Wrist & Hand Complexes: Kinesiology
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
provides a dynamic base of support for the wrist and hand
shoulder
provides ability to reach away from the body
elbow
allows for adjustment of the "approach" of hand to object
forearm
acts as a "functional spacer" and affects the function of the hand
wrist
primary effector organ for our most complex motor behaviors
hand
______ different muscles drive the ______ bones and 19 articulations within the hand
29 different muscles, 19 bones
carpals are ______ joints
planar
angle of the radius toward the ulna
25 degrees
greater amount of ulnar deviation is possible in comparison to radial deviation (T/F)/
true
radial deviation end feel
hard
radius angle toward the palm (allows for greater flexion compared to extension)
10 degrees
ulnar deviation end feel
firm
carpal bone most likely to dislocate
lunate
the "keystone" of the hand
Capitate
pisiform is a _________ joint
syndesmosis
radiocarpal is an _______ joint
ellipsoidal
true wrist bones
distal end of radius, scaphoid, and lunate
carpal shaped like a "boat"
scaphoid
very stable carpal bone; "captain" of ship
capitate
what makes lunate the most unstable carpal bone
lack of connections to capitate
patient's using high velocity, oscillatory type tools are more prone to _____________ syndrome
carpal tunnel
in ulnar deviation, the roll is _________ the ulna and the slide is toward the ____________
roll is toward the ulna, slide is toward the radius
in radial deviation, the roll is __________ the radius and the slide is ______________ the ulna
roll is toward the radius, slide is toward the ulna
what muscles provide the radial collateral ligament with support (radial deviation support)
abductor pollicus longus and extensor pollicus brevis
what muscles provide the ulnar collateral ligament with support (ulnar deviation)
palmar ulnar ligament, TFCC, FCU, ECU
the carpal rows all move as one (T/F)
true
Neuman states that distal to proximal carpal row is like a __________ joint
ball and socket
compartment of the hand that has the most mobility
medial; scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, capitate, hamate
carpal row of the hand that has more movement potential
proximal
compartment of the hand that has the least mobility
lateral
medial compartment (midcarpal joint)
scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum; capitate and apex of hamate
lateral compartment (lateral joint)
scaphoid, trapezium, trapezoid
ligaments of the carpals are short/long (choose 1)
short
the angle of the radius towards the palm (10 degrees) allows for better..
flexion
a "ray" includes
metacarpal and all its associated phalanx's
arches of the hand
proximal transverse, distal transverse, and longitudinal arches
function of the arches of the hand
-allow the hand to securely hold and manipulate objects
-give the hand integrity; unique curves allow for functionality
proximal transverse arch of hand
formed by the distal carpal bones and forms the carpal tunnel. the keystone is the capitate.
distal transverse arch of hand
formed by the MCP joints, mobile and passes through metacarpal heads
longitudinal arch of the hand
begins at the wrist and follows the 2nd and 3rd rays of the hand. keystone is the 2nd and 3rd MCP joints
the CMC joints (2nd through 5th) are ________ joints
complex saddle
complex saddle joints at the 2nd and 3rd CMC joints allow for...
very little to no motion
complex saddle joints at the 4th and 5th CMC joints allow for...
slight flexion and internal rotation
potential for movement at the CMC joints is..
challenged
thenar eminence
the fleshy mass at the base of the thumb (abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis)
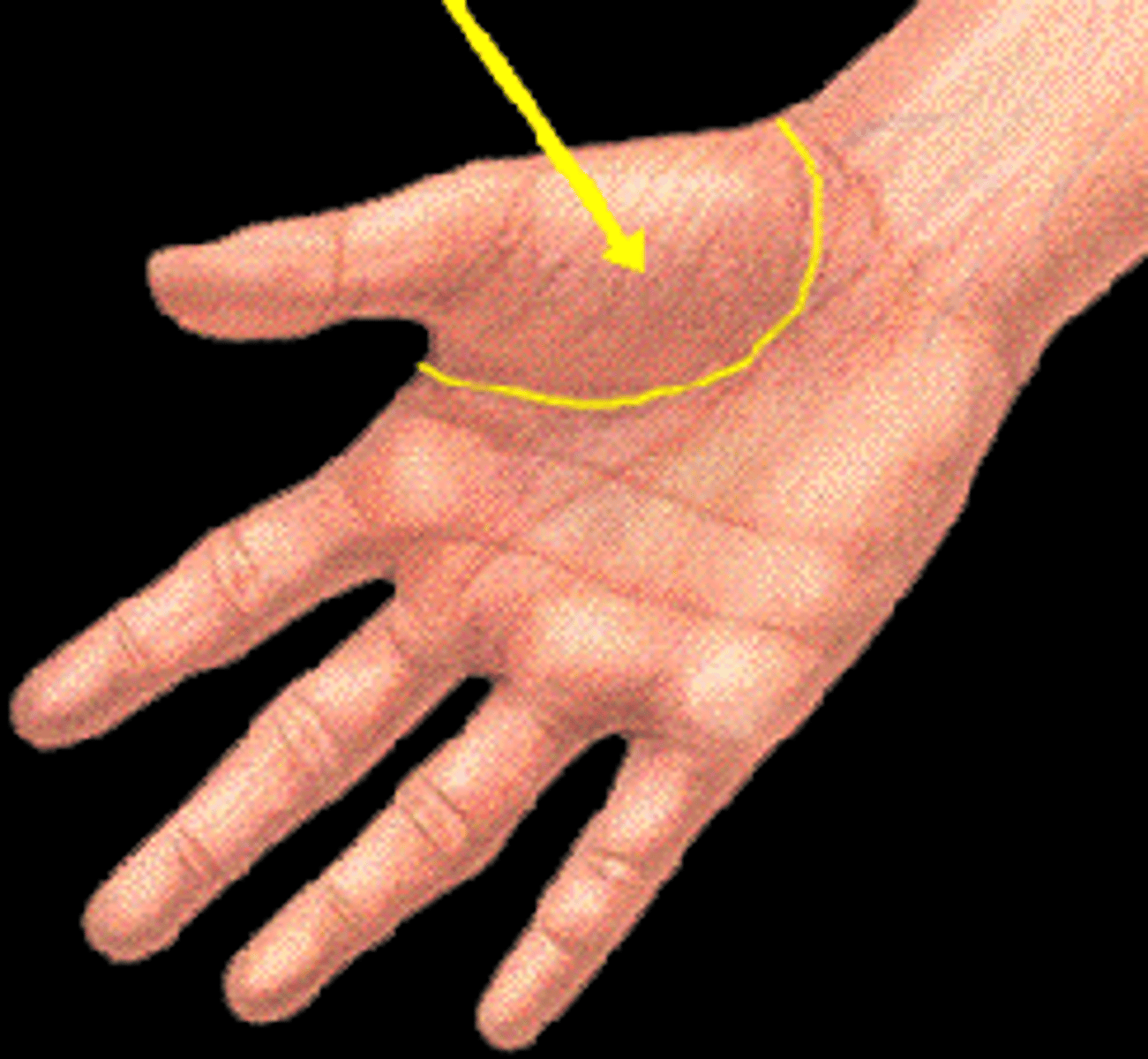
hypothenar eminence
the fleshy mass at the base of the little finger (abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis, opponens digiti minimi, palmaris brevis)
the distal phalanx is CC/CV (choose one) upon the middle phalanx
concave (CC)
the middle phalanx is CC/CV (choose one) upon the distal phalanx
convex (CV)
the middle phalanx is CC/CV (choose one) upon the proximal phalanx
concave (CC)
the proximal phalanx is CC/CV (choose one) upon the middle phalanx
convex (CV)
the proximal phalanx is CC/CV upon the second metacarpal
concave (CC)
the 2nd metacarpal is CC/CV upon the proximal phalanx
convex (CV)
MCP joints are _______ joints
condyloid
roll and slide of the phalanx on metacarpal for flexion occurs in the ___________ direction
same
the PIP and DIP joints are ________ joints
hinge
the 1st CMC joint is a _____________ joint
saddle
the 1st CMC joint is roughly _______ degrees compared to the rest of the hand
90
during radial adduction and abduction, the proximal end of the metacarpal is CC/CV (choose one)
concave (CC)
during adduction, the 1st metacarpal rolls _________ the ulna
toward
during abduction of the 1st metacarpal, the MC rolls _________ the radius
toward
during palmar adduction and abduction, the proximal end of the metacarpal is CC/CV (choose one)
convex (CV)
radial adduction is the same as thumb flexion (T/F).
true
opposition
-palmar adduction and flexion/medial rotation combined
-multiple planes of movement involved
radiocarpal open packed position
neutral with slight ulnar deviation
CMC open packed position
midway between abduction-adduction and flexion-extension
MCP open packed position
slight flexion
IP open packed position
slight flexion
radiocarpal close packed position
extension with radial deviation
MCP (fingers) close packed position
full flexion
MCP (thumb) close packed position
full opposition
IP close packed position
full extension
radiocarpal capsular patterns (limited ROMs)
flexion and extension equally limited
MCP capsular patterns (limited ROMs)
flexion > extension
IP capsular patterns (limited ROMs)
flexion > extension
primary wrist flexor muscles
flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus
secondary wrist flexor muscles
flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and flexor pollicis longus
primary wrist extensor muscles
extensor carpi radialis longus
extensor carpi radialis brevis
extensor carpi ulnaris
secondary wrist extensor muscles
Abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, extensor pollicis longus, extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, extensor indicis
other intrinsic muscles of the hand
adductor pollicis, lumbricals, interossei
the line of the pull is anterior/posterior to the MCP and anterior/posterior to the PIP and DIP.
anterior, posterior
in the hand, the __________ muscles have the longest lever arm
lumbricals
the _____________ muscles of the hand have the largest cross sectional area, so they primarily flex MCP and extend PIP and DIP
interossei
a disrupted tendon is going to ___________ the ability to flex
decrease
"bowstringing" of tendons
when the tendons come away from the joints over which they pass (moving away from its osseous counterpart)
is adductor pollicis a PAD or a DAB?
PAD
the way the lumbricals travel
-anterior to the MCP
-posterior to the PIP and DIP
muscles that produce radial deviation
ECRL, ECRB, FCR, EPL, EPB, APL, FPL
muscles that produce ulnar deviation
ECU, FCU, FDS, FDP, ED
functional ROM for wrist flexion/extension
40 degrees
combined ulnar/radial deviation (arc)
40 degrees
functional ROM for finger flexion (MCP)
45 degrees
functional ROM for PIP flexion
60 degrees
functional ROM for DIP flexion
50 degrees
functional range of motion usually pertains to
ADL completion
bones of the wrist/hand that are most commonly fractured (from greatest to least prevalence)
1. scaphoid
2. lunate
3. triquetrum (most lateral to medial)
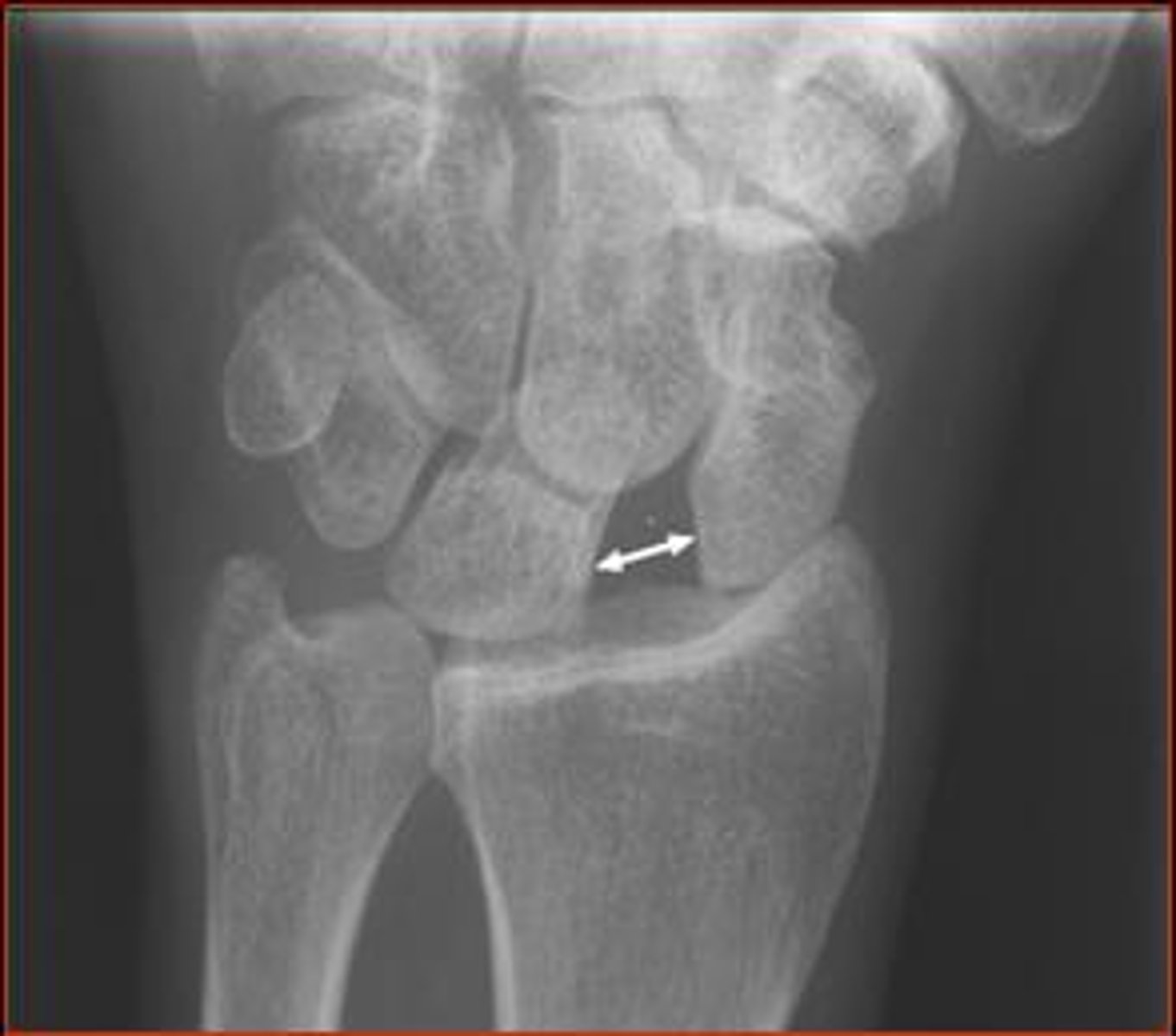
Terry Thomas sign
scapholunate dislocation
typically, the wrist bone we see fail in FOOSH is the ______________
radius
Boxer's fracture
5th metacarpal fracture
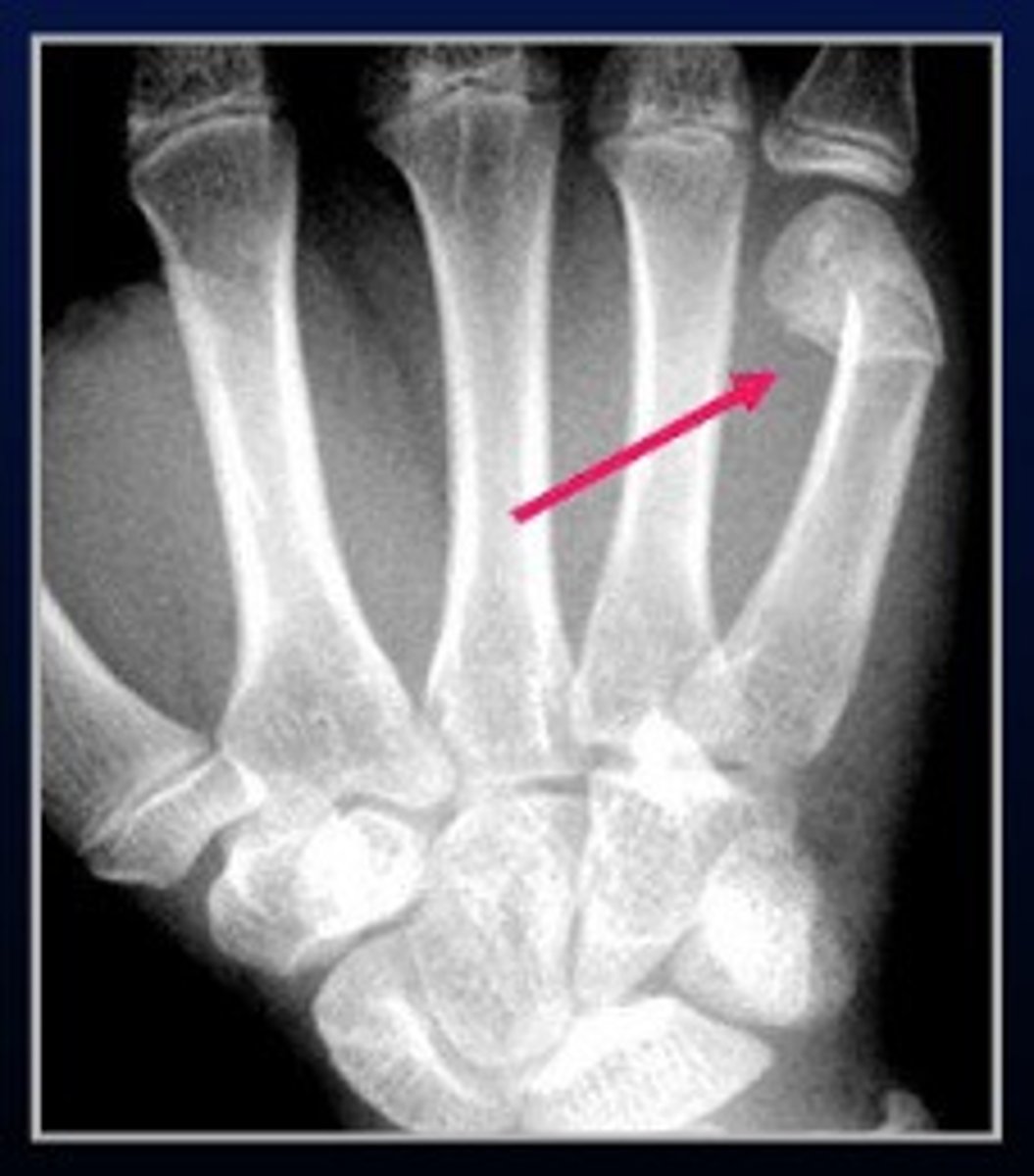
in Boxar's fracture, the radius moves volarly/dorsally (choose one)
volarly
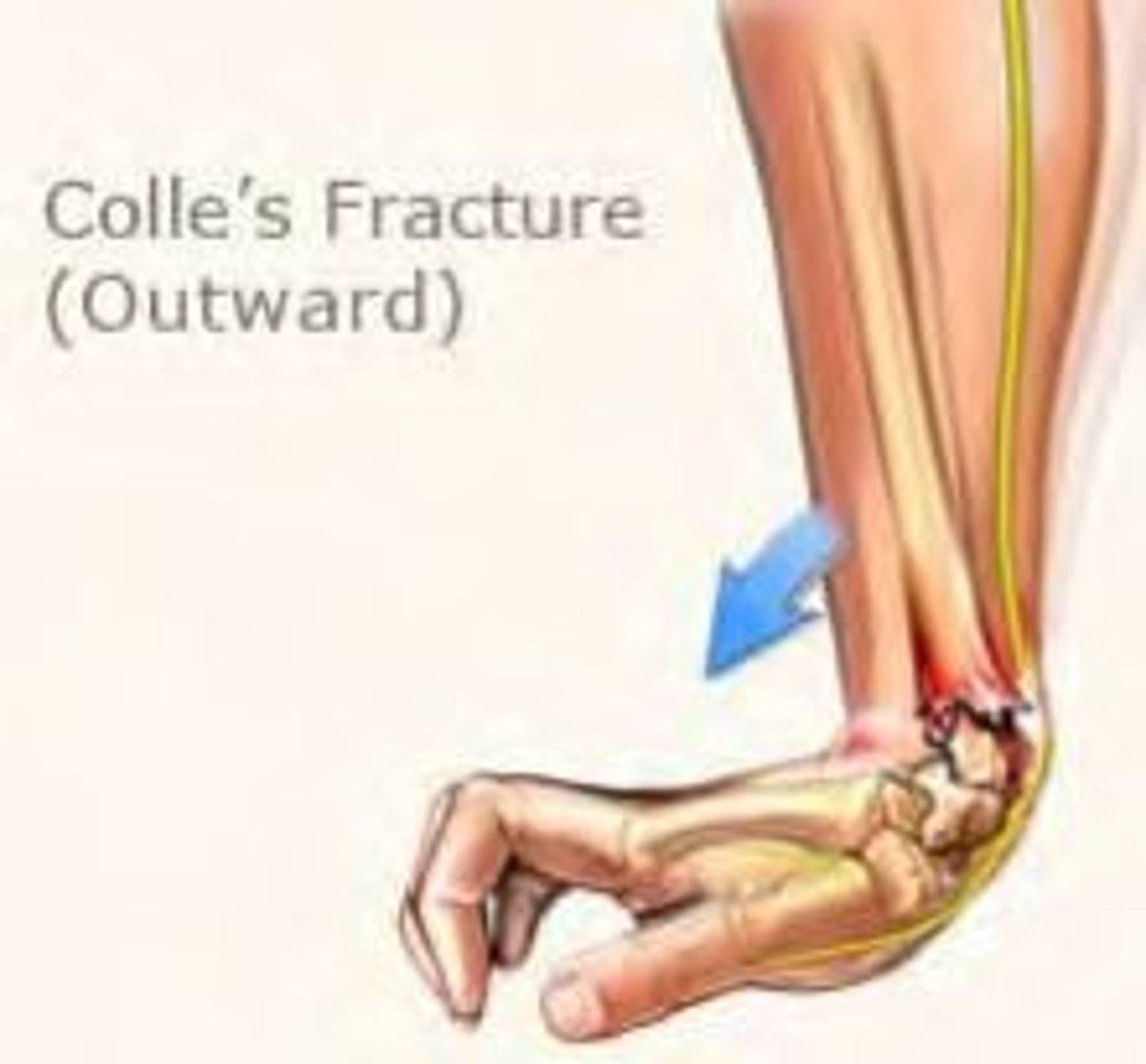
Colle's fracture
-fracture of the distal radius at the wrist; radius moves palmarly
-extension fracture