POLYMERISATION
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
condensation polymerisation
involves 2 different types of monomer, each with at least 2 functional groups
each functional group reacts with a group on another monomer to form a link
creating polymer chains
as each link is formed
a small molecule is lost, usually water hence the name
examples of condensation polymers
polyesters
polypeptides (proteins)
polyamides
polyester link
(-COO-)
polyamide/polypeptide link
(-CONH-) aka peptide bonds
Dicarboxylic acid + diamides =
polyamides + H2O
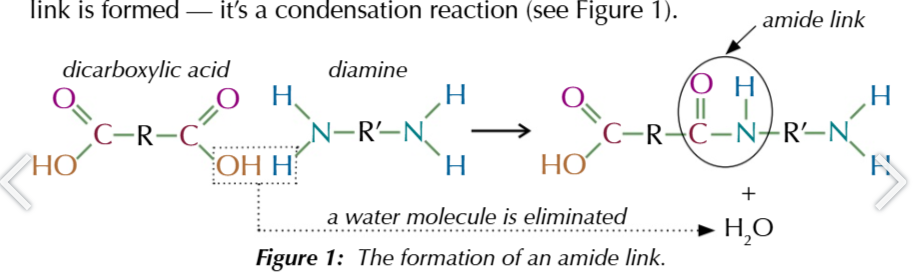
because dicarboxylic acids and diamines have functional groups on both ends
they cna each form 2 amide links and long chains can be formed
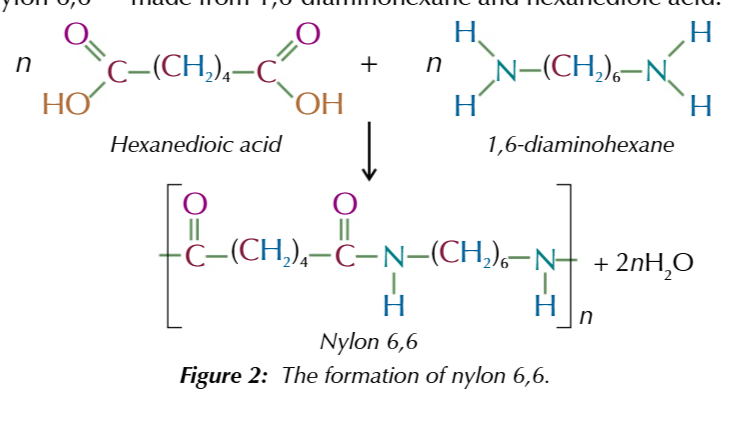
important polyamine reaction 1:
n [hexanedioic acid] + n [1,6-diaminohexane] = [nylon 6,6]n +[2H2O]n
![<p>n [hexanedioic acid] + n [1,6-diaminohexane] = [nylon 6,6]n +[2H<sub>2</sub>O]n</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5636f019-20f7-4247-a014-685f1a9ca307.png)
nylon is strong and resistant to abrasion so has many uses:
clothing
carpet
rope
airbags
parachutes
important polyamide reaction 2:
n [benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid] + n [1,4-diaminobenzene] = [Kevlar]n+ [2H2O]n
Kevlar is light and strong so has many uses:
bulletproof vests
boat construction
car tyres
lightweight sports equipment
amino acids contain 2 functional groups
carboxylic acid and amine functional groups
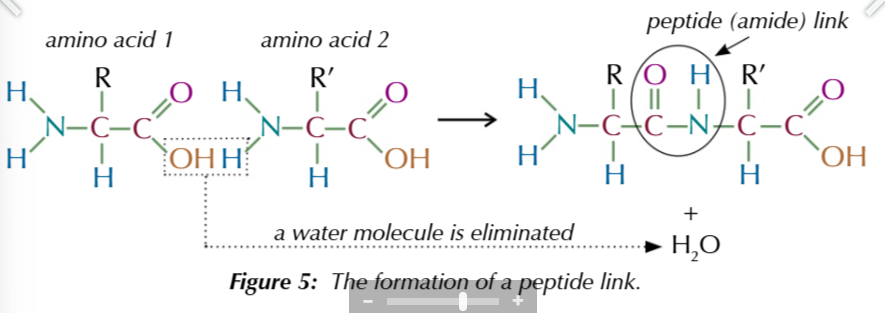
amino acids react in a condensation reaction to form
peptides
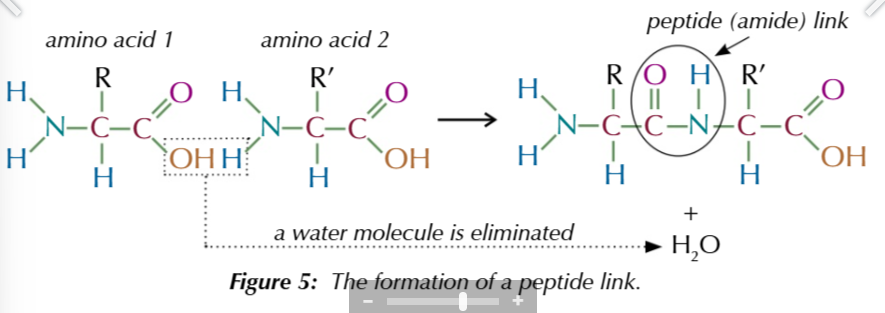
amino acids contain chiral carbons
1 carbon is attached to NH2,H,COOH and R
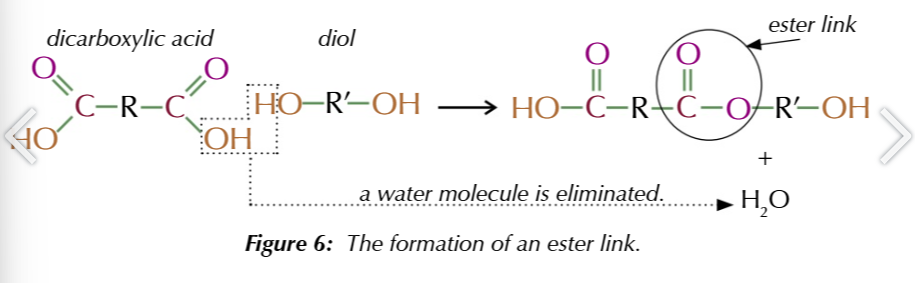
dicarboxylic acids + diols =
polyesters, the H from diol and OH from dicarboxylic form the water released +ester link
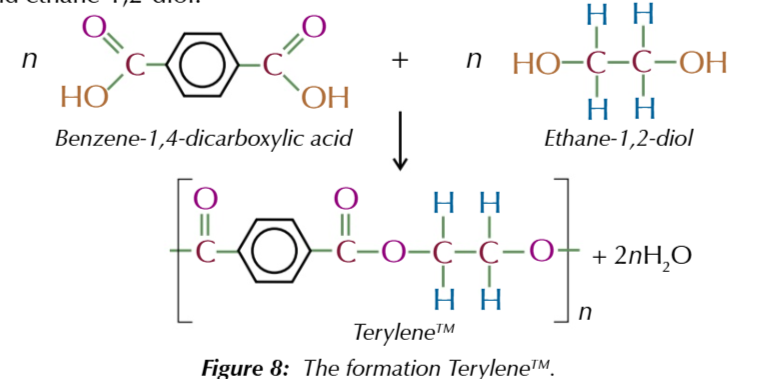
important polyester reaction:
n [benzene 1,4-dicarboxylic acid] + n [ethane-1,2-diol] → n[Terylene] + 2n[H2O]
hydrolysis
using water to split a molecule
![<p>n[monomer]<sup> condensation</sup>⇄<sub>hydrolysis</sub> polymer + water</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/22a3cdef-182c-40e8-8394-a4349d7fda5e.png)
n[monomer] condensation⇄hydrolysis polymer + water
n [polyamide] + 2n[H2O] → n [dicarboxylic acid] + n [diamine]
![<p>n [polyamide] + 2n[H<sub>2</sub>O] → n [dicarboxylic acid] + n [diamine]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/aa3f2cf5-9a77-4ccd-9c7d-a57ae9785c70.png)
n [polyester] + 2n [H2O] → n [dicarboxylic acid] + n [diol]
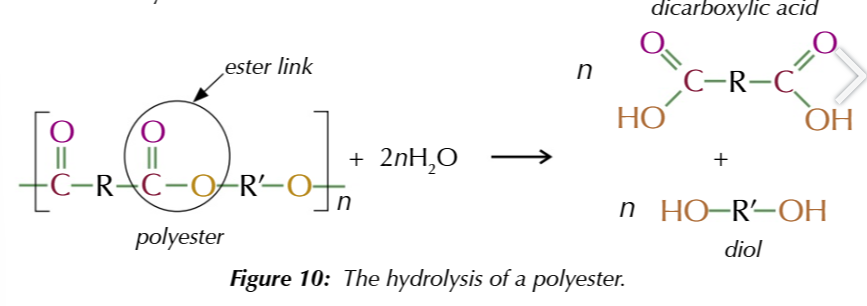
in practice, water hydrolysis is too slow
in a lab the reaction is done using acids/alkalis
polyamides hydrolyse better in acidic conditions
polyesters hydrolyse more easily in basic conditions
condensation polymers are generally stronger and more rigid than addition polymers
because condensation polymers chains consist of C=O and C=N polar bonds
these bonds + induced dipole-dipole forces + permanent dipole-dipole forces + hydrogen bonds between the polymer chain make it extremely strong
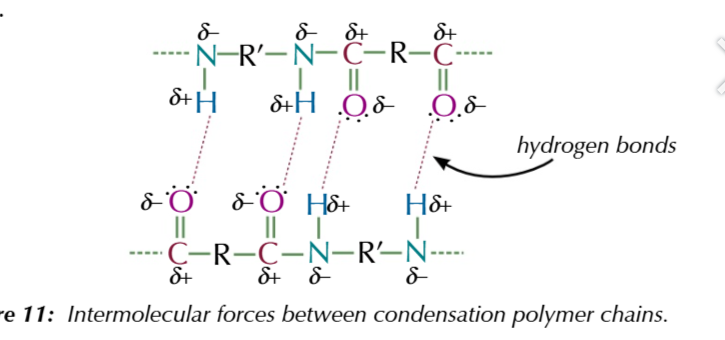
condensation polymers are made up of repeating units
if you know the formula of a pair of monomers you can work out the repeating unit of condensation polymer you form
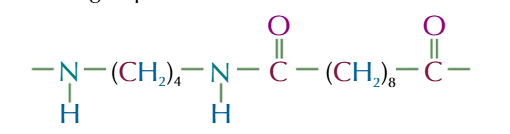
steps to find the repeating unit of polyamides from diamines and dicarboxylic acids
draw out the 2 monomers
remove the OH from the dicarboxylic acid and the H from the diamine to create a water molecule
coin the C=O AND N together to make an amide link
take the H off the other NH2 and OH off the other COOH at the ends of your molecule
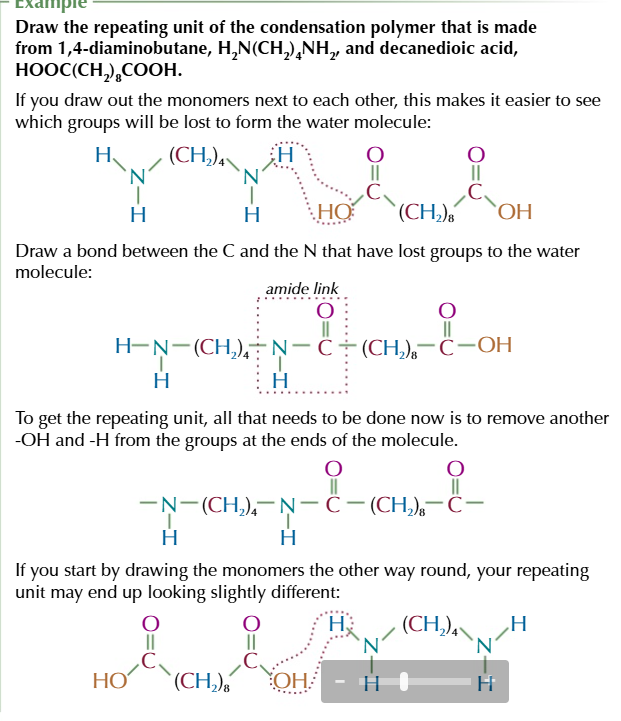
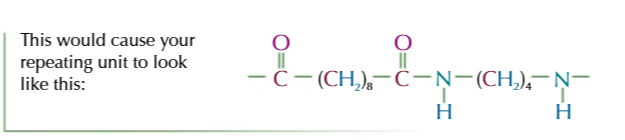
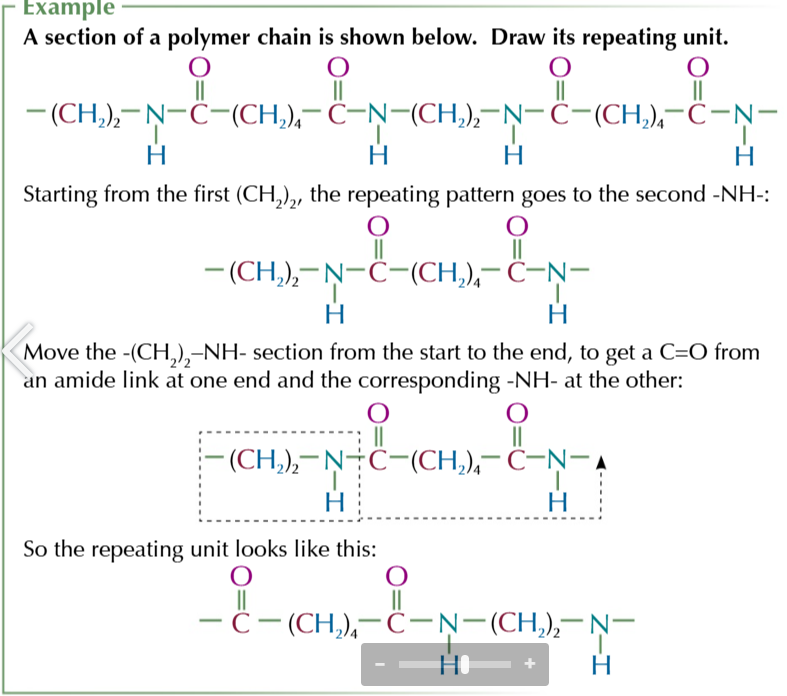
how to find the repeating unit from a longer chain section of polyester/polyamide
look along the chain and find the repeating pattern
starting from 1 end write out the chain until you get the end of the repeating section
the repeating unit should have a C=O from an ester/amide link and 1 end and the -O-/-NH- part of the link at the other end
if the secon youve written DOESNT find the amide/ester link, breake it and move the bit you’ve broken off from one end of the unit to the other
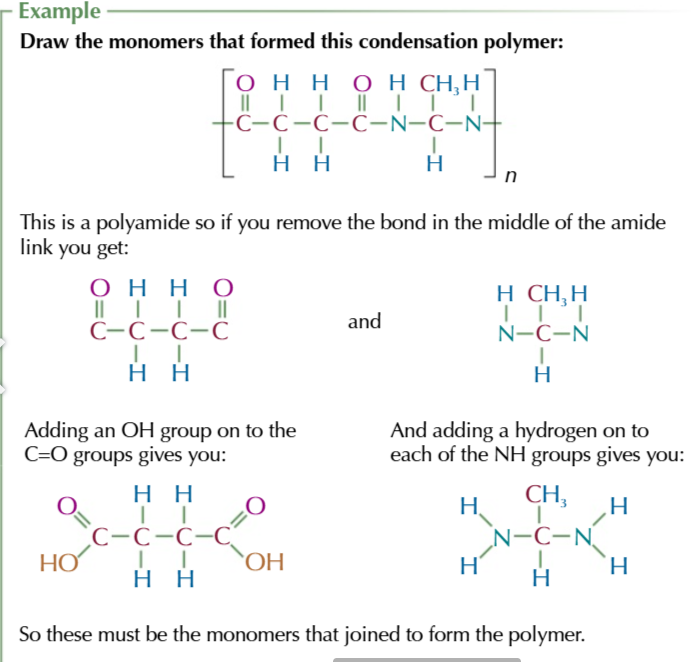
how to identify monomers
find the repeating unit
remove the bond in the middle of the central amide/ ester link:
-C=O group and -NH group in polyamides
-C=O group and Oxygen in polyesters
add -OH groups to the -C=O to make carboxylic groups
add H to NH to make NH2 in polyamides
add H to Oxygen to make -OH groups and add it to any terminal carbon atoms in polyesters
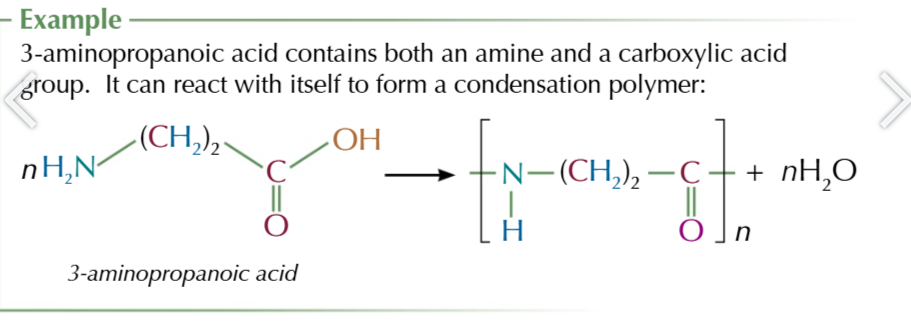
if an molecule can contain a carboxylic acid group AND an alcohol group/ amine group
it can polymerise with itself to form a condensation polymer with only 1 monomer
this is the case for amino acids which contain a carboxylic acid group AND amine group
they polymerise to form peptides
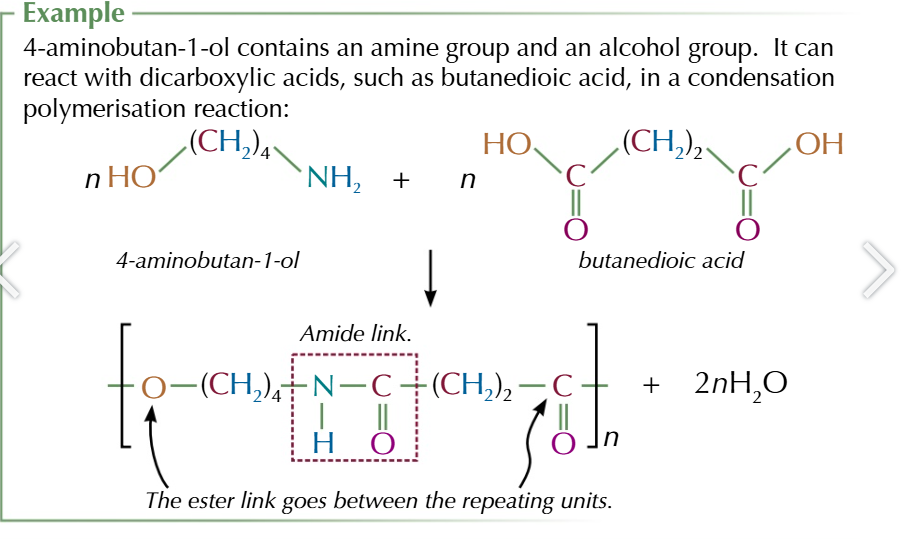
molecules with an amine group AND alcohol group can react with dicarboxylic acids in a condensation polymerisation reaction
the polymer they form contain both amide and ester links
synthetic polymers have loads of advantages
they are incredibly widespread

polyalkenes examples
polystyrene and polyethene
polyalkenes are chemicall inert
because the bonds between the repeating units are non polar (so not prone to nucleophilic attacks)
an advantage of being chemically inert
polystyrene wont react with coffe
disadvantage of being chemically inert
non biodegradable (their bonds can’t be hydrolysed and wont break down naturally)
condensation polymer examples
PET (a polyester that’s used to make fizzy drink bottles and carrier bags)
nylon (a polyamide)
condensation polymers CAN be broken down via hydrolysis
because the bonds between repeating units are polar so susceptible to nucleophilic attacks like by water
condensation polymers are biodegradable
they will break down naturally over a long period of time
since plastics are either non biodegradable or biodegrade over a long period of time
the question becomes what to do with the 3 million tons of plastics thrown away every year
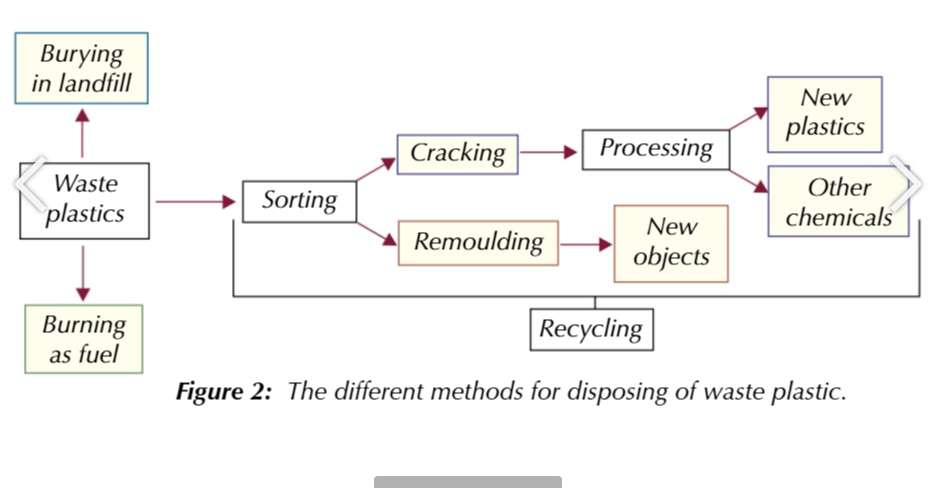
landfills are used when plastics are difficult to seperate from other waste
and what can be seperated is too little for the process to be financially worthwhile
and too difficult to recycle
landfill is a relatively cheap and easy method of waste disposal HOWEVER:
required areas of land
as waste decomposed it can release methane (GHG)
as waste decomposes it can release toxins which can be washed away and contaminate water supplies
waste plastics can be burned
and their heat used to generate electricity
burning plastics can release toxic gases so you must be careful
for example, polymers containing chlorine like PVC when burnt can release HCl
waste gases from the combustion are passed through scrubbers
this neutralises gases such as HCL by reacting them with bases
carbon dioxides is also a waste gas
which will contribute to global warming
many plastics are made from non renewable oil fractions
plastics need to be recycled as much as possible
after sorting into different types of plastics
they can be melted and remoulded OR cracked into momomers which can me used to make more plastics/chemicals
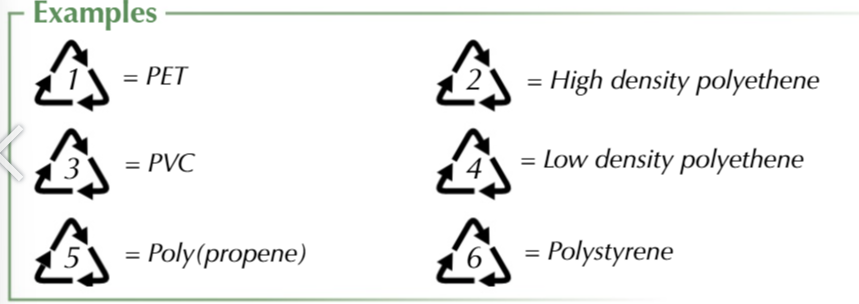
plastic products are marked ot make sorting easier
advantages of recycling plastics
reduces the amount of waste going to land fills
saves raw materials which is important because oil is non renewable
the cost of recycling plastics is lower than making new plastics from scratch
produces less CO2 emission than burning plastcs
disadvantages of recycling plastics:
technically more difficult to recycle plastics
collecting sorting and processing plastics is mroe expensive than burning/landfills
often cant remake the plastic you started with, will have to make something else
plastics can be easily contaminated during recycling