computer science paper 2
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
181 Terms
abstraction
when you ignore unnecessary information and focus only on the important facts
why is abstraction used
it simplifies a problem to make it less complex, which makes it more straightforward to understand the problem and create a solution
what is decomposition
when you break a problem down into smaller tasks so that it is easier to solve, each individual problem can be separately tested and solved
what does decomposition allow
enables different people to work on the different parts of a larger problem that can later be recombined to produce a full solution
algorithmic thinking
final stage as logical steps are followed to solve the problem
what happens in algorithmic thinking
the problem is broke down using decomposition into smaller problems, the relevant data structures are considered using abstraction
what is an algorithm
set of instructions presented in a logical sequence
why do programs create algorithm designs
as a method of planning a program before writing any code to help them consider the potential problems of the program and make it easier to start creating source code
flowcharts
can be used to visually represent an algorithm

start/stop terminator

operation (process)

decision (if statement)

input/output

subroutine
direction of low
structure diagrams
display the organisation of a problem in a visual format, showing the subsections to a problem and how they link to other sections
trace tables
used to track the value of a variable as a program is run
how can trace tables be used
can be used to manually track the values in order to investigate why the program isn’t working as intended
what do rows and columns represent in trace tables
each row in the trace table represents another iteration, each column stores the value of a variable as it changes
linear search
the most simple search algorithm, each data is searched in order from the first value to the last as if they were all laid out in a line
sequence of linear search
the list does not have to be in any order before it is searched (aka sequential search as the list is searched in a sequence from the start to the end
linear search for large list
for large lists this search is not very efficient
key features of a linear search (loops)
used to check the first value in a list and increment by 1, checking each value for a match to the target
key features of a linear search (values not included)
reaching the last element of the list without finding a match means the value is not included
binary search
more more efficient searching algorithm as it generally searches through fewer data and is often much quicker - especially for large data sets
what happens in a binary search
the middle point of the data is selected with each iteration and compared to the value being searched for, when the midpoint matches the target value it has been found as the search can stop
what happens before using a binary search
the list of data must already be sorted
what is a prerequisite
a condition that must be satisfied before an algorithm will work correctly
key features of a binary search (calculations)
a midpoint, lowpoint and highpoint are calculated
key features of a binary search (while loop)
used to repeatedly compare the midpoint to a target value
key features of a binary search (upper/lower half)
the upper half or lower half of the data is ignored if the midpoint does not equal the target
merge sort
divides a list into half, again and again until each data item is separated, and then combined in the same way as they were divided but now in the correct order
what happens when the individual lists are all merged together in merge sort
then the data is in order and the algorithm will end
key features of a merge sort (recursive algorithm)
this algorithm calls itself from within the subroutine
key features of a merge sort (sublists)
it continually splits sublists into a left side and a right side until each sublist has a length of 1
bubble sort
data elements are swapped if they are not in the correct order, the algorithm will only stop when a complete iteration through the data is completed with no swaps made
bubble sorts with large sets of data
a bubble sort is not suitable for large sets of data
key features of a bubble sort (outer while loop)
uses an outer while loop (condition controlled) to check no swaps have been made
key features of a bubble sort (inner for loop)
uses an inner for lop (count controlled) to repeat through the length of the data set
key features of a bubble sort (flag)
uses a flag (a Boolean value) to track if a swap has been made and uses a temporary value to help correctly swap elements
insertion sort
the list is logically split into sorted values on the left and unsorted values on the right
how does insertion sort work (1)
starting from the left, values from the unsorted part are checked and inserted at the correct position in the sorted part
how does insertion sort work (2)
this continues through all elements of the list until the last item is reached, and sorted
adv/dis adv insertion sorts
insertion sorts are efficient for small data sets but would be slow to sort large sets compared to alternatives such as a merge sort
key features of a insertion sort (outer for loop)
uses an outer for loop (count controlled) to iterate through each value in the list
key features of a insertion sort (inner while loop)
uses an inner while loop (condition controlled) to find the current values correct position in the sorted part of the list
key features of a insertion sort (movement)
an insertion sort moves ‘backwards’ to find the correct position of each value, by decreasing the index within the while loop
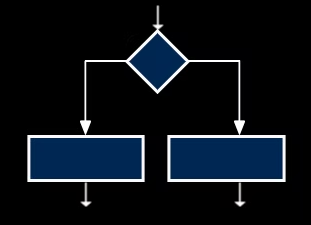
programming constructs: sequence
structuring code into a logical, sequential order
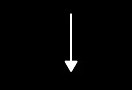
programming constructions: selection
decision making using if statements
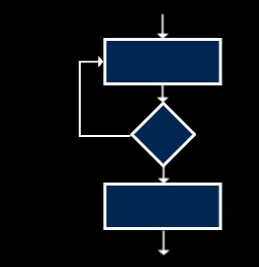
programming construction: iteration
repeating code using for or while loops
variables
used to store data in programs, they can be changed as the program runs
two parts of a variable
the data value and the identifier
efficient programs utilisation of variables
an efficient program will use variables with sensible identifiers that immediately state their purpose in the program
why use variable names like ‘TotalNum’ and ‘Profit’ rather than ‘num1’ and ‘num2’
means that other programmers will be able to work out the purpose of the code without the need for extensive comments
local variables
declared within a specific subroutine and can only be used within that subroutine
global variables
can be used at any point within the whole program
local variable advantages (saves memory)
only uses memory when that local variable is needed, global variables use memory whether they are used or not
local variable advantages (easier to debug)
easier to debug local variables as they can only be changed within one subroutine
local variable advantages (reusability)
you can reuse subroutines with local variables in other programs
global variable advantages (versatility)
variables can be used anywhere in the whole program and in multiple subroutines
global variable advantages (maintenance)
makes maintenance easier as they are only declared once
global variable advantages (constants)
can be used for constants - values that remain the same
what is a constant
data that does not change in value as the program is run - it is fixed and remains the same
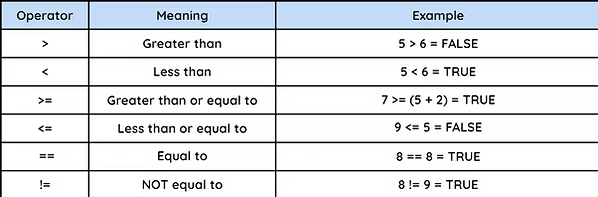
comparison operators
used to compare two data values
arithmetic operators
used to mathematically manipulate values
arithmetic operators: modulo division
reveals the remainder from the last whole number
arithmetic operators: integer division
reveals the whole number of times a number can be divided into another number
logical operators
typically use TRUE or FALSE values which is known as Boolean
data types: character
a single character such as a letter, number or punctuation symbol
data types: string
a sequence of characters, including letters, numbers and punctuation
data types: integer
whole number
data types: real
decimal number
data type: Boolean
an answer that only has two possible value
telephone numbers
are always stored as a string, not an integer
casting
converting the value of a variable from open data type into another
what is a subprogram
large programs are often broken down into smaller subprograms also called subroutines, each focuses on a specific function of the code helping to decompose a complex problem into more manageable chunks
define subprogram (python)
def command
calling subprograms
running a line of code that includes the name of a subprogram will call it, when called, the program will run the subprogram code before returning back to the lien that called it, subprograms are only run when called, so depending on decision made a program may end without calling every subroutine
parameters
value that is passed into a subprogram when it is called, allowing the value to be used within the subprogram, a subprogram may not use a parameter
any parameter must be identified when the subprogram is defined
return (1)
the return command will send a value back to the line the subprogram was called on, allowing it to be used there

return (2) example
e.g the ‘quad’ subprogram returns the value of the result variable back to the main program, allowing it to be printed
return (3)
a subprogram will end either by reaching the last line of code within it, or when it reaches a return command
functions
subprograms that return a value are called functions

why is the subprogram called in the main program in the example
the subprogram is called in the main program, multiplies the number passed in as a parameter by 4 and returns a value back to the main program to be printed
types of subprograms: functions
returns the value, using the return command, which allows the value to be used in the line of code the function was called in
the divide function below returns the value of the variable total to the main program to be printed
types of subprograms: procedure
does not return a value
advantages of using subprograms (breaking down)
break a complex program down into smaller parts, making it easier to design and test, each subroutine can be tested separately and abstraction can be used to simplify a complicated problem
advantages of using subprograms (reusability)
using subprograms allow code to be easily reused in other programs, as it has already been written, making it quicker to develop new programs or build on existing work
advantages of using subprograms (repetition)
using subprograms avoid code repetition as they can be called as many times as necessary, making programs shorter and quicker to develop, making them easier to maintain and debug
advantages of using subprograms (work)
work can easily be split up between team members to work on different subprograms at the same time
array
static data structure that can hold a fixed number of data elements, each data element must be iof the same data type
how are the elements in an array identified
by a number that indicates their position in the array, known as the index, the first element in an array always has an index of 0
difference and similarity in array and two dimensional array
the data in a two dimensional array must still all be of the same data type, but can have multiple rows and columns
records
can store data of different data types, each record is made up of information about open person or thing and each piece of information is called a field
key field
records should have a key field: this is unique data that identifies each record
key field (2) example
student ID is a good key field for a record on students as no two students can have the same student ID
2D array and records
a 2D array may be used to represent databse tables of records and fields
SQL
language that can be used to search for data in a database
format of an SQL statement
SELECT field1, field2, field3…
FROM table
WHERE criteria
factors to consider when creating a secure program: anticipating misuse
planning ahead to take steps against potential misuse e.g the app X prevents the same tweet sent twice in a row as it might be spam