BIOL 251 Microbiology Week 12 Lecture Notes
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microbiology: An Introduction 13th Edition - Ch. 13
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Virus
Genetic element that cannot replicate independently of a living host cell
Virology
Study of viruses
Virus Particle
Extracellular form of virus
Facilitates transmission from one host to another
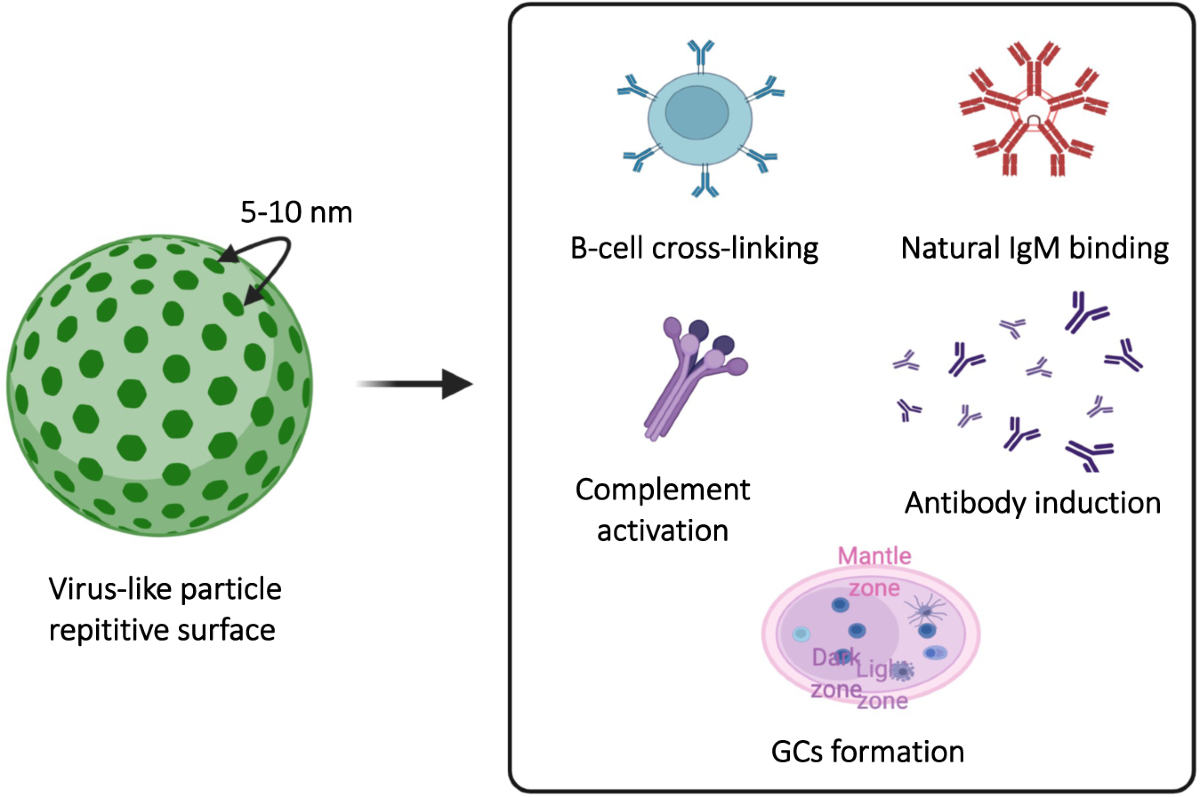
Virion
Infectious virus particle
Obligate
_____ Intracellular Parasites: Require living host to replicate
Contain DNA or RNA
Contain a protein coat
NO Ribosomes
Host range
The spectrum of host cells a virus can infect
Determined by specific host attachment sites and cellular factors
Classification based on host: bacterial, animal, plant viruses
Nucleic Acid
_____ _____
DNA or RNA
Single- or Double-stranded
Linear or circular
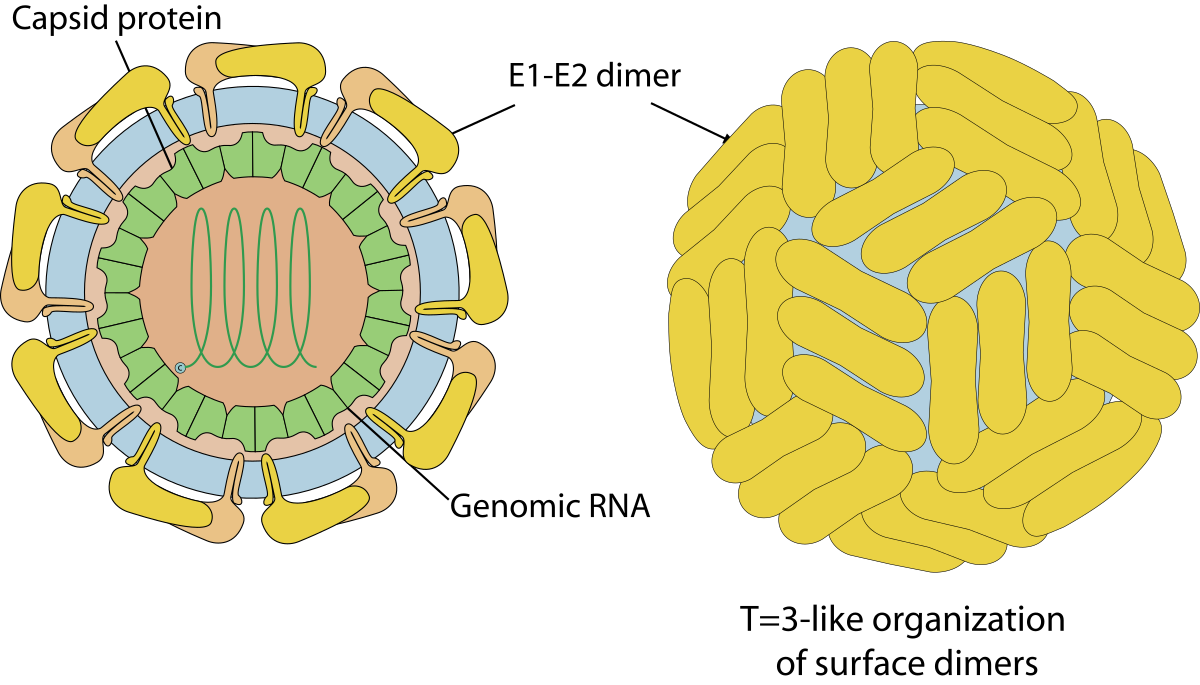
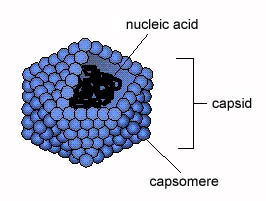
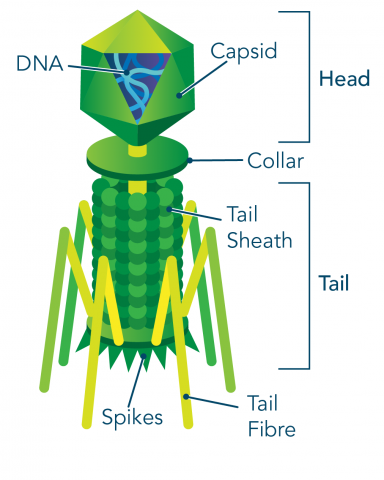
Capsid
_____
Protein coat made up of capsomeres (subunits)
Capsomere
A protein subunit that makes up the capsid of a virus. Determines shape and structure of virus.
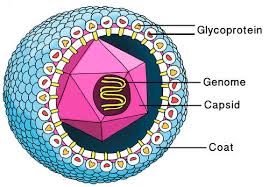
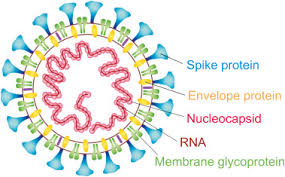
Envelope
Spikes
A lipid, carbohydrate, or protein coat on some viruses
Enveloped vs Nonenveloped viruses
_____: Projections from outer surface
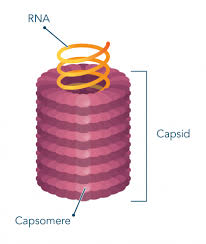
Helical
_____ Viruses: Shaped like long rods
Capsids are hollow cylinders with a helical structure
Polyhedral
_____ Vir
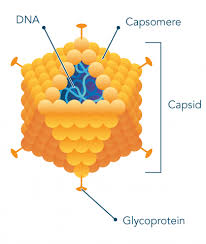
uses: Capsids are many-sided.
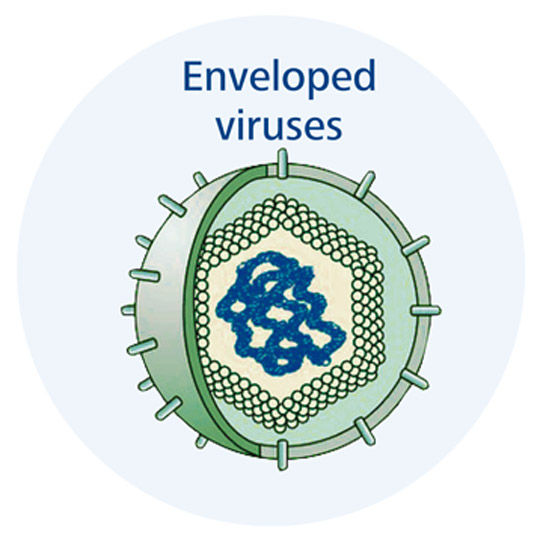
Enveloped
_____ Viruses: Has an outer envelope (derived from the host cell's membrane) surrounding its core structure. These viruses often have spikes on their surface.
Complex
_____ Viruses: Have irregular shapes and structures, often consisting of multiple types of proteins and sometimes other components. They can include bacteriophages and some animal viruses.
Order
Family
Subfamily
Genus
International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV)
____: ends in -ase
____: ends in -viridae
____: ends in -virinae
____: ends in -virus
Species designated by common designated name and number
living
Viruses must be grown on _____ cells. One method is embryonated eggs
Bacteriophages form plaques on a lawn of bacteria
Plaque Forming Unit (PFU)
Cytopathic
Continuous
Testing Viruses in Cell Cultures
Tissues treated with enzymes - separate cells
Infected cells detected - deterioration - _____ Effect (CPE)
_____ Cell lines are used
host
metabolic
For a virus to multiple;
It must invade a _____ cell
Must take over host’s _____ machinery
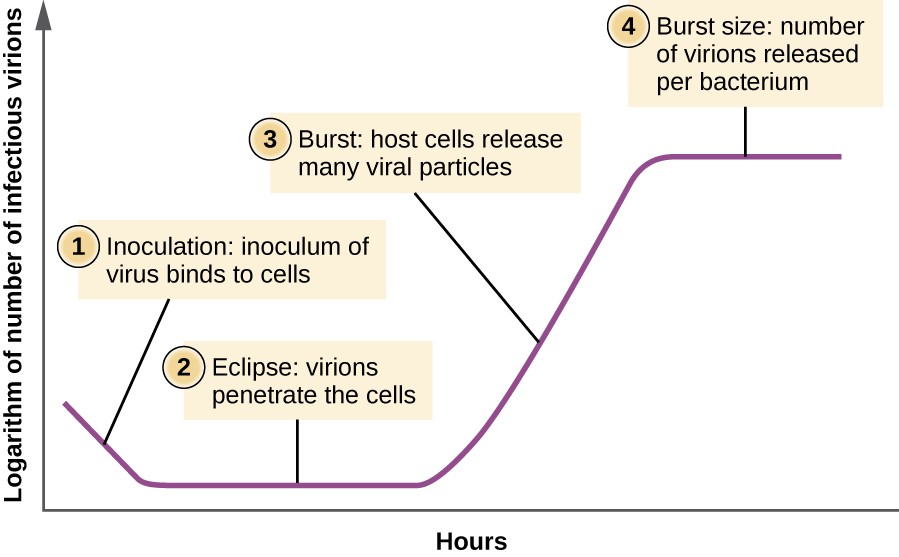
Eclipse
Viral One-Step growth curve
_____ period: The time when a virus is replicating within a host cell, but is not yet producing any new infectious virions
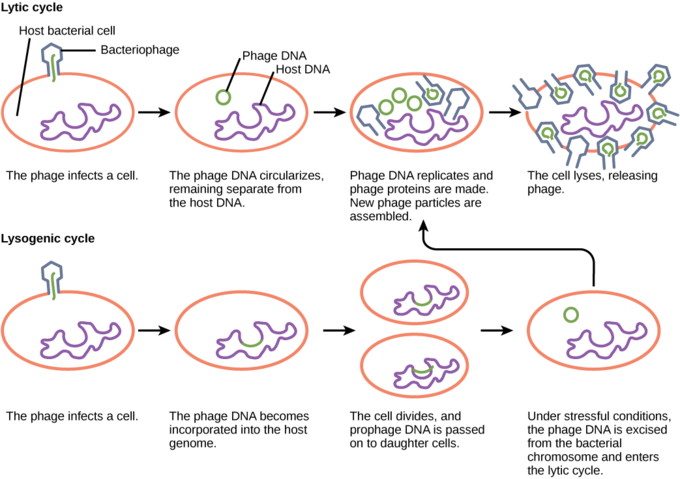
Lytic
Lysogenic
Multiplication of Bacteriophages
_____ Cycle: Phage causes lysis and death of host cell
_____ Cycle: Phage DNA is incorporated in the host DNA
No cell death
Oncogenic
_____ Viruses: a virus that can cause cancer
DNA Viruses - HPV, HBV
RNA Viruses - T-cell Leukemia, Lymphoma
Viroids
Short pieces of naked RNA
Small, circular, single stranded
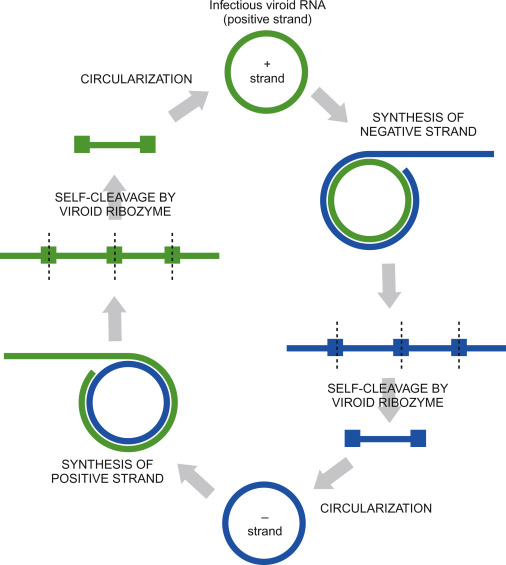
Prions
Infectious agents composed of misfolded proteins that cause neurodegenerative diseases. They propagate by inducing normal proteins to misfold.
PrPc: Normal cellular protein, on cell surface
PrPSc: Scrapie protein; accumulates in brain cells to form plaques
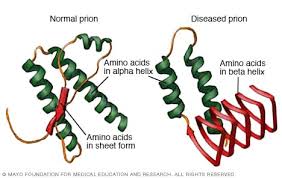
Budding
The mechanism whereby an enveloped virus leaves a host cell
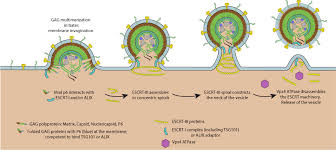
Transduction
The process by which viruses transfer genetic material from one bacterium to another
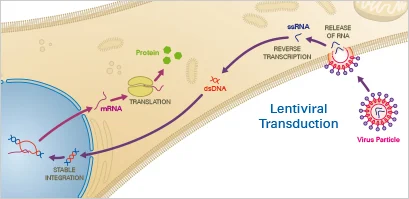
Lysogeny
A viral life cycle in which the viral genome integrates into the host DNA and replicates along with it without immediately destroying the host
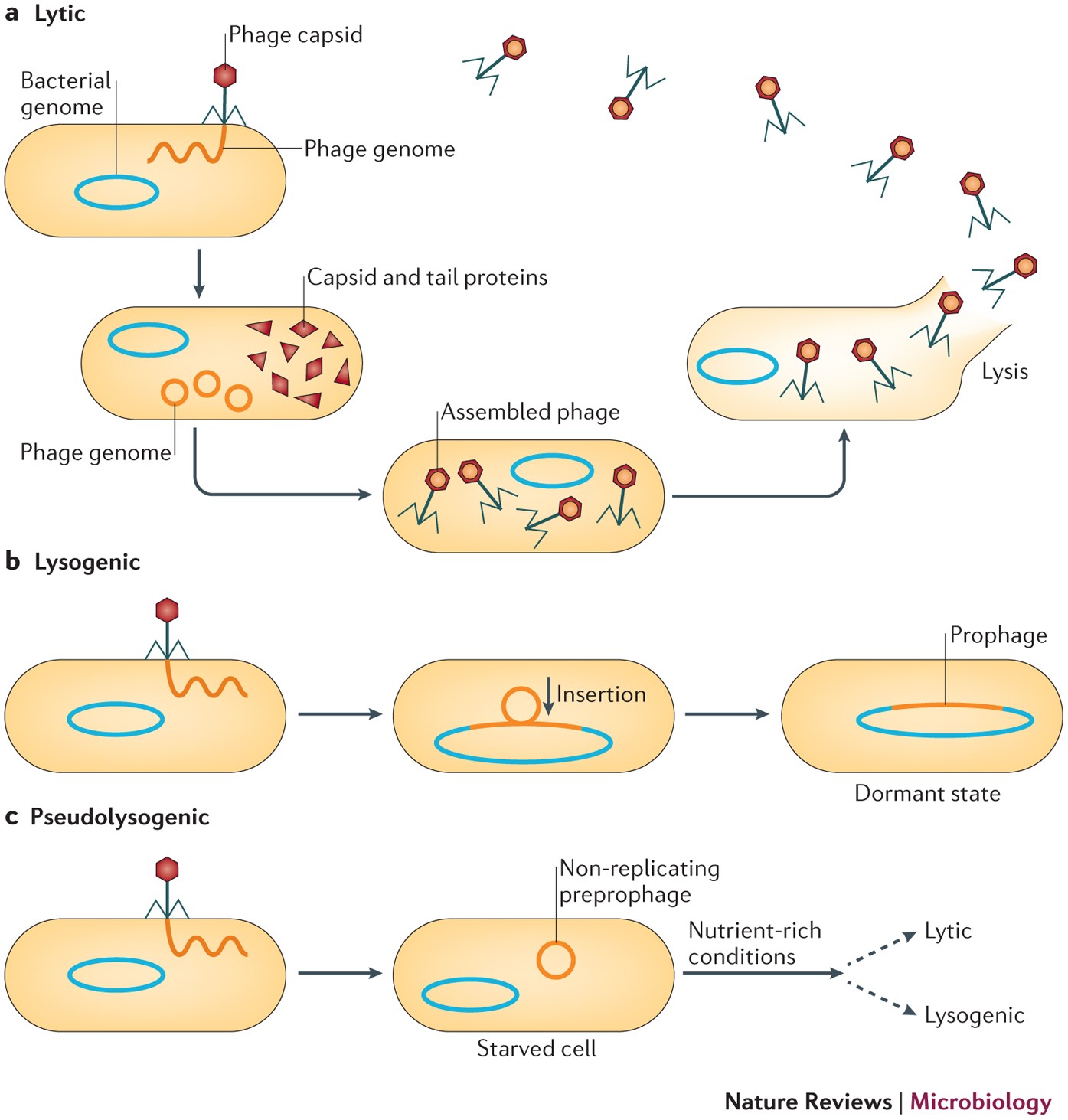
Absorption
The initial step in viral infection where the virus attaches to specific receptors on the surface of a host cell
Viruses are not composed of cells
How do ALL viruses differ from bacteria?
Cannot reproduce by themselves
Viruses are not considered living organisms because they…?
is read by ribosomes during the process of translation
DNA does all but which of the following?
Serves as the genetic material passed from parent to offspring
Provides the instructions for the synthesis of messenger RNA
Is read by ribosomes during the process of translation
DNA to RNA to protein
According to the central dogma, which of the following represents the flow of genetic information in cells?
Protein to DNA to RNA
DNA to RNA to protein
RNA to DNA to protein
DNA to protein to RNA
ligase
Which of the following is NOT involved in the initiation of replication?
Ligase
DNA gyrase
Helicase
Primase
True
More primers are used in lagging strand synthesis than in leading strand synthesis.
True
False
3′-GTCAAGCCT-5′
Which of the following would be synthesized using 5′-CAGTTCGGA-3′ as a template?
3′-AGGCTTGAC-4′
3′-TCCGAACTG-5′
3′-GTCAAGCCT-5′
3′-CAGTTCGGA-5′
The polypeptide is released
When the ribosome reaches a nonsense codon, which of the following occurs?
A methionine is incorporated
The polypeptide is released
A peptide bond forms
promotor
Which of the following components is involved in the initiation of transcription?
Primer
Origin
Promotor
Start codon
mRNA
What is the final product of transcription?
nonsense mutation
Which of the following is a change in the sequence that leads to formation of a stop codon?
Missense mutation
Nonsense mutation
Silent mutation
Deletion mutation
Deletion of one nucleotide
Which of the following is an example of a frameshift mutation?
Deletion of a codon
Missense mutation
Silent mutation
Deletion of one nucleotide
Direct repair
Which of the following is the type of DNA repair in which thymine dimers are directly broken down by the enzyme photolyase?
Direct repair
Nucleotide excision repair
Mismatch repair
Proofreading
Plasmids
What are transferred by conjugation?
Transformation
Which of the following refers to the uptake of naked DNA from the surrounding environment?
Conjugation
Generalized transduction
Specialized transduction
Transformation
Conjugation
Which of the following refers to the mechanism of horizontal gene transfer naturally responsible for the spread of antibiotic resistance genes within a bacterial population?
Conjugation
Generalized transduction
Specialized transduction
Transformation
Vector
A DNA molecule that transports foreign DNA into a cell is called a
Clone
Vector
Nanosphere
Mutagen
Tryptophan
Indole is from the enzymatic hydrolysis of what biomolecule?