BIOENERGETICS
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Sun
Major source of energy trapped by green/photosynthetic organisms
This energy is used in Active transport, Cilia/flagella movement, mitosis, protein synthesis, and other cellular processes
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate
contains adenine, ribose (5-carbon sugar molecule), and 3 phosphate groups serially bonded
contains phosphate which are charged molecules
energy high molecule primarily used in cellular and other biological processes
energy that can be stored again after use
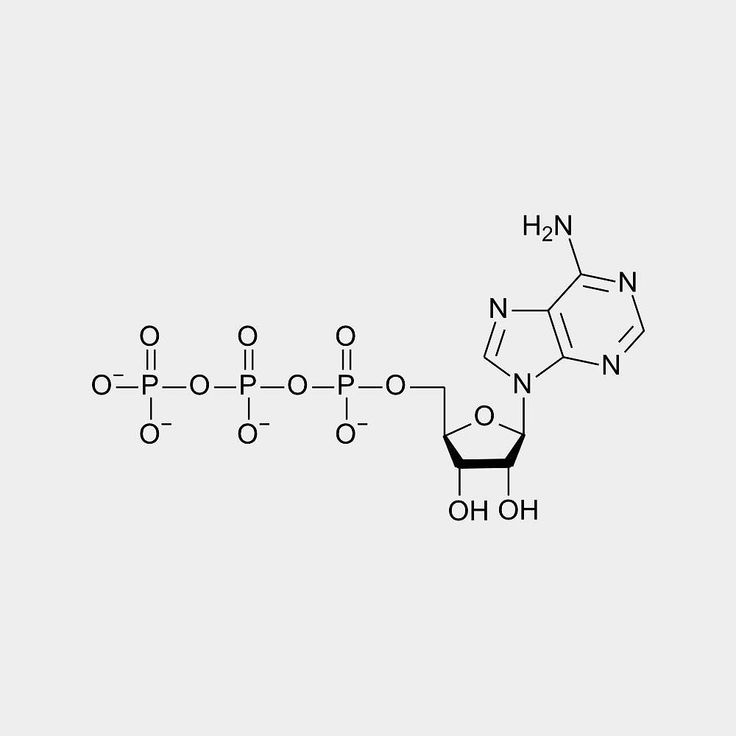
Why is ATP better than ADP and AMP
ATP contains 3 phosphate bonds that provides alot of energy, specifically located in the last bond of phosphate bond. ADP and AMP only have 2 and one phosphate groups bonded that only contains some to only a little bit of energy
ATP > ADP > AMP
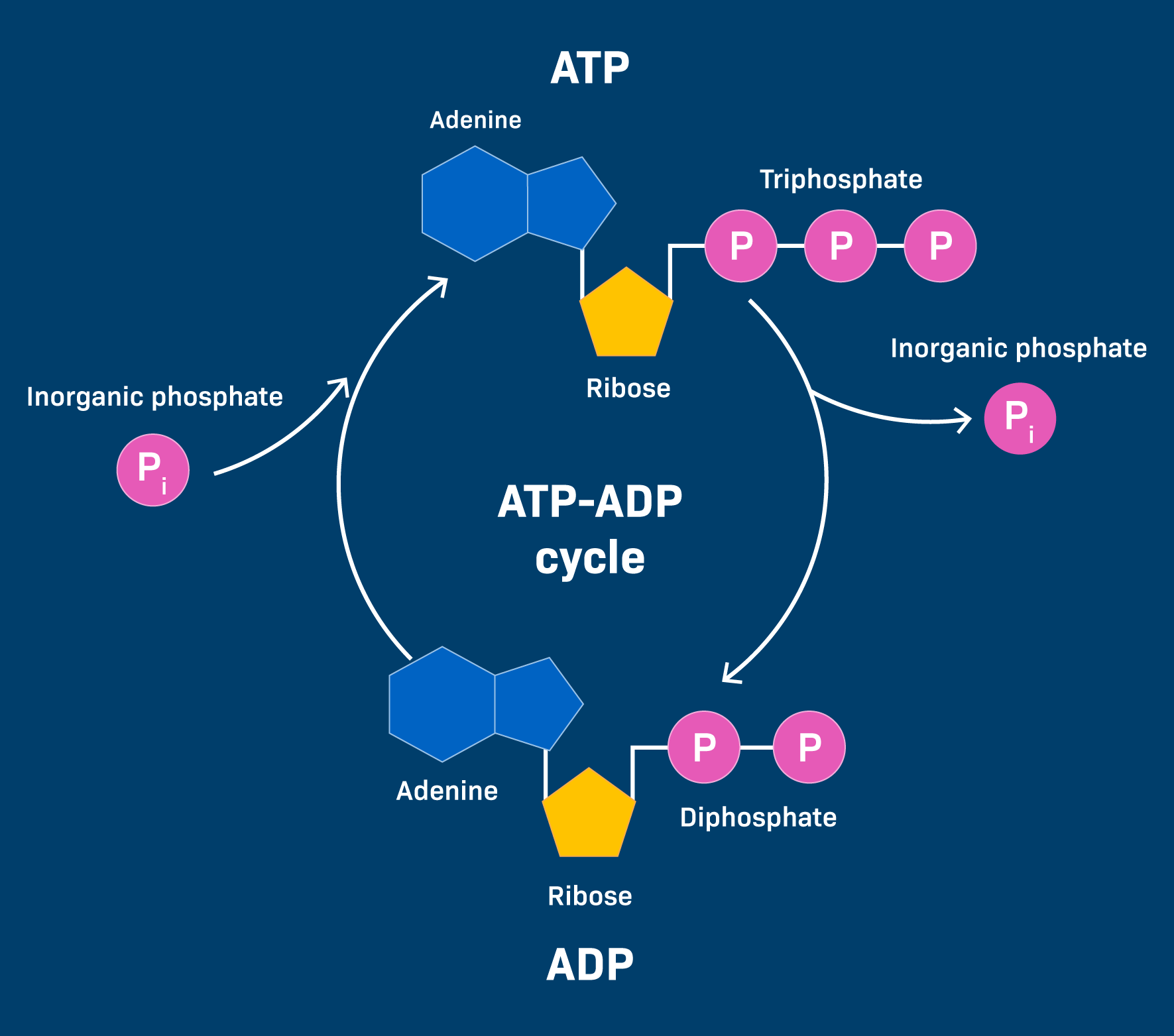
Phosphorylation
reattachment of phosphate to form ATP
ATP —> ADP and ADP —> ATP back again
Photosynthesis
makes use of phosphorylation
uses sun’s energy to make simple sugars
6CO2 + 6H2O -sunlight→ C6H12O6 + 6O2
carbon dioxide + water -sunlight→ sugar + oxygen
occurs in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast
Cellular Respiration
produucts of photosynthesis (C6H12O6 + 6O2) are utilized in cellular respiration
done in the mitochondrion
Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis in Plants and Animals
Plants can both undergo cellular respiration and photosynthesis
Humans can undergo cellular respiration because they are not photosynthetic and lacks chloroplasts.
Chlorophyll
photosynthetic pigments embedded in the thylakoid membrane
it is green because it absorbs every other wavelength of light except green, which is instead reflected
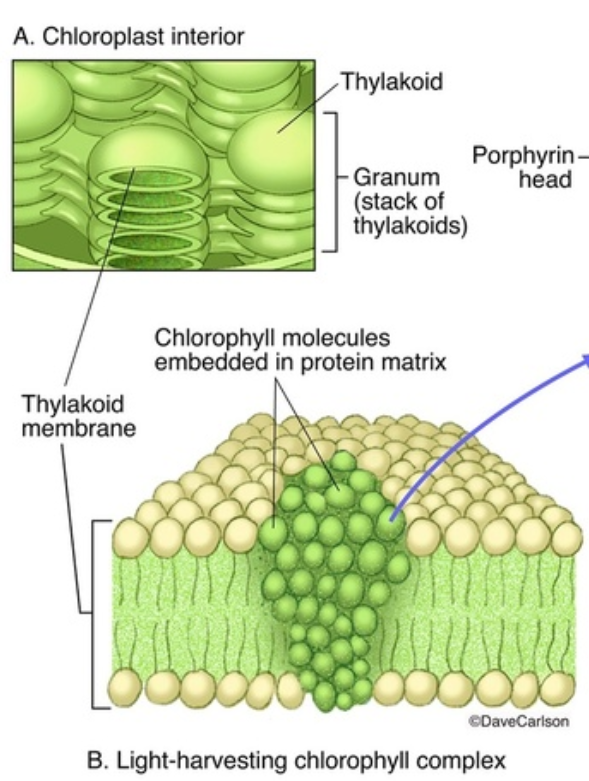
Thylakoid Membrane
where chlorophyll is embedded
has a phospholipid bilayer structure
have light-absorbing pigments
chlorophyll a
C55H77N4O5
principal photosynthetic piigment
absorbs energy from blue to violet, and orange to red
chlorophyll b
C55H70MgN4O6
accessory photosynthetic pigment
collects energy and passes it to chlorophyll a, absorbs energy from green wavelength
Photosystems
structural units of protein complexes with clusters of chlorophyll which are involved in the photosynthesis
found in thylakoid membrane
where chlorophylls absorb light energy and release electrons
carries out:
absorption of light
transfer of energy and electrons
Light Dependent Reaction
Sun strikes in photosystem ii
light energy excites/energizes electrons
electrons are passed on from chlorophyll to an electron transport chain embedded in the thylakoid membrane
electrons get re-energized in photosystem II
At the end of ETC, electrons are carried to stroma for later use
NADP+ turns into NADPH+ as it transfers to the stroma
Photolysis
used in LDR when electrons may run out
occurs in photosystem ii
light breaks down H2O to produce ½ O2, 2 H+, and 2 electrons
Uses of lost/spilled energy from Electron Transport Chain
forming ATP from ADP
pumping hydrogen ions in the thylakoid membrane, which produces a concentration gradient, which powers ATP synthase to produce ATP
Light Dependent Reaction
series of reactions that us CO2 to form sugars
occurs in the stroma
produces phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGA)
Phosphoglycyeraldehyde
known as PGA
known as G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate)
a molecule essential for cellular respiration
Carbon Fixation
Phase 1 of calvin-benson cycle
6RuBP + 6CO2 = 12 3-PGA
Reduction
phase 2 of the calvin-benson cycle
12 3-PGA + 12ATP + 12NADPH = 10G3P + 2G3P