Honors Biology - Chapters 2 and 3
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Terms from chapters 2 and 3 including macro molecules, carbs and lipids
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Carbohydrates (sugar), Protein, Lipids (Fats), Nucleic Acids (DNA)
What are the four types of macromolecules?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen (CHON)
What elements make up 96% of the human body?
2 or more different elements in a fixed ratio; covalently or ionically bonded
Compound
2 or more elements in a fixed ratio; only covalently bonded
Molecule
two atoms interact to complete their valence shells (two types, ionic and covalent)
Chemical bond
transfer of electrons between atoms to fill valence shells. between non-metals and metals.
Ionic bonds
If each atom has equal pull on e- then there is equal sharing, leading to a nonpolar covalent bond. However, if each atoms has an unequal pull, because of high differences in electronegativity (like between C and O), then there is unequal sharing, resulting in a polar covalent bond
Polar Covalent vs. Non Polar Covalent
Low e- neg | high e- neg |
C | O |
H | N |
interactions between low and high create polar covalent bonds
Electronegativity Table for CHON
Intramolecular forces hold atoms in a molecule together (covalent and ionic). Intermolecular forces are forces that exist between molecules (LDF, dipole-dipole, hydrogen bonds)
Intermolecular vs. intramolecular forces
temporary, unequal distribution of electrons that is the weakest intermolecular force
London Dispersion Force (LDF)
a dipole-dipole(partial charges) IMF between H, and a molecule of NOF (indicated by dotted lines)
Hydrogen Bond
are cohesive, b/c hydrogen bonds = strongest so more attracted to itself than other molecules
Have high surface tension
Ice is less dense than liquid water because in ice, h bonds are equally spread apart, but in water are closer together
Properties of Water (caused by hydrogen bonds)
solute = being dissolved, solvent = doing dissolving, and water is a universal solvent (only with polar bonds)
Solute, Solvent, Aqueous Solution
Nonpolar molecules lack charge, so they can’t bond with water because of LDFs. Also, LDFs are temporary and too weak.
Water has high cohesion, so it is more attracted to itself because of H-bonds and other polar molecules because of their partial charges
Why can water not dissolve non-polar molecules?
a compound with carbon covalently bonded to other atoms (ex. macromolecule and hydrocarbon)
Organic compound
very large molecule made up of many atoms
Macromolecule
molecule of only hydrogen and carbon. Good for combustion reactions. (butane, propane, methane…)
Hydrocarbon
Differences in length, branching, double bonding, and rings of a carbon skeleton, but with the same molecular formula.
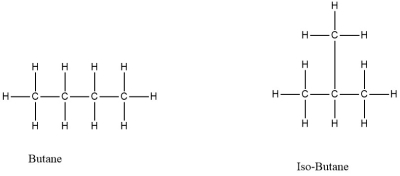
What are isomers?
groups of atoms that affect a molecule’s function (like spice in food) include: hydroxyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, and phosphate groups. make molecules polar.
functional group
-OH

Hydroxyl Group
>C=O
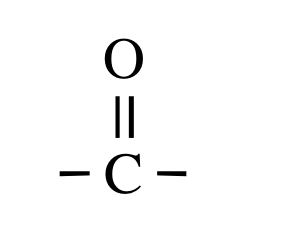
Carbonyl Group
=Hydroxyl + Carbonyl (just know diagram)
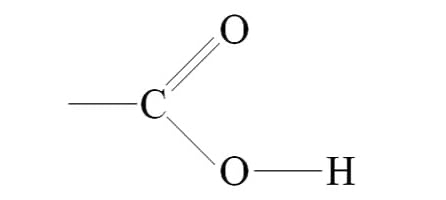
makes carboxylic acid
Carboxyl Group
-NH2 (“ami-” means nitrogen)
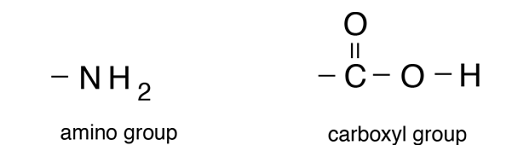
Amino Group
be able to ID it -OPO3-
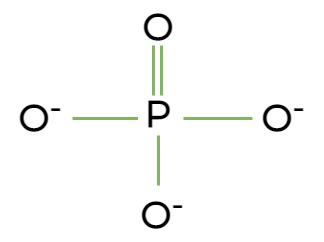
Phosphate Group
a macromolecule is a polymer made up of monomers
Polymer
built by removing water from monomers to form a polymer. Chemical reaction to join monomers/form polymers

Dehydration (synthesis) Reaction (DHS)
Breaks polymers into monomers by adding water; Opposite of a DHS reaction
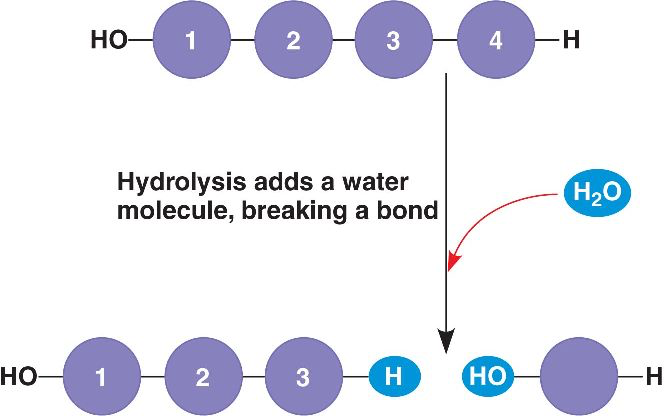
Hydrolysis Reaction
polysaccharide also called complex sugars or carbs
general name for a sugar polymer
monosaccharide (ex. Gluctose and Fructose) also called simple sugars
general name for a sugar monomer
a sugar of any size or length
carbohydrate
short term quick energy
monosaccharide function
2 mono saccarides (linked covalently). Formed by DHS and broken apart by hydrolisis (enzymes help to speed up the reactions[biological catalysts]).
disaccaride
sucrose (glucose + fructose) and lactose (galactose + glucose)
examples of disaccharides
Function is short term, quick energy
disaccharide function
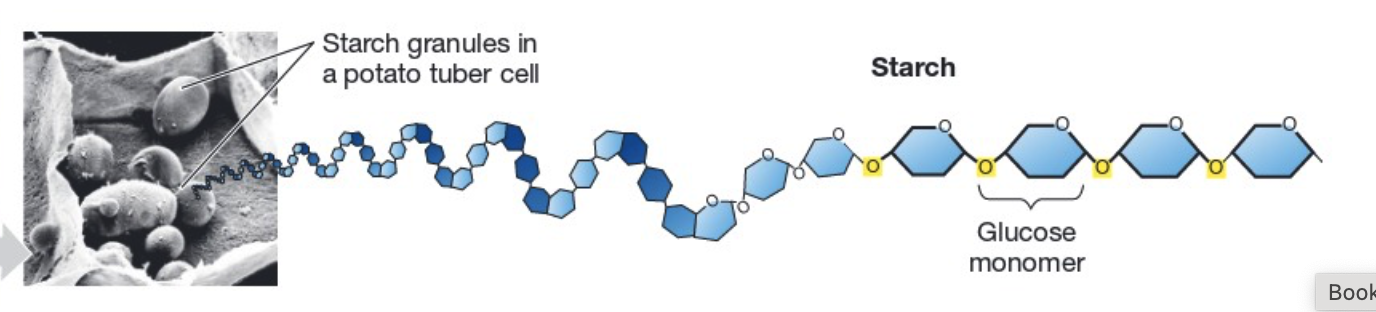
structure: polysaccharide with large amounts of monosaccharides.
made by: plants.
function is long-term energy storage. Ex. potatoes and grains.
Starch (structure, made by, function)
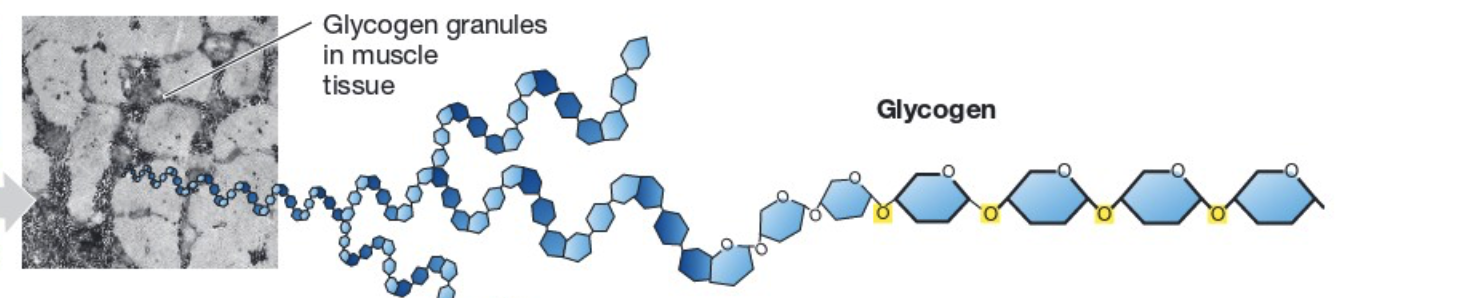
Structure: a polymer of glucose and branched (allows for quick breakdown) and ⍺ 1,4 and ⍺ 1,6.
Made by: animals.
Function: long-term energy (glucose) storage.
Found: liver and muscle tissue
Glycogen (structure, made by, function, location)
Structure: polymer of glucose + h-bonded with other fibers
Made by: Plants
Function: Structural molecule (holds up plant)
Uses beta (1-4)
Cellulose (structure, made by, function)
a hydrophobic molecule. ex. fats, waxes, and steroids.
Lipid
repels water b/c non polar, hydrocarbon, and no functional groups
hydrophobic molecule
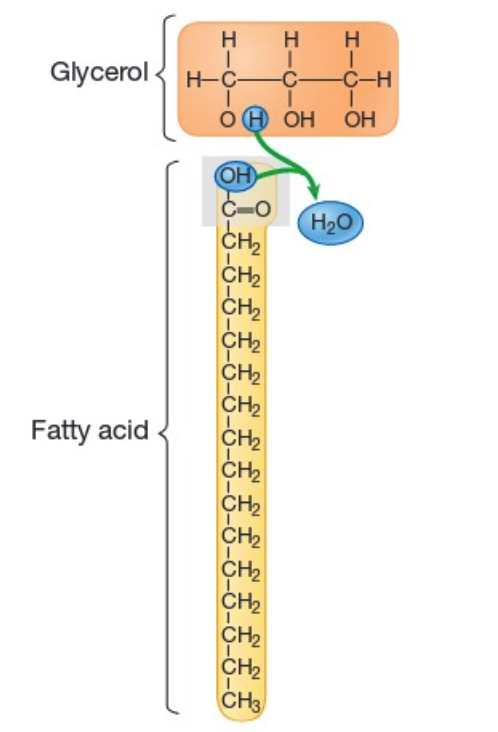
type of lipid. The polymer is called triglyceride, and the monomer is made of one glycerol and 3 fatty acids. The image shown is a saturated fatty acid chain.
Fat
Saturated fatty acid chains contain carbon skelton where the carbon atoms are bound to the maximum amount of H atoms as possible (only contains C-C single bonds).
An unsaturated fatty acid chain, on the other hand, contains C atoms that are not bound to the maximum amount of H atoms, containing at least one C=C double bond (so, C-C and C=C bonds).
Saturated vs. Unsaturated Fatty Acid Chains
made in animals
molecules are compact, so can tightly pack, so solid at room temperature
ex. butter
is not good for heart health
Saturated Fats
made in plants
molecules are bulky, so they can’t tightly pack, so they are liquid at room temperature, e.g., Oils
It’s better for heart health
Unsaturated fats
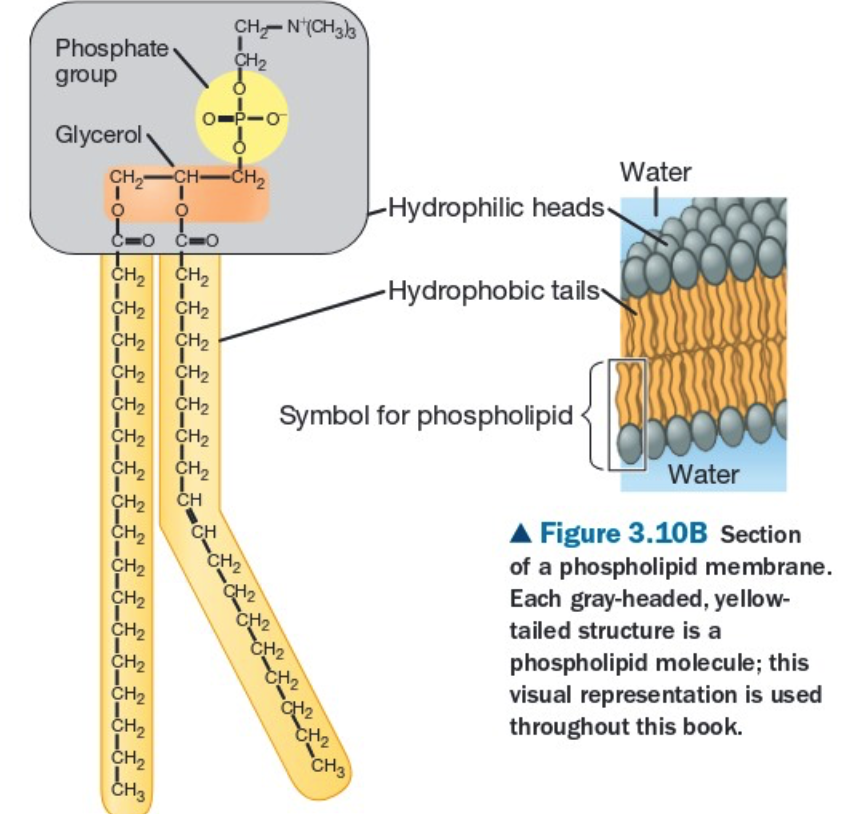
structure: phosphate head (polar, glycerol + phosphate group) and fatty acid tails (can be saturated or unsaturated and non-polar)
is amphipathic, meaning that it has both a hydrophilic region(phosphate head) and a hydrophobic region(fatty tail),
Function: used in the cell membrane.
Phospholipids structure
very long term energy (stored in fat cells), provide insulation/cushioning for nerves.
Function of Triglycerides
fused with 4 hydrocarbon rings. Is in cell membrane and helps to keep structure intact. and non polar
cholesterol
enzyme
help to speed up reactions (biological catalysts).
glycosidic bond
A glycosidic bond is a covalent bond that links a sugar molecule (monosaccharide) to another molecule, which can be another sugar or a different type of molecule, through an oxygen atom.