BIO 202: Chapter 1.1 and 1.2 Endocrine System Anatomy and Physiology and Endocrine Organs and Hormones
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
endocrine system
uses hormones released into the bloodstream, produces slower but longer lasting effects, can affect many tissues and organs at once
exocrine glands
release their products through ducts to the surface of an organ or the body
includes sweat, salivary, lacrimal, digestive, and mammary glands
endocrine glands
secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to travel to target tissues throughout the body
nervous system
uses electrical impulses and neurotransmitters, produces immediate but short-term effects, acts on specific and localized targets
functions of hormones
stimulate production of enzymes or other hormones, changing a cell’s metabolic activity, and modifying permeability of the plasma membrane or receptor sensitivity
tropic hormones
target other endocrine glands to cause them to release additional hormones
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones
non-tropic hormones
act directly on non-endocrine tissues to trigger physiological changes
insulin acting directly on liver and muscle cells to lower blood glucose
steroid hormones
derived from cholesterol, lipid-soluble so they can pass through cell membrane, bind to intracellular receptors, typically alter gene expression
includes cortisol, aldosterone, estrogen, and testosterone
amine hormones
derived from amino acids, water soluble or lipid soluble depending on specific hormone
includes epinephrine, norepinephrine, melatonin, thyroid hormones
water soluble hormones
dissolve easily in blood and do not need transport proteins but they cannot cross the lipid membrane so they bind receptors on outside of target cell membrane so activate a second messenger system
includes insulin, epinephrine, and most peptide and protein hormones
lipid soluble hormones
require transport proteins to move through the blood because they do not dissolve in water but can pass directly through lipid bilayer and bind to receptors inside cell to work by changing gene expression
includes cortisol, estrogen, thyroid hormones
heart
secretes atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) to help lower blood pressure by causing kidney to remove excess salt and water
adipose tissue
secrete leptin to signal brain to reduce hunger when enough fat is stored in the body
kidney
secrete erythropoietin (EPO) to stimulate production of red blood cells when oxygen levels are low
liver
secrete thrombopoietin to stimulate platelet production in bone marrow and angiotensinogen to help regulate blood pressure and fluid balance
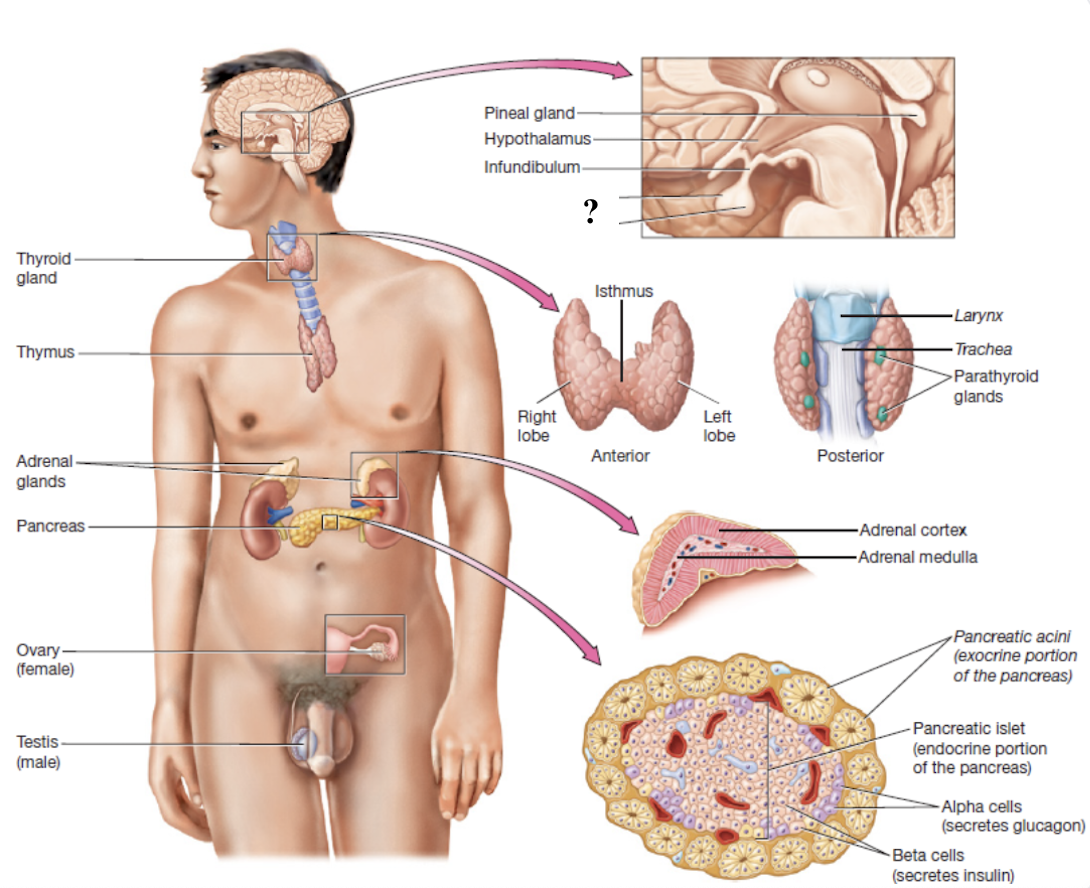
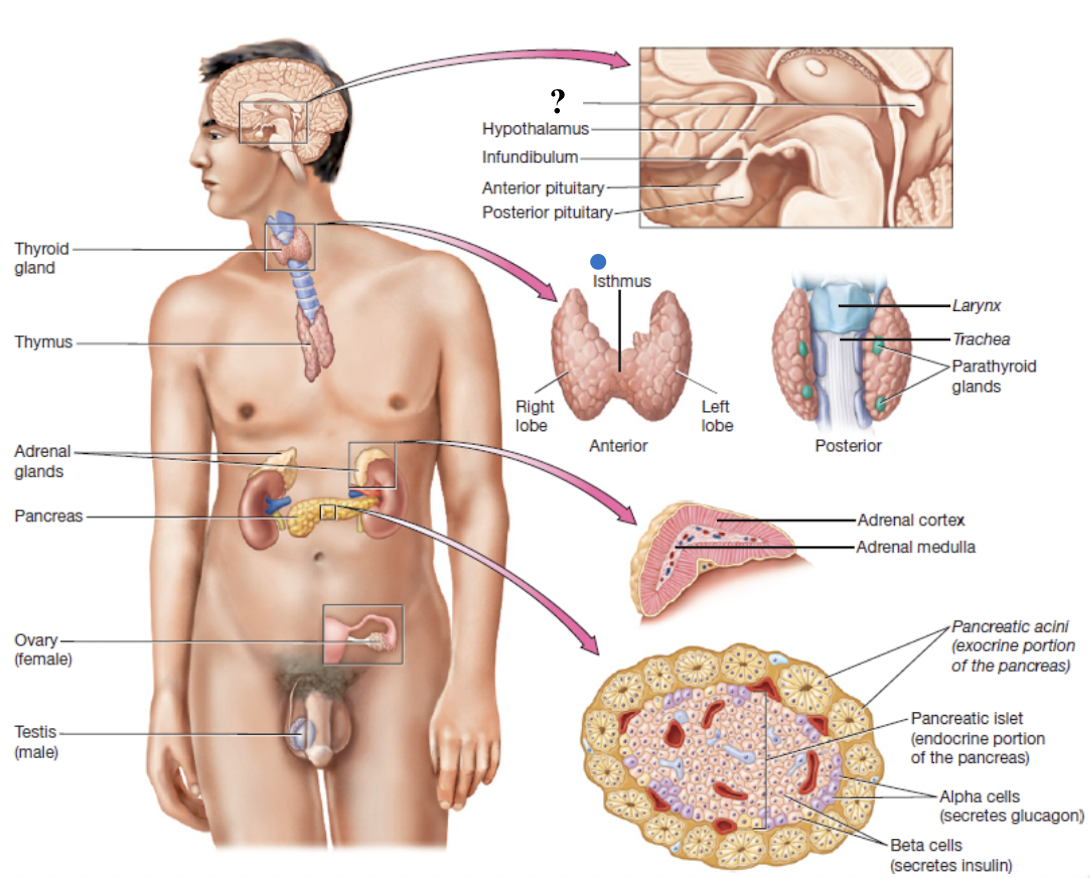
hypothalamus
connects to the pituitary gland via the infundibulum
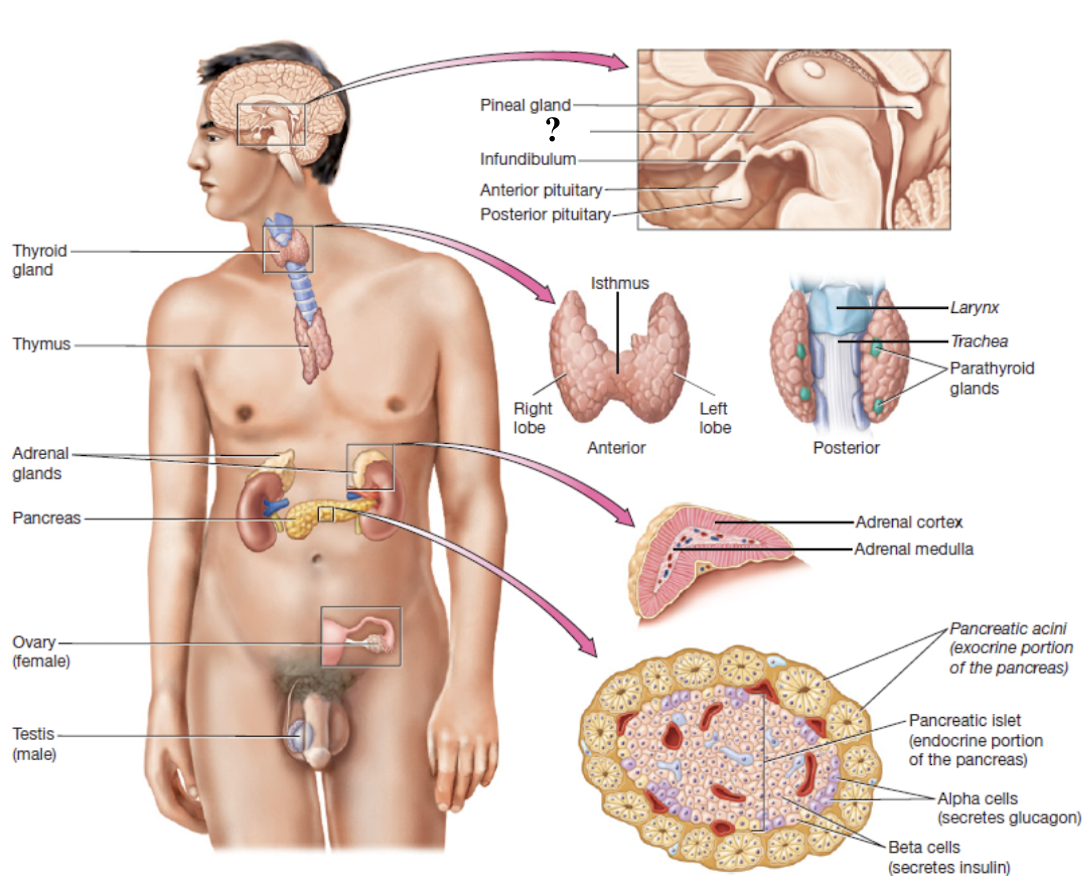
pituitary gland
sits in a depression called the hypophyseal fossa within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone
anterior pituitary gland
composed of glandular epithelium and accounts for anterior ¾ of the pituitary gland
produces and secretes several hormones
posterior pituitary gland
composed of nervous tissue and accounts for posterior ¼ of the pituitary gland
does not produce hormones but stores and releases hormones made by hypothalamus
pineal gland
midline structure in posterior diencephalon and is tiny and pine cone-shaped
thyroid gland
butterfly-shaped and wraps around the trachea with two lobes connected by an isthmus
largest endocrine gland
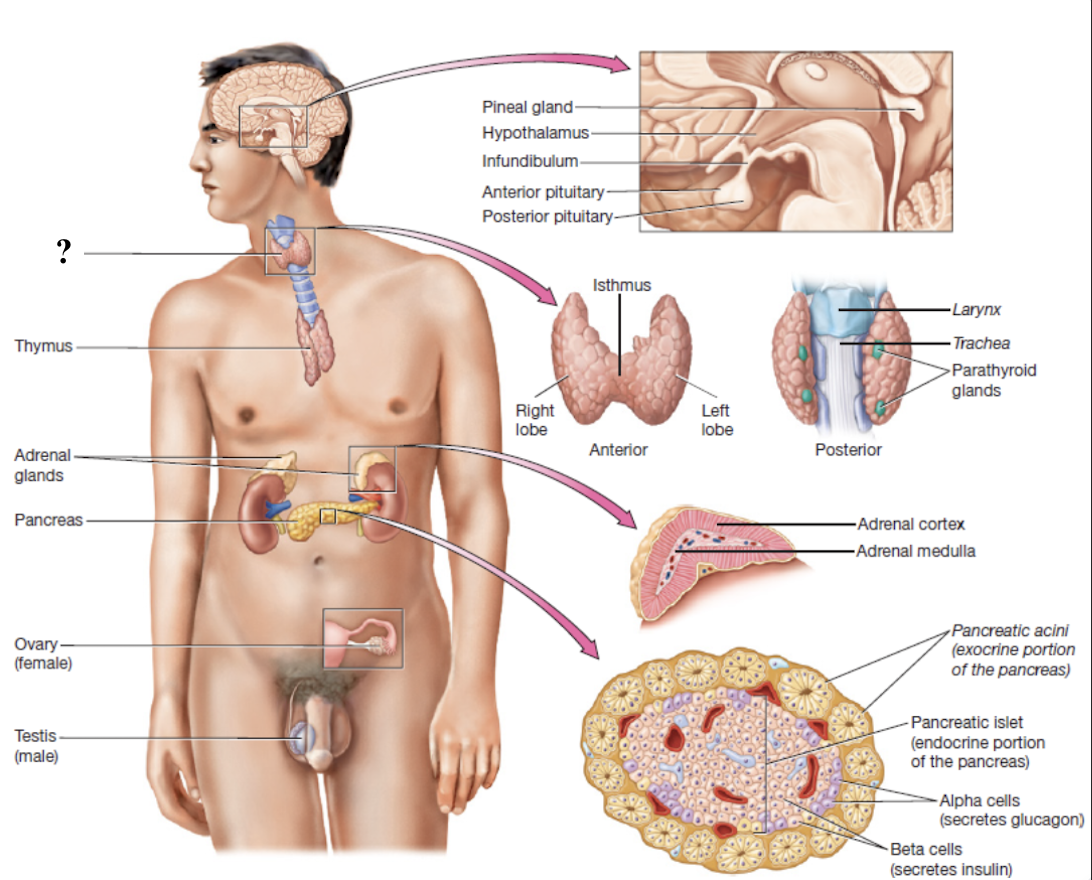
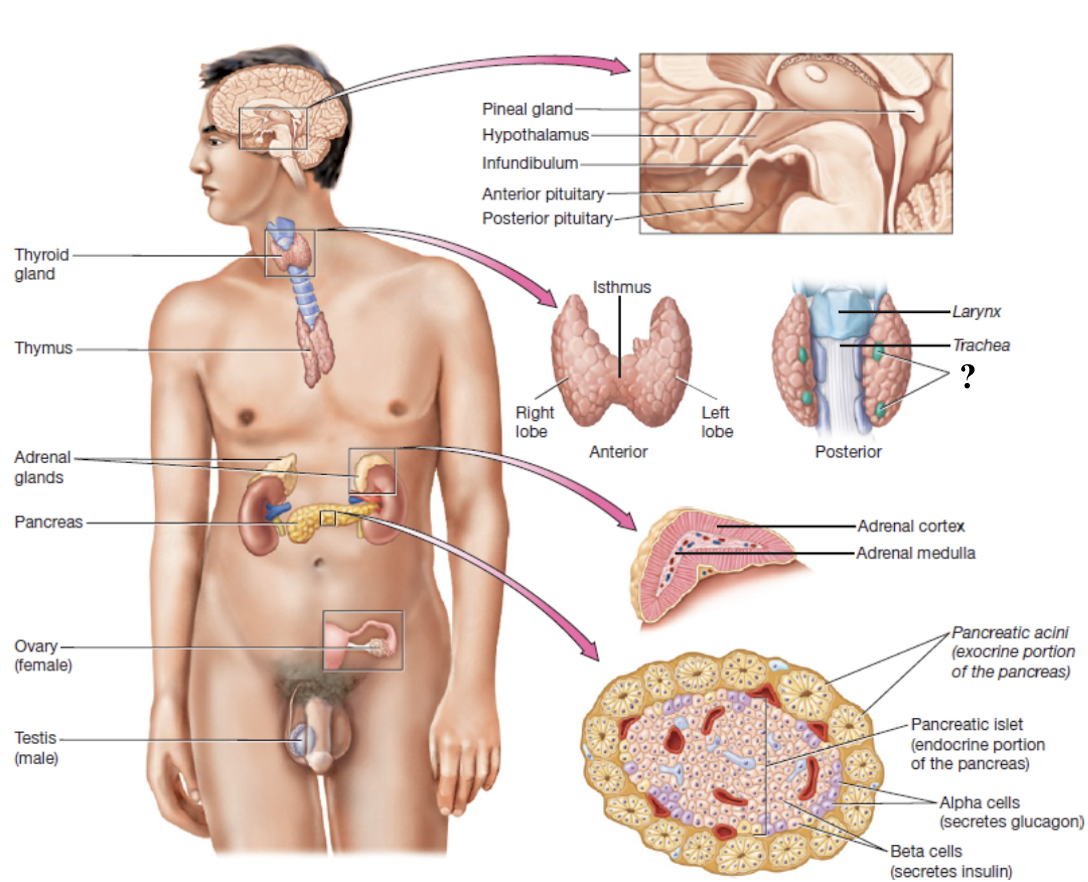
parathyroid gland
four small oval nodules on posterior surface of the thyroid
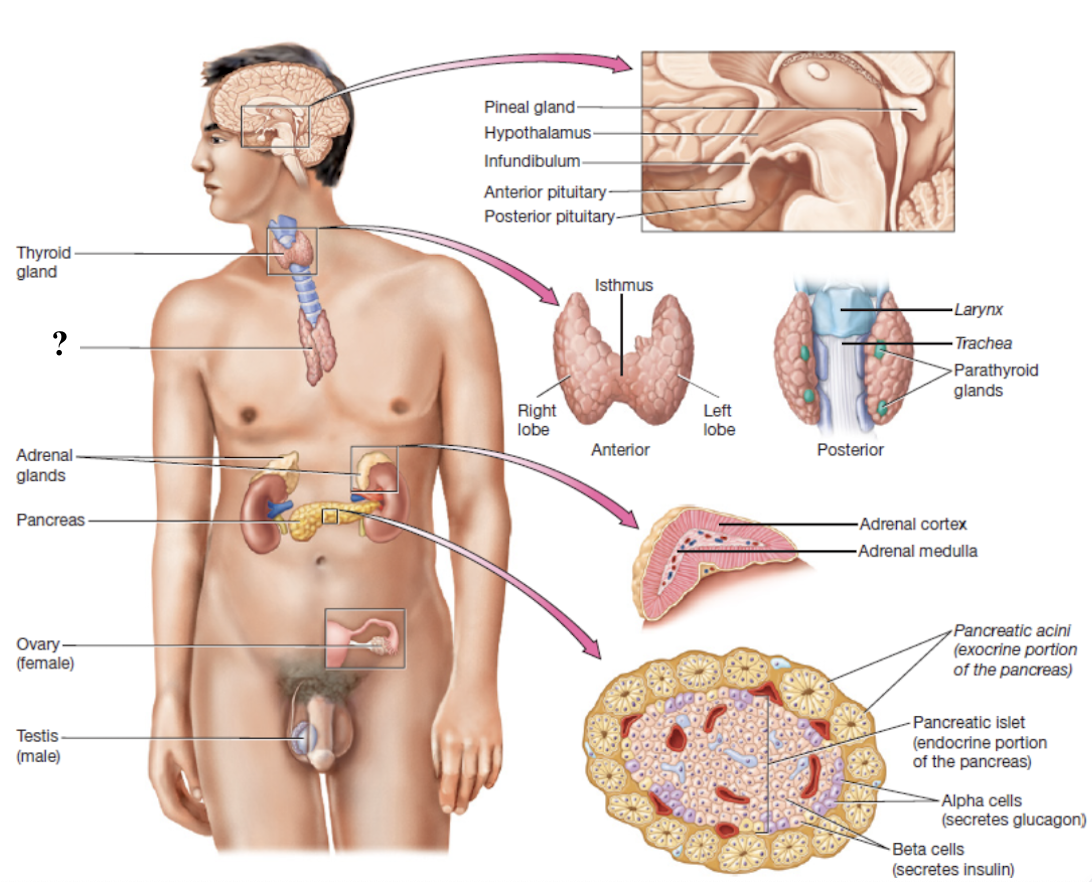
thymus gland
located in anterior mediastinum behind the sternum, large in children but small and fatty in adults
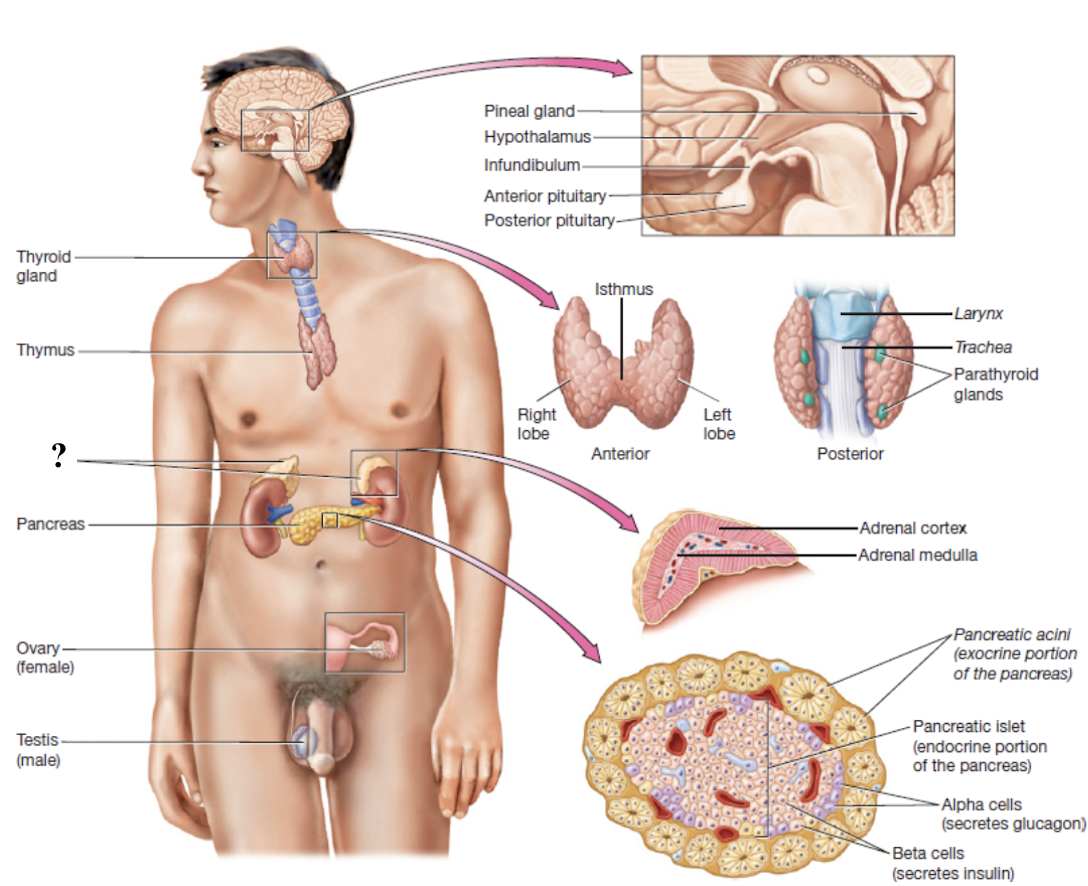
adrenal glands
sit atop each kidney, right is triangular and left is crescent-shaped
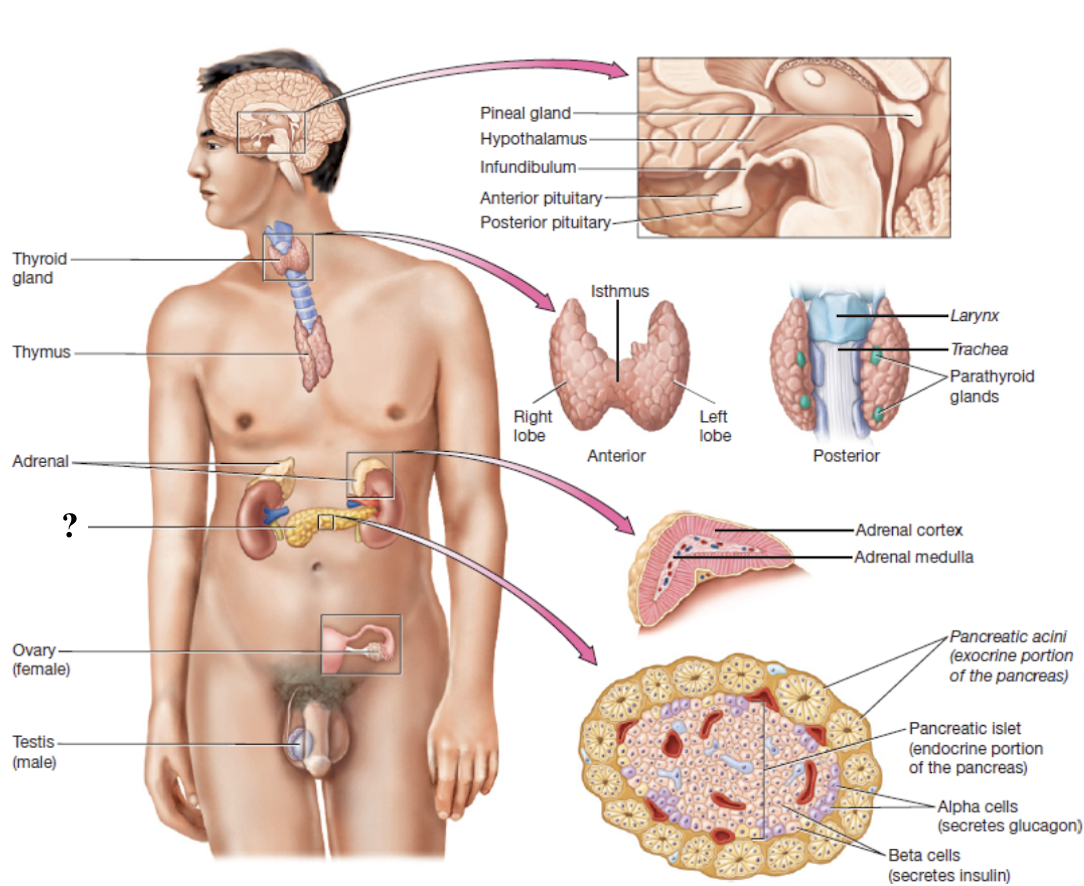
pancreas
elongated gland across the posterior abdomen
has both endocrine and exocrine functions
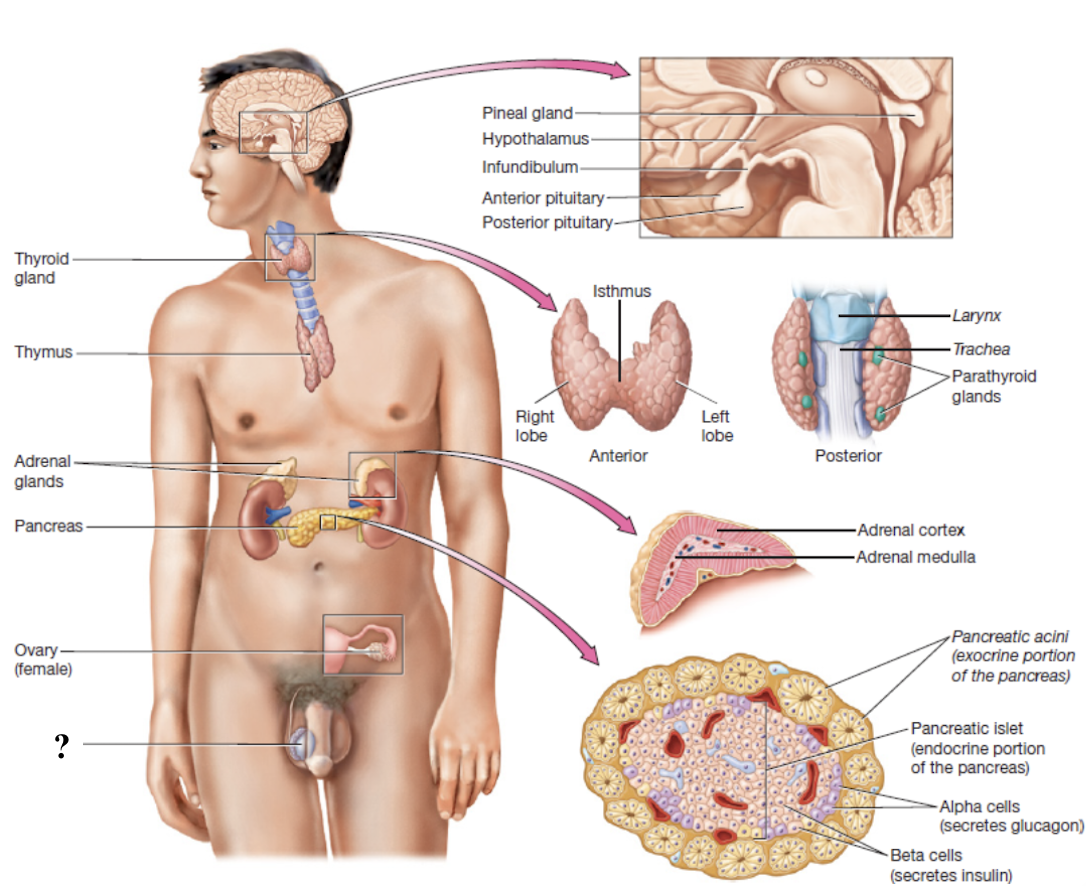
ovaries
almond-shaped, lateral to uterus near uterine tube ends
produce oocytes, the female gametes, and secrete sex hormones
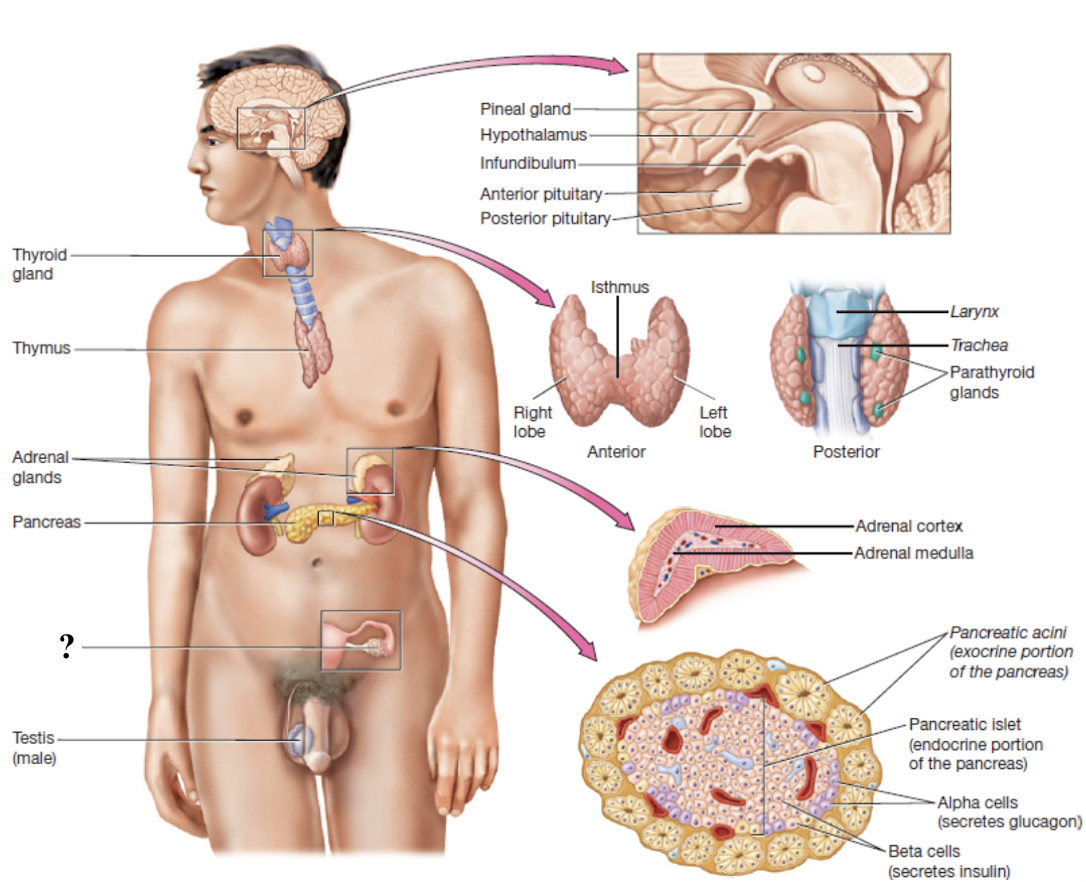
testes
oval organs in the scrotum that contain coiled seminiferous tubules and interstitial cells
thyrotropin releasing hormone
released by hypothalamus and interacts with anterior pituitary gland to stimulate secretion of thyroid-stimulating hormone and prolactin
corticotropin releasing hormone
released by hypothalamus and interacts with anterior pituitary gland to stimulate secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone
gonadotropin releasing hormone
released by hypothalamus and interacts with anterior pituitary gland to stimulate secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone
growth hormone releasing hormone
released by hypothalamus and interacts with anterior pituitary gland to stimulate secretion of growth hormone
prolactin inhibiting hormone
released by hypothalamus and interacts with anterior pituitary gland to inhibit secretion of prolactin
somatostatin
released by hypothalamus and interacts with anterior pituitary gland to inhibit secretion of growth hormone and thyroid-stimulating hormone
hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal system
specialized blood vessel in which the hypothalamus communicates with the anterior pituitary
releasing and inhibiting hormones synthesized by neurons in hypothalamus
hormones enter primary capillaries located in hypothalamus
hormones travel through small veins called portal venules in the infundibulum
hormones enter secondary capillaries in the anterior pituitary and exit blood to influence hormones-secreting cells
oxytocin
released by hypothalamus and interacts with posterior pituitary gland to trigger uterine contractions during childbirth and stimulates milk ejection
antidiuretic hormone
released by hypothalamus and interacts with posterior pituitary gland to promote water retention by the kidneys and helps regulate blood pressure
hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract
consists of neurons extending from the hypothalamus down through the infundibulum into the posterior pituitary and is the means by which hypothalamus hormones are transported
follicle stimulating hormone
produced by anterior pituitary gland to stimulate the development of follicles in the ovaries and sustentacular cells for sperm production in the testes
luteinizing hormone
produced by anterior pituitary gland to trigger ovulation development in the ovaries and stimulate interstitial cells in the testes to produce testosterone
adrenocorticotropic hormone
produced by anterior pituitary gland to stimulate hormone secretion from the adrenal cortex during stress response
thyroid stimulating hormone
produced by anterior pituitary gland to stimulate thyroid gland to grow and secrete hormones that regulate metabolism and temperature
prolactin
produced by anterior pituitary gland to promote milk production
growth hormone
produced by anterior pituitary gland (also called somatotropin) to stimulate cell division and protein synthesis
true
true or false: the posterior pituitary gland does not synthesize any hormones but instead stores and releases oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone that are produced by the hypothalamus
melatonin
secreted by the pineal gland in response to decreased light levels to help trigger the onset of sleep
thyroid follicles
hollow spheres that compose the thyroid gland and are lined by simple cuboidal epithelial cells called follicle cells
colloid
gelatinous, iodine-rich substance inside each follicle that stores the raw materials needed for thyroid hormone synthesis
tetraiodothyronine
produced by thyroid gland, contains four iodine atoms, known as thyroxine
triiodothyronine
produced by thyroid gland, contains three iodine atoms, more active thyroid hormone
parafollicular cells
located between or at the periphery of follicle cells and secrete the hormone calcitonin
calcitonin
released when blood calcium levels are high and stimulate osteoblast activity to increases bone deposition and formation to decrease blood calcium levels
parathyroid hormone
secreted by parathyroid glands to maintain calcium ion homeostasis when blood calcium levels are low through …
stimulating osteoclast activity to break down bone tissue
increasing calcium ion absorption from the intestines
increasing calcium ion reabsorption from the kidneys
antagonistic
parathyroid hormone and calcitonin are _____ hormones because they have opposite effects on blood calcium levels
endocrine, lymphatic, and immune systems
the thymus gland is unique as it functions in three systems which are the …
thymosin, thymulin, thymopoietin
hormones secreted by the thymus gland to stimulate development of other lymphatic organs and regulate development and activity of T lymphocytes
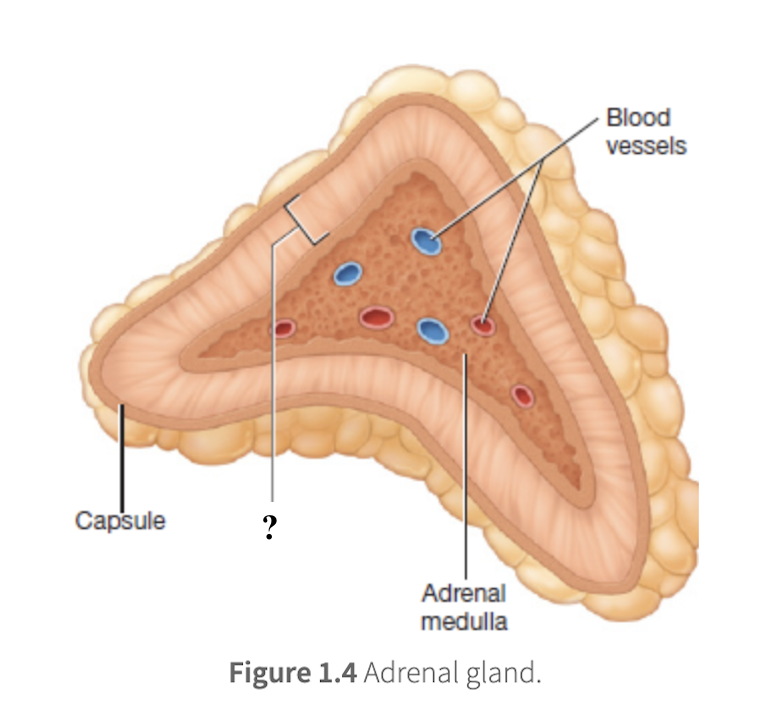
adrenal cortex
outer, yellowish region that surrounds the adrenal medulla on all sides, makes up about 80 to 90 percent of the adrenal gland, secretes steroid hormones derived from cholesterol, and is organized into 3 distinct layers
zona glomerulosa
thin outermost layer of the adrenal cortex of the adrenal gland
mineralocorticoids
hormone type secreted by zona glomerulosa to regulate electrolyte balance, fluid volume, blood pressure, and pH
ex: aldosterone to stimulate kidneys to retain sodium and water, promote excretion of potassium, and regulate acid-bade homeostasis
hyperaldosteronism
overproduction of aldosterone which leads to high blood pressure and low potassium
addison’s disease
underproduction of aldosterone which causes dehydration, low blood pressure, and electrolyte imbalance
underproduction of cortisol which results in fatigue, low glucose, and poor stress response
zona fasciculata
thick middle layer that makes up ¾ of the adrenal cortex of the adrenal gland
glucocorticoids
hormone type secreted by zona fasciculate to regulate glucose metabolism, stress response, and inflammation
ex: hydrocortisone to reduce inflammation, increase blood glucose, promote protein and fat breakdown, inhibit glucose uptake, and suppresses immune response
cushing’s syndrome
overproduction of cortisol which causes muscle wasting, extreme fatigue, hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, redistribution of fat, and obesity
zona reticularis
narrow innermost layer of the adrenal cortex of the adrenal gland
glucocorticoids and gonadocorticoids
hormone type secreted by zona reticularis to support reproductive development and secondary sex characteristics
ex: androgens to promote pubic and axillary hair growth, skin oil production, and support muscle and bone mass
ex: estradiol to maintain bone density
adrenal medulla
inner core of the adrenal gland, makes up 10 to 20 percent of its volume, secretes adrenal catecholamines directly into the bloodstream in response to stress
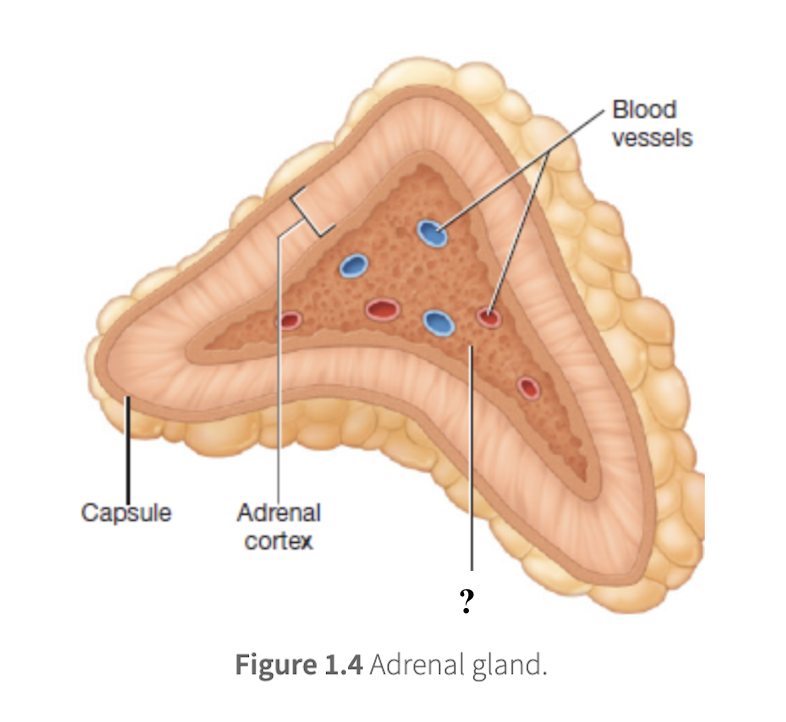
adrenal catecholamines
hormones secreted by adrenal medulla of the adrenal gland to trigger and sustain the fight of flight response
ex: epinephrine and norepinephrine which increase heart rate and contractile strength, elevate blood pressure, dilate bronchioles and pupils, increase blood glucose, and suppress digestion and urination
pheochromocytoma
overproduction of epinephrine and norepinephrine which causes tumor of the adrenal medulla, anxiety, palpitations, and high blood pressure
pancreas exocrine function
pancreatic acini (cells) produce pancreatic juices that are secreted into pancreatic ducts and then released into the small intestine to neutralize hydrochloric acid and help digest proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates with enzymes
pancreas endocrine function
pancreatic islets (cells) responsible for the hormonal regulation of blood glucose which contain two types of hormone-secreting cells
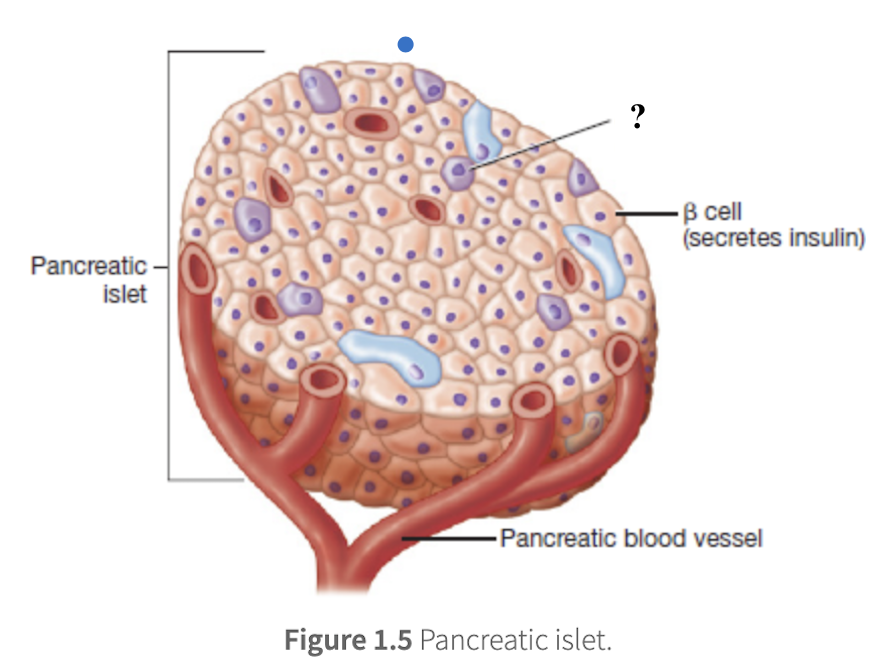
beta cells
make up 70% of pancreatic islet cells and secrete insulin
insulin
triggers the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into body cells, stimulates cells to store glucose as glycogen, promotes fat storage and protein synthesis
overall effect of lowering blood glucose concentration
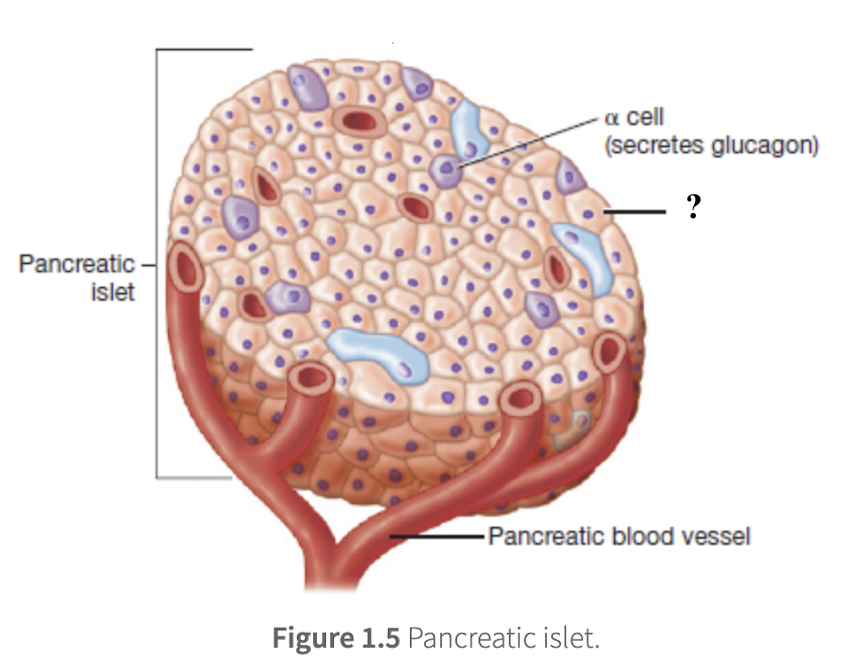
alpha cells
make up 20% of pancreatic islet cells, located towards the edges of a pancreatic islet, and secrete glucagon
glucagon
stimulates the liver to break down stored glycogen into glucose to promote gluconeogenesis which id the production of new glucose from non-carbohydrate sources
overall efect of raising blood glucose concentration
diabetes mellitus
results from an imbalance or failure in insulin production or function
type 1: immune system destroys beta cells → little to no insulin
type 2: body resists effects of insulin or doesn’t produce enough
hypoglycemia
too much insulin is present or not enough glucose is available
testosterone
secreted by the interstitial cells of within the testes and is the principal male sex hormone
stimulates spermatogenesis or the production of sperm
promotes development of male secondary sex characteristics
estrogen
secreted by the ovaries to support the development and maturation of oocytes, promote female secondary sex characteristics, and regulate several reproductive processes like the menstrual cycle
progesterone
secreted by the ovaries to prepare the uterus for implantation of a fertilized egg, support pregnancy by maintaining the uterine lining, and regulate the menstrual cycle with estrogen