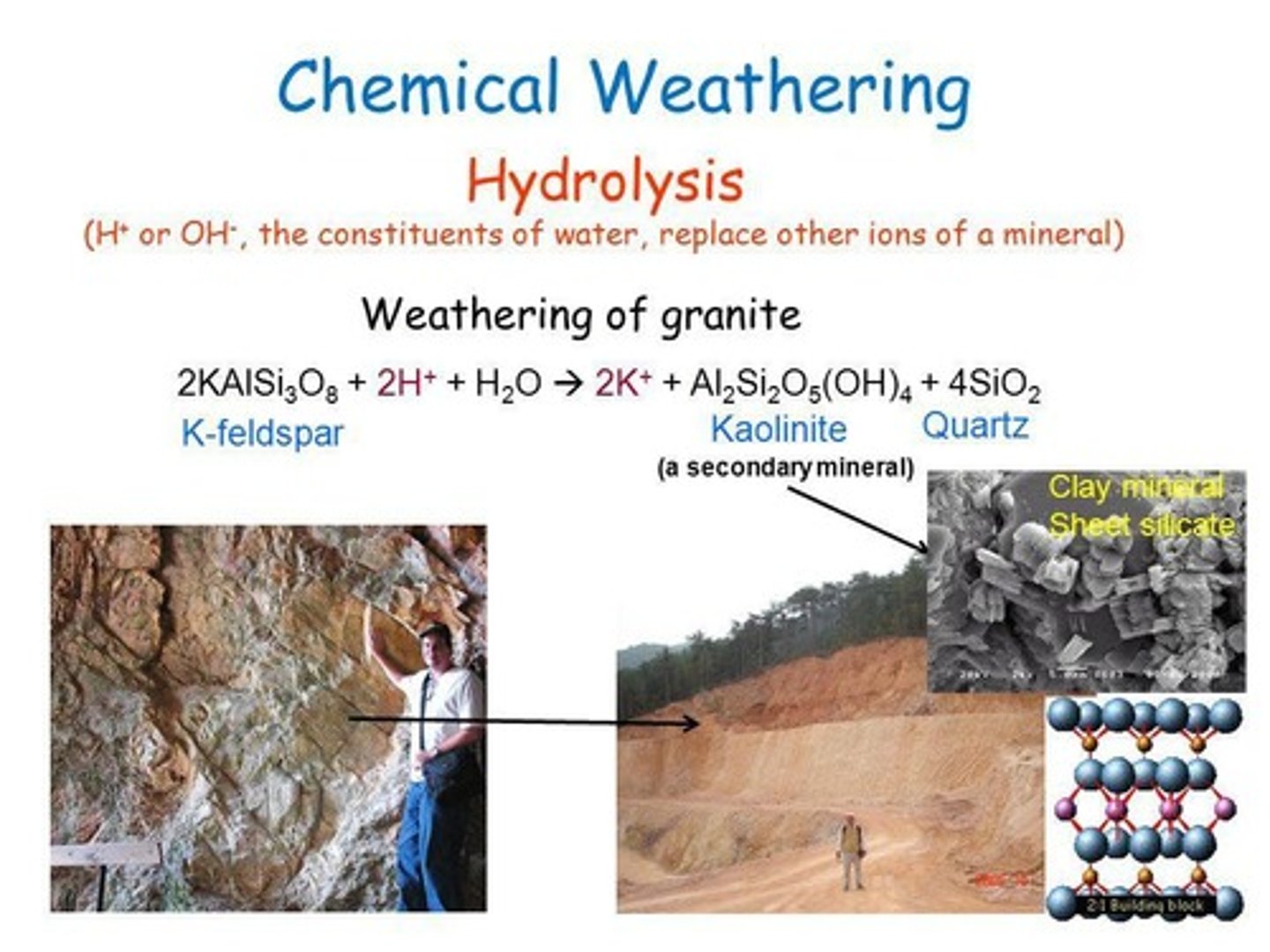
Chemical Weathering
The erosion or disintegration of rocks caused by chemical reactions, chiefly with water and substances dissolved in it.
Hydrolysis
A chemical weathering process that occurs when acid rain reacts with rock-forming minerals to produce clay and salts.
Well-sorted clastic sediment of high primary porosity
Great aquifer material.
Poorly sorted clastic sediment of restricted primary porosity
Not the best.
Well-sorted clastic sediment with extremely high primary porosity
Due to the porous character of the grains (good).
Well-sorted clastic sediment with cement infill of the primary porosity
Poor.
Secondary porosity due to dissolving of rock
Example: limestone (can be good).
Secondary porosity along fractures in a systematically fractured rock
Can be good if lots of fractures.
Particle Size
Does NOT affect porosity alone; shape, packing, and sorting do.
Spherical particles
Have a higher porosity than angular particles.
Well sorted particles
Have a higher porosity than angular particles.
Sorting
If all particles are the same size, they are sorted; if different sizes, they are unsorted (poorly sorted).
Packing
The more closely packed the particles are, the lower the porosity.
Shape
Well rounded particles have greater porosity than angular particles.
Porosity of sorted particles
The same for sorted particles, but not for unsorted particles.
Big spaces
Not a lot of them.
Little spaces
But lots of them.
Groundwater availability
Determined by the amount of porosity in the sediment.
Capillarity
The process of water adhering to rock particles (cohesion) in small spaces, resulting in an upward movement of the water through rock sediment.
Zone of Aeration
Zone above the water table where the soil pores can be filled with a mixture of air and water (but < 100% water).
Zone of Saturation
Zone below the water table where the soil pores are 100% filled with water.
Aquifer
An underground deposit of sediment or material that is capable of holding and transmitting water.
Aquitard/Aquiclude
A material that does not allow water to pass through it readily (e.g., clay, granite).
Recharge Area
Area of land above an aquifer that allows water to infiltrate through the soil to fill up the soil pores with water.
Unconfined Aquifer
An aquifer that is open to the atmosphere and only has one confining layer.
Confined Aquifer
An aquifer that is not open to the atmosphere and is confined by two aquitards.
Artesian Well
A well dug into a confined aquifer that has its water table at a higher elevation than the top of the well so that it flows freely without pumping.
Cone of Depression
A lowering of the water table due to excess pumping.
Groundwater Contamination
Wells can get contaminated by sucking up pollutants from far away areas.
Land Subsidence
Land can sink over large areas due to groundwater withdrawal.
Groundwater Depletion
Groundwater can be depleted due to overuse.
Salty Wells
Wells can become salty if they are near ocean areas.
Recharge and Gaining Stream
When the water table is at a higher elevation than the lake or stream, water passes from the groundwater into the lake or stream.
Soil Texture and Capillary Water
The relationship between soil texture and the capillary water content of the soil.
Effect of Soil Permeability
The effect of soil permeability on the amount of runoff in an area.
Groundwater Movement
Describes how groundwater moves in different experiments.