I NEED AN 80 PLEASE
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
The majority of glucose is reabsorbed through the walls of the
renal duct.
proximal convoluted tubule.
glomerular capsule.
distal convoluted tubule.
proximal convoluted tubule.
Urine flow from the renal pelvis to the urinary bladder is produced by
peristalsis of the ureters.
ciliary action in the renal pelvis.
hydrostatic pressure from the small intestine.
contraction of the detrusor muscle.
peristalsis of the ureters.
Above the renal threshold for glucose,
a kidney transplant is necessary.
the urine has too little glucose.
blood volume is so great that nephrons cannot keep up.
hemodialysis is needed.
more glucose is in the filtrate than active transport can handle.
more glucose is in the filtrate than active transport can handle
The longest part of the male urethra that is encased within a cylinder of erectile tissue in the penis is the _______ urethra.
prostatic
spongy
membranous
spongy
Which choice describes the countercurrent mechanism of the nephron loop?
Water moves in the descending limb; sodium moves out of the descending limb
Water moves out of the descending limb; calcium moves out of the ascending limb
Water moves in the ascending limb; sodium moves out of the ascending limb
Water moves out of the descending limb; sodium moves out of the ascending limb
Water moves out of the descending limb; sodium moves out of the ascending limb
Mesangial cells help keep the basement membrane clean by
engulfing macromolecules caught in its basement membrane.
secreting emulsifying agents that dissolve trapped particles.
opening larger pores in the membrane so that trapped particles move accross.
secreting antibodies that attack the molecules caught in the endothelium.
engulfing macromolecules caught in its basement membrane.
How are proteins transported from the tubule lumen into the peritubular capillaries?
Absorbed directly across the tubule cell membrane
Attached to carriers to get across the luminal membrane
Moved by facilitated diffusion across the luminal surface
Transported by pinocytosis across the luminal membrane and digested into amino acids
Transported by pinocytosis across the luminal membrane and digested into amino acids
To measure GFR, an individual's urine is examined for the concentration of a test substance that they received by injection. How is that test substance treated by the kidney?
It is filtered and secreted, but not reabsorbed.
It is neither filtered nor reabsorbed, but it is secreted.
it is filtered, reabsorbed, and excreted, but it is not secreted.
It is not filtered, but it is secreted and reabsorbed.
It is filtered but neither reabsorbed nor secreted.
It is filtered but neither reabsorbed nor secreted.
The main parts of the jutaglomerular apparatus are the
granular cells and intercalated cells.
granular cells and macula densa.
intercalated cells and principal cells.
principal cells and macula densa.
granular cells and macula densa
Which is not correct regarding the innervation of the kidney?
Sympathetic stimulation causes vasoconstriction of the renal blood vessels.
The kidney is served by the renal plexus.
Sympathetic innervation is from segments T10-12 of the spinal cord.
Parasympathetic stimulation decreases the rate of filtrate formation.
Parasympathetic stimulation decreases the rate of filtrate formation.
A specific gravity of value ___________ in urine indicates relative hydration (enough water intake).
about 1.020
below 1.000
below 1.020
above 1.030
below 1.020
Granular cells synthesize and release the enzyme
angiotensinogen.
calcitriol.
renin.
antidiuretic hormone.
renin
When a kidney is sectioned along a coronal plane, there is an outer renal ___________ and an inner renal ___________.
cortex; medulla
medulla; cortex
cortex; medulla
Filtration occurs when
filtered fluid passes from the nephron tubules to the peritubular capillaries.
filtered fluid passes from the nephron tubules to the efferent arteriole.
filtered fluid leaves the afferent arteriole and enters the glomerular capsule.
filtered fluid leaves the glomerulus and enters the glomerular capsule.
filtered fluid passes from the peritubular capillaries to the nephron tubules.
filtered fluid leaves the glomerulus and enters the glomerular capsule.
Which layer is not found in the wall of the urinary bladder?
Muscularis
Submucosa
Mucosal
Adventitia
No exceptions; all layers are found in the wall of the urinary bladder
No exceptions; all layers are found in the wall of the urinary bladder
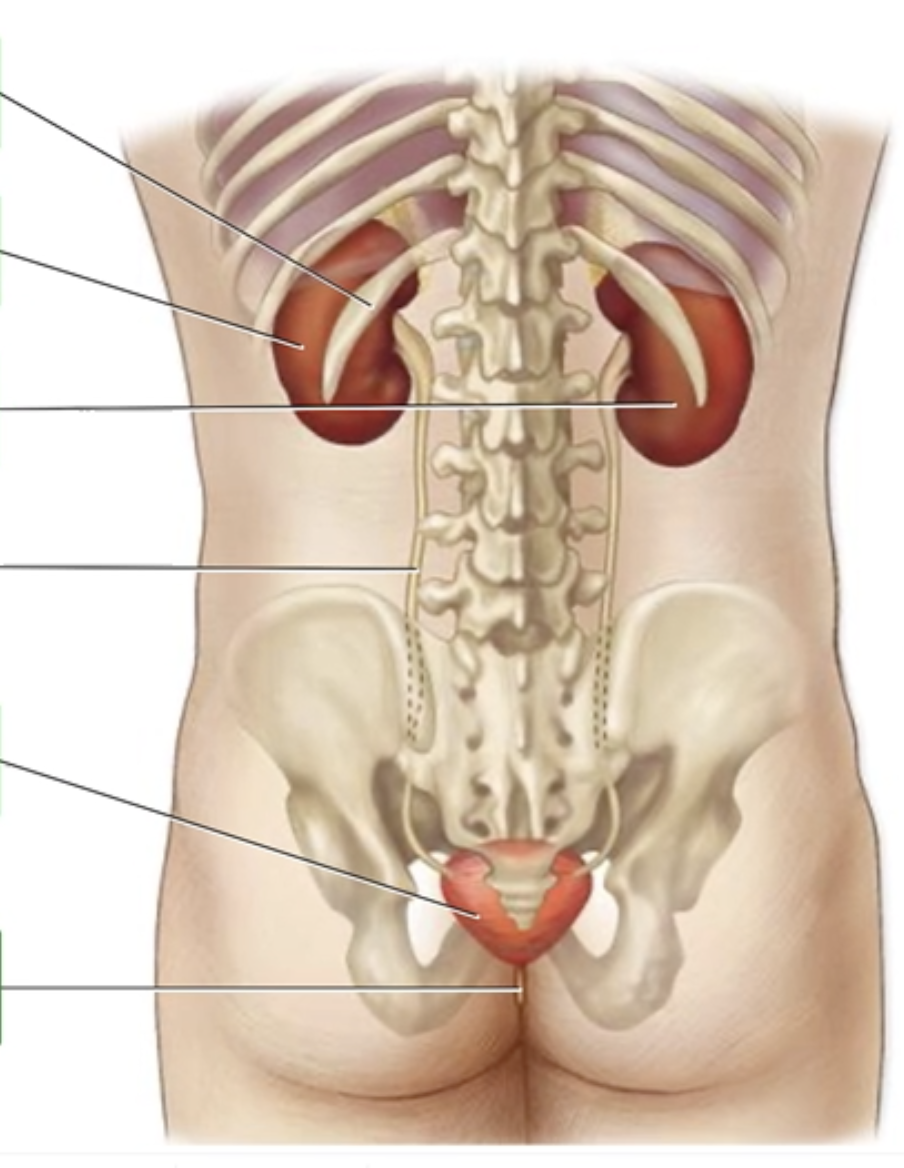
The Urinary System - Posterior View
Correctly label the following components of the urinary system.
Right kidney
Ureter
Urinary bladder
12th rib
Urethra
Left kidney
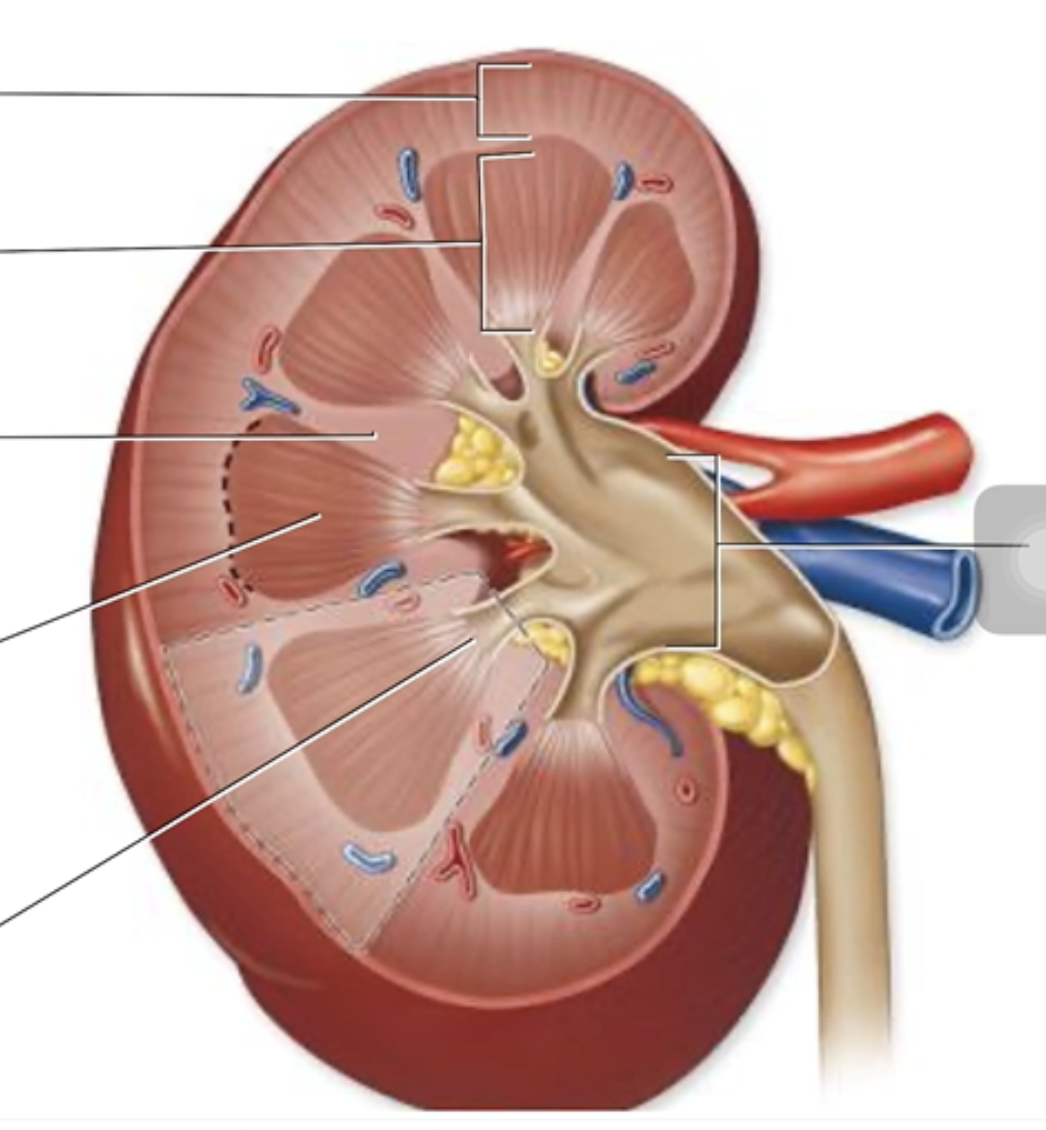
Label the structures of the kidney.
Renal pyramid
Renal column
Renal pelvis
Renal papilla
Renal cortex
Renal medulla
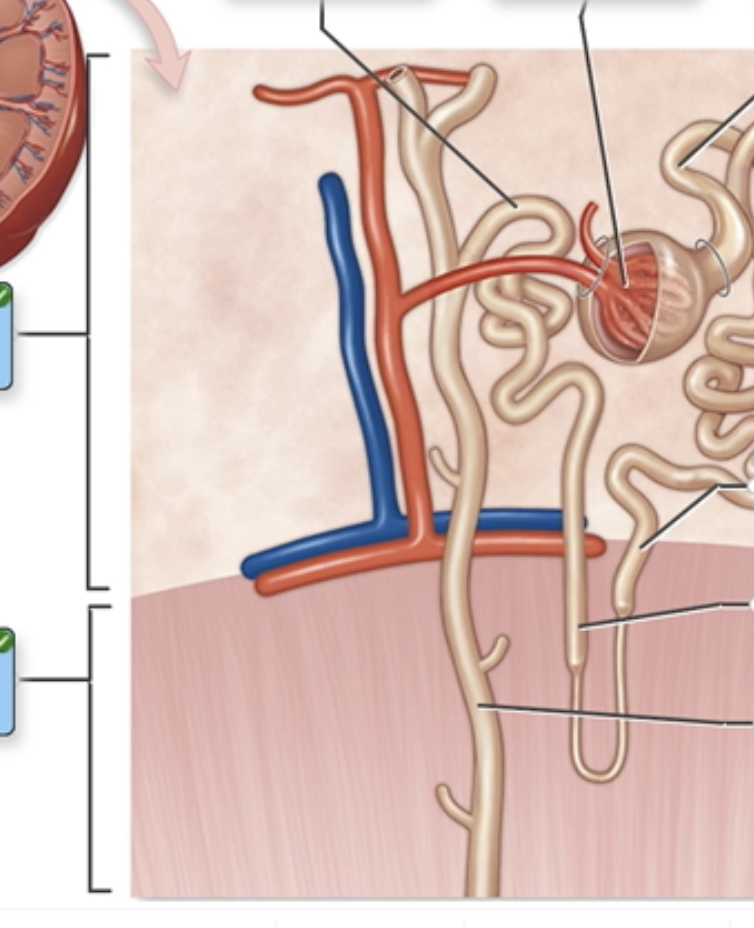
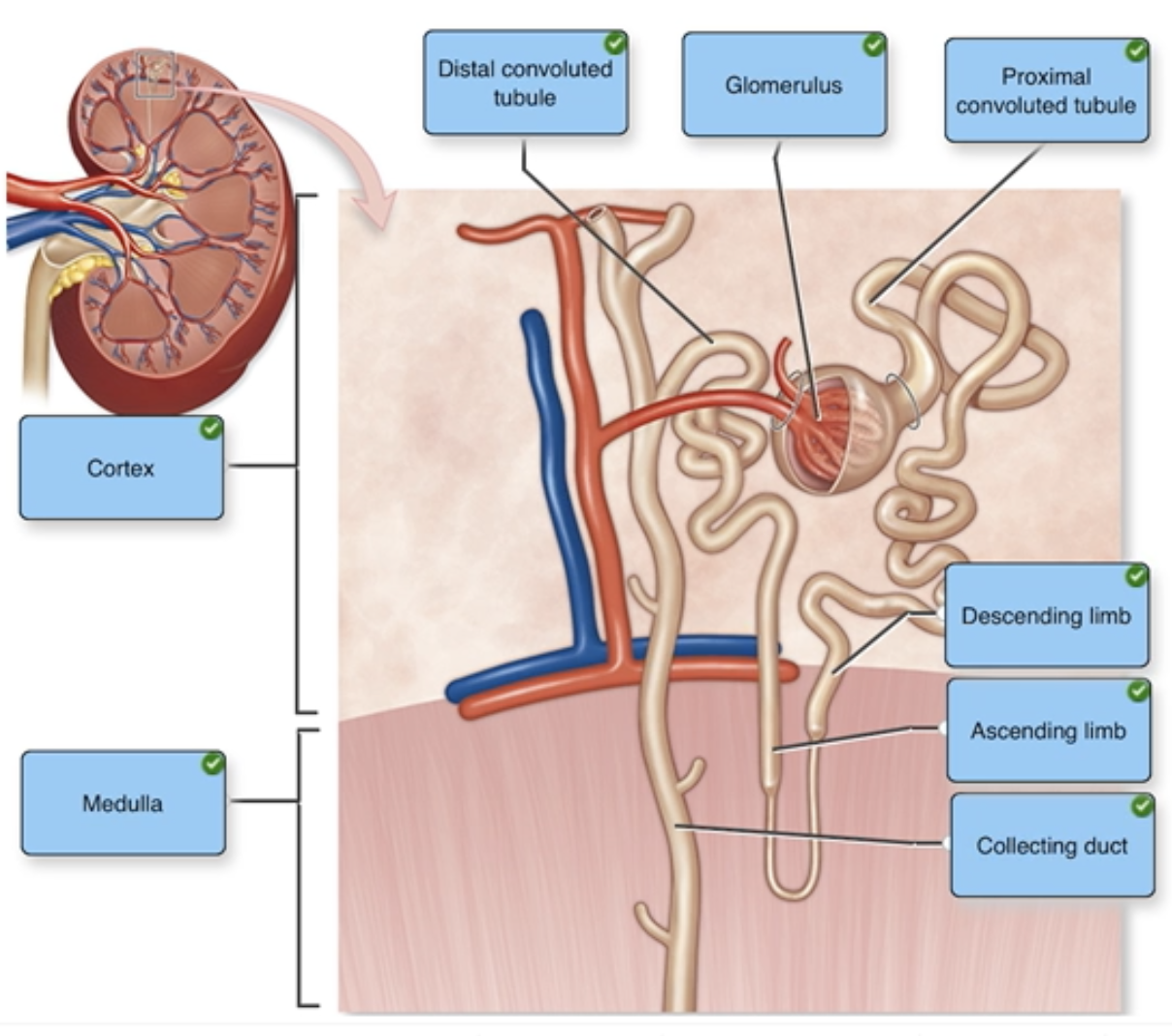
Nephron Structure
Label the structures of a nephron in the figure.
Distal convoluted tubule
Descending limb
Ascending limb
Collecting duct
Proximal convoluted tubule
Medulla
Cortex
Glomerulus
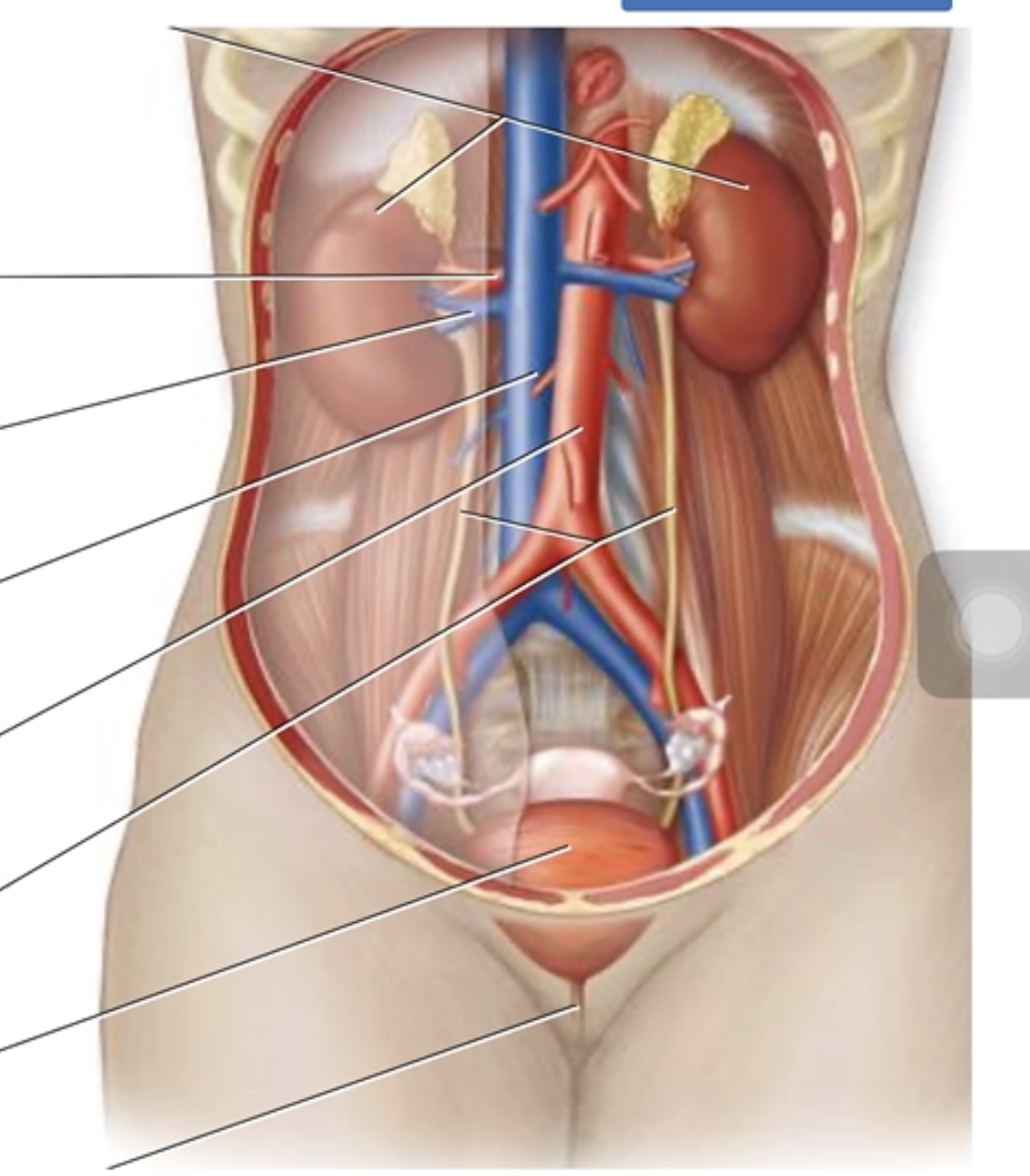
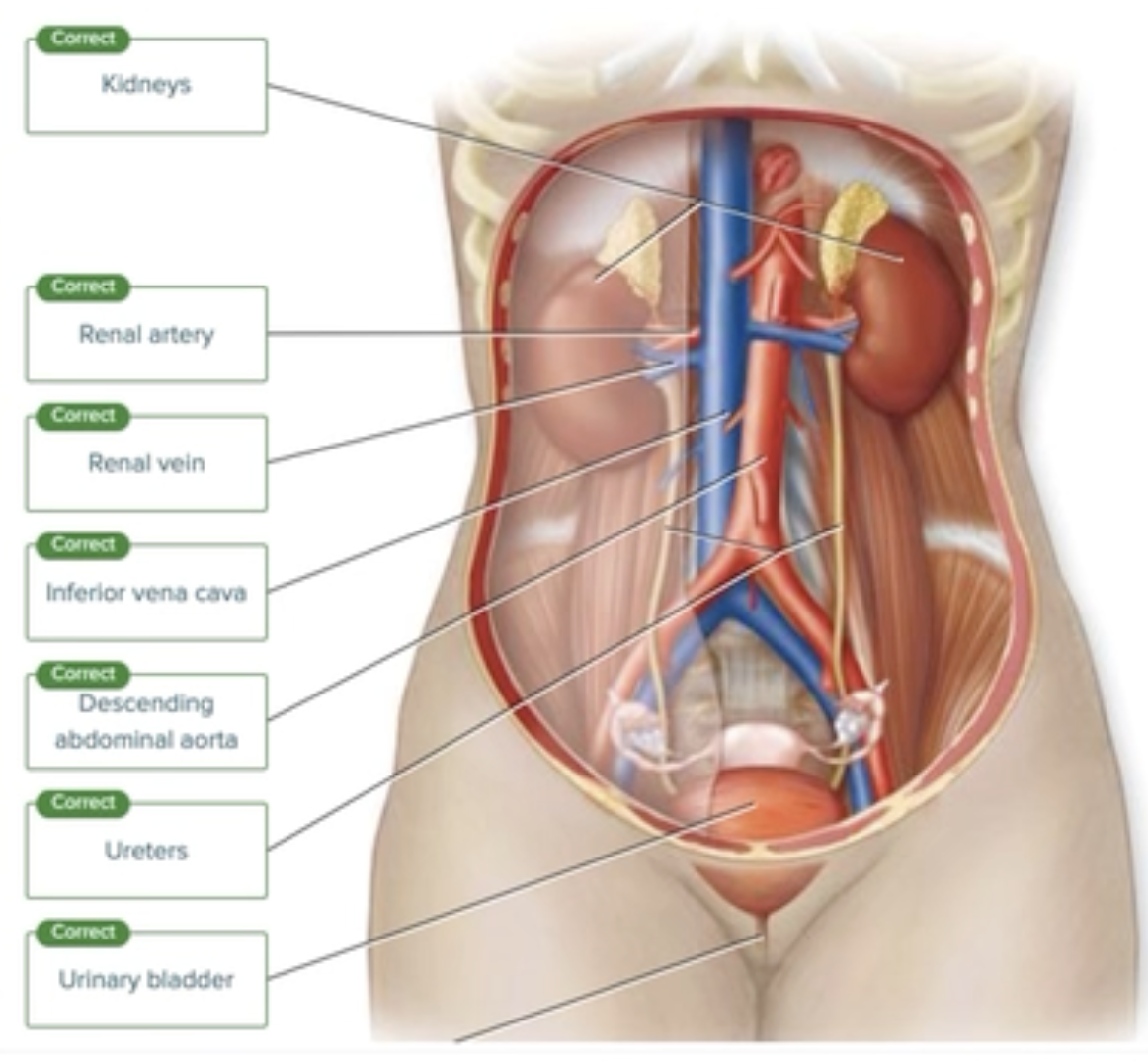
Urinary System Anatomy
Label the parts of the urinary system and surrounding structures.
Ureters
Urinary bladder
Inferior vena cava
Kidneys
Renal artery
Renal vein
Descending abdominal aorta
Urethra
urethra
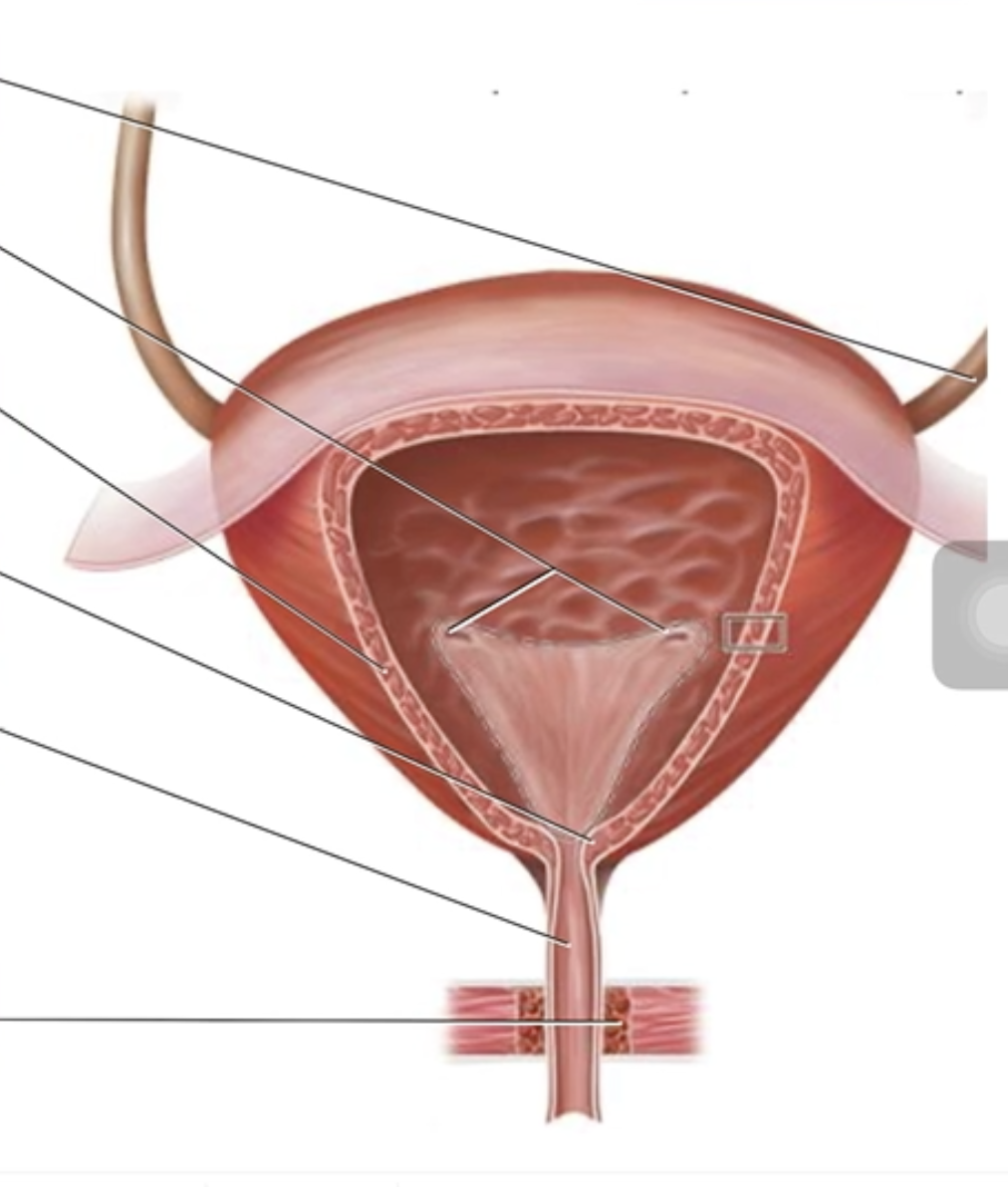
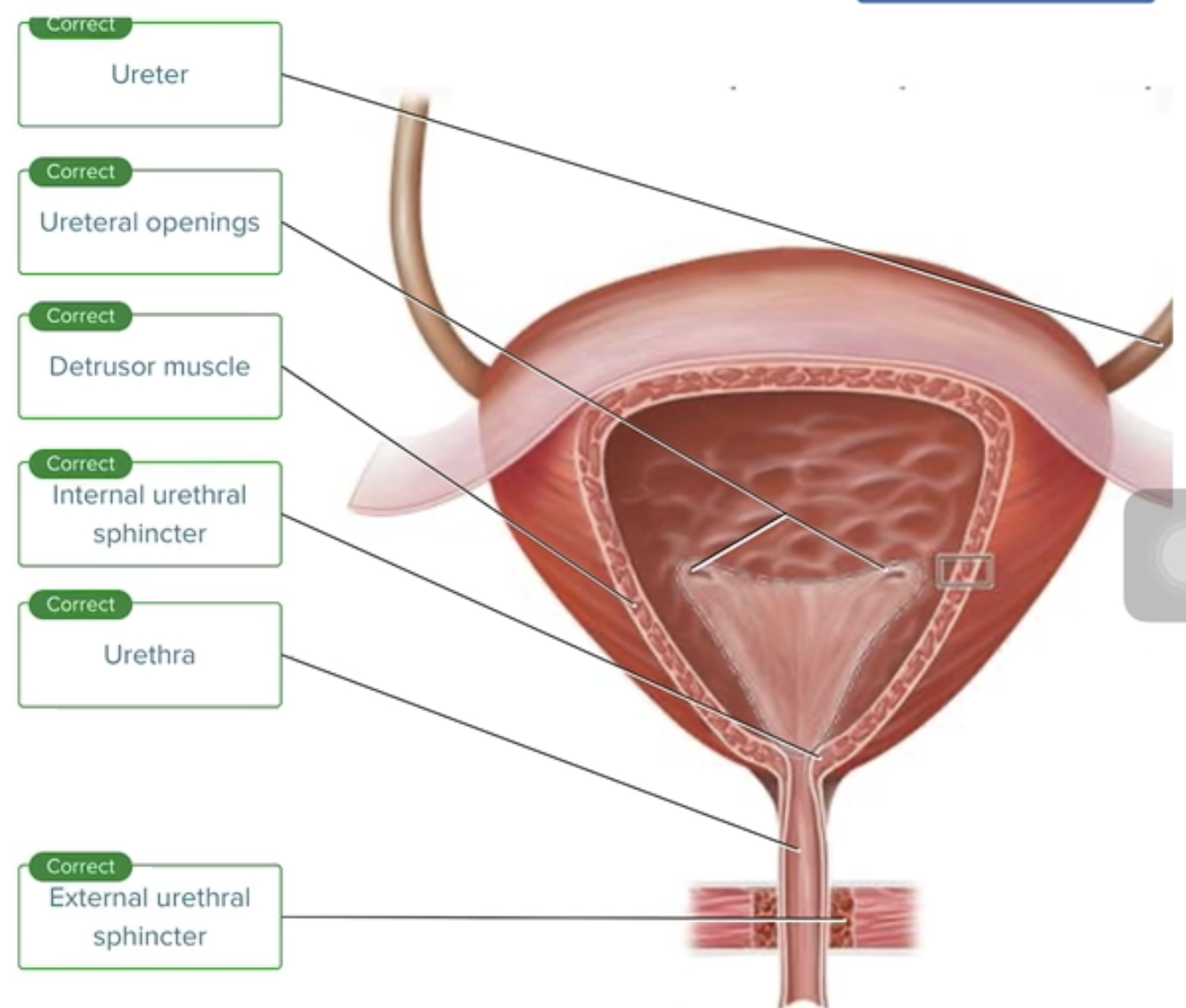
The Female Urinary Bladder and Urethra
Correctly label the following anatomical structures of the female urethra and urinary bladder.
Urethra
Ureter
Internal urethral sphincter
External urethral sphincter
Detrusor muscle
Ureteral openings
How many secondary oocytes ultimately develop from each primary oocyte?
1
2
5
4
3
1
The process by which double-stranded, homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material is known as
crossing over, and it occurs in interphase.
crossing over, and it occurs in mitosis.
crossing over, and it occurs in meiosis.
interphase, and it occurs in meiosis.
interphase, and it occurs in mitosis.
crossing over, and it occurs in meiosis.
The external urethral orifice is found at the ___________ of the penis.
glans
crus
body
corpus cavernosum
bulb
glans
Fimbriae
are extensions of the ovarian ligament.
assist in the movement of sperm through the female reproductive tract.
enclose the ovary at the time of ovulation.
are sloughed off during menstruation.
enclose the ovary at the time of ovulation.
Ovulation is induced by a peak in the secretion of
inhibin.
progesterone.
estrogen.
ovulin.
LH.
LH
Which of these structures contains sebaceous glands?
Prepuce
Labia minora
Clitoris
Vestibular bulb
Mons pubis
Labia minora
The male homologue to the labia majora is the
bulbourethral gland.
scrotum.
prostate gland.
testis.
penis.
scrotum.
In males, the labioscrotal swellings form the
scrotum and ventral side of the penis.
scrotum and testes.
scrotum and root of the penis.
scrotum and dorsal side of the penis.
scrotum.
scrotum.
Menarche is
the first four days of menstruation.
the stage immediately preceding menopause.
the final phase of the uterine cycle.
a female's first menstrual cycle.
marked by a dramatic decline in androgen secretion.
a female's first menstrual cycle.
The normal site of fertilization is the
ampulla of the uterine tube.
uterine part of the uterine tube.
fundus of the uterus.
vagina.
body of the uterus.
ampulla of the uterine tube.
The _________ nervous system facilitates increased blood flow to the penis by facilitating local release of ________.
parasympathetic, nitric oxide
parasympathetic, norepinephrine
sympathetic, norepinephrine
sympathetic, nitric oxide
somatic, acetylcholine
parasympathetic, nitric oxide
Inhibin is secreted by
hypothalamic cells, and it inhibits LH production.
follicular cells, and it inhibits FSH production.
the posterior pituitary, and it inhibits ovulation.
uterine lining cells, and it inhibits development of ovarian follicles.
the anterior pituitary, and it inhibits GRH production.
follicular cells, and it inhibits FSH production.
The volume of the antrum is largest in a(n) ________ follicle.
secondary
antral
mature
primordial
primary
mature
Ovulation typically occurs on day 14 of the ovarian cycle, and the luteal phase occurs on days
1-5.
15-28.
6-14.
8-18.
15-28
A cell that contains 23 pairs of chromosomes is
monoid.
diploid.
haploid.
polyploid.
diploid
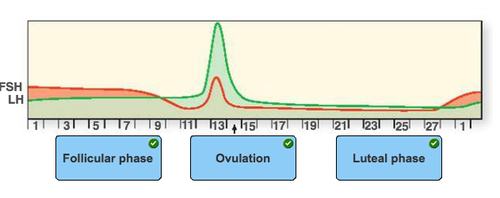
Ovarian Cycle
Label the stages of the ovarian cycle in the figure, based on the levels of FSH and LH, and days of the month.
Ovulation
Follicular phase
Luteal phase
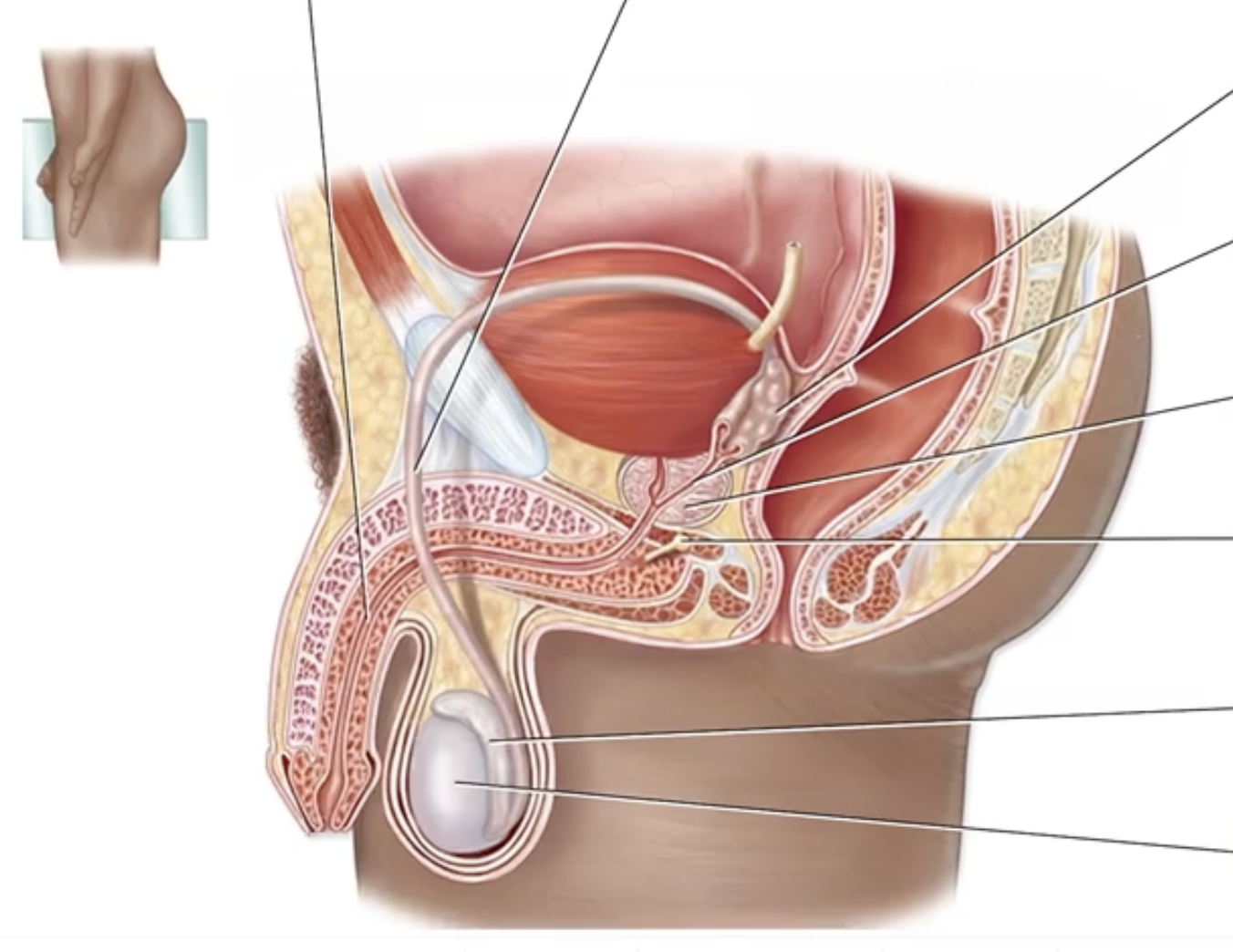
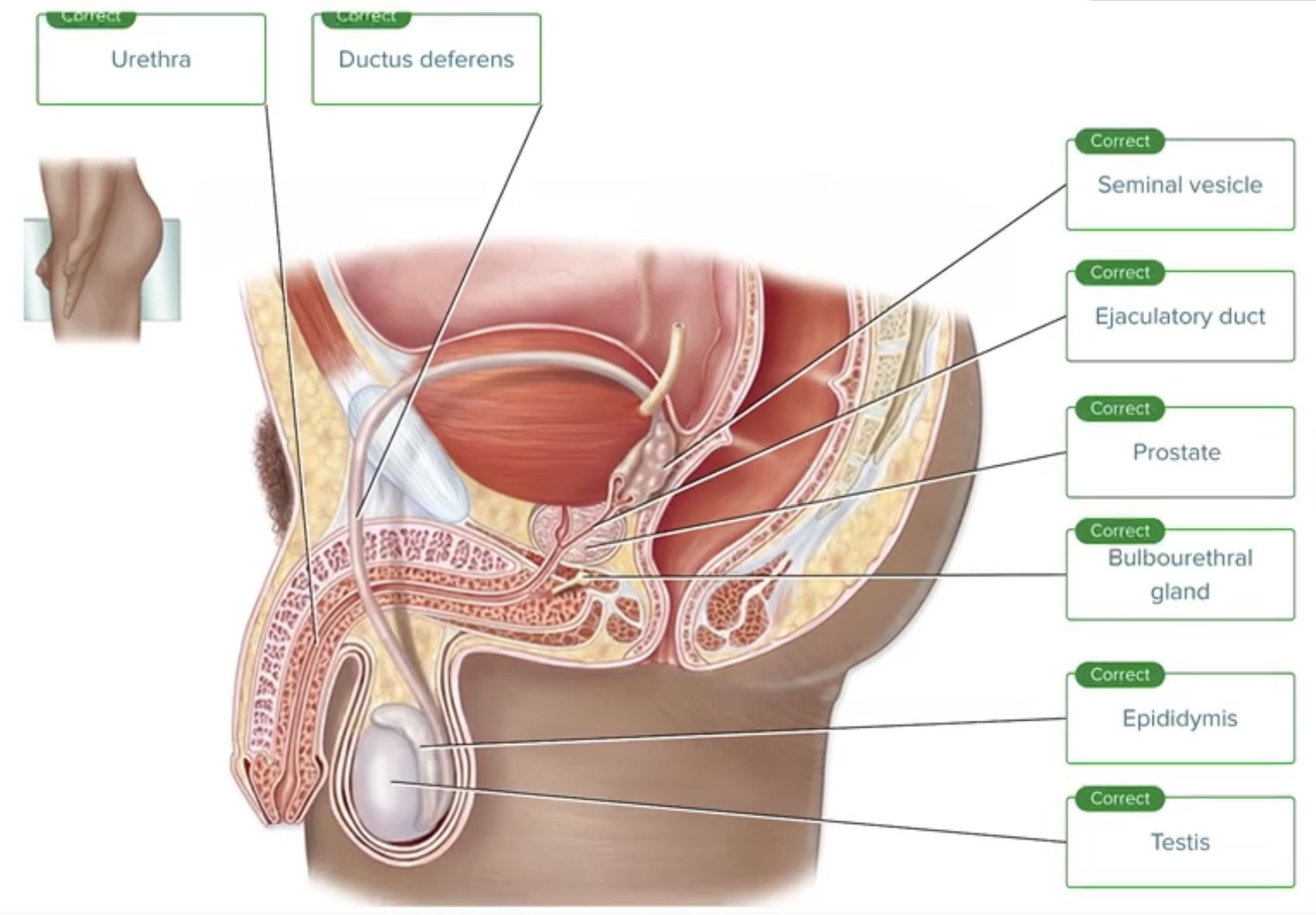
Male Reproductive System
Label the following structures of the male reproductive system.
Spermatogenesis: Order of Events
Germ cells in the testes produce diploid cells called __________. Meiosis begins with primary __________. Meiosis I ends with the production of _________ spermatocytes, which are the first haploid cells in the process. Meiosis Il results in the production of 4 haploid _________. Maturation of the sperm occurs in the _________ tubules and epididymis.
spermatocytes
seminiferous
spermatogonia
spermatids
secondary
Germ cells in the testes produce diploid cells called spermatogonia. Meiosis begins with primary spermatocytes. Meiosis I ends with the production of secondary spermatocytes, which are the first haploid cells in the process. Meiosis Il results in the production of 4 haploid spermatids. Maturation of the sperm occurs in the seminiferous tubules and epididymis.
Uterine Cycle: Timing of Events
Before or After Ovulation
Rapidly rising FSH
Menses
Progesterone peak
Rapidly declining gonadotropins
Proliferative phase of uterine cycle
Estrogen low
Rapidly rising LH
Secretory phase of uterine cycle
BEFORE ovulation: Rapidly rising LH, Rapidly rising FSH, Proliferative phase of uterine cycle, Estrogen low
AFTER ovulation: Rapidly declining gonadotropins, Menses, Progesterone peak, Secretory phase of uterine cycle
Ovarian Cycle
Before or After Ovulation
Second meiotic division completion
Corpus luteum
Mature follicle
First polar body formation
Second meiotic division begins
Primordial follicles
Second polar body formation
BEFORE ovulation: Primordial follicles, First polar body formation, First meiotic division, Second meiotic division begins, Mature follicle
AFTER ovulation: Corpus luteum, Second polar body formation, Second meiotic division completion
What happens to the zona pellucida once a sperm cell has penetrated it?
It secretes hCG
It hardens.
It generates electrical impulses.
It disintegrates.
it hardens
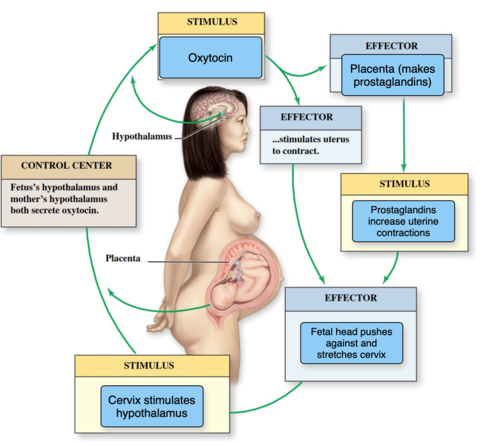
A patient is having contractions that are increasing in intensity and frequency, and her cervix is dilated. She is likely experiencing
true labor.
menses.
false labor.
true labor.
What is the most significant cause of hemorrhoids during pregnancy?
Compression of veins
Acid reflux
Edema
Morning sickness
Compression of veins
Cleavage occurs during the ________ stage.
pre-embryonic
neonatal
embryonic
fetal
pre-embryonic
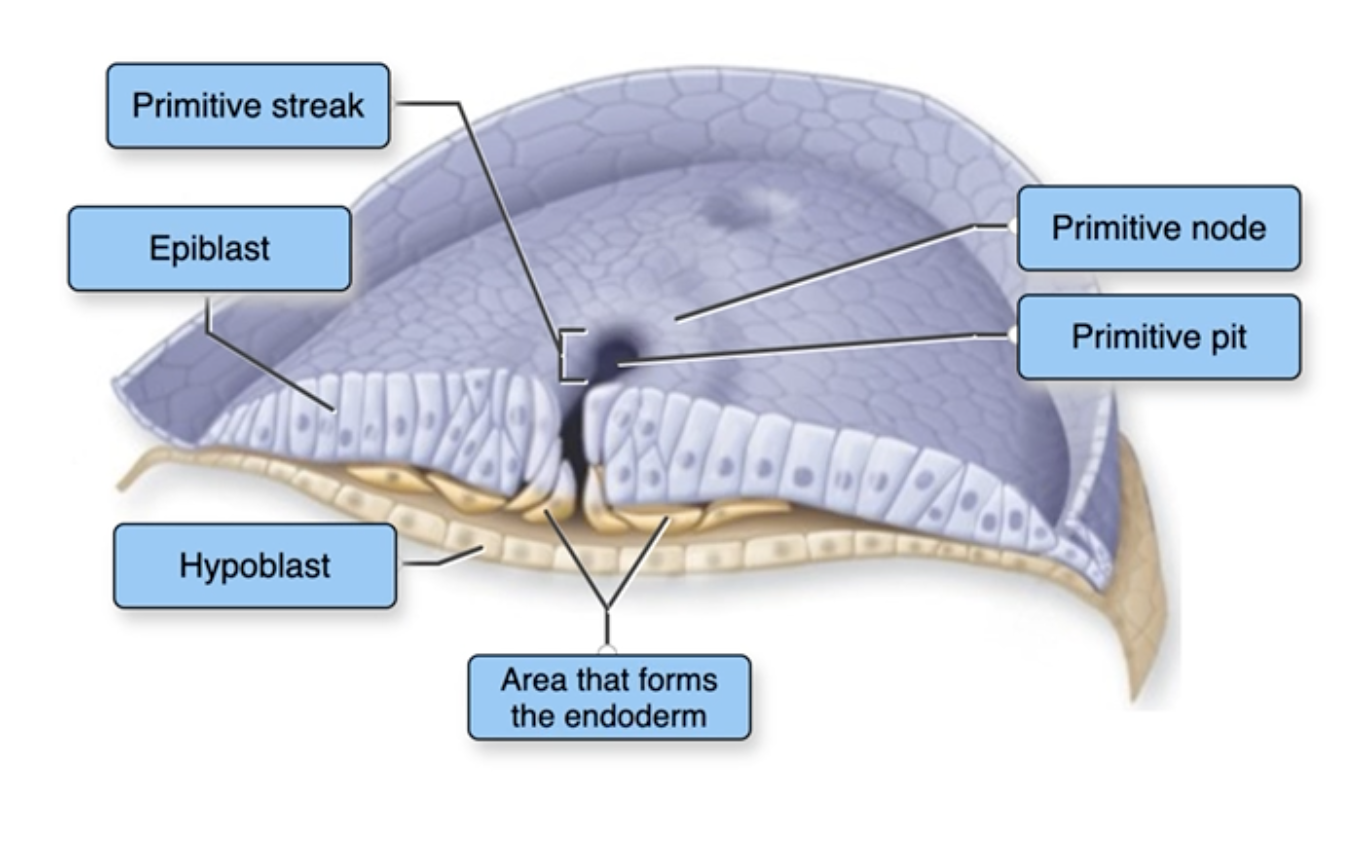
Together, the hypoblast and epiblast form the
trophoblast.
cytotrophoblast.
bilateral germinal disc.
syncytiotrophoblast.
bilateral germinal disc.
The disease osteogenesis imperfecta is caused by a dominant allele. However, not all people with this allele actually suffer from symptoms of the disease. What is this phenomenon called?
Codominance
Dominance
Incomplete dominance
Incomplete penetrance
Recession
Incomplete penetrance
Initially, sperm are not capable of fertilizing the oocyte. They must first undergo
fertilization.
meiosis II.
compaction.
capacitation.
capacitation
After birth, the foramen ovale is closed as a result of
increasing pressure in the right atrium.
increasing pressure in the left atrium.
increased resistance in the pulmonary circuit.
decreased blood volume in the pulmonary veins.
increasing pressure in the left atrium.
The portion of a blastocyst that will form the embryo is called the
trophoblast.
pronucleus.
chorion.
embryoblast.
embryoblast
Many pregnancy tests detect human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). If a patient's pregnancy test was positive, the embryo was at least __________ old when she took the test.
1 day
2 weeks
7 days
4 weeks
2 weeks
During the embryonic stage, the primary germ layers develop from the
blastocyst.
uterus.
embryonic disc.
morula.
embryonic disc
The placenta allows
oxygen and nutrients to diffuse from maternal blood to the embryo.
carbon dioxide and other wastes to diffuse from the maternal blood to the embryonic blood.
movement of anesthetics from the maternal blood into the fetus.
the fetus to enlarge without rupturing the mother's abdomen.
All of these choices are correct.
oxygen and nutrients to diffuse from maternal blood to the embryo
An increase in blood pressure during the first trimester of pregnancy is due to
decreased heart rate.
increased blood volume.
decreased blood viscosity.
decreased hematocrit.
increased blood volume
Which allows sperm to penetrate the zona pellucida?
Electrical impulses
Their motility
The acrosomal reaction
Local hormones
The acrosomal reaction
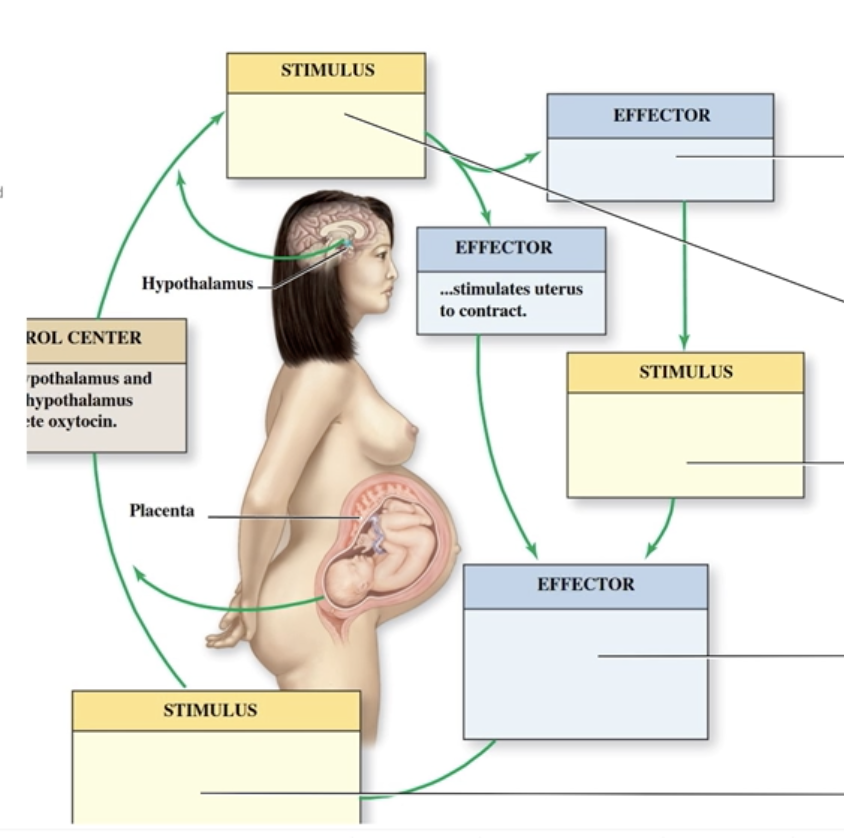
True Labor Stages
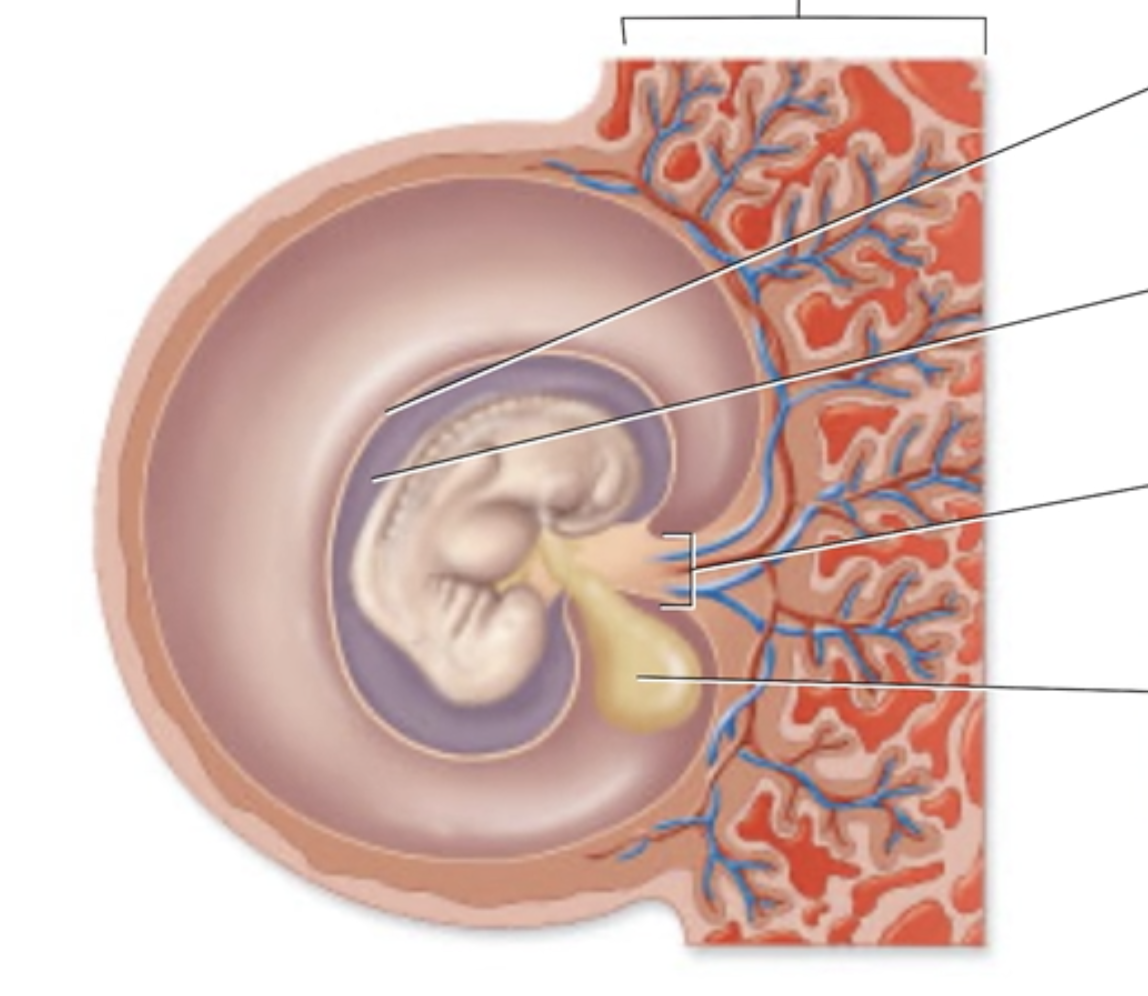
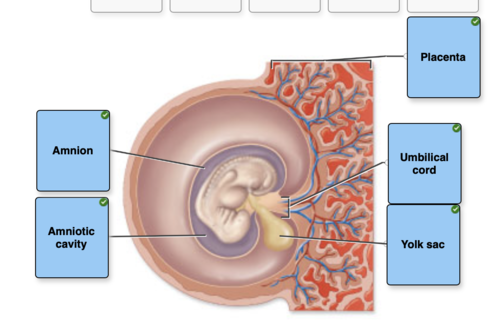
Structures Surrounding Four Week Embryo
Label the structures surrounding a late 4-week-old embryo.
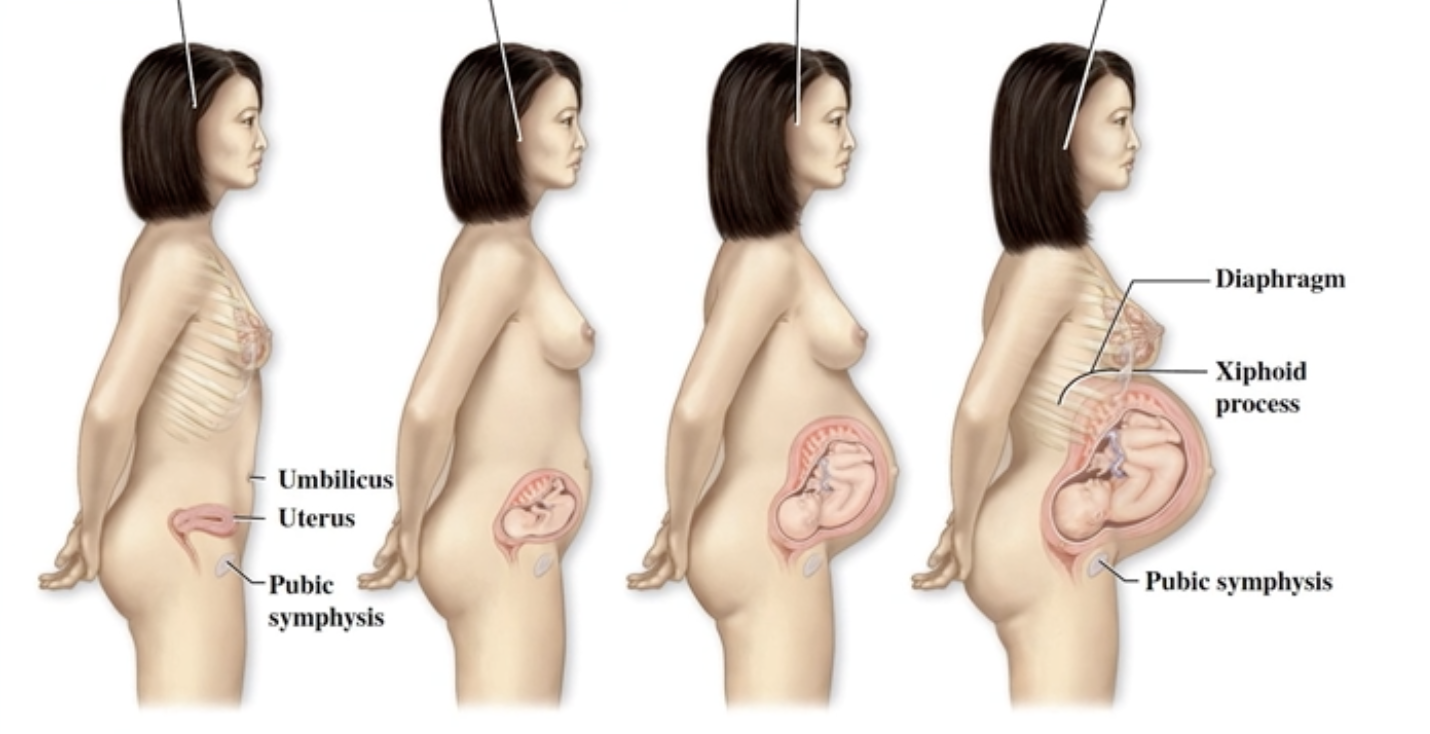
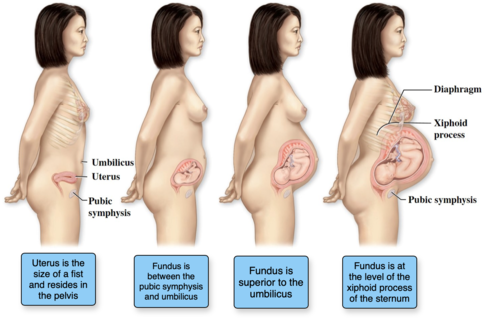
Uterine Changes During Pregnancy
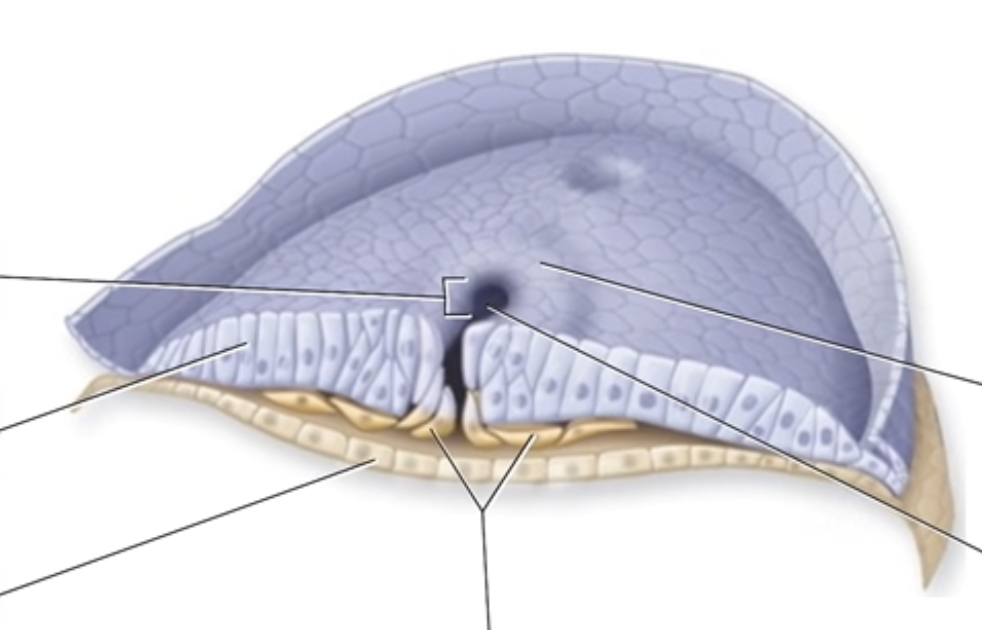
Gastrulation at Week 3
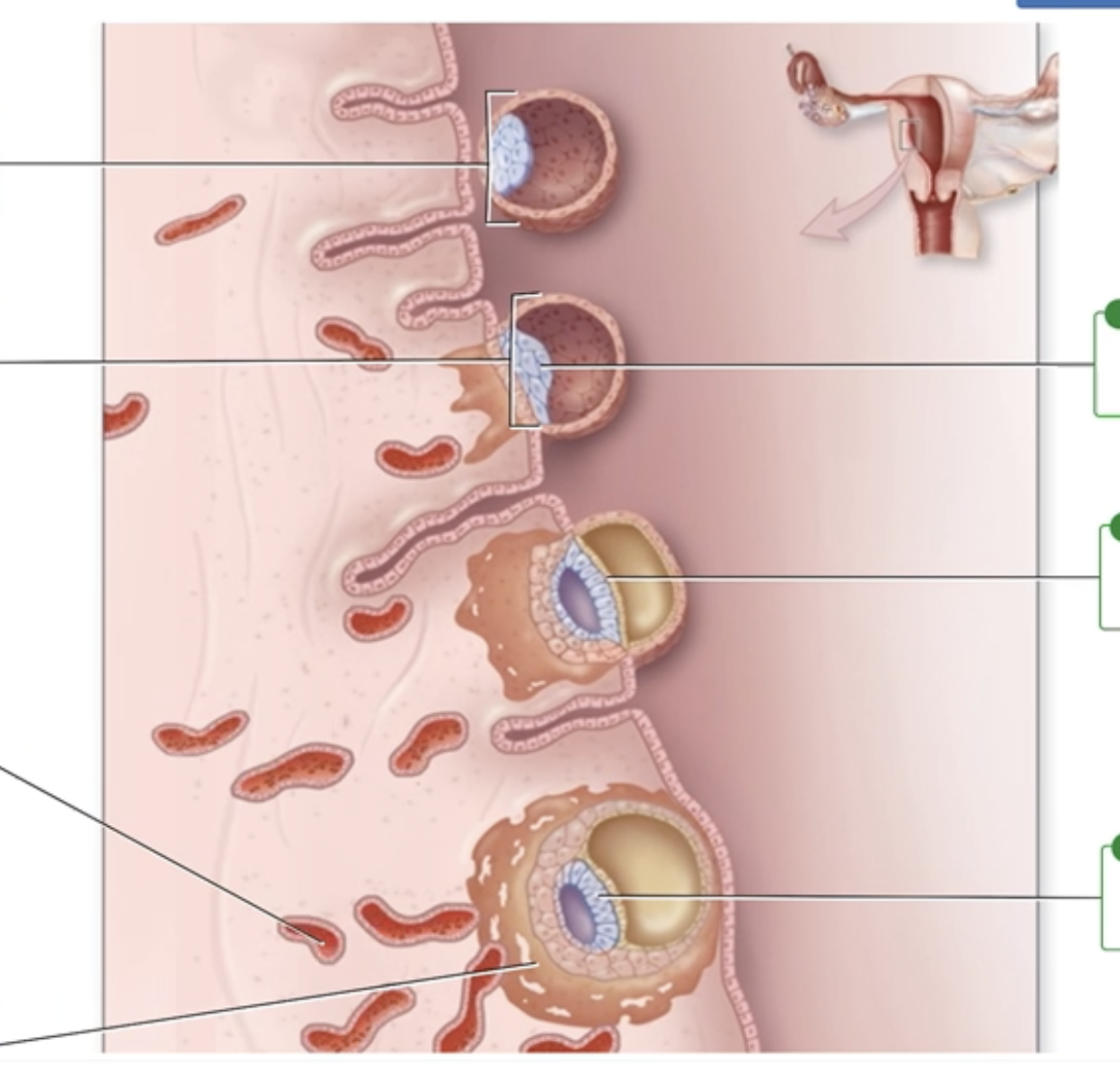
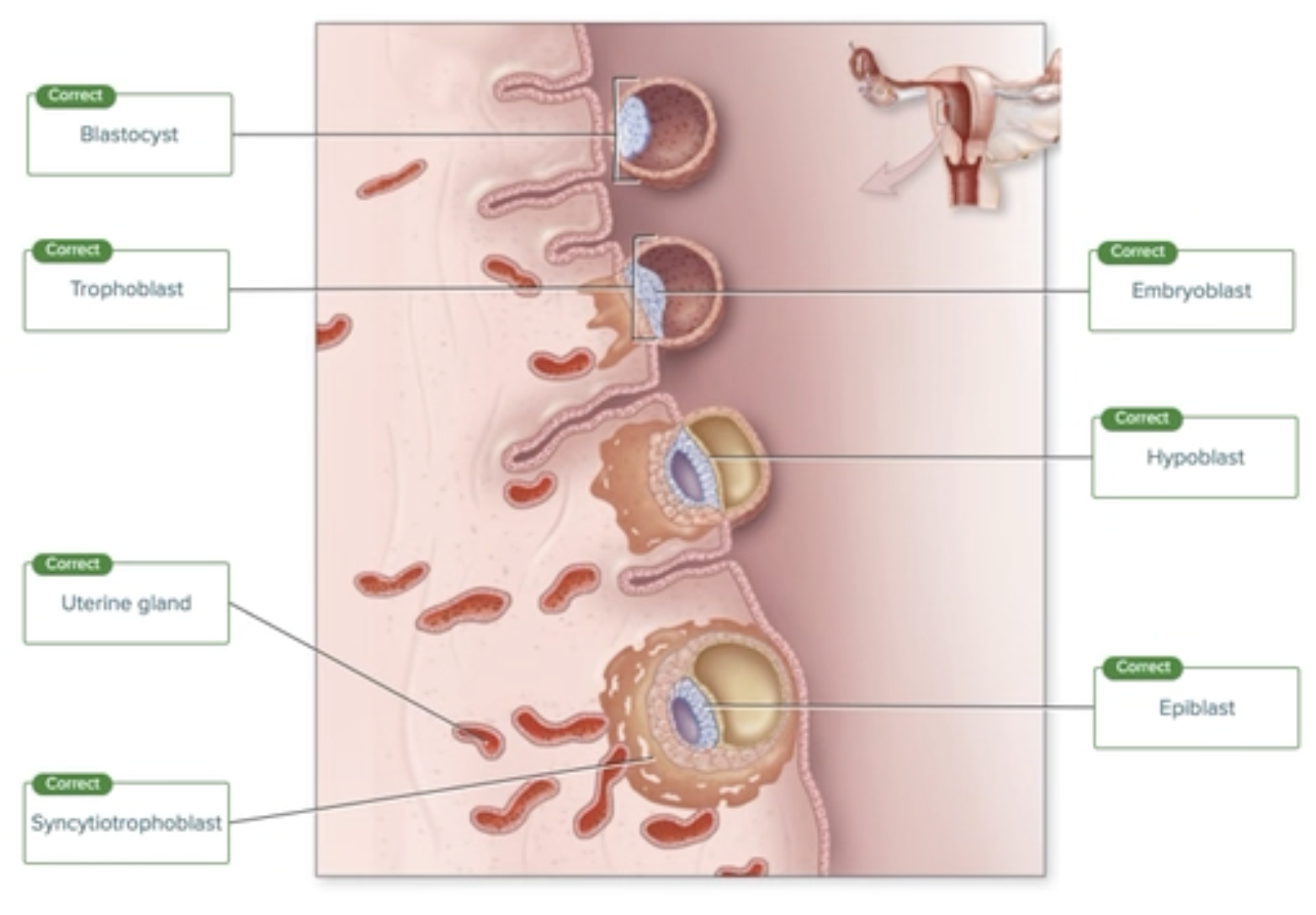
Implantation: 6-8 Days
Correctly label the following structures involved in the different stages of implantation.
Place the regions of the nephron in the correct order for the process of urine formation.
a. Capsular space of glomerulus
b. Nephron loop
c. Collecting duct
d. Distal convoluted tubule
e. Proximal convoluted tubule
b, d, c, e, a
a, c, b,e, d
a, e, b, d, c
b, e, c, d, a
e, d, b, a, c
a, e, b, d, c
Which of the following would increase the rate of glomerular filtration?
a constricted afferent arteriole
drinking water
decreased blood pressure
a dilated efferent arteriole
increased blood pressure
increased blood pressure
The __________ inside the bladder is formed by imaginary lines connecting the two ureter openings and the urethral opening.
mucosa
trigone
detrusor
muscularis
trigone
To calculate GFR, the concentration of a marker molecule is measured in both the blood and the urine, and the total volume of urine produced is also measured. Which of the following sets of results indicates the highest GFR?
High concentration of the marker in the urine, high volume of urine, low concentration of the marker in the blood
High concentration or the marker in the brood, high volume of urine, low concentration of the marker in the urine
High concentration of the marker in the blood, low volume of urine, high concentration of the marker in the blood
High concentration of the marker in the urine, low volume of urine, high concentration of the marker in the blood
High concentration of the marker in the urine, high volume of urine, low concentration of the marker in the blood
The ___________ transfer urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
urethras
efferent arteries
ureters
vas deferens and uterine tubes
ureters
If renal plasma clearance is a test to measure the volume of a substance that can be completely cleared in 1 minute, and if the GFR of urea is 125 mL/min, and renal plasma clearance of urea is 70 mL/min, that means the remainder of the urea is
filtered
cleared
degraded
reabsorbed
reabsorbed
The proximal convoluted tubule is lined with a
stratified squamous epithelium with a large surface area.
stratified squamous epithelium with a tough, durable surface.
simple squamous endothelium that makes a slick surface.
cuboidal epithelium with a large surface area
simple columnar epithelium with a slick smooth surface.
cuboidal epithelium with a large surface area
The normal pH for urine
ranges between 8.0 and 9.0 for someone with a diet high in protein.
ranges between 3.0 and 6.0.
is anyhting below 7.0.
Is anything above 7.0
ranges between 4.5 and 8.0.
ranges between 4.5 and 8.0.
The presence of proteins in the plasma tends to
push tud aross the hitason membrane.
draw fluid back into the glomerulus.
draw fluid back into the glomerulus.
Generally, a very __________ percent of Na' in the tubular fluid is reabsorbed, and the reabsorption takes place _____________.
small, only in the nephron loop
high; only in the nephron loop
small; along the entire tubule
high; along the entire tubule
high; along the entire tubule
Podocytes and pedicels are part of the
collecting duct.
peritubular capillaries.
distal convoluted tubule.
urethra.
glomerular capsule.
glomerular capsule
Which is not correct regarding the urinary bladder?
The mucosa has rugae for distension.
The inferior portion of the bladder is called the apex.
The peritoneum covers only the superior surface of the bladder
There are two ureteral operings.
The inferior portion of the bladder is called the apex
The expulsion of urine from the bladder is referred to as
Incontinence.
diuresis.
retention.
micturition.
micturition
The hormone ANP is released from the heart and causes the urinary system to
increase urine volume and decrease blood volume.
decrease urine volume and blood volume.
decrease urine volume and increase blood volume
increase urine volume and blood volume
increase urine volume and decrease blood volume
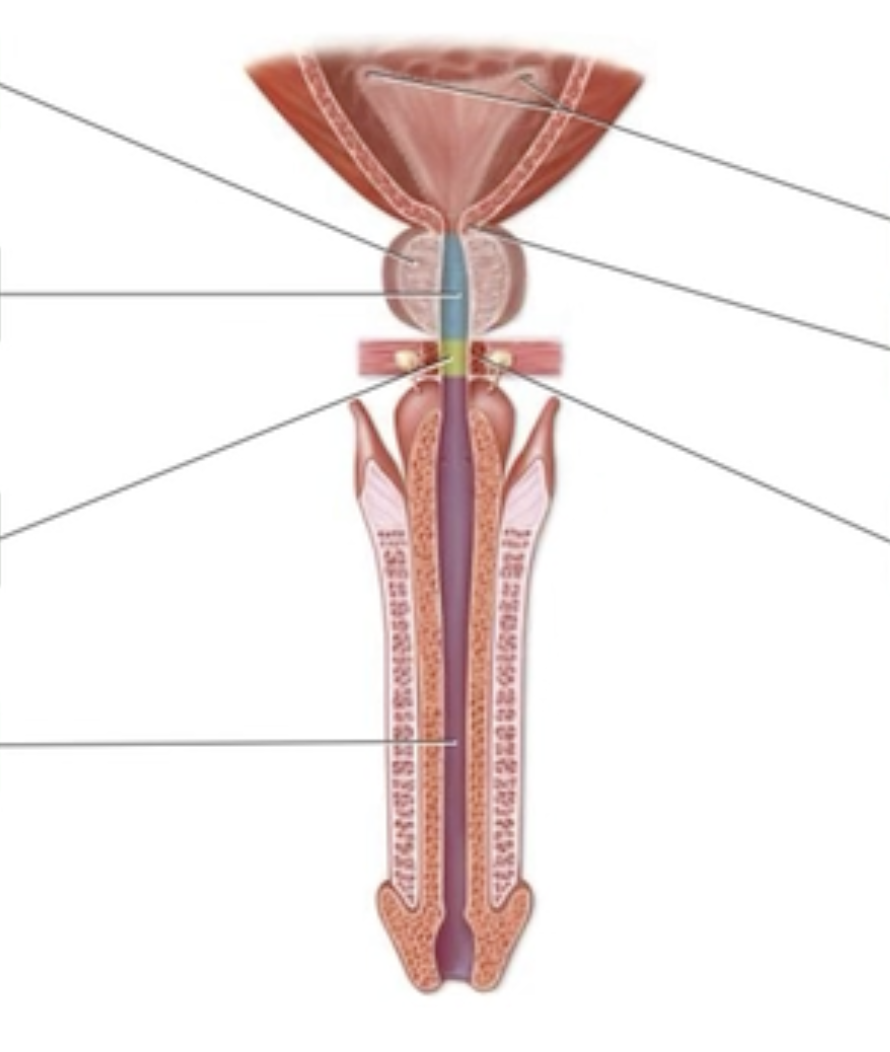
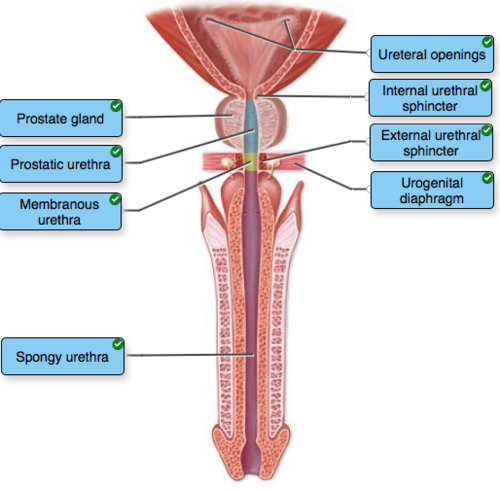
The Male Urinary Bladder and Urethra
Prostatic urethra
Internal urethral sphincter
Prostate gland
Ureteral openings
Spongy urethra
Membranous urethra
External urethral sphincter
Paramesonephric ducts degenerate when the hormone ___________ is present.
TSH
testosterone
inhibin
estrogen
AMH
AMH
What fibromuscular structure is about 10 centimeters long and serves as the birth canal?
Uterus
isthmus
vagina
Fallopian tube
vagina
When the process of melosis is complete, the result is
two daughter cells that are diploid.
two daughter cells that are haploid.
four daughter cells that are diploid
four daughter cells that are haploid
four daughter cells that are haploid
The male homologue to the labia majora is the
scrotum
prostate gland
bulbourethral gland
testis
penis
scrotum
Which choice best distinguishes between mitosis and meiosis?
Mitosis produces somatic cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell, whereas meiosis produces sex cells that are genetically different from the parent cell.
Miosis produces sex cells that are genetically different from the parent cell, whereas meiosis produces somatic cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.
Mitosis produces sex cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell, whereas meiosis produces somatic cells that are genetically different from the parent cell.
Mitosis produces somatic cells that are genetically different from the parent cell, whereas meiosis produces sex cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.
Mitosis produces somatic cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell, whereas meiosis produces sex cells that are genetically different from the parent cell.
The rete testis
is a venous network that cools the arterial blood traveling to the testis
transports seminal fluid to the efferent ductules
receives sperm from the seminiferous tubules
is the nerve plexus that supplies the testis
is the site of spermiogenesis
receives sperm from the seminiferous tubules
Which of the male accessory glands encircles the urethra?
Urethral gland
Bulbourethral gland
Cowper’s gland
Seminal vesicle
Prostate gland
Prostate gland
The portion of the uterine wall that includes the basal layer is the
myometrium.
serosa.
perimetrium.
muscularis.
endometrium.
endometrium
Ovulation occurs when an oocyte is released from a ruptured ________ follicle.
primary
primordial
mature
cogonial
secondary
mature
A secondary oocyte arrests in
anaphase Il
metaphase Il.
prophase I.
metaphase I.
prophase II.
metaphase Il.
Which of the following is true?
Sperm are composed of seminal fuid within a cell membrane.
Seminal fluid is composed of semen and sperm.
The three ingredients of ejaculate are sperm, semen, and prostate-specific antigen.
Semen is composed of seminal fluid and sperm.
Semen is composed of seminal fluid and sperm.
When a woman in her fifth decade of life is not pregnant and has stopped having menstrual cycles for _________, she is said to be in menopause.
1 year
18 months
4 months
2 months
6 months
1 year
The appearance of the external genitalia determines an individual's
phenotypic sex.
genetic sex.
genotypic sex.
gender identity.
phenotypic sex
Which is not a uterine function?
Passogeway for sperm
Site of implantation
Protection and support of developing embryo
Muscle contraction for labor and delivery
Usual site of fertilization
Usual site of fertilization
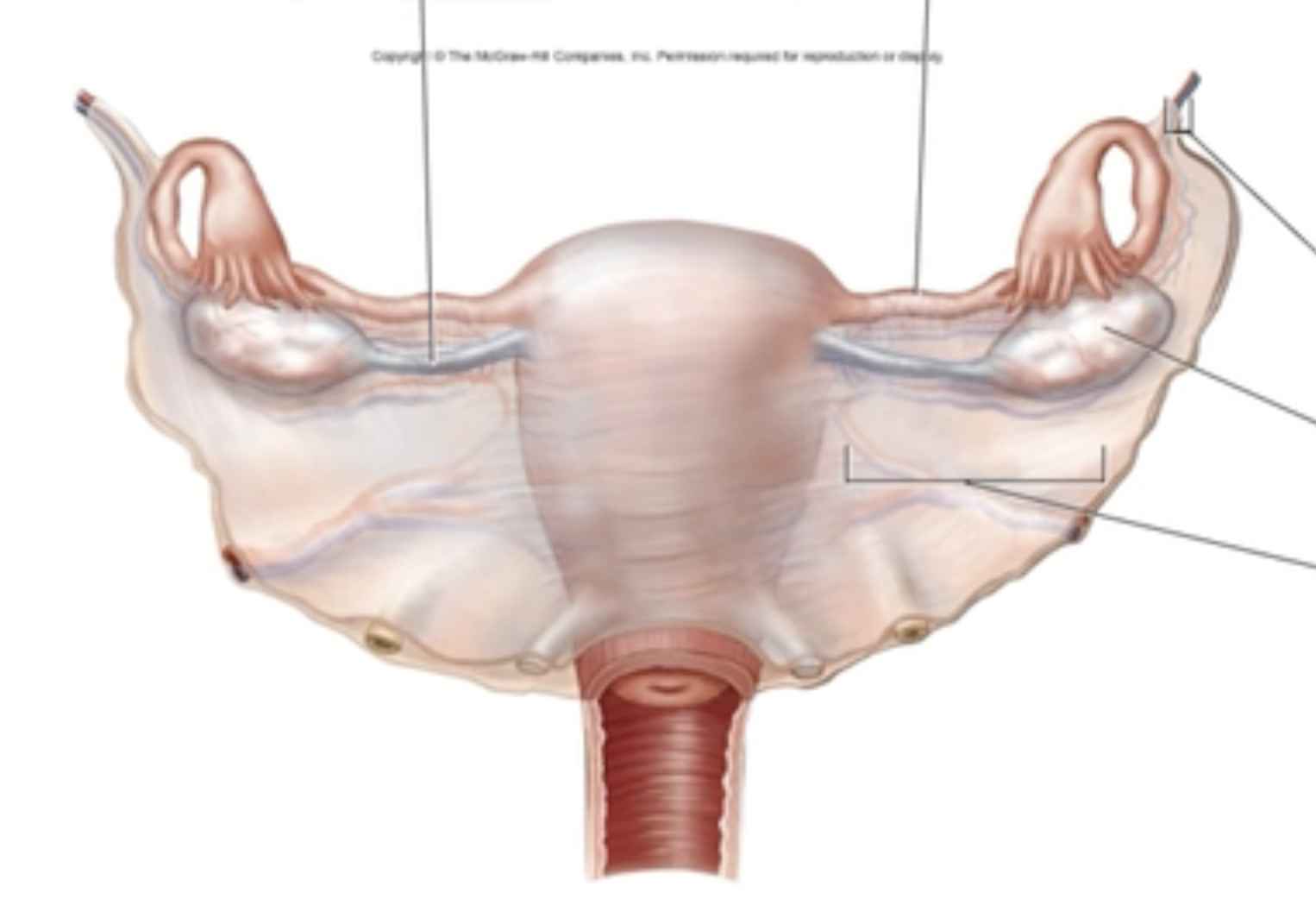
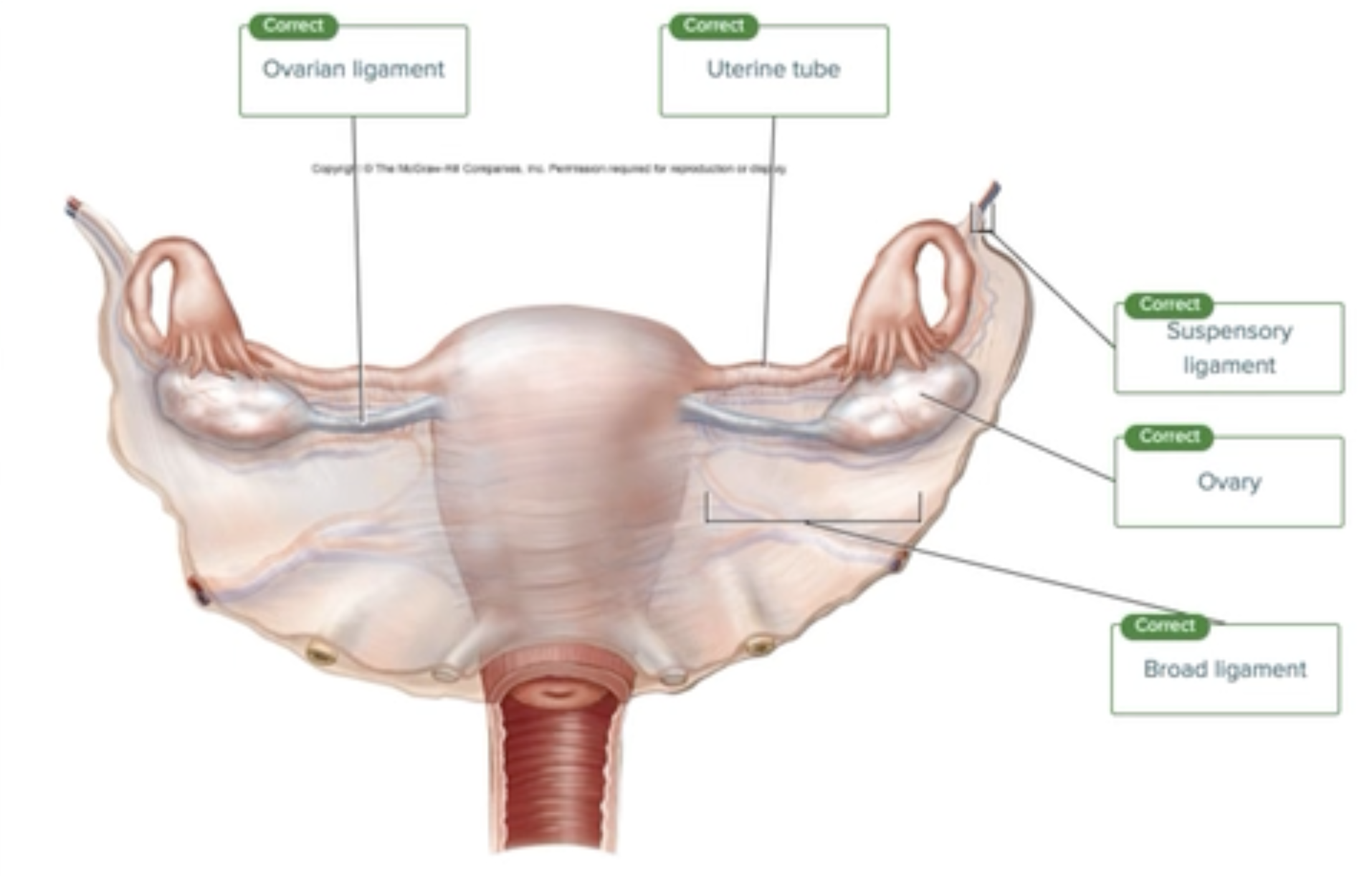
Gross Anatomical Structures of the Ovaries
Label the structures surrounding the ovary in the figure.
broad ligament
suspensory ligament
uterine tube
ovary
ovarian ligament
Gamete Formation
Spermatogenesis or Oogenesis
One gamete is produced
Of the two, this process is much more rapid
An acrosomal region must be present in mature cells
The zona pellucida is present around mature cells
Meiosis is completed only if fertilization occurs
Polar bodies are formed
Four gametes are produced that can potentially contribute to a zygote

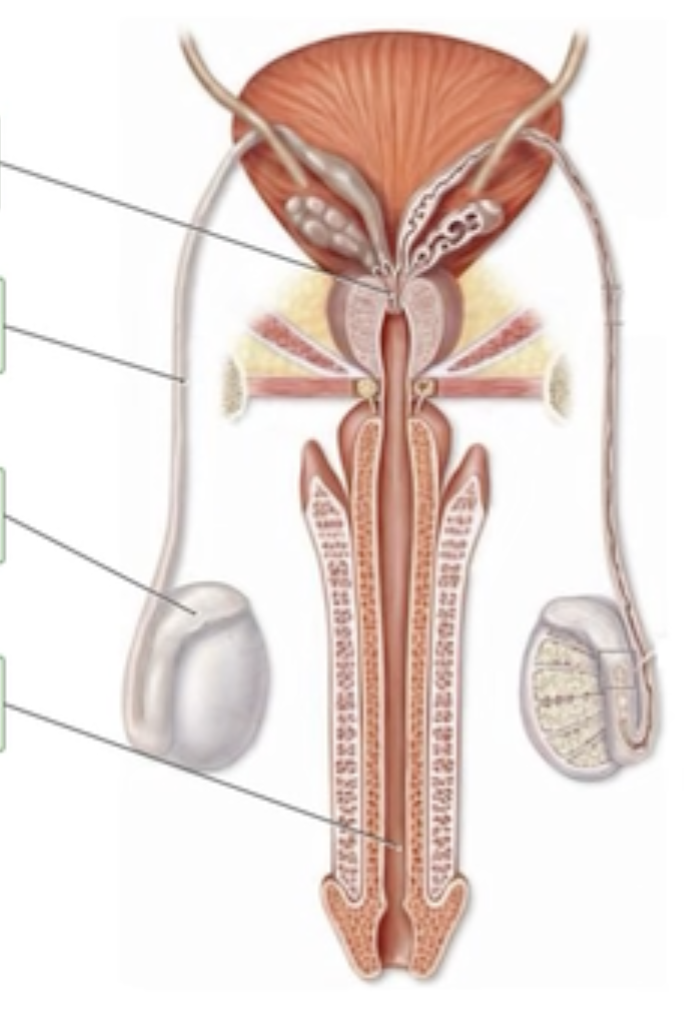
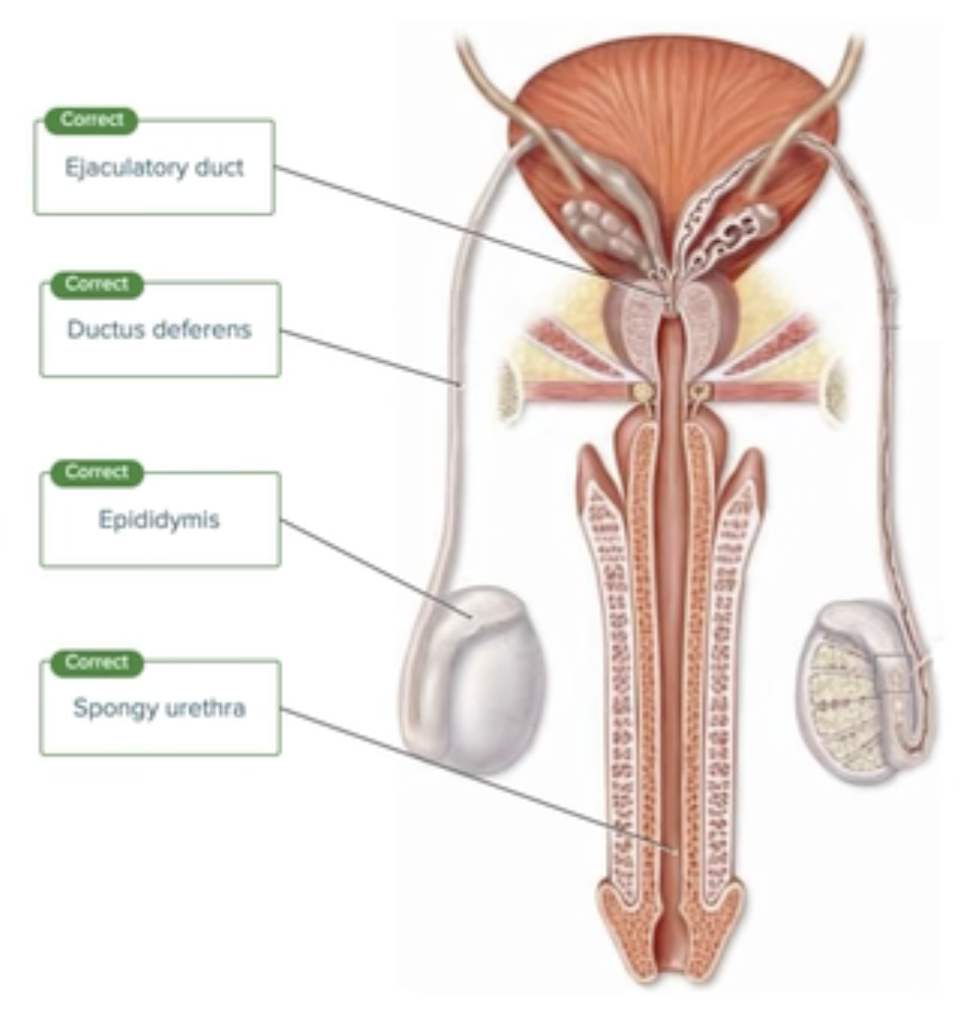
Ducts of the Male Reproductive System
Nutrients and wastes are exchanged between mother and fetus through the
amniotic cavity
yolk sac
amnion
placenta
placenta
A patient has weak contractions that are irregularly spaced. She is likely experiencing _________ labor.
true
false
false
Which of the following statements about lactation is false?
High levels of estrogen and progesterone inhibit the effect of prolactin on the mammary glands.
Other hormones responsible for breast growth during pregnancy include growth hormone, parathyroid hormones, and glucocorticoids.
Prolectin stimulates milk production.
Suckling and/or mechanical stimulation of the breasts causes secretion of prolactin releasing factor
Both colostrum and breast milk contain antibodies.
Other hormones responsible for breast growth during pregnancy include growth hormone, parathyroid hormones, and glucocorticoids.
During pregnancy, the placenta secretes ______________, which helps stimulate a darkening of the areolae, nipples, and linea alba.
follicle-stimulating hormone
human chorionic thyrotropin
relaxin
melanocyte-stimulating hormone
melanocyte-stimulating hormone
Fertilization usually occurs in the
uterus.
uterine tube.
ovary.
vagina.
cervix.
uterine tube
What allows sperm to penetrate the corona radiata?
The acrosomal reaction
Local hormones
Electrical impulses
Their motility
Their motility
The chorion is the ____________ and the amnion is the _________.
site where an embryo is implanted into the uterus; outer protective membrane around the embryo
outermost covering of an embryo and helps form the placenta; a membrane that encircles a developing embryo
site from which primary germ layers develop: site from which secondary germ layers develop
part of the blastocyst that is not the inner cell mass, inner cell mass
outermost covering of an embryo and helps form the placenta; a membrane that encircles a developing embryo
Each pronucleus contains a ________ number of chromosomes.
diploid
haploid
haploid
After birth, the foramen ovale is closed as a result of
Increasing pressure in the right atrium.
Increasing pressure in the left atrium.
increased resistance in the pulmonary circuit.
decreased blood volume in the pulmonary veins.
Increasing pressure in the left atrium.