B7 Human nutrition
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What is a balanced diet?
A balanced diet includes all essential nutrients in the correct amounts
Why do balanced diets vary between people?
it depends on age, gender and amount of physical activity
What are the 7 most important nutrients?
carbohydrates, fats and oils, proteins, vitamins(C&D), mineral ions(calcium and iron), fibre (roughage), water
Where is carbohydrates found and what is its importance?
Found in pasta, rice and potatoes
Used as a source of energy in respiration in cells.
Where is fats and oils found and what is its importance?
Found in fatty meats, cheese and butter
Used for long-term energy, insulation, waterproofing, structure and protection around delicate organs.
Where is proteins found and what is its importance?
Found in meat, fish and eggs
Used in protein synthesis (new cells for growth and repair0, produces antibodies, enzymes and hormones, carries other proteins
Where is vitamin c found and what is its importance?
Found in citrus fruits and vegetables
Used in the synthesis of proteins which help make up the skin, ligaments and blood, repair of tissues/healing wounds, supports immune system
Where is vitamin d found and what is its importance?
Found in dairy products, eggs and fish oil
Used in the absorption of calcium during digestion, maintaining healthy bones.
Where is calcium found and what is its importance?
Found in dairy products and fish
Used for healthy bones and teeth, helps blood clotting
Where is iron found and what is its importance?
Found in red meats and green vegetables
Used in: Key component in haemoglobin in red blood cells which help transport oxygen around the body
Where is fibre found and what is its importance?
Found in vegetables, fruits and whole grains
Used in: It is not digested and which helps food to move through the stomach and intestines
Where is water found and what is its importance?
Comes from both drinks and food, moves into the body by osmosis during digestion.
Used in: acts as a solvent for chemical reactions, help maintain body temp, removes waste product through urine and sweat
What is the cause of scurvy?
Caused by lack of vitamin C
Leads to bleeding under the skin and gums, premature stopping of bone growth in children leading to stunted growth, and very dry skin and hair
What is the cause of rickets?
Caused by lack of vitamin D (sunshine)
Causes weak and soft bones and stunted growth in children as the bones cannot develop correctly.
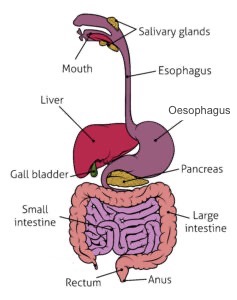
Draw the digestive system
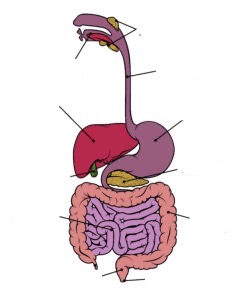
Label this diagram
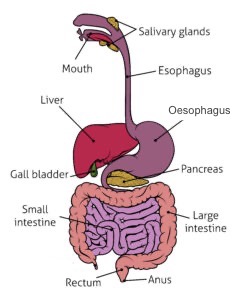
What is the alimentary canal and what is in it?
a long tube which runs from the mouth to the anus
mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum and ileum) and large intestine (colon, rectum and anus)
What are the associated organs?
salivary glands, pancreas, liver and gall bladder
What is the pathway food takes?
mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine
Mouth and salivary glands function
food is mechanically digested in the mouth by the teeth. the salivary glands release saliva which contains amylase that begins the chemical digestion of starch into simple sugars
Oesophagus function
allows food to pass from the mouth to the stomach by peristalsis
Stomach function
-muscles contract and relax to churn the food into smaller pieces by mechanical digestion. secrets gastric juice which contains;
-protease enzymes break down protein in chemical digestion
-hydrochloric acid
What is the function of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice?
-killing harmful microorganisms in food with its high acidity which causes the denaturation of enzymes
-providing an acidic pH for optimum enzyme activity of proteases in the stomach
Small intestine function
consists of the duodenum and ileum
-duodenum is where the acidity from the stomach is neutralised and the enzymes are secreted into from the pancreases to break down molecules
-ileum is where the products of digestion are absorbed into the blood
Pancreas function
secretes pancreatic juices into the small intestine which contains lipase, protease and amylase enzymes to break down food so that it can be absorbed
Liver function
makes bile that is secreted into the small intestine
What are the two things that bile does?
bile is an alkaline mixture
-neutralises the acidic conditions from the stomach (bile is alkaline) to provide a suitable pH for enzymes to work at
-emulsifies fats, increasing their surface area so enzymes can digest them more quickly for chemical digestion
Gall bladder function
bile made in the liver is stored here before being secreted into the small intestine
Large intestine function
consists of the colon, rectum and anus
-remaining salt and water is absorbed from the undigested food in the colon
-indigestible food, bacteria and dead cells form faeces which are passed out through anus
What is ingestion?
taking in substances (food and drinks) into the body.this occurs in the mouth.
What is digestion?
the breakdown of large molecules into smaller molecules (food into nutrients). There are two types of digestion:
-Physical digestion - occurs in the mouth and stomach
-Chemical Digestion - occurs mainly in the small intestine
What is absorption?
the movement of nutrients from intestines into the blood
-in small intestines, most nutrients in the food are absorbed
-in large intestine, remaining water and salts are absorbed
What is assimilation?
uptake and use of nutrients by cells. This occurs throughout the body but mainly in the small intestines
-nutrients absorbed into the blood and transported to the cells where they are used
What is egestion?
removal of indigestible remnants of food from the body as faeces. This occurs in the anus.
What is the difference between excretion and egestion?
excretion- is the removal of metabolic waste that originate inside cells and cross membranes during transport and elimination
egestion- removes undigested food that has never entered the cells or crossed membranes
What is physical digestion?
the breakdown of food into smaller pieces without chemical change to the food molecules
What is the role of physical digestion?
increases the surface area of food for the action of enzymes in chemical digestion
Role of teeth in physical digestion
incisors and canines at the front of the mouth are used to bite and tear food, before it is passed to the premolars and molars at the back of the mouth which are used for chewing and grinding food into smaller sections
Role of stomach in physical digestion
the walls in the stomach contain muscle which contract to mix and grind the food
Role of bile in physical digestion
used to emulsify fats and oils, increasing their surface area for chemical digestion
What is chemical digestion?
the breakdown of large insoluble molecules into small soluble molecules
What is the purpose of chemical digestion?
producing small soluble molecules that can be absorbed and used in the body
What does amylase do?
breaks down starch to simple reducing sugars
-breaks down starch into maltose then maltase breaks down maltose into glucose
Where is amylase secreted and acts? [2]
secreted by salivary glands in saliva
acts in mouth
secreted by pancreas in pancreatic juice
acts in small intestine (duodenum)
What does protease do?
break down protein to amino acids
What are the two types of proteases?
pepsin and trypsin
Where is pepsin secreted and acts?
secreted by stomach in gastric juice
acts in acidic conditions of stomach
Where is trypsin secreted and acts?
secreted by pancreas in pancreatic juice
acts in alkaline conditions of the small intestines
What does lipase do?
breaks down fats and oils to fatty acids and glycerol
Where is lipase secreted and acts? [2]
secrets by pancreas in pancreatic juice
acts in small intestine (duodenum)
secreted by cells covering the villi
acts in small intestine (ileum)
Fill in the substrate → enzyme → product:
starch →
proteins→
fats →
starch → amylase → maltose
proteins→ protease (pepsin/trypsin) →polypeptides
fats → lipase → fatty acids and glycerol
What 2 things aid chemical digestion?
hydrochloric acid and bile
Role of hydrochloric acid in chemical digestion
-increases the stomach's acidity which will kill any harmful bacteria in the food by denaturing it
-the low pH is the optimum pH for protease so it can effectively break down proteins
Role of bile in chemical digestion
an alkaline mixture that neutralises the acidic mixture of food and gastric juices entering the duodenum from the stomach, to provide a suitable pH for enzyme action in the small intestine