EXAM 1 - Lecture 1-8
1/220
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
221 Terms
The CNS is composed of two primary structures...
Brain and Spinal Cord
Name the 3 components of the Brain
Cerebellum ( 2 hemispheres + diencephalon)
Cerebellum
Brain Stem: Bridge to Spinal Cord
Nucleus
collection of neurons in CNS
Identify the Major Components of the brain
A. Cerebrum
B. Diencephalon
C. Cerebellum
D. Brainstem
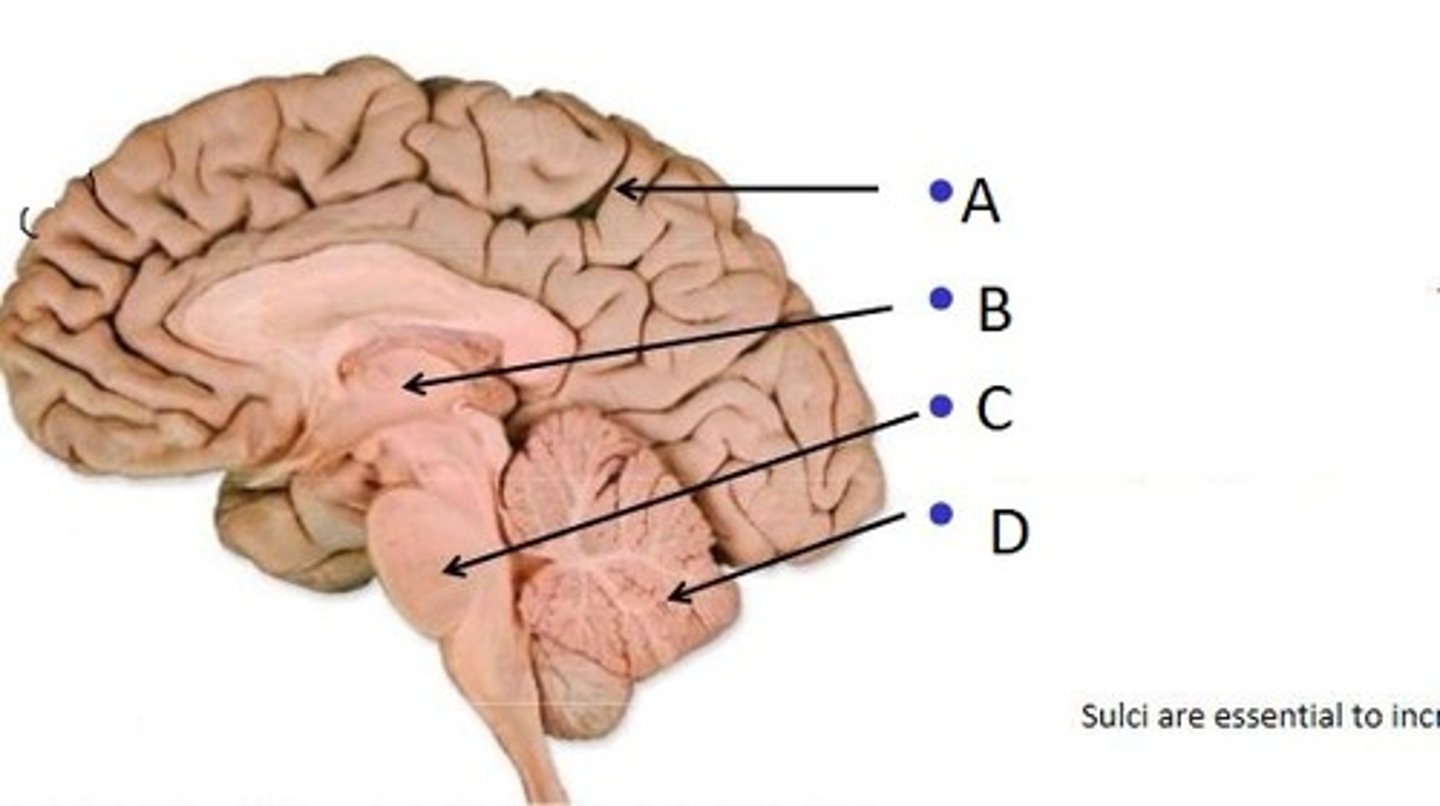
What is the function of the brainstem?
Bridge to spinal cord
What are the two sets of nerves of the PNS?
cranial nerves and spinal nerves. Sensory and Motor Ganglia
What is a collection of neurons in the PNS?
ganglion
Cranial Nerves go out of...
brain
Spinal nerves go out of...
spinal cord
What are the 3 planes to view the brain
Horizontal, Coronal, Sagittal
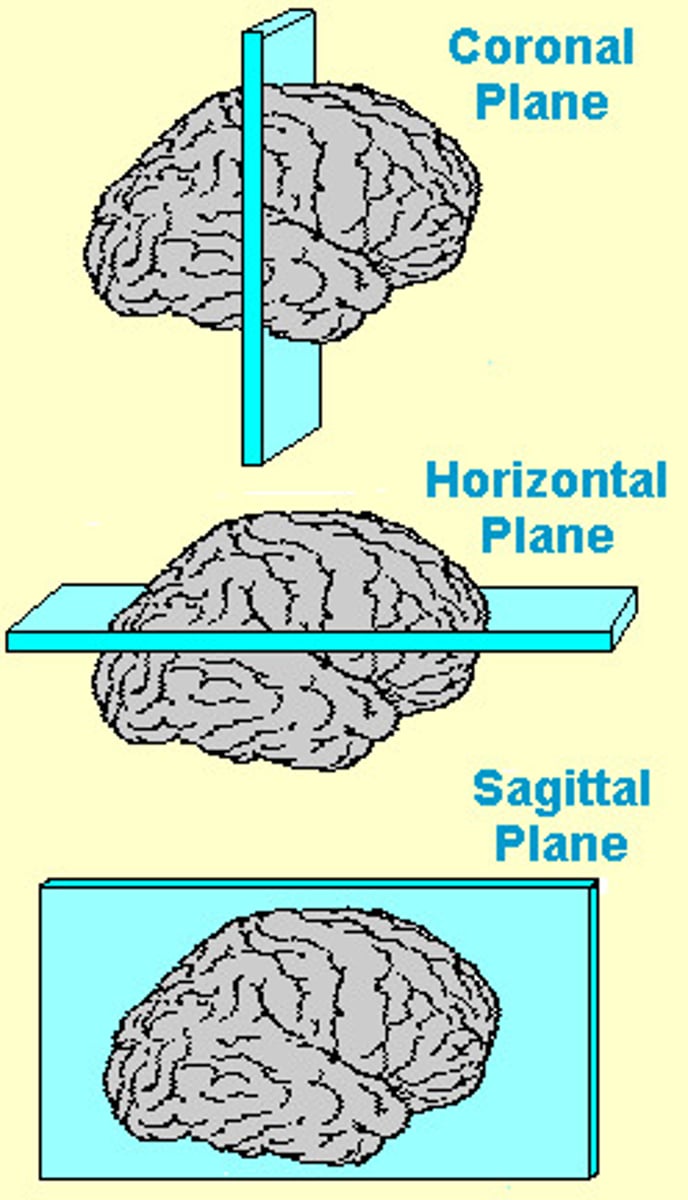
Which of the 3 planes is most commonly used for MRI?
Horizontal view
What are all the directions across the Brain?
Ventral (inferior) : Toward Stomach
Dorsal (superior) : Toward back
Anterior (rostral): In front
Posterior (caudal): In back
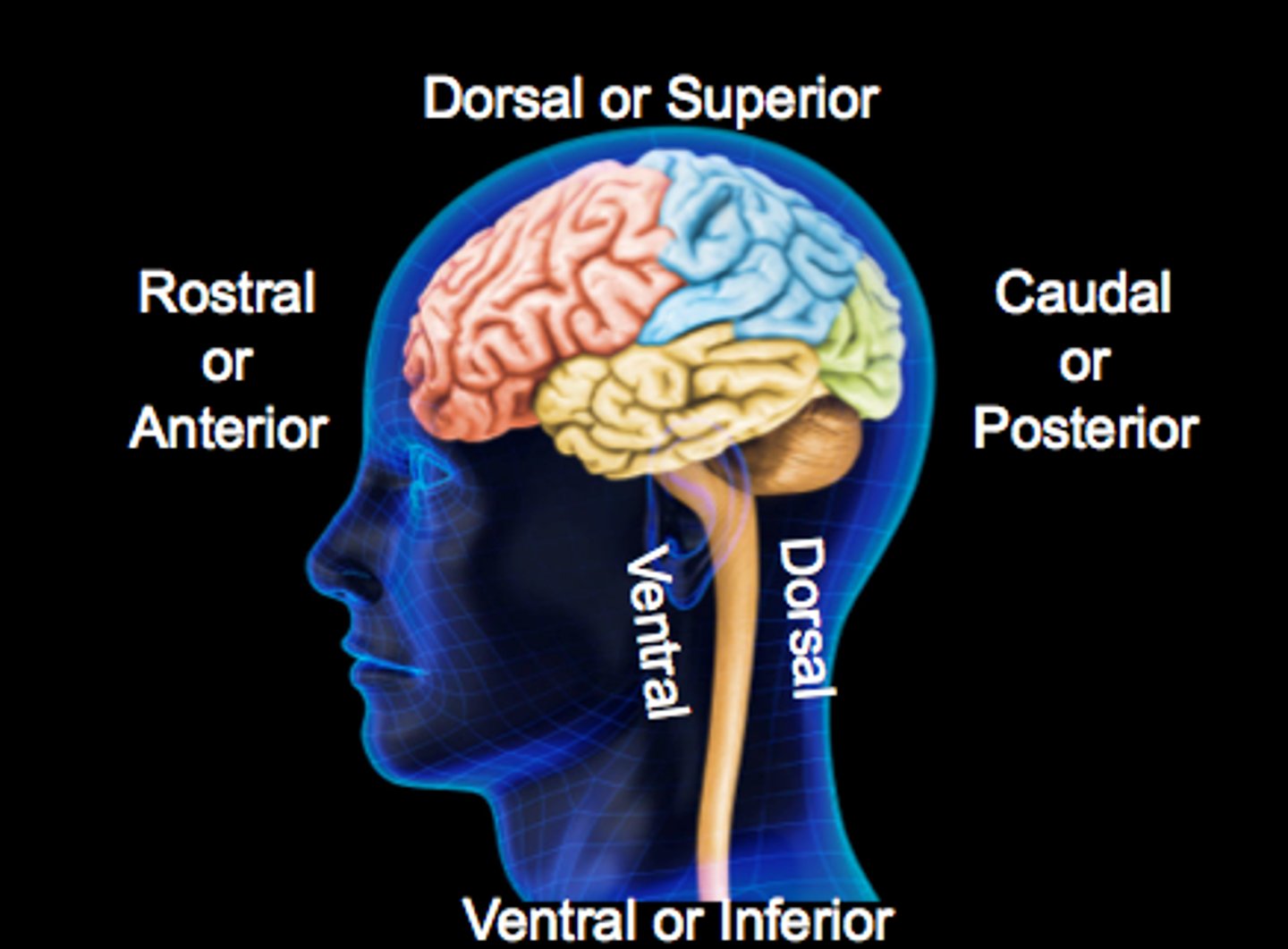
(T/F) All animals have superior and inferior planes
FALSE. Since we stand up straight we only have superior and inferior
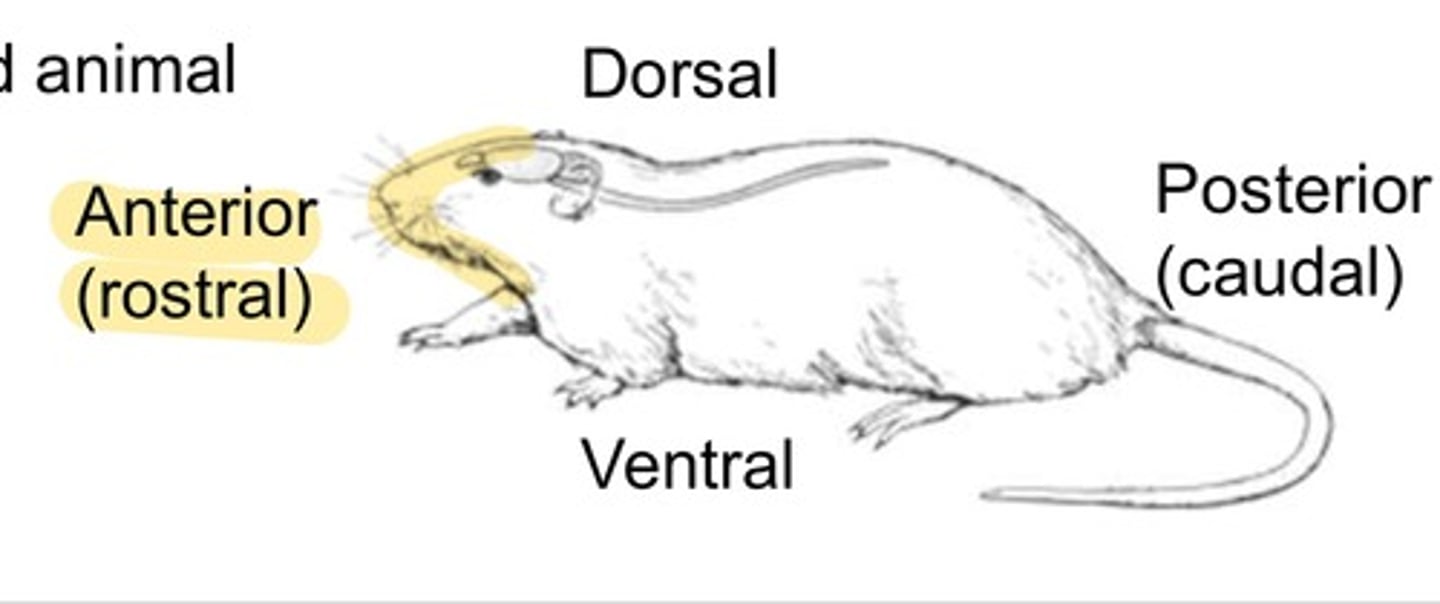
What are the planes across animal?
Dorsal = Back
Ventral = stomach
Rostral = toward nose
Caudal = toward ass
Where does the cerebellum sit on the brain?
Dorsal part of brain
(T/F). You can see the cerebellum from the dorsal view in ALL animals
FALSE. you cannot see the brain in dorsal view for higher apes and humans. Rest of animals you can
The Brainstem includes...
pons + medulla
The Hindbrain is made of...
brainstem (pons + medulla) and cerebellum
The forebrain is made of...
cerebral hemispheres + diencephalon
How many cervical nerves are there?
8 (C1-C8)
Are sensory neurons afferent or efferent?
afferent so they carry info towards the CNS
Are motor neurons afferent or efferent?
efferent so the carry info away from CNS
Sensory and motor neurons are fall into a group called....
spinal nerves (cranial nerves not covered)
What are the two types of SENSORY root ganglion
Dorsal Root ganglion: for body; only spinal nerves
Cranial ganglion: for head; only cranial nerves
What does the motor root ganglion control?
Autonomic Nervous System:
Sympathetic NS : Fight or Flight
Parasympathetic NS: Rest and Digest
What does ipsilateral mean?
same side
What does contralateral mean?
opposite side
What are these structures of the neuron:
Soma
Dendrite
Axon
Synapse
Myelin Sheath
Nodes of Ranvier
Soma: Cell body
dendrite: receive transmission
axon: transmit signal ( 1 per neuron)
synapse: contact point between neuron
myelin sheath: covering around axon
Nodes of ranvier: gaps between myelin sheath
afferent
toward CNS
efferent
away from CNS
Commissure
any collection of axons that connect one side of the brain with the other side (SAME LEVEL)
Decussation
crossing of the midline that occurs in many tracts so that brain senses and controls contralateral side of body (DIFFERENT LEVEL)
(T/F). Commissure occurs at same level
True
(T/F). Decussation occurs at same level
False. Different levels
What do you call axon bundles travelling in CNS?
Tract
What do you call axon bundles travelling in PNS?
Nerves
What is white matter?
myelinated axons
What is grey matter?
cell bodies
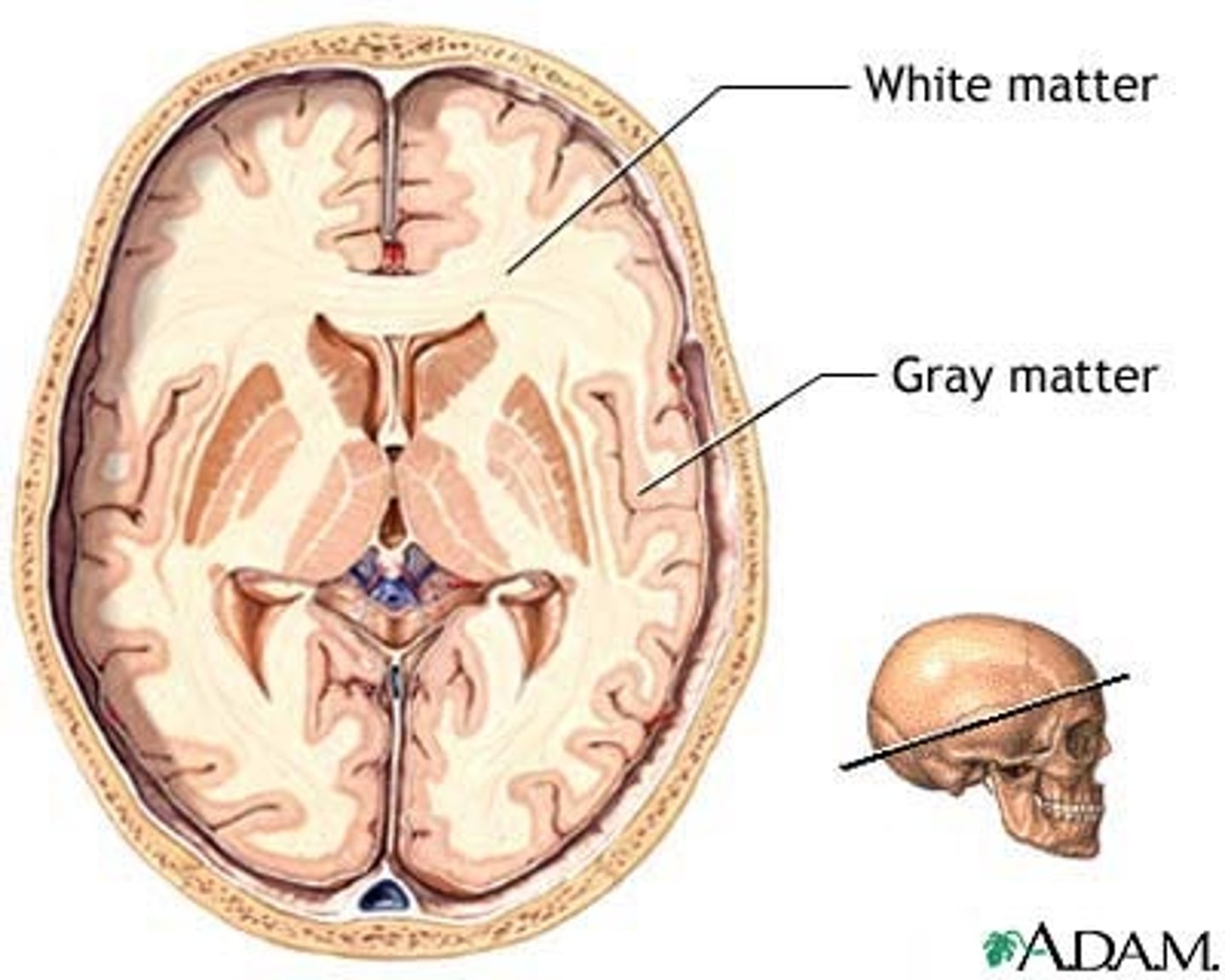
In the Brain, (white/grey) matter surrounds (white/grey) matter
In the Brain, grey matter surrounds the white matter
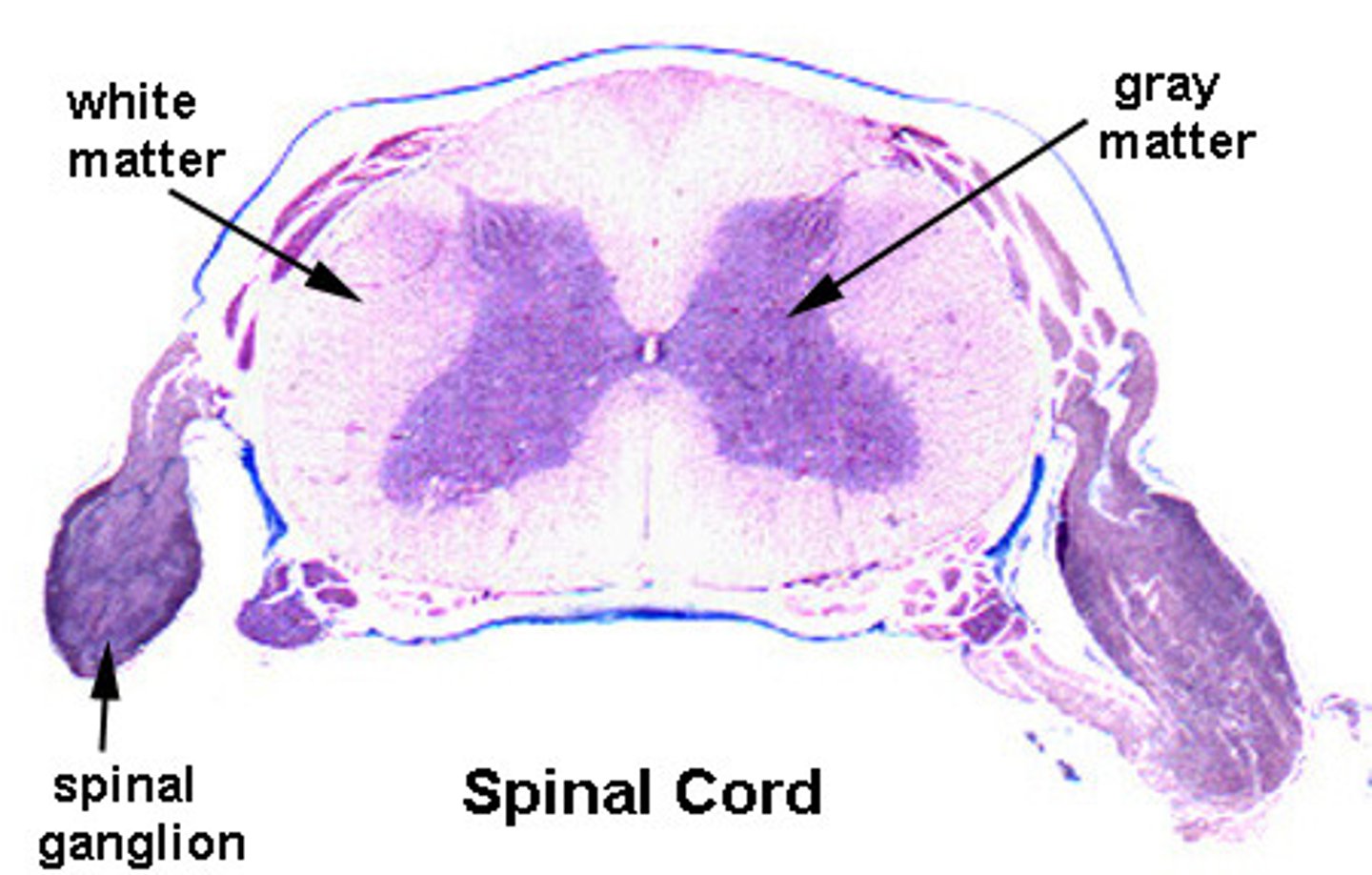
In the Spinal cord, (white/grey) matter surrounds (white/grey) matter
In the Spinal cord, white matter surrounds grey matter
Soma
cell body of a neuron
Dendrites
receive messages from other neurons
Synapse
A junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to the next.
How many axons does a neuron have?
one
Nissl bodies
RER in neurons -- synthesize enzymes (e.g., ChAT) and peptide neurotransmitters.
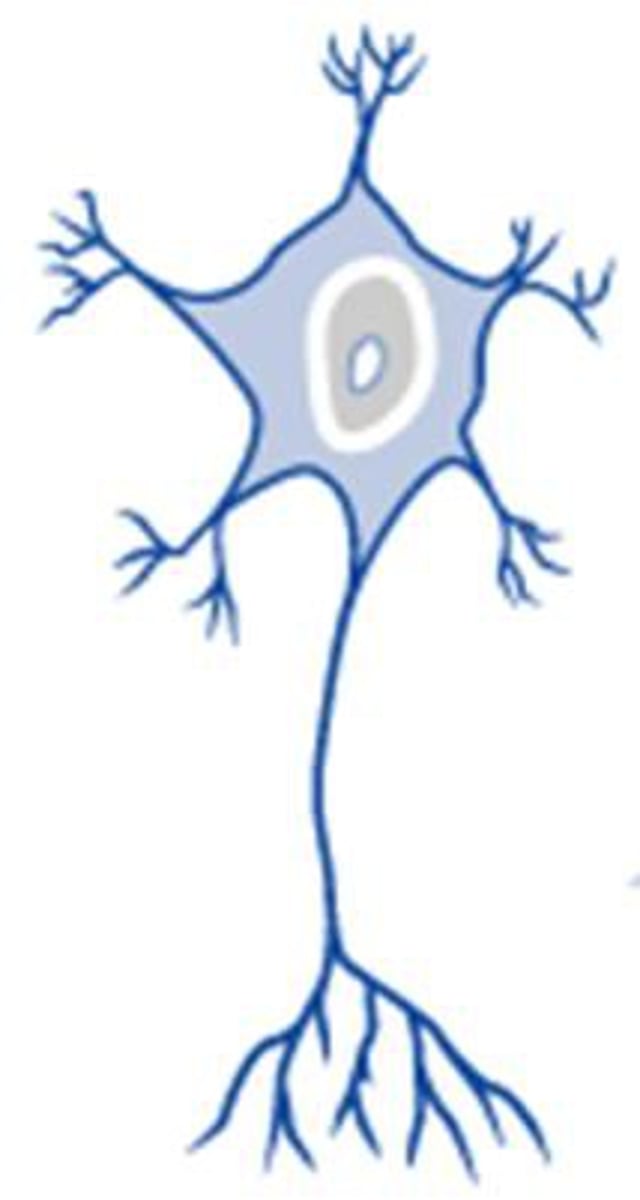
multipolar neuron
A neuron with a single axon and multiple dendrites; the most common type of neuron in VERTEBRATES
bipolar neurons
A neuron that has only two projections (one axon/one dendrite) from the cell body
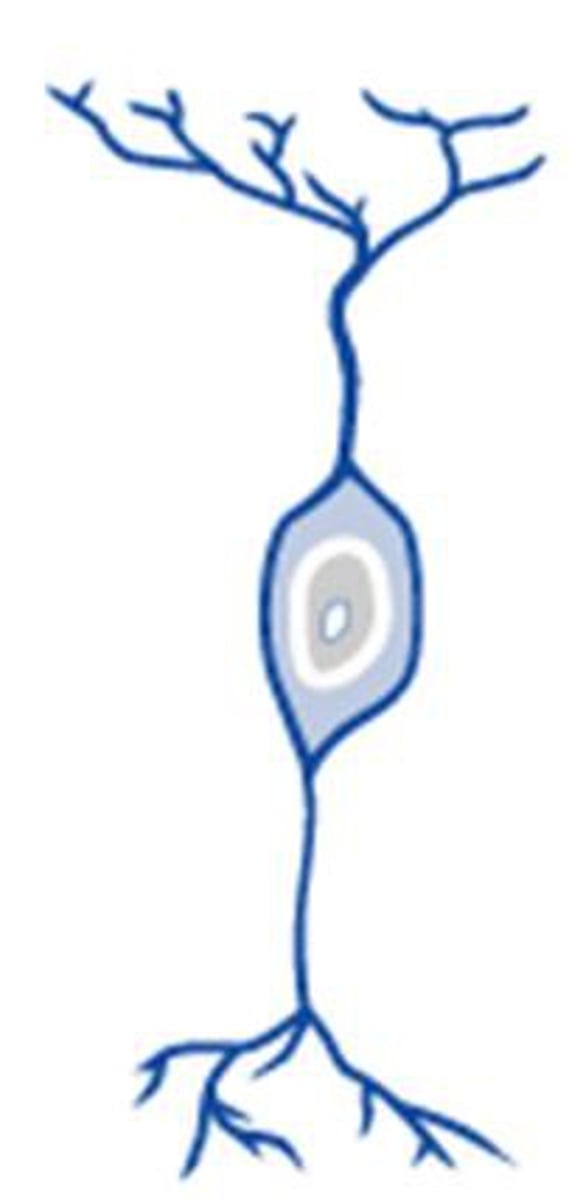
What are the given examples of Bipolar Neurons?
Spiral ganglion of auditory system
olfactory epithelium
Bipolar neurons in retina
pseudounipolar neurons
starts as a bipolar neuron; has two processes that merge into one.
Process one: axon --> cell body
Process two: cell body ---> axon
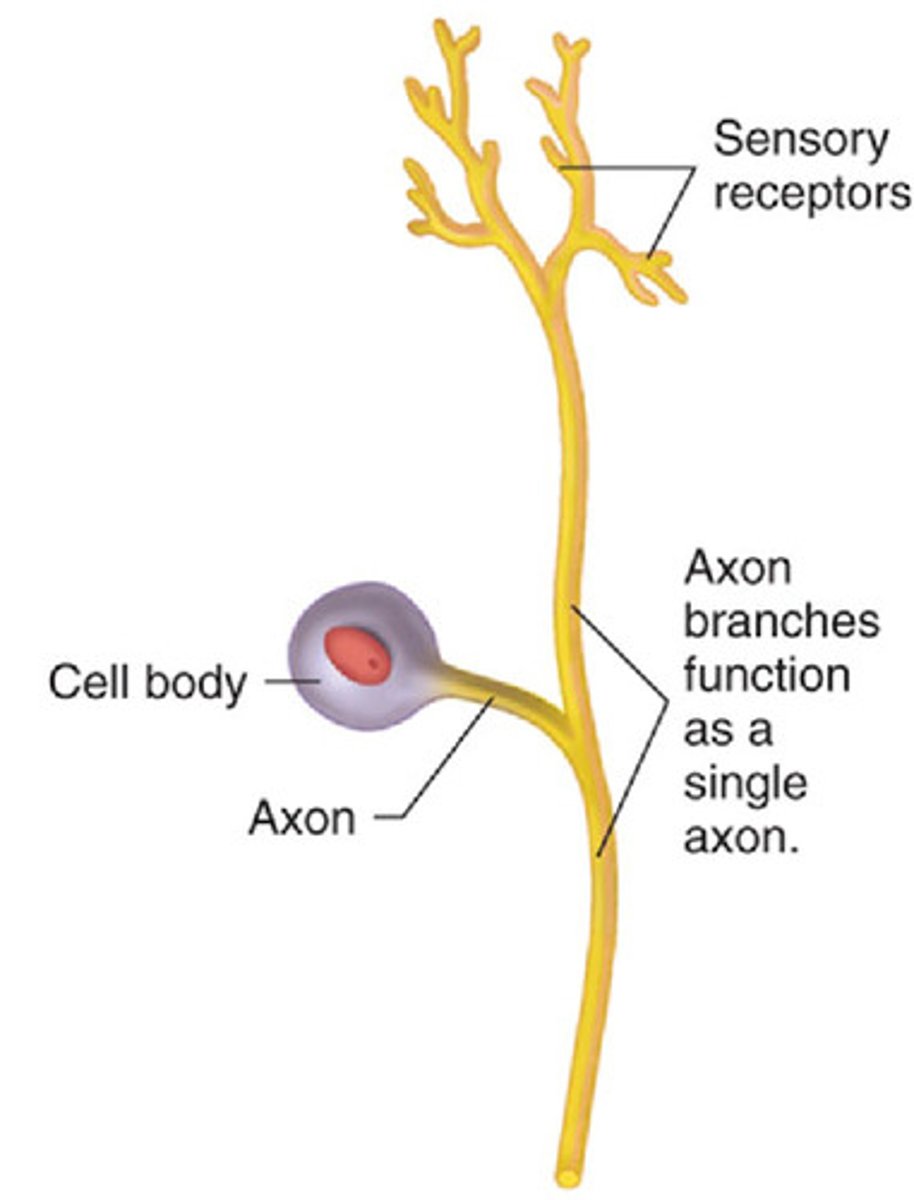
When are pseudounipolar neurons used?
Spinal Dorsal root ganglia --- sensory information
unipolar neuron
a neuron with one process extending from its cell body
ONLY in invertebrates
(T/F) Lower Motor Neurons end directly on muscles, glands, and effectors
TRUE
(T/F) Upper Motor Neurons end directly on muscles, glands, and effectors
False. The UMN is the general. The LMN is the soldier. UMN only tells the LMN what to do.
Which neuron is the most abundant in nervous system
Interneurons
Interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory neurons and motor neurons
What are the two types of interneurons?
local and projection
Local interneurons: locally interconnect other neurons, confined to small area
Projection Interneuron: Long axes connecting different areas
local interneurons
Local interneurons: locally interconnect other neurons, confined to small area
projection interneurons
Projection Interneuron: Long axes connecting different areas
(T/F). Interneurons are key in reflex arc
TRUE
Another name for the cell membrane in neurons is...
neurolemma
polyribosomes
free floating ribosomes
What are the 3 components of the NEURAL cytoskeleton
Microtubules, Neurofilaments, Microfilaments
(T/F). The Neural cytoskeleton is static
False. Very fluid
Microtubules are ____(large, small, middle) and made of_____ proteins
Large and made of tubulin proteins
Neurofilaments are ____(large, small, middle) and made of_____ proteins
Middle and made of family of cytokeratin proteins
Microfilaments are ____(large, small, middle) and made of_____ proteins
small and made of actin
What is the function of microtubules in the neuron?
transport large organelles
What is the function of neurofilaments in the neuron?
support and maintain shape of neuron
What is the function of microfilaments in the neuron?
anchor membrane proteins
What are the 3 parts of the axon structure?
Axon Hillock: Beginning
Axon Proper: Middle
Axon Terminal: End
Nissl bodies are found everywhere in the neurons but ____
Axon Hillock
(T/F). The ER extends into the axon
False it does not. It's the greatest difference between the axon and soma
What is the "initial segment" in neurons?
starting point of Action potential
high concentration of Na+ channels
What does the "initial segment" lack?
no rER found here. (Rough ER)
anterograde transport
soma ---> axon terminal
retrograde transport
axon terminal ---> soma
Anterograde transport facilitated by ____ ,which is a cytoskeletal protein of ____
Kinesin, Microtubules
Retrograde transport facilitated by ____ ,which is a cytoskeletal protein of ____
Dynein, Microtubules
Retrograde & Anterograde transport are (FAST/SLOW) transport
FAST
The axon terminal has a large number of ____ to support the energy demands of neurotransmitter transport
mitochondria
What are 4 types of synapses and their direction of travel?
Axosomatic: Axon --->soma
Axodendritic: Axon --->dendrite
Axoaxonic: Axon ---> Axon
Dendrodritic: Dendrite ---> Dendrite
(T/F). All synapses use chemical neurotransmitters.
FALSE. Dendrodendritic use electrical synapses
What glial cells are found in the CNS?
oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells
What is the role of oligodendrocytes?
myelination in CNS
What is the most abundant glial cell in the CNS?
astrocyte
What is an astrocyte?
glial cell in CNS
Provide nutrition to neurons
clears out neurotransmitters in synaptic cleft
What glial cell forms the blood-brain barrier?
astrocytes
What is K+ spatial buffering?
astrocytes digest extracellular K+ pumped out
1 oligodendrocytes myelinate ___ axon segement (s).
1 Schwann cell myelinate ___ axon segment
Oligodendrocytes = several
Schwann cells = one
What do satellite cells do?
support neurons in PNS
Under what condition will an axon in the PNS be wrapped by several Schwann cells?
unmyelinated axon so conduction is slow
microglial cells
glial cell in CNS that digest waste
Can act as phagocytes
What is role of ependymal cells?
Produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Ependymal cells work with ____ to generate CSF
Choroid plexus
How is electric current generated in neuron?
movement of ions
How do ion channels and ion pumps differ?
Ion channel: control resting and action potential
Ion pump: consume ATP to drive movement of ions
What are the major properties of ion channels?
1. Ion Selectivity
2. Ion permeability
3. Gating property
Ion channels allow movement ___ gradient
Ion pumps allow movement ___ gradient
Ion channels: Down
Ion pumps: Against
What ion channel maintains resting membrane potential?
K+ leak channels
Diffusion of K+ across neuron membrane maintains negative charge within neuron
What ion pump re-establishes resting membrane potential after Action potential?
Na+/K+ Pump
3 Na+ out
2 K+ in