pre ap bio study
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What is an example of a monosaccharide?
An example of a monosaccharide is glucose and fructose.
How are photosynthesis and carbohydrates related?
They both create glucose and provide energy,
What is the monomer of carbohydrate?
The monomer of carbohydrates is a monosaccharide.
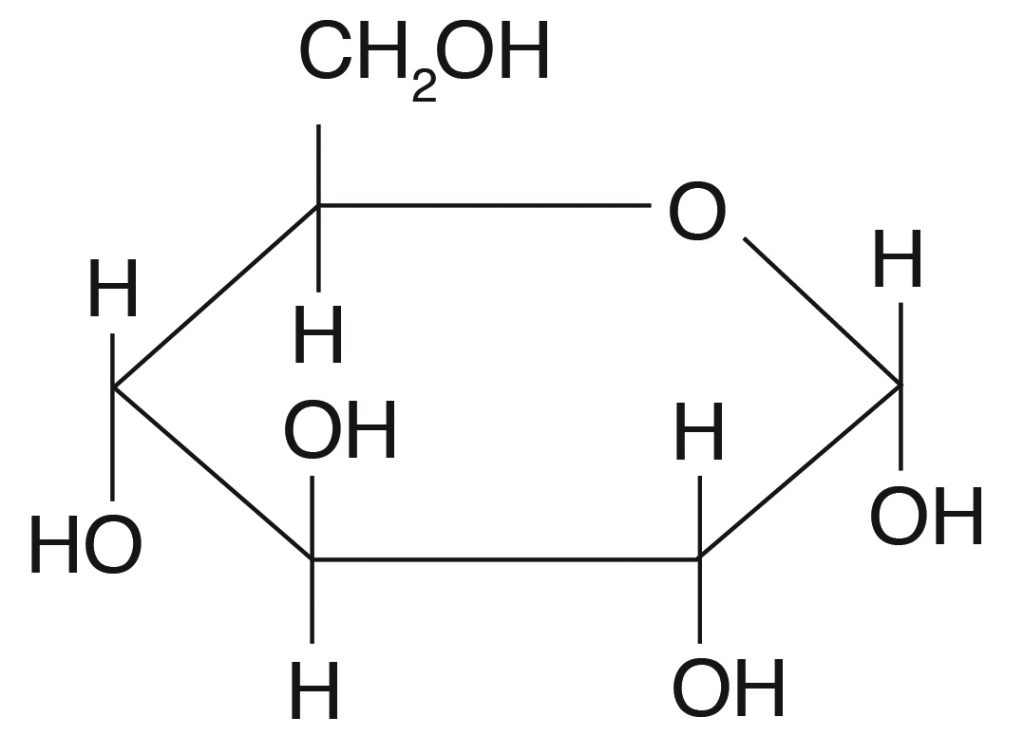
How do carbohydrates help maintain homeostasis?
They help by giving energy to the body and they fuel cellular respiration.
Name three roles of proteins.
Help with pigmentation
Builds body structure
Acts as enzymes
Acts as horomones
Used as storage
What is the monomer of proteins?
The monomer of proteins is Amino Acids. (20)
Lipids do not mix with water, true or false?
False, lipids do not mix with water.
What are two functions of lipids?
They build up the cell membrane.
They store energy.
They help with waterproofing.
How do lipids help maintain homeostasis? (Think cell membrane)
They help build up the cell membrane.
Which Macromolecule is DNA?
Nucleic Acid is the macromolecule.
The monomer of nucleic acid is _______.
Nucleotides are the monomer.
What is an organic compound?
Compounds in which carbon atoms are combined with hydrogen and oxygen.
Carbon can form covalent bonds with as many as 4 atoms (elements) true or false?
True, carbon can form covalent bonds. Its promiscuous.
What is dehydration synthesis?
The creation of polymers by removing water between monomers.
What is hydration synthesis?
Separating monomers by adding water.
What is the organelle of a carbohydrate?
The organelle is the mitochondria, the power house of the cell.
What are some examples of carbohydrates?
Some examples are starch and glucose.
What is the basic unit/macromolecule of lipids?
The basic unit/macromolecule are Fatty Acids.
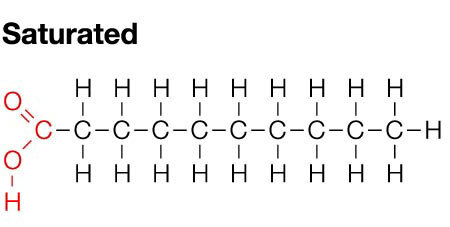
What are saturated lipid structures?
Saturated lipids are unbroken structures and they are not good for the body. These do have a double bond.
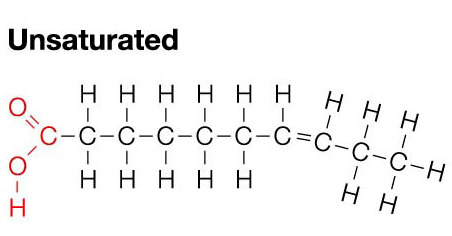
What are unsaturated lipid structures?
Unsaturated lipids are broken structures and they are good and beneficial for the body. These do have 2 double bonds.
What is a phospholipid?
A lipid containing a phosphate group in its molecule. (Typically the cell membrane containing a phosphate head)
What do nucleic acids do?
They help with genetic information by carrying it.
Makes RNA and proteins.
What are some examples of Nucleic Acids?
Some examples are DNA and RNA.
What is homeostasis?
Organism maintaining stability while adjusting to conditions that are best for its survival.
What macromolecule is C,H,O
The macromolecule is Carbohydrates and Lipids.
What macromolecule is C,H,O,N
The macromolecule is Proteins
What macromolecule is C,H,O,N,P
The macromolecule is Nucleic Acids
What is a monosaccharide?
A carbohydrate consisting of one sugar unit.
What is a polysaccharide?
A carbohydrate that consists of many sugar molecules bonded together.
What is a monomer?
A molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
What is a polymer?
Structure consisting of a large number of similar units bonded together. (Monomers)
What is a double bond?
A chemical bond in which two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms
What special element is in Nucleic Acid?
The special element is Nitrogen.