Mitosis/Cell Differentiation/Cancer
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Prophase
nucleus begins to break down. spindle fibers begin to form. DNA is condensed from chromatin to chromatin.

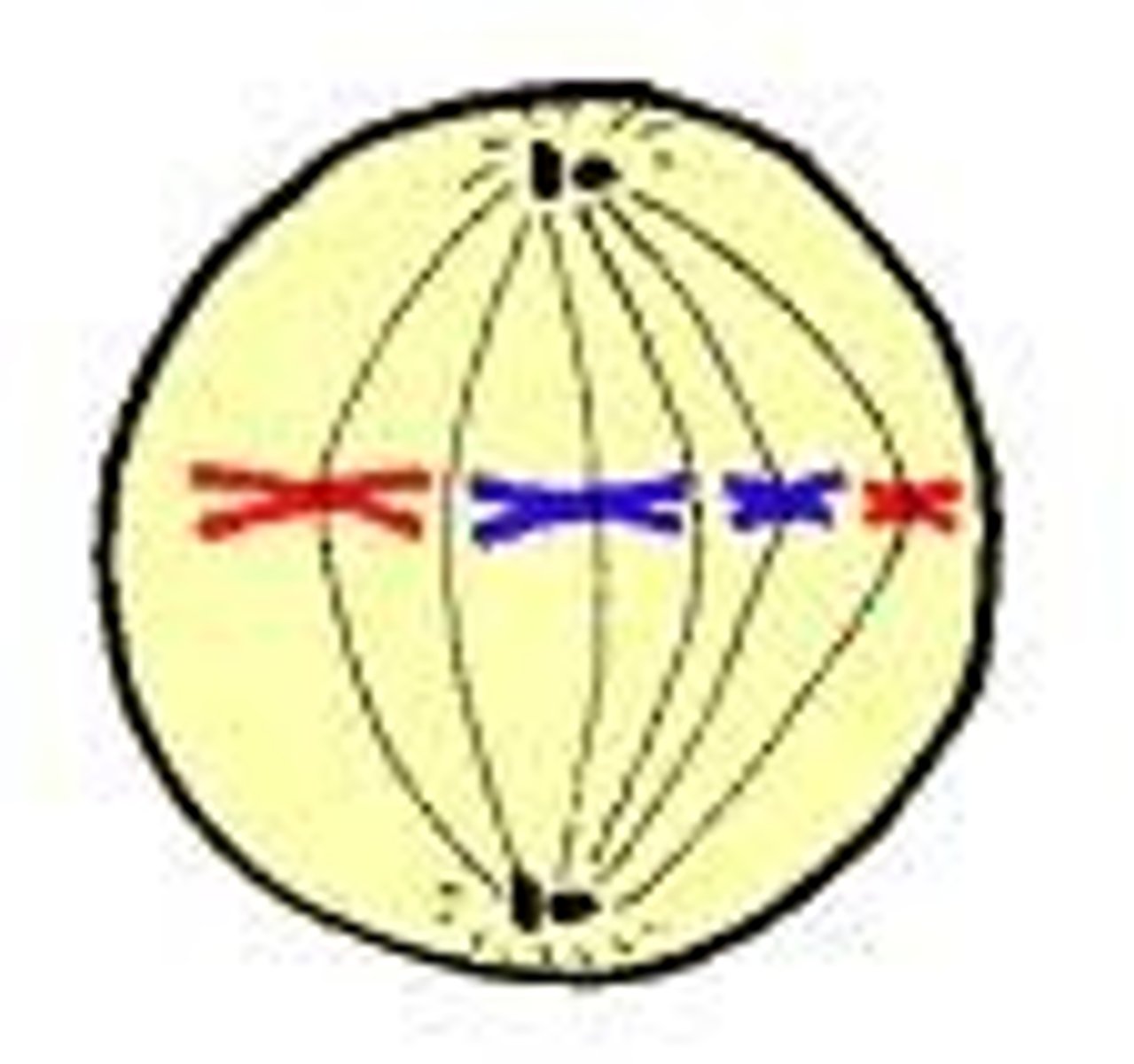
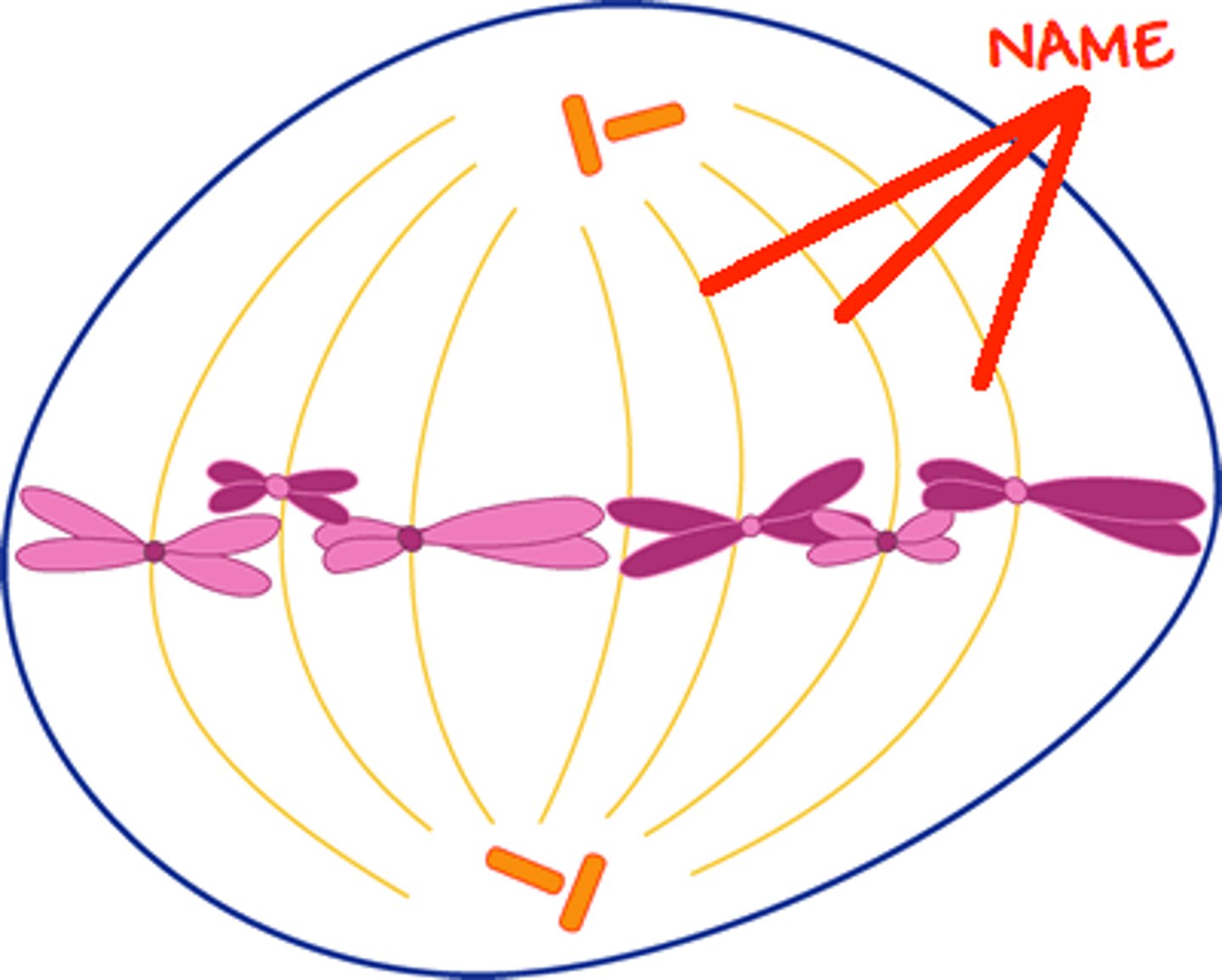
Metaphase
the individual chromosomes begin to line up in the middle of the cell. they DO NOT find their homologous pair. the spindle fibers attach at the centromeres
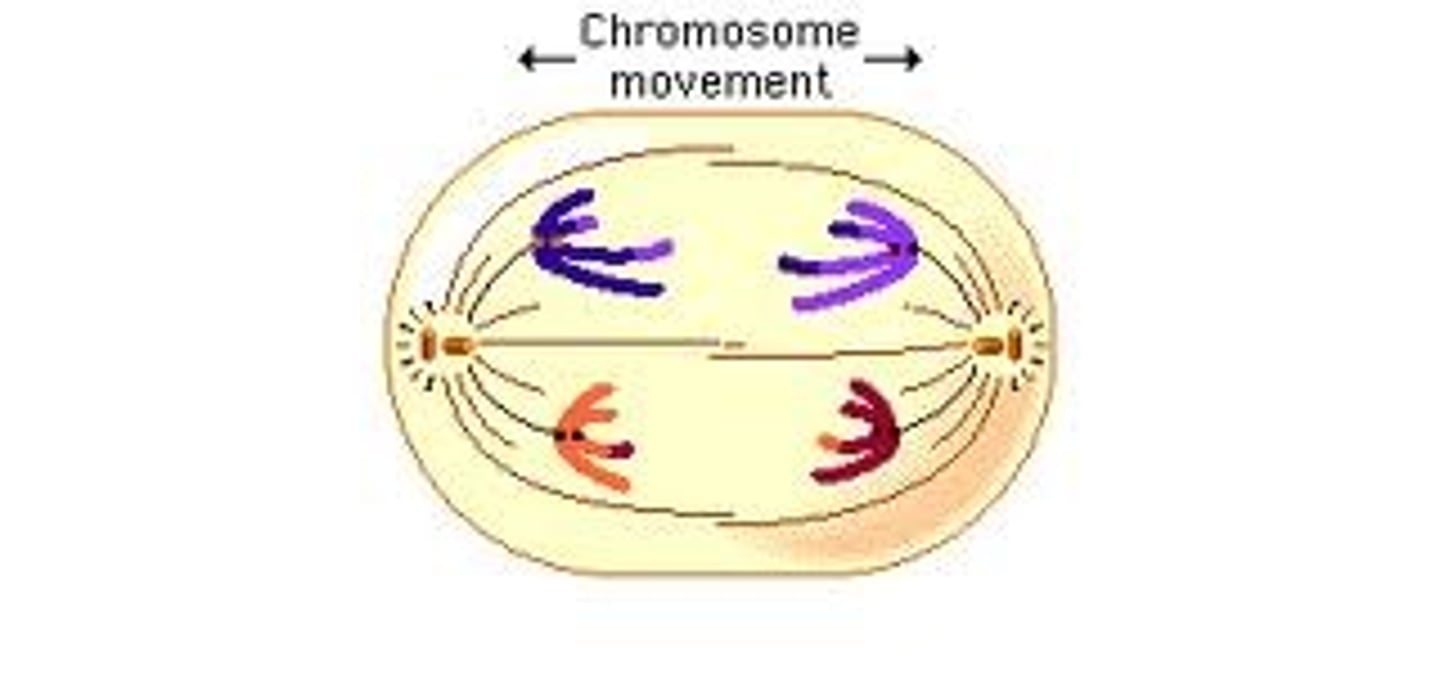
Anaphase
the sister chromatids are pulled apart from one another. they head to opposite poles of the cell.
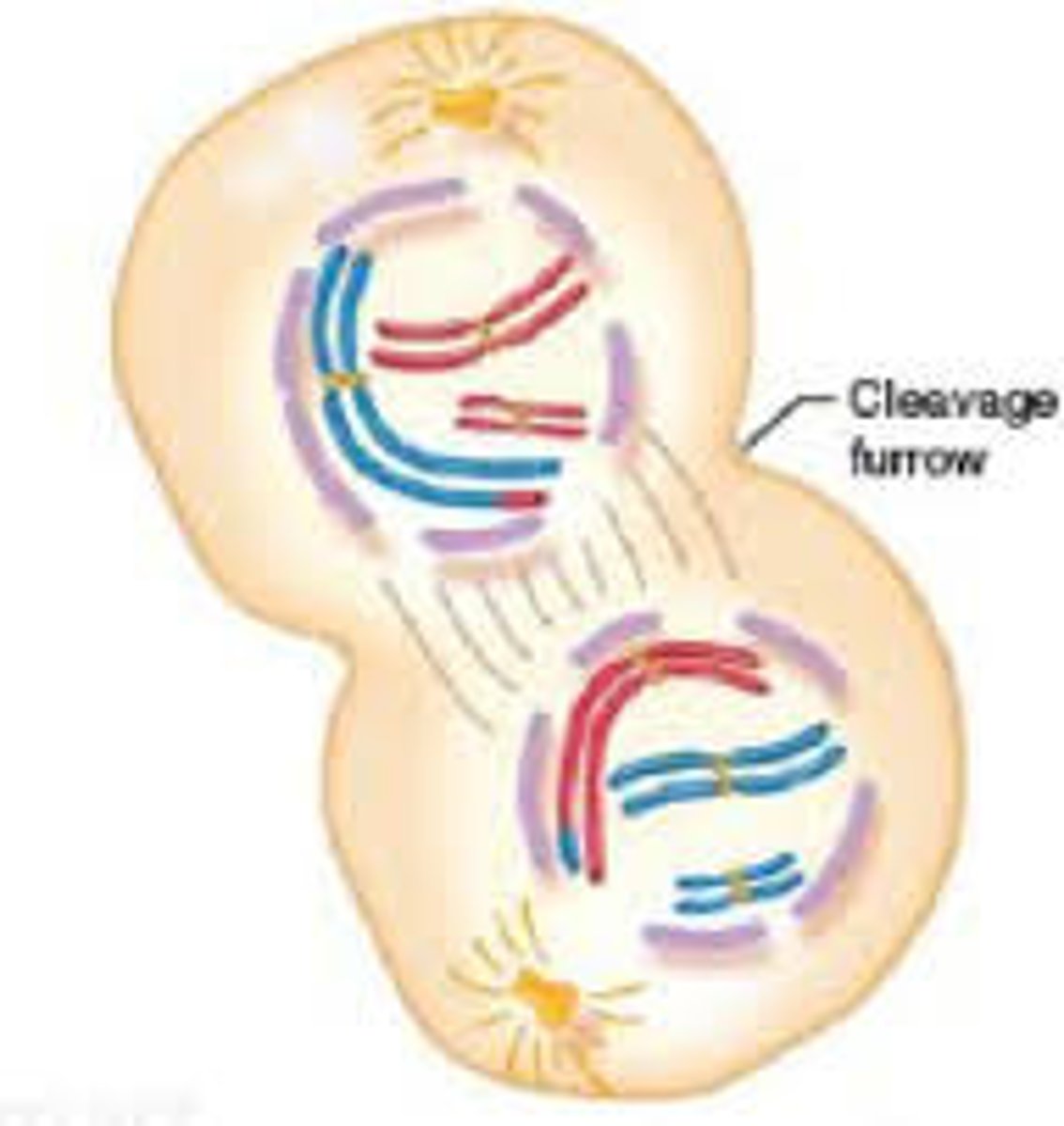
Telophase
This stage is the opposite of prophase. the nucleus is rebuild, spindle fibers are broken down and the chromatids unwind
Mitosis
A type of cell division in which each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell. makes somatic body cells. makes two diploid daughter cells.
Interphase
Includes G1, Synthesis, and G2. The cell grows and DNA is replicated. Takes about 70-90% of a cells life
Cytokinesis
cell pinches in on itself to split the cytoplasm in two.
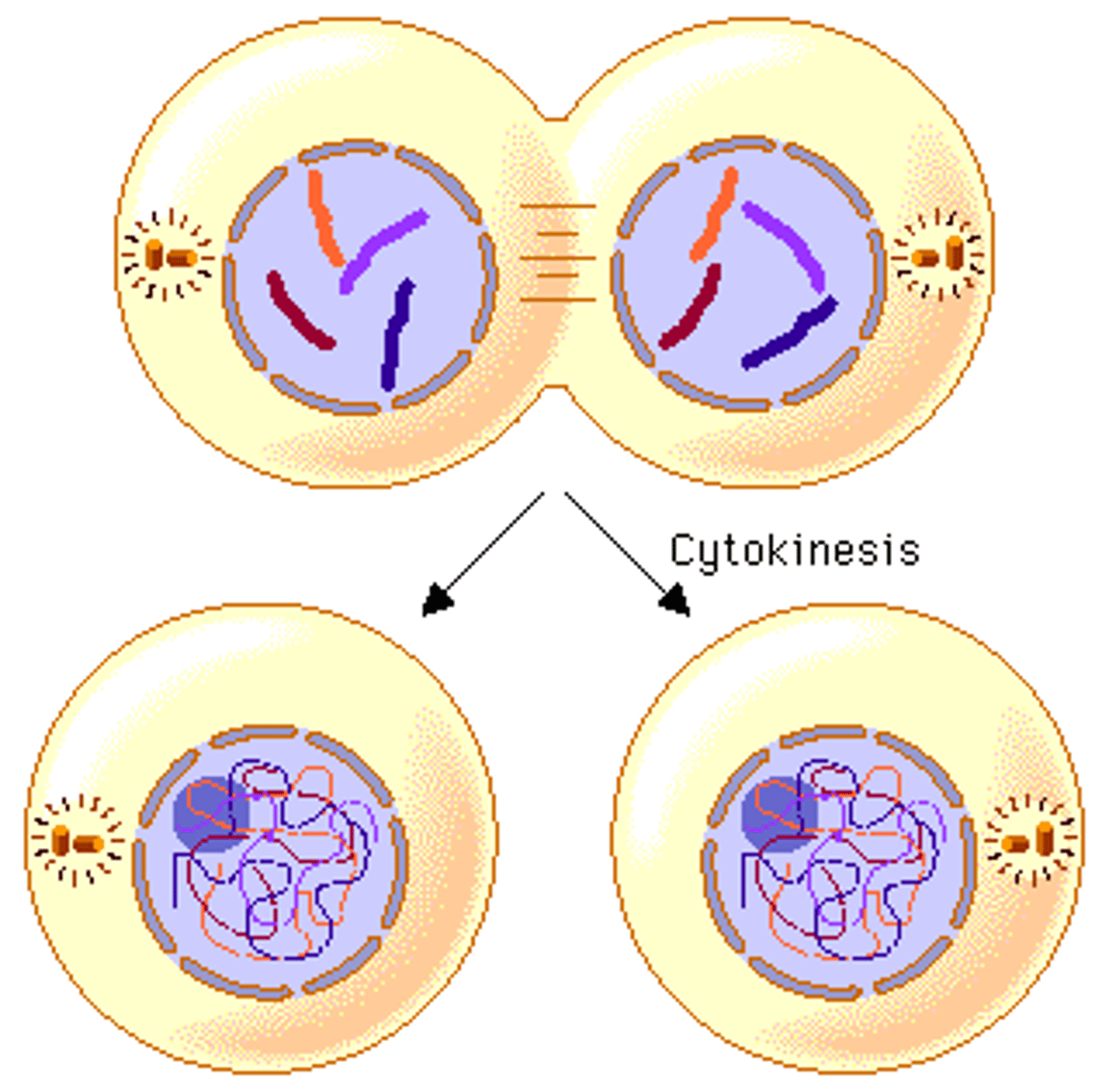
G1
The cell grows and replicates organelles
G2
Cell check for errors in organelle or DNA replication
S Phase
The cell replicates all DNA.
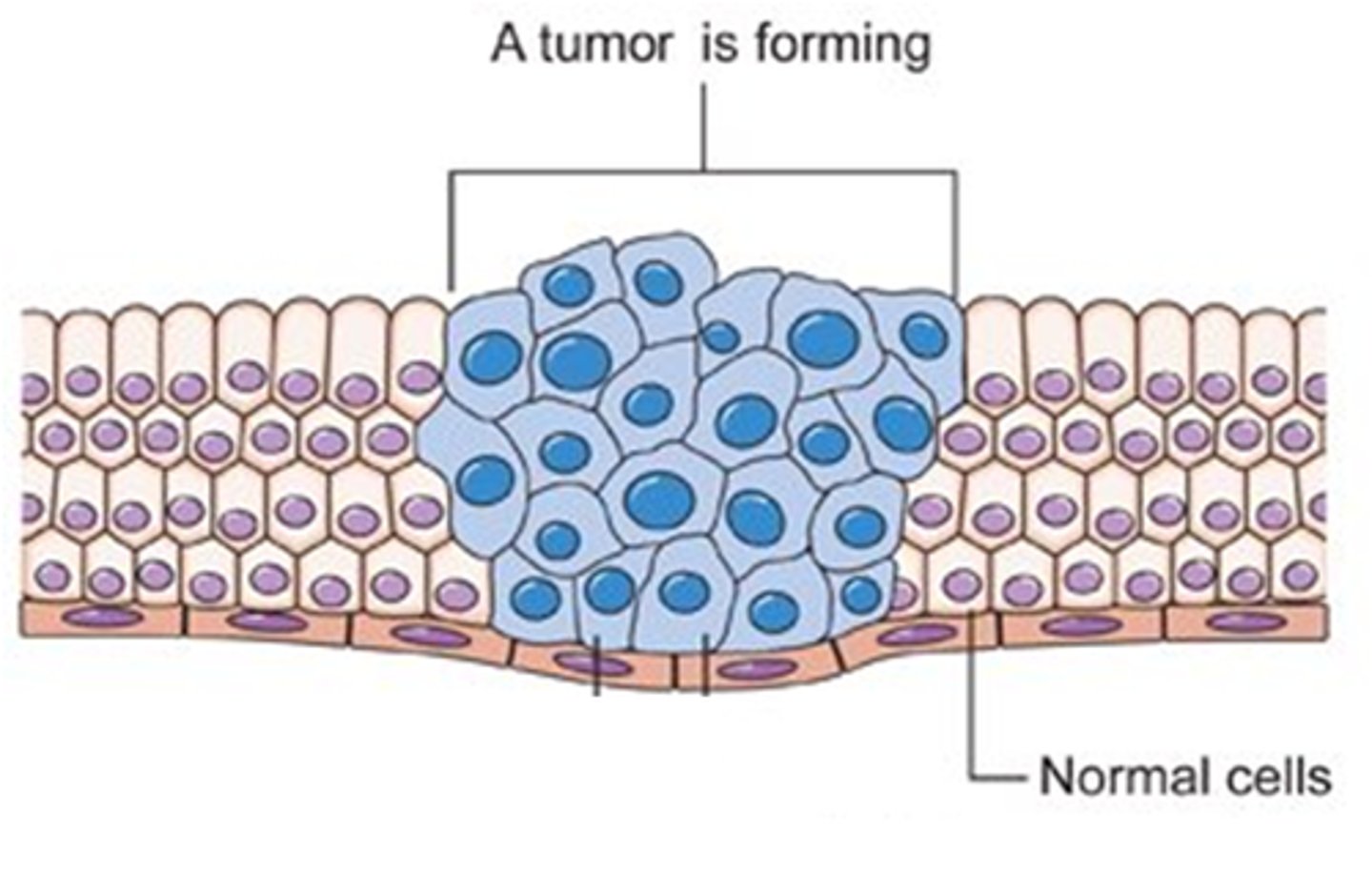
Cancer
Disease caused by the uncontrolled division cells
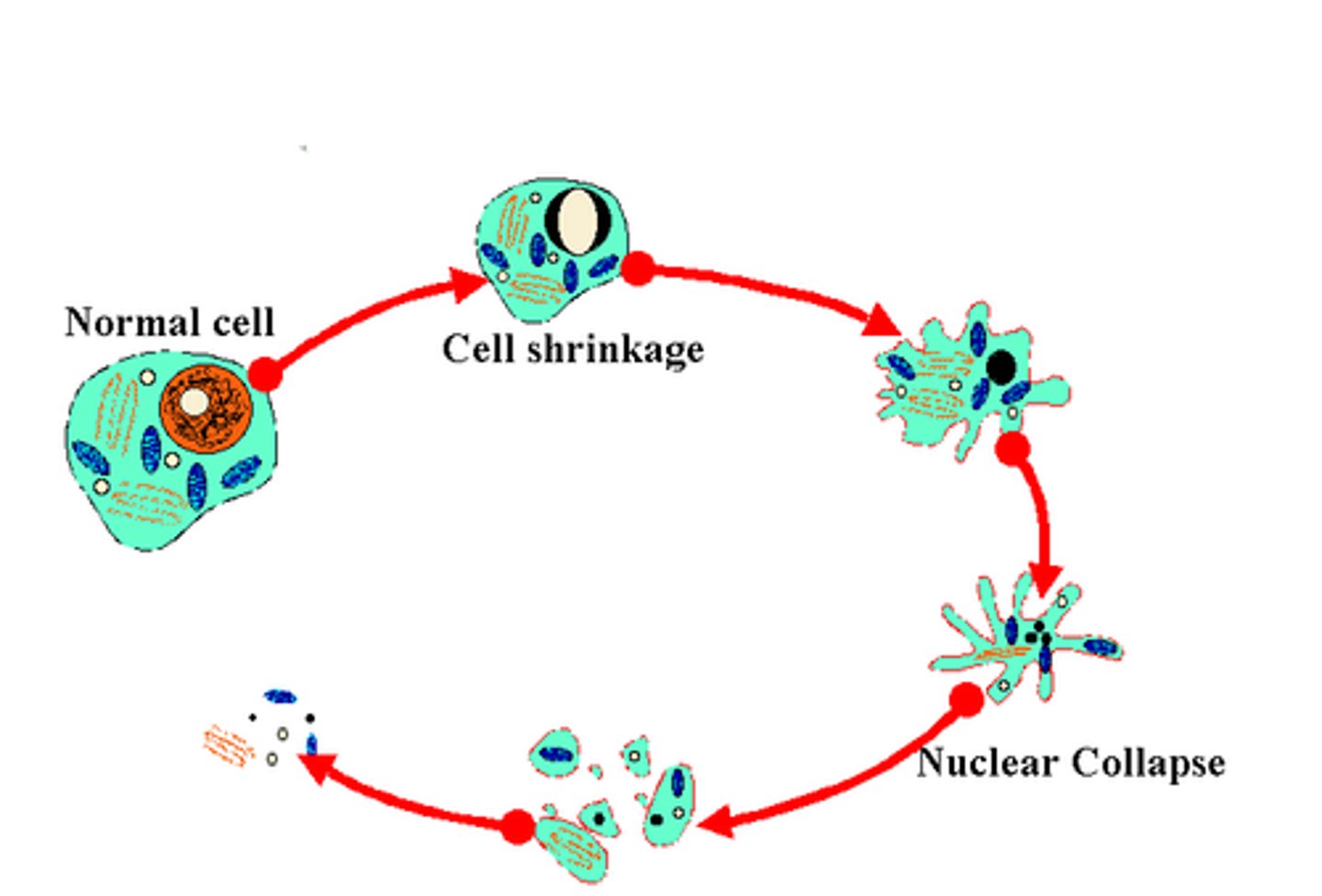
Apoptosis
programmed cell death. beneficial if the cell has damaged DNA, it wont make copies of itself; it will just die.
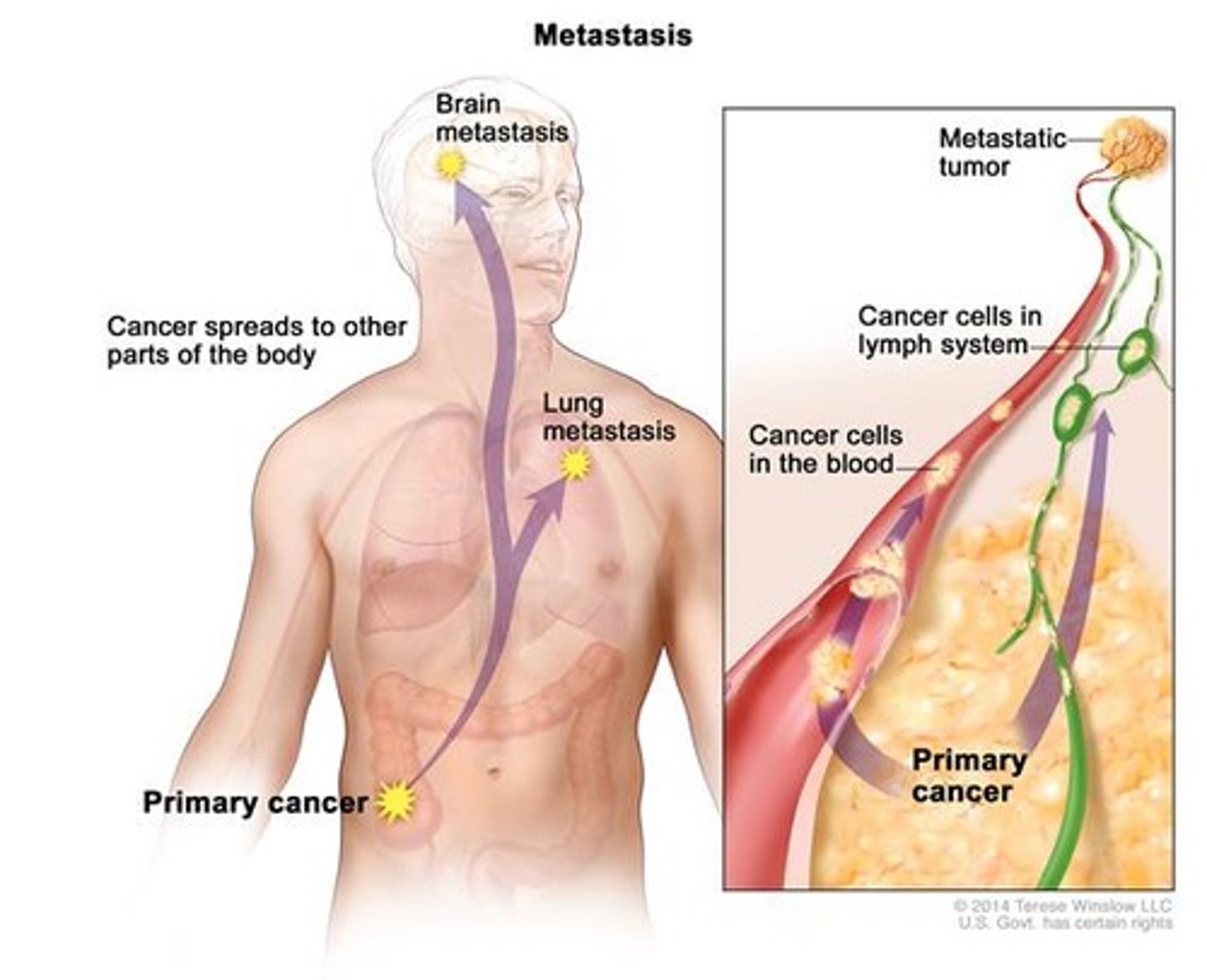
Metastasis
the spreading of cancer (through the blood). Tumor are set up in other parts of the body
Benign tumor
a non-cancerous tumor. not dangerous
Malignant tumor
a cancerous tumor; can spread
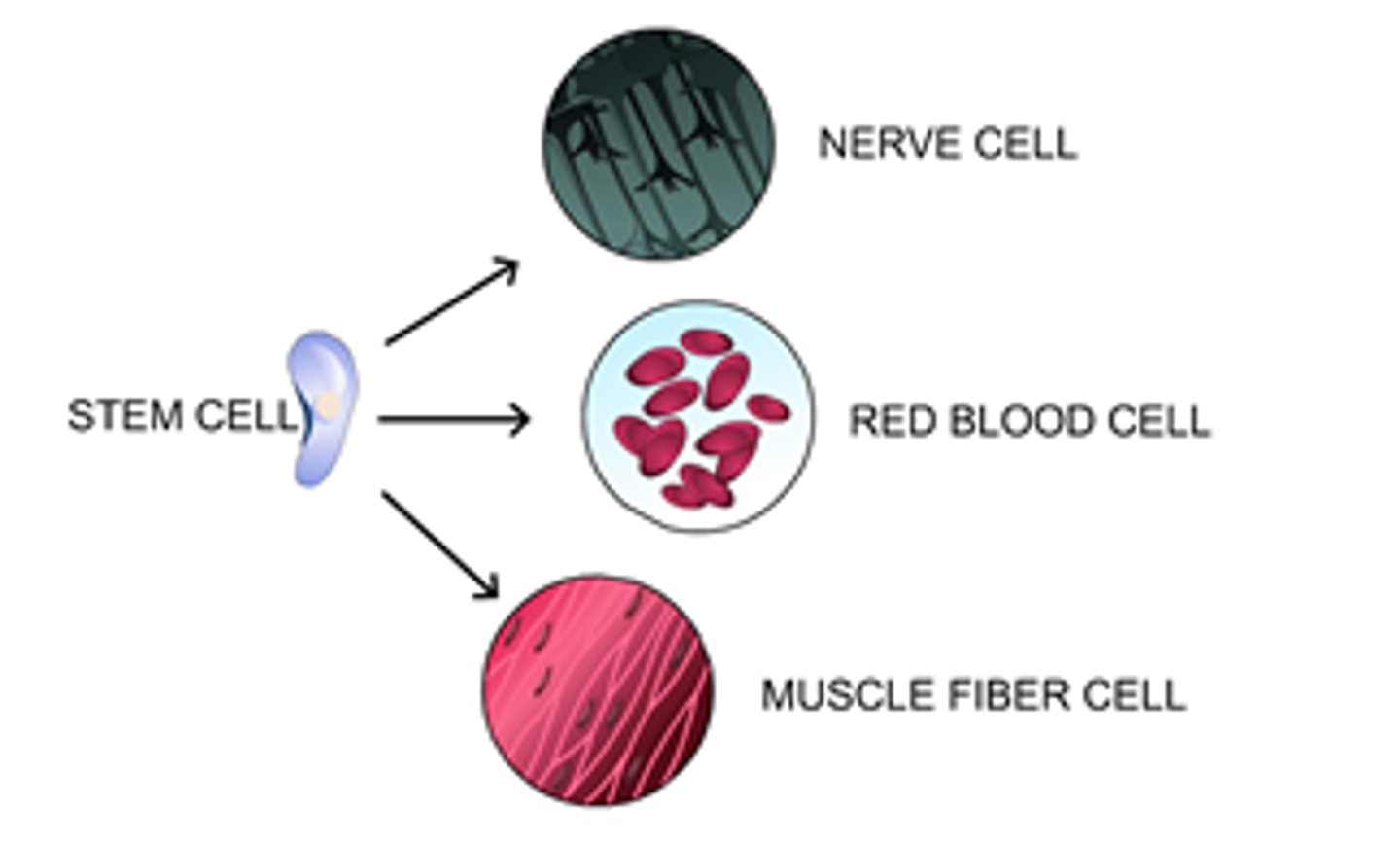
Cell differentiation
the process by which a cell becomes specialized to do a particular job. ie: a cell becomes a stomach cell or a blood cell.
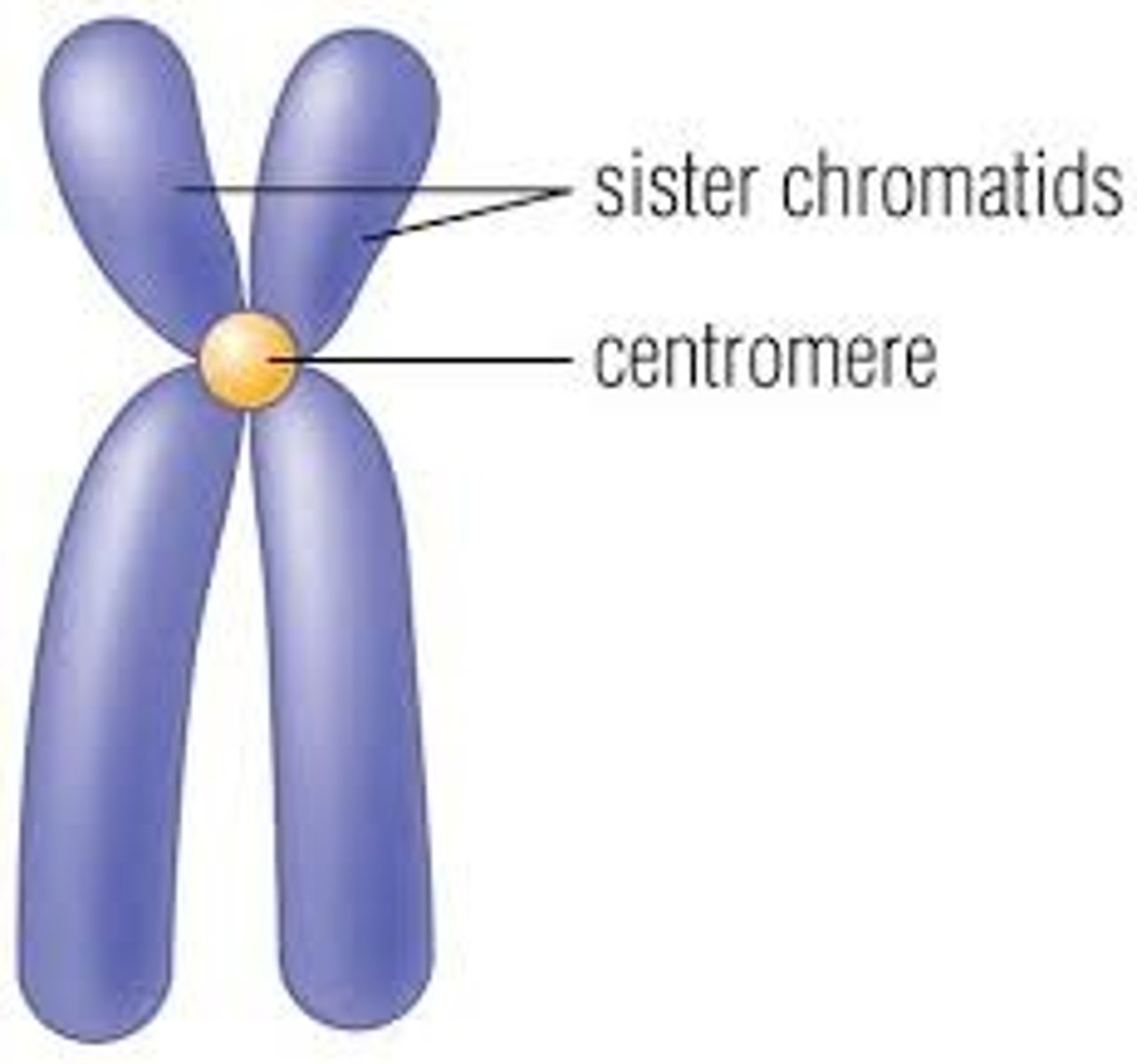
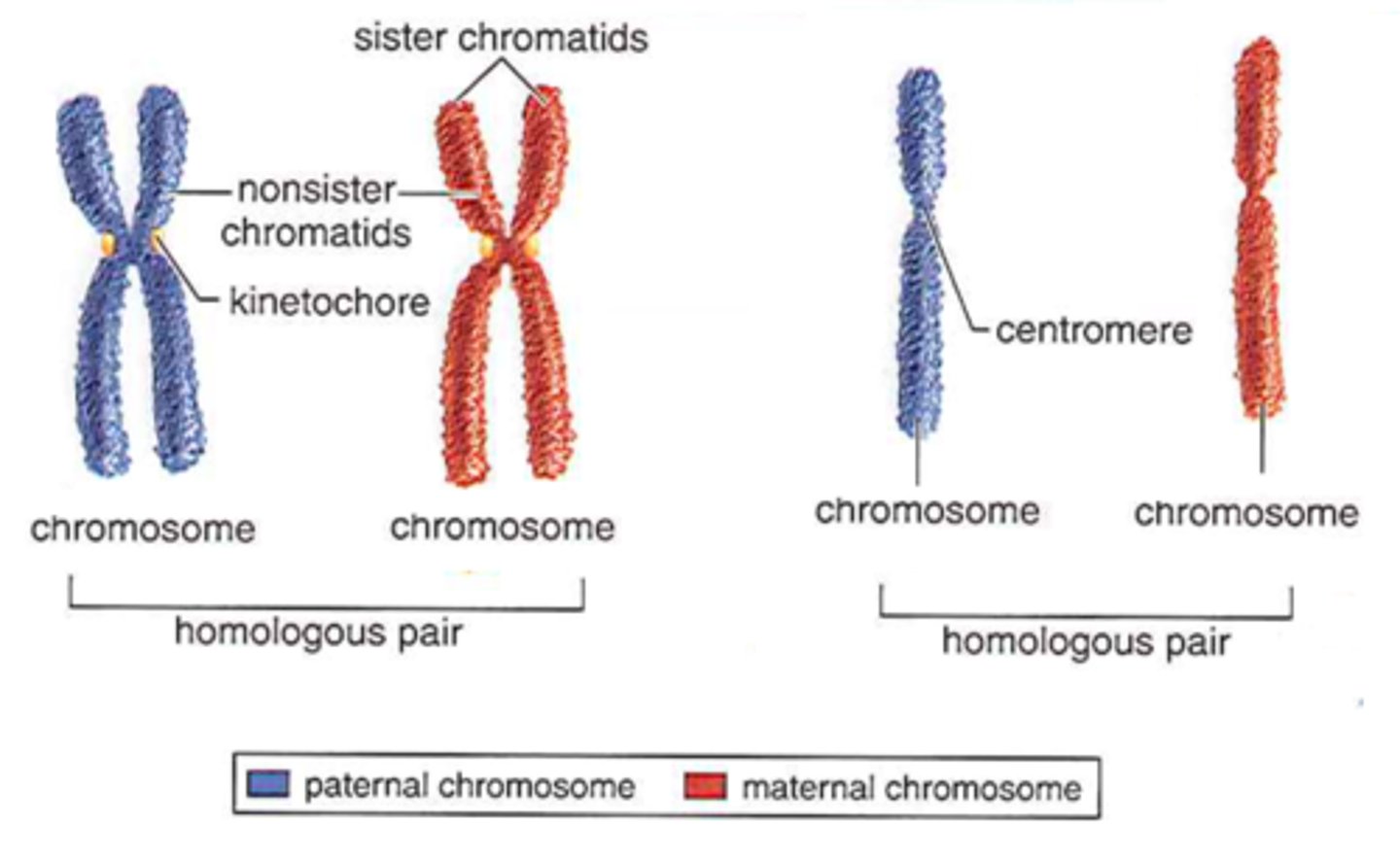
Centromere
where the spindle fibers attach; hold the sister chromatids together
spindle fibers
the long, rope-like tubes of proteins that pull the chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell during cell division
Carcinogen
cancer causing agents Ex: xrays, smoking, UV light

sister chromatids
identical copies of a chromosome. made during S phase. joined together by the centromere and eventually separated during mitosis.
metastasize
cancer spreads from one place to another
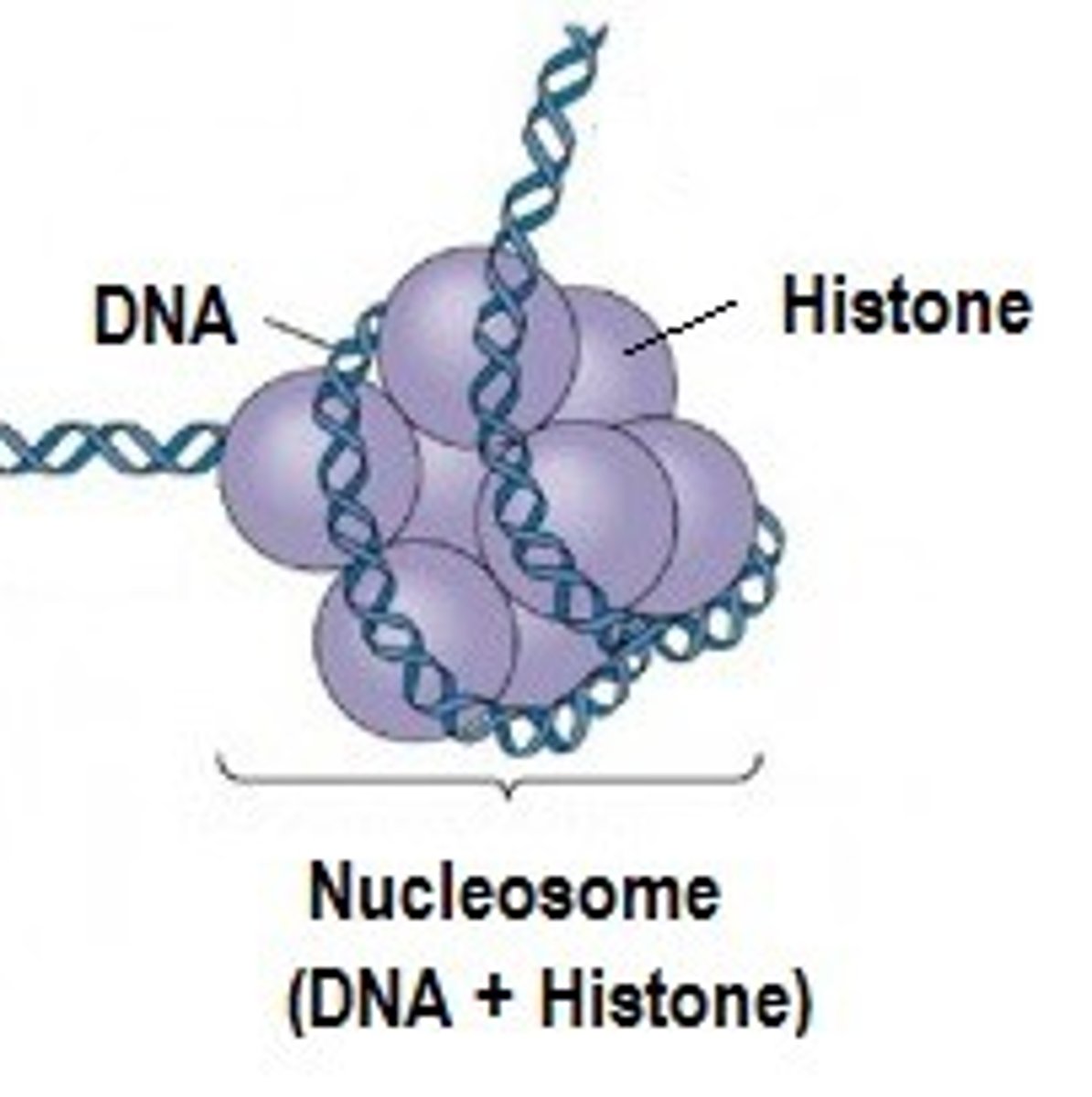
Histones
protein around which DNA is tightly coiled into condensed chromosomes
protooncogenes
genes whose normal job is to stimulate the cell cycle
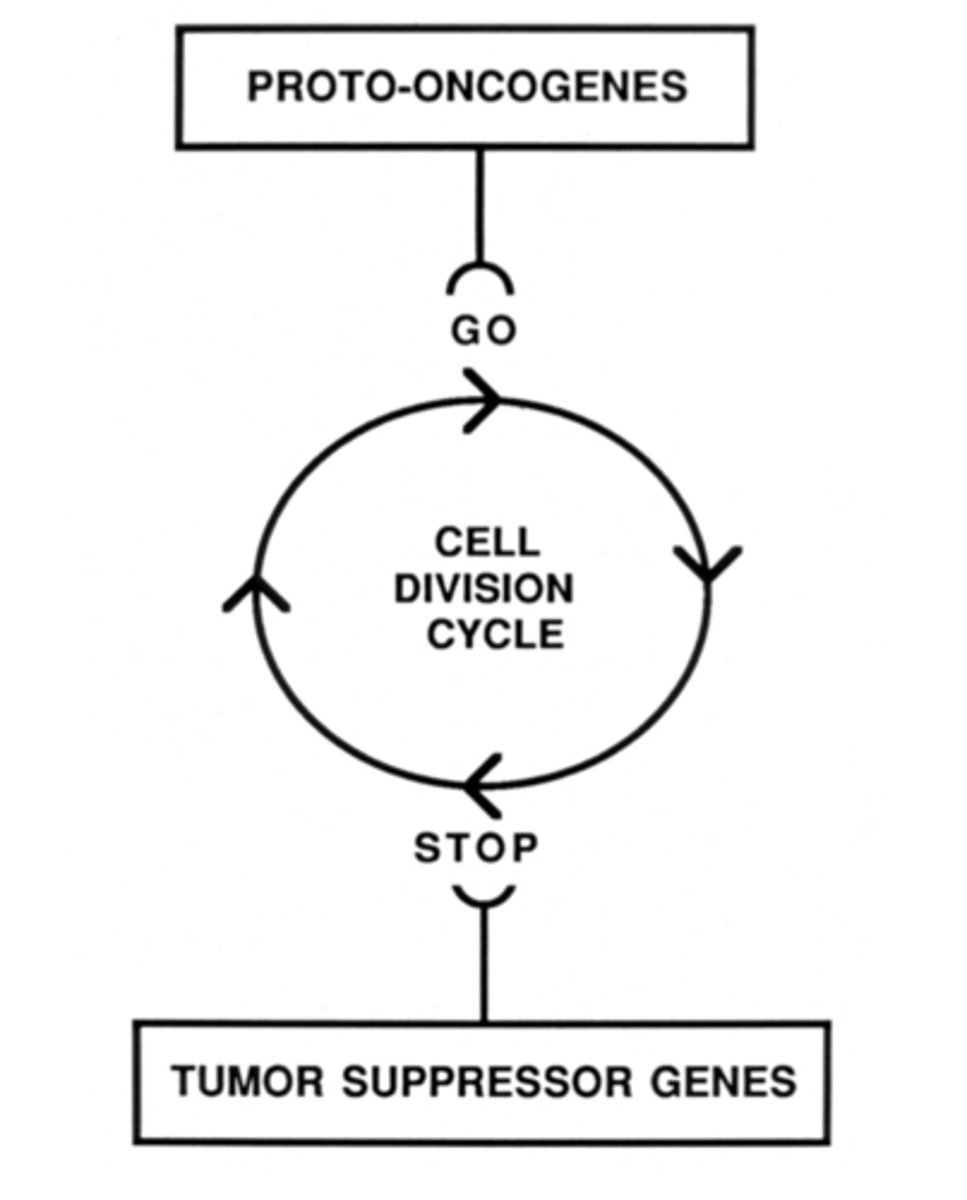
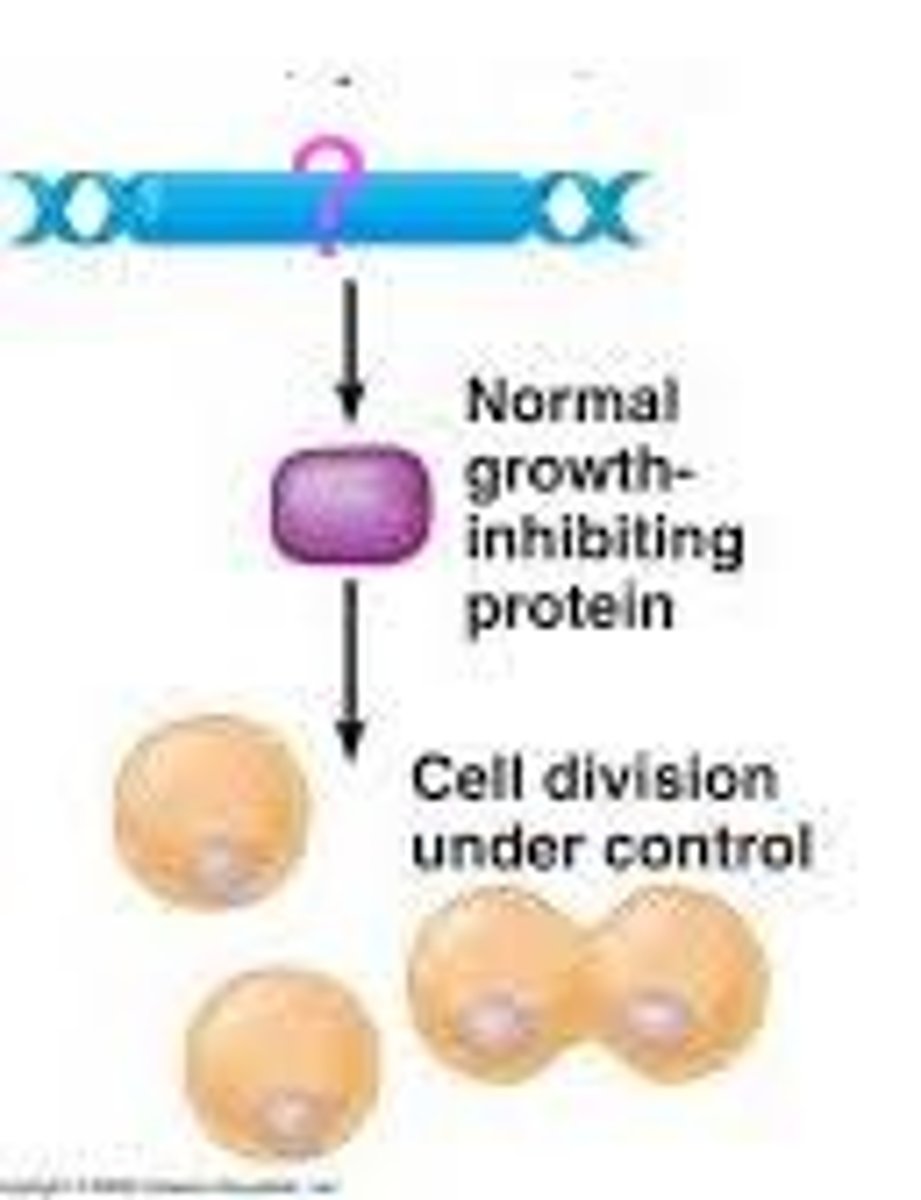
tumor suppressor genes
A gene whose normal job is to inhibit cell division, thereby preventing the uncontrolled cell growth that contributes to cancer.