2535 Lecture 3: Legal/Ethical, Pt-Focused, Gene Therapy/Pharmacogenomics, Med Erros
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
canadian food and drug act
primary legislation of governing food, drugs, cosmetics, med devices
drugs must comply with official prescribed standards
recognized formularies
various schedules
controlled drugs and substances act (CDSA)
replaced narcotic control act 1997
provides requirement for control/sale of narcotics, controlled drugs, substance misuse
letter N and DIN symbol printed on label of every narcotic drug
RCMP responsible for enforcement of CDSA
narcotic reconciliation (narcotic count)
see P&P at organization
must be done every shift
cannot leave until count is correct
marijuana use
marijuana medical access program replaced in 2014 with marijuana for medical purposes regulation
health canada regulates the producers of marijuana for this purpose but not involved in decision-making process
consumed in resins, oils, extractions, edible formed, dried for smoking
new drug develpment
ongoing process
system of drug research and development most stringent in the world
developed out of concern for pt safety and drug efficacy
canadian national health products regulations (2003)
health canada drug approval process
once approved, drug assigned to DIN
4 clinical phases of investigational drug studies
1st, informed consent obtained
phase I = small # of health subjects (fewer than 100)
phase II = larger 3 of volunteers who have the disease or ailment (100-300)
phase III = larger # of pt who are followed by medical research centres (1,000-3,000)
phase IV = postmarketing studies voluntarily conducted by drug companies to obtain info of therapeutic and adverse effects of new drug
pt access to and cost of prescription drugs
high drg expense significant barrier for access to prescription drugs that are not covered under Canada Health Act
low income, no drug benefits, poor health
OHIP+ = children and Youth Pharmacare
special Access Programme
allows health care providers compassionate access to drugs not available for sale in canada
limited to those with serious or life-threatening conditions
legal nursing considerations
nursing practice standards of care (CNO)
scope of practice (RHPA)
case law or common law consisting prior to court rulings
CNA is national voice for nurses
accreditation canada requires accredited hospitals to fulfill certain standards regarding nursing practice
liable for negligence and malpractice
failure to assess or re-evaluate
failure to ensure safety
medication errors
ethical considerations
ethical principles useful strategies
autonomy, beneficence, nonmaleficence, justice, fidelity, veracity
CNA code of ethics for RN
international council of nurses (ICN) code of ethics for nurses
legal and ethical nursing considerations
safe, compassionate, competent, ethical care
privacy and confidentiality
promotion of justice
accountability
preservation of dignity
informed decision making
promotion of health and well-being
right of nurse to refuse care
violates nurse personal ethical principles
nurse speaks to supervisor/manager to request unit transfer, must not abandon pt
nurse responsible for providing non-judgemental nursing care
nurse always acts in best interest of pt while remaining objective to pt advocate
use of placebos
drug dosage form without pharmacological activity
used in experimental drug studies
considered unethical (creates mistrust among nurses, prescribers, pt)
not specific formal guidelines
use of placebos in research
informed consent process followed
pt informed of their right to
leave study without pressure/coercion
leave student with no consequences to medical care
receive full and complete info about study
made aware of alternative options and receive info on all treatments, including placebo therapy
drug therapy during pregnancy
drug cross placenta via diffusion
factors affecting safety
drug properties
fetal gestational age
maternal factors
motherisk program
US food and drug (FDA) implemented pregnancy safety categories
drug therapy during breastfeeding
BF infants are at risk to exposure to drugs consumed by mother
consider risk-benefit ratio
absorption - neonatal/pediatric pharmacokinetics
gastric pH acidic util 1-2 yrs
gastric emptying slowed
first-pass elimination reduced
reduced bile salt formation decreases bioavailability
intramuscular absorption faster and irregular
distribution - neonatal/pediatric pharmacokinetics
total body water differences result in increased distribution and dilution of water (soluble drugs)
greater total body water = lower fat content
decreased level of protein binding = increased distribution
immature blood-brain barrier = more drug enters brain
metabolism - neonatal/pediatric pharmacokinetics
liver immature = not produce enough microsomal enzymes
older children increased metabolism = higher more frequent doses than infants
liver enzyme production
genetic differences
substance to which mother expose during pregnancy
excretion - neonatal/pediatric pharmacokinetics
kidney immaturity affects glomerular filtration rate and tubular secretion
decreased perfusion rate of kidneys = reduced excretion of drugs
factors affecting pediatric drug dosages
skin in thin/permeable
stomach lacks acid to kill bacteria
lungs have weaker mucus barrier
body temp less regulated, dehydration occurs easily
liver and kidneys immature, impairing drug metabolism and excretion
methods of dosage calculations of PED pt
body surface area method = west nomogram
always use weight in kg, not Ibs
always use height in cm, not inches
body weight dosage cals = mg/kg
Calculate the dose of amoxicillin suspension in mLs for otitis media for a 1-yr-old child weighing 22 lb. The dose required is 40 mg/kg/day divided BID and the suspension comes in a concentration of 400 mg/5 mL.
Step 1. Convert pounds to kg: 22 lb × 1 kg/2.2 lb = 10 kg
Step 2. Calculate the dose in mg: 10 kg × 40 mg/kg/day = 400 mg/day
Step 3. Divide the dose by the frequency: 400 mg/day ÷ 2 (BID) = 200 mg/dose BID
Step 4. Convert the mg dose to mL: 200 mg/dose ÷ 400 mg/5 mL = 2.5 mL BID
general considerations - peds med admin
prepare all equipment and supplies 1st
have caregivers stay as appropriate
assess for comfort methods before, during, after drug admin
infants
toddlers
preschoolers
school-aged children
adolescents
considerations for older adult pts
65+
high use of meds
polypharmacy
nonadherence
increased incidence of chronic illnesses
sensory/motor deficits
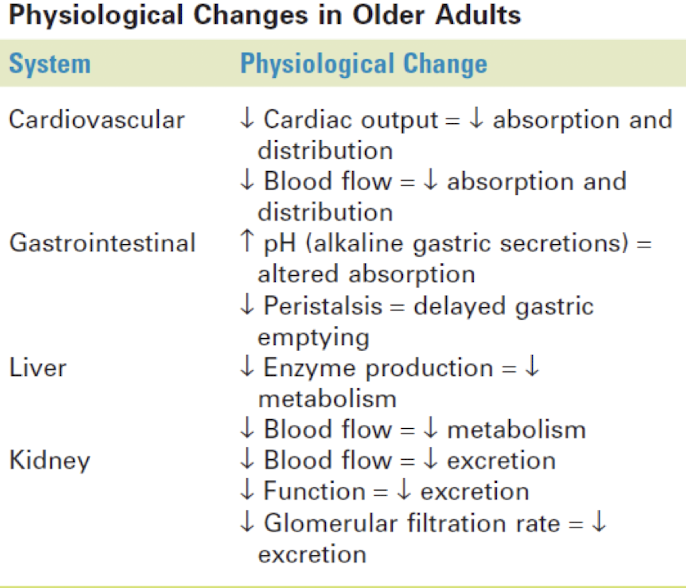
absorption - older adults pharmacokinetics
gastric pH less acidic
gastric emptying slowed
movement through GI tracts slowed b/c of decreased muscle tone and activity
blood flow to GI tract reduced
absorptive surface of GI tract reduced
distribution - older adults pharmacokinetics
lower total body water percentage
increased fat content
decreased production of proteins by liver = decreased protein binding = increase circulation of free drugs
metabolism - older adults pharmacokinetics
aging liver produces fewer microsomal enzymes
blood flow to the liver reduced
excretion - older adults pharmacokinetics
decreased glomerular filtration rate
decreased number of intact nephrons
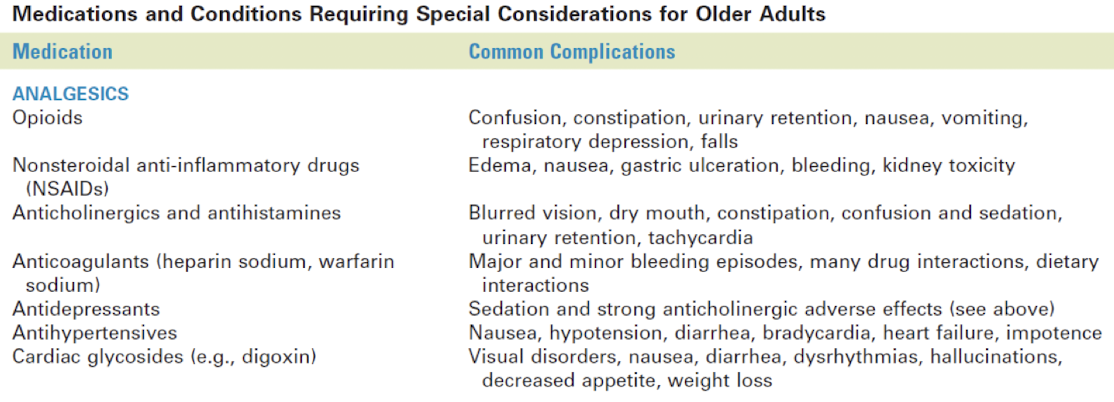
older adults med requiring special considerations
opioids
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
anticoagulants
antidepressants
antihypertensives
cardiac glycosides
beers criteria for prevention of adverse drug events - older adults
listing of drug and drug classes to be avoided in older adults
identified disease states considered to be contraindication for some drugs
three categories
potentially inappropriate drugs and classes in order adults
potentially inappropriate meds to avoid certain diseases
meds used with caution in older adults
enthnopharmacy
expanding body of knowledge for understanding specific impact of cultural factors on pt drug response
hampered by lack of clarity in terms of race, ethnicity
ethnocultural assessment needs to be part of the assessment phase of nursing process
not every pt from same country shares same culture
ethnocultural influences and genetics on drug response
polymorphism
medication response depends on the level of pt adherence
use of natural health remedies may alter a drug response
environmental and economic factors
awareness of ethnocultural differences
ethnocultural assessment
languages
health practices and beliefs
past uses of medicine
use of herbal treatment, folk/home remedies, natural health products
use of over-counter drugs
usual response to illness
responsiveness to medical treatment
religious practices and beliefs
support for pt ethnocultural community
dietary habits
ethnocultural nursing considerations and drug therapy
important to be knowledgeable about drugs that may elicit varied responses in culturally diverse pts
recognition that patterns of communication may differ
thorough ethnocultural assessment needed
maintaining, protecting, restoring health
human genome project
1990-2003
identified 30,000 genes, 3 billion base pairs in DNA of entire human genome
improved prevention, treatment, cures for disease
new tools for genetic data analysis and storage
gene therapy
experimental technique using genetic material to treat/prevent disease
replacing mutated gene with a healthy copy of the gene
introducing a new gene into the body to help fight a disease
inactivating mutated gene that is functioning improperly
gene transfer
segments of DNA injected into pt body
recombinant DNA (rDNA) artificially produces DNA splices
limitations to gene therapy
viruses used for gene transfer can induce viral disease and can be immunogenic in human host
proteins produced by artificial methods can be immunogenic
rDNA technology
use of rDNA vectors in the lab to make recombinant forms of drugs
hormones, vaccines, antitoxins, monoclonal antibodies
Escherichia coli bacterial genome: used to manufacture a recombinant form of human insulin
biologics and genetic therapies directorate of health canada
oversees gene therapy research in canada
eugenics: intentional selection before birth of genotypes that are considered more desirable than others
canadian gene therapy research limited to somatic cells only
gene therapy in germ-line (reproductive) cells is currently not approved for funding in canada
pharmacogenetics
general term for the study of genetic variations in drug response
focuses on single-gene variations
pharmacogenomics
combination of pharmacology and genomics
involves how genetics (genome) affect the body’s response to drugs
individualized drug therapy based on a pt’s genetic makeup
nursing implications
take thorough pt, family, drug hx
recognize situations that may warrant further investigation through genetic testing
identify resources for pt
teach pt
maintain confidentiality and privacy
ensure that informed consent is obtained
medication errors
preventable
common causes of adverse health care outcomes
drugs commonly involved in severe medication errors
CNS
anticoagulants
chemotherapeutic drugs
more potential for harm with “high-alert” medications
adverse drug event
medication errors
adverse drug rxn (ADRs)
allergic rxn
idiosyncratic reaction
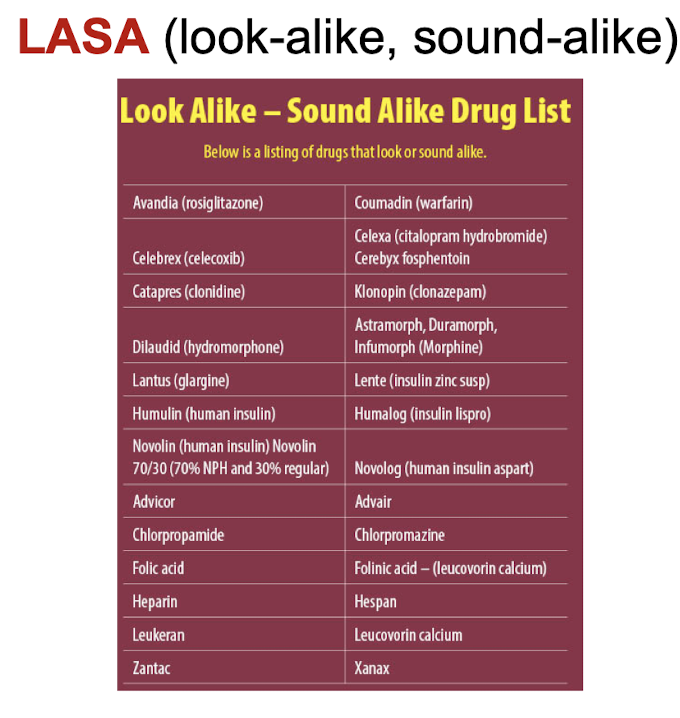
SALAD (sound-alike, look-alike drugs)
cisplatin - carboplatin
ephedrine - epinephrine
fentanyl - sufentanil
lantus - lente
humalog - humulin
novolog - novolin
humulin - novolin
humalog - novolog
TALLman lettering
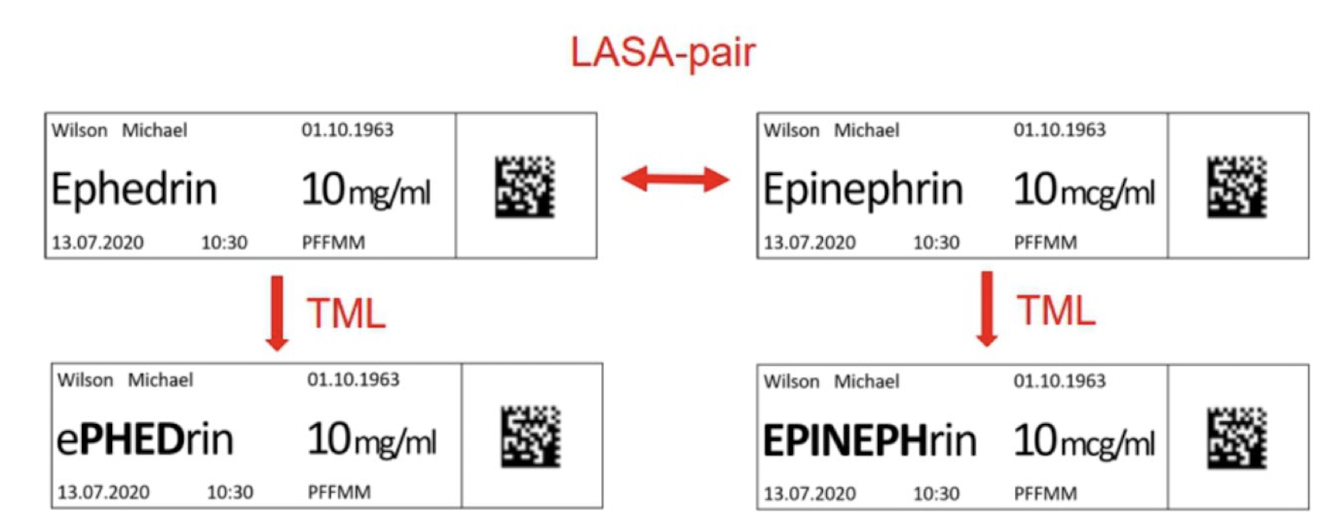
issues contributing to errors
errors can occur during any step of med process
procuring
prescribing
transcribing
dispensing
administering
monitoring
organizational issues
educational system issues
sociological factors
use of abbreviations
types of med errors
near miss, although circumstances or events occured that could have led to an error
no-harm error (med error causes no harm)
medication error that causes harm
critical incident (med error that results in serious harm)
preventing medication erros
multiple systems of checks and balances should be implemented to prevent medication errors
prescribers must write legible orders that contain correct info, or orders should be entered electronically
authorize resources such as pharmacists or current (past 3-5yrs) drug references or literature must be consulted
Nurses need to always check the medication order three times
before giving the drug.
Faculty members should not be the student’s research source
regarding medications.
The 10 rights of medication administration should be used consistently
responding to, reporting, and documenting med erros
professional responsibility
follow-facility policy
follow-up procedures or tests
nurses highest priority is pt physiological status and safety
complete all necessary forms
document with factual info (accurate, thorough, objective)
avoid using judgemental words (ex) error)
not observed changes in pt physical or mental status
document that the prescriber was notified and any follow-up actions or orders that were implemented
ongoing pt monitoring
medication reconciliation
continuous assessment and updating of pt med hx
verification
clarification
reconciliation
designed to ensure that there are no discrepancies between what the pt was taking at home and in hospital
process in which med are reconciled at all points of entry and exit from a heath care entity
pt provide a list of all meds they are currently taking (including natural health products and over-counter drugs)
should be done at each stage of heath care delivery
admission
statu change
pt transfer within/between facilities or provider teams
discharge (updated with latest meds)
ethical issues
notification of pt
possible consequences for the nurse
preventing med errors
assessment
two pt identifiers
do not admin if you did not draw-up or prepare yourself
minimize verbal or telephone orders
repeat order to prescriber
spell drug name aloud
speak slowly and clearly
list indication to each order
avoid abbreviations
never assume anything about items not specified in a drug order (ex) route)
do not hesitate to question a medication order for any reason when in doubt
do not try to decipher illegibly written orders (contact prescriber for clarification)
NEVER use trailing zero with med orders (ex) NOT 1.0 mg, only 1 mg)
ALWAYS uses leading zero for decimal doses
DO NOT use .25 mg, use 0.25 mg
take time to learn special admin techniques for certain dosage forms
always verify new med admin records
always listen to and honour any concerns expressed by pt regarding med
check all pt allergies and identification
preventing pediatric med erros
report all med errors
know drug thoroughly
follow 10 rights of med amin
avoid verbal orders in general
avoid distractions
communicate with everyone
DOUBLE CHECK ALL CALCULATIONS