3.1.2 Metabolic Fates of Pyruvate
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are the three metabolic fates of pruvate?
aerobic oxidation
alcohol fermentation
lactic acid fermentation
Where does aerobic oxidation of pyruvate occur in the cell?
In the mitochondrial matrix
Which enzyme complex catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA?
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
Is the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA reversible or irreversible?
Irreversible
What is the overall reaction of pyruvate oxidation/decarboxyaltion (per 2 pyruvate)?
2 pyruvate —> 2 Acetyl-CoA + 2 CO2 + 2 NADH
What happens to acetyl-CoA after pyruvate oxidation?
It enters the TCA (Krebs) cycle by combining with oxaloacetate to form citrate.
Acetyl-CoA enters the TCA (Krebs) cycle by combining with __ to form citrate.
oxaloacetate
What are the three main catalytic subunits of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase
Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
Which enzyme in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex uses thiamine phosphate (TPP) as a cofactor?
pyruvate dehydrogenase
What cofactor does pyruvate dehydrogenase use?
thiamine pyrophosphate
Which enzyme in the PDC uses lipoic acid and Coenzyme A as cofactors?
dihydrolipoyl transacetylase
What cofactors does dihydrolipoyl transacetylase use?
lipoic acid, coenzyme A
Which enzyme in the PDC uses FAD and NAD+ as cofactors?
dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
What cofactors does dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase use?
FAD, NAD+
What is the ultimate purpose of aerobic oxidation of pyruvate?
Energy generation via the TCA cycle and NAD+ regeneration through the ETC
Biochemically, what is the main purpose of fermentation?
To regenerate NAD+ for glycolysis
Why is NAD+ regeneration critical for glycolysis?
It requires NAD+ as an electron acceptor.
What type of respiration is alcohol fermentaion?
Anaerobic fermentation, in the absence of mitochondria
What are the 2 main steps of alcohol fermentation?
Pyruvate is converted to acetaldehyde by pyruvate decarboxylase
Acetaldehyde is converted to ethanol via alcohol dehydrogenase
What ezyme catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to acetaldehyde (+ CO2)?
Pyruvate decarboxylase
What cofactors are required by pyruvate decarboxylase?
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
Mg2+
Is the pyruvate decarboxylase reaction (pryuvate to acetaldehyde) reversible or irreversible?
Irreversible
What enzyme catalyzes the conversion of acetaldehyde to ethanol?
Alcohol dehydrogenase
Is the alcohol dehydrogenase reaction (acetaldehyde to ethanol) reversible?
Yes
What is the overall reaction of alcohol fermentation?
2 pyruvate —> 2 ethanol + 2 CO2 + 2 NAD+
Draw a diagram for alcohol fermentation.
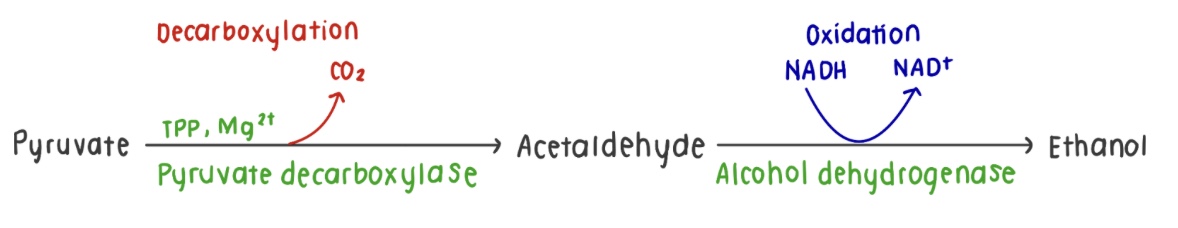
Which organisms perform lactic acid fermentation?
Humans and some bacteria
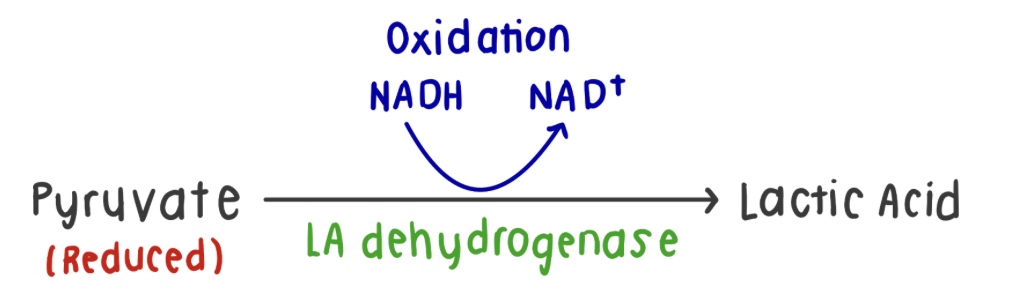
Which enzyme catalyzes lactic acid fermentation?
lactate dehydrogenase
What happens to pyruvate in lactic acid fermentation?
Pyruvate is reduced to lactate by lactate dehydrogenase
Is lactic acid fermentation reversible?
Slightly reversible
Its main purpose is to maintain NAD+ levels so glycolysis can continue under anaerobic conditions.
lactic acid fermentation
What is the drawback of lactic acid fermentation in humans?
accumulation of lactate lowers pH, resulting to acidosis (muslce fatique)
It is a condition in which there is too much acid in the body fluids.
acidosis
What is the overall reaction of lactic acid fermentation?
2 pyruvate + 2 NADH —> 2 lactate + 2 NAD+
Draw a diagram for the overall reaction of lactic acid fermentation.