6.5 - 6.9
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Bid rent theory
The value land is influenced by distance to the city center or CBD (central business district)
The businesses closest to the CBD make substantial profits and need to be available for customers
Manufacturing and warehouses need space and access to transportation services
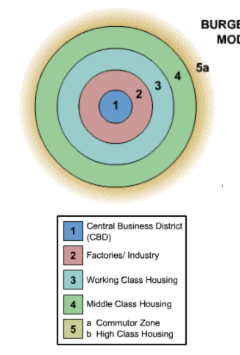
Burgess Concentric Zone Model
Based on 1920 Chicago development
Ring 1: (middle point) Bid rent theory → CBD has the most expensive land and major economic activity
Ring 2: (zone of transition) industry and low income appartments
Ring 3: also low income housing. High population density and poor living conditions
Ring 4 & 5: Lower population density. Cheaper land. Single family homes
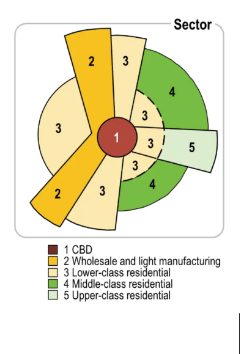
Hoyt Sector Model
Based on improving the Concentric Zone Model. Uses sectors and wages to determine land use pattern
Sectors develop a long transportation routes
Low income housing surrounds industry and transportation routes
Middle and high income housing developed further from CBD and industry (pollution)
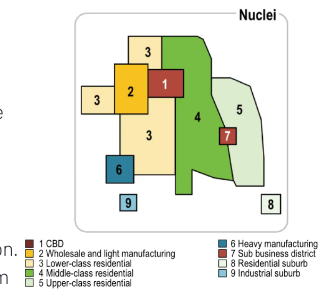
Harris and Ullman Multiple Nuclei Model
Cities develop around multiple focal points and build outwards. Sight and situationtal factors influence land-use patterns.
smaller business districts in various locations as well as major CBDs
Manufacturing and industry near transportation routes
smaller businesses locate near each other to take advantage of labor pools and suppliers
middle/high income farther from industry
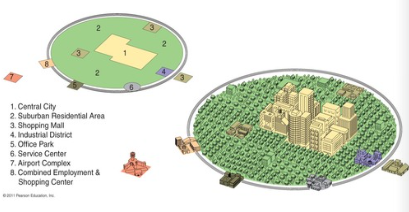
Galactic City Model
Most modern, Developed in the 1980s
Focuses on the decentralization and suburbanization of urban environments
Automobiles in the 1950s caused cities to develop differently
Includes edge cities (located near transportation routes)
Ex: Detroit
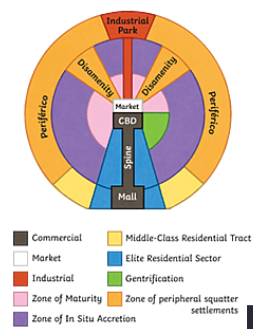
Latin American City Model
Characterized by “spine” from the modernized CBD in the center, through wealthy housing and connects to a secondary urban center called the mall
Spine: High-end commercial sector
Market: traditional market
housing becomes less expensive farther from the CBD due to lack of critical infrastructure
Disamenety Zones: Typpicaly steep, mountainous locations that are not connected to city services due to dangerous terrain (chiled protective services)
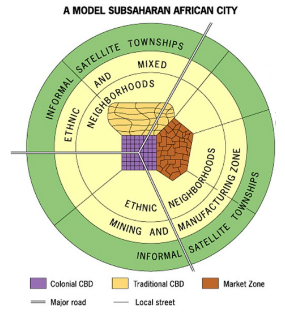
African City Model
characterized by 3 CBDs
Reflects colonialism
Traditional CBD: Small shops, narrow streets
Colonial CBD: Big straight streets, often in a grid. Government buildings with European architectural styles
Market zone: Traditional open-air markets
Mostly outdated but 3 CBDs can still be seen in some African cities
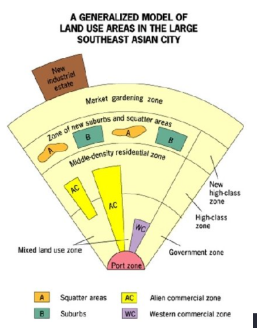
Southeast Asian City Model
Characterized by a Port Zone, export oriented (no CBD)
Alien commercial zone: Chinese immigrant businesses
Western commercial zone: European merchants (result of colonialism)
Market gardening zone: distinctive to other models due to the climate and land use in South East Asian countries
Older cities developed before transportation technology →
residential and areas of work are within waking distance
more apartment buildings in city center, higher population densities, and less space for cars.
Newer cities developed after transportation technology →
People own larger plots of land (suburbs)
suburban sprawl, economic segregation, and culture of privacy
Zoning is ___
Zoning is a regulation about what type oft development or land use can occur in a specific location.
floor limit
residential, commercial, or industrial
zoning changing from allowing single family homes to allowing apartment buildings →
housing density would increase
increasing affordable housing and access to infrastructure and high quality services.
Infilling definition?
The redevelopment of vacant land to improve the surrounding area.
industrial to offices, housing, or residential. → increasing density and changing land use pattern
Ex: Longworth Hall in Cincinnati, Ohio; warehouse → offices, wedding venue, and entertainment.
Infrastructure Definition?
The basic support systems needed to keep a society and economy running smoothly
(Transportation systems, Wifi, Power lines, Schools, Fire departments, etc.)
favelas are
poor slums
Locations within a city have high quality infrastructure are typically ___
more economically and socially developed
Infrastructure is typically funded by the government via tax revenue
(economically prosperous areas will have better infrastructure)
Locations within a city have low quality infrastructure are typically ___
less economic and socially developed
(favelas/squatter settlements, periphery and semi-periphery countries)
Infrastructure may be informally developed by people due to lack of assistance from the government
How does access to a strong network of hospitals encourage social development?
Available high-paying healthcare jobs → less unemployment
Treatment and prevention of disease → less spread of illness → healthier population
How does access to transportation routes encourage economic development?
Employees are able to easily travel to work, spend less on transportation, and stimulate the economy
Businesses have reliable ways to transport goods → stimulate the economy → higher more workers
How does a lack of access to hospitals negatively impact social development?
Less high-paying healthcare jobs available → more unemployment
Less treatment and prevention of disease and illness → more illness → unhealthy population
How does a lack of access to transportation routes negatively impact economic development?
Employees are unable to easily travel to work, more money spent on transportation rather than stimulation the economy.
Businesses cannot reliably transport goods → they spend more on transportation → they make less money
qualitative data vs quantitative data?
qualitative data: memories (Dolores Wilson, age 83 discusses the impact of the demolition of the infamous Cabrini-Green housing project in Chicago)
quantitative data: the census, population data
How they are both used: Both quantitative and qualitative data are used by city governments, policy-makers, and other organizations in order to analyze the cause and effects of urban changes.
qualitative: public opinions towards urban change
quantitative: data
Consider what the City of Cincinnati government could conclude based on this data. What infrastructure could be developed to alleviate this issue?
Affordable housing? ASK

Smart Growth/New Urbanism policies
The two terms are used interchangeably
Attempts to reduce urban sprawl and develop sustainable urban spaces. (Less suburbia)
Utilization of mixed-use development zoning policies to increase the use of already existing urban structures
Creates walkable cities
Maintains Spence of place

what is Mixed-Use Development and what is its intent?
Planned urban development that includes multiple uses (retail, residential, educational, recreational, and business)
Traditional zoning policies only allow for one type of development
Intended to increase resedential density and reduce travel times
Increases walkability
Key characteristic of smart growth policies/New Urbanism

What are the effects of walkability?
(characteristic of mixed-use developments)
Greatly decreases urban sprawl
reduces pollution
Caused by the implementation of infrastructure to safely accommodate and encourage pedestrians and bicyclists

Sustainable Urban Design Characteristics
Transportation Oriented Development
Greenbelts
Slow Growth Cities
What are the effects of Transportation Oriented Development?
(aspect of sustainable urban development)
Decreases air pollution
Reduces traffic
allows valuable urban land to be used to create mixed-use developments instead of parking lots
(busses, Subway systems, Commuter train lines)
40% of Washington DC residents use public transportation
It located mixed- use communities near mass transit stops → more compact cities → decreased automobile need
What are Greenbelts?
An area of green space (parks, agricultural land, or forests) intended to limit urban sprawl
Allows cities to annex land
AKA, urban growth boundary
Limits pollution and protect wildlife habitats
Historically used in Great Britain but wildly spread
What are the negatives of urban sprawl?
Placelessness, lack of identity or culture
Dependence on automobiles results in pollution and traffic congestion.
Economically exclusive - often those who remain in the city are in poverty and do not pay enough taxes to sustain the urban core.
Leads to economic decline, urban decay
Government investment in continued suburban growth resulted in a lack of investment in inner cities
What are slow Growth cities?
Another sustainable urban design policy
An initiative intends to decrease the rate that cities grow outward in an attempt to reduce urban sprawl
Similar smart growth but within the CBD
Achieved through:
greenbelts
zoning policies to restrict the development of land
Utilizes urban growth boundaries to place a geographic limit on development surrounding a city.
Ex: Boulder, Colorado and Portland, Oregon
What are the positives of sustainable urban design?
Reduction of urban sprawl
Improved walkability
Improved transportation
Diverse housing Options
Improved Livability
Reduction of negative environmental impact of cities
What are the negatives of sustainable urban design?
Increased housing costs
New developments are desirable → real estate prices rise. Not affordable for low income residence
Limits single family home and school choices
Limits the autonomy of automobile ownership
De facto segregation
Low income families and families of color cannot afford to live in the city and are forced to move out.
Potential loss of historical or place character or increase placelessness
Do this and that one sheet
Smart growth vs slow Growth?
Both are “intransitives” that intend to reduce urban sprawl
Smart growth: outside of the CBD
Ex: greenbelts
Mixed-Use Development
Slow Growth: Inside the CBD
Ex: greenbelts, Walkability
what is functional zonation?
portions of a city have distinct purposes (Zones)
peripheral model
A variant of the multiple-nuclei that describes suburban neighborhoods surrounding an inner city with nodes of commercial activity along a ring or beltway
what is fitering?
when houses pass from one social group to another in suburbs. Typically when wealthier residents move out, when less wealthy residents move, it creates a ripple effect.
what is invasion/succession?
terms used to describe when one social group or ethnicity gradually replaces another through filtering.
what is Urban infill?
the process of increasing the residential density of an area by replacing open space and vacant housing with residences.
Ex: Central Park Colorado, Civita California (mixed housing, public transit, and solar panels)
what is the suburbanization of business?
the movement of commerce out of cities to suburbs due to cheaper rent → decreased job opportunities, consumer choices, and services in cities
strip malls
offices and businesses services have been moved to the suburbs
Does land become cheaper as you move farther from the CBD everywere?
No, only in America and Canada. Many European countries have high-rise apartments farther from the CBD due to its history.
what is municipal?
A therm used to describe local government and the services it provides.
What is municipality?
A local entity under the same jurisdiction. (local government)
What is Incorporation?
The act of legally joining together to form a new city. They usually lack a true CBD and function as bedroom communities
What are bedroom communities?
A residential suburb inhabited largely by people who commute to a nearby city for work.
What are unincorporated areas?
Areas that do not follow under the legal boundary of any city.
Frankfort vs Lagos
Frankfort: highly integrated into transportation and communication networks and is a very important data exchange center as telecommunications is an integral part of the cities infrastructure
Lagos: due to unplanned population growth it lacks vital infrastructure
Examples of US states that use Greenbelt policies
New Jersey, Rhode Island, Washington, Tennessee, and Oregon
What are New urbanism’s major obstacles
The existed system of zoning continues to sprawl
People accustomed to traditional land-use patterns in cities were not easily convinced that the new urbanism was an improvement
Denver example of new urbanism
A new urban neighborhood changed its name to disassociate with a closed airport named after a racist former politician
What is Livability?
A set of principles that supports sustainable urban designs
Affordable and equitable housing
Access to employment
Access to community services
multiple and accessible transportation modes
social and civic engagement
Equitable: fairness in treatment
What is Urban Decay?
When a city falls into disrepair