week 4 co2
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
How can you improve your slit-lamp technique?
optimise lighting/mag
What are common errors with slit lamp?
patient not set up correctly
Eyepieces not focussed correctly
When beam is narrower, brightness should be increased
Angle of illumination arm should be varied, greater when looking at cornea than lens and lined up for fundus
Magnification should be varied throughout
What is the process of setting up the slit lamp?
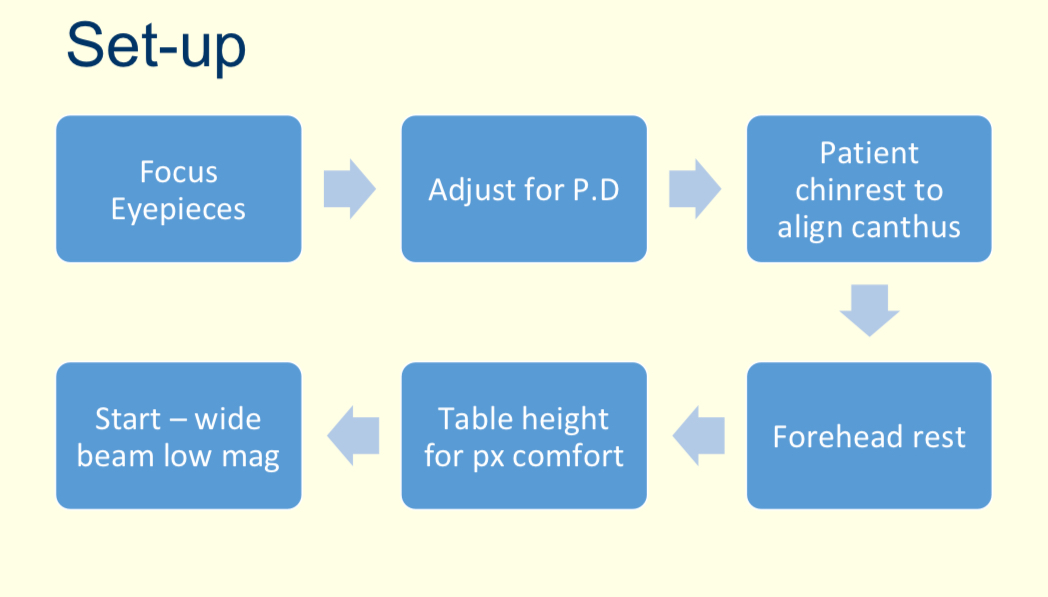
What is the suggested routine of what structures you should look for?
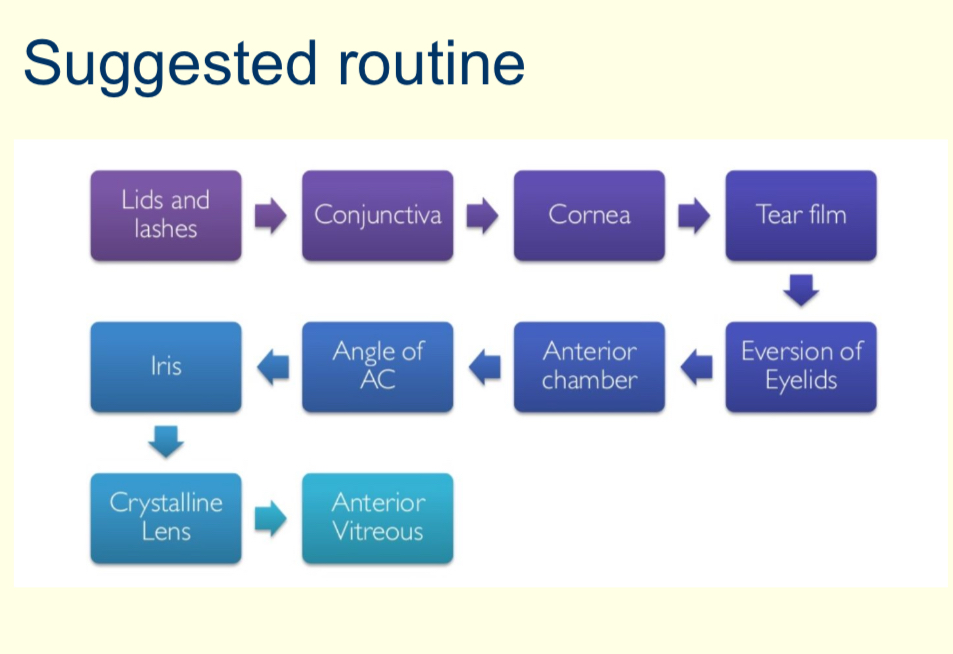
What are the key aspects of diffuse illumination?
low illumination
Low magnification
What do you use diffuse illumination for?
Lids, lashes, eyelid disease, conjunctiva, corneal abnormalities
make sure to look under lids
Ask px to look in all directions
What do you use eyelid eversion for?
look under the upper lid to examine palprebral conjunctiva
Looking for excessive redness and roughness
What do you use parallelepiped and optic section for?
Detailed examination of the cornea
What are the key features of parallel piped?
width of beam, similar to depth of cornea
Use this illumination to scan across cornea - upper, middle and lower
What are the key features of optic section?
ensure slit is as thin as it can be
Illumination at max
What can you see with optic section?
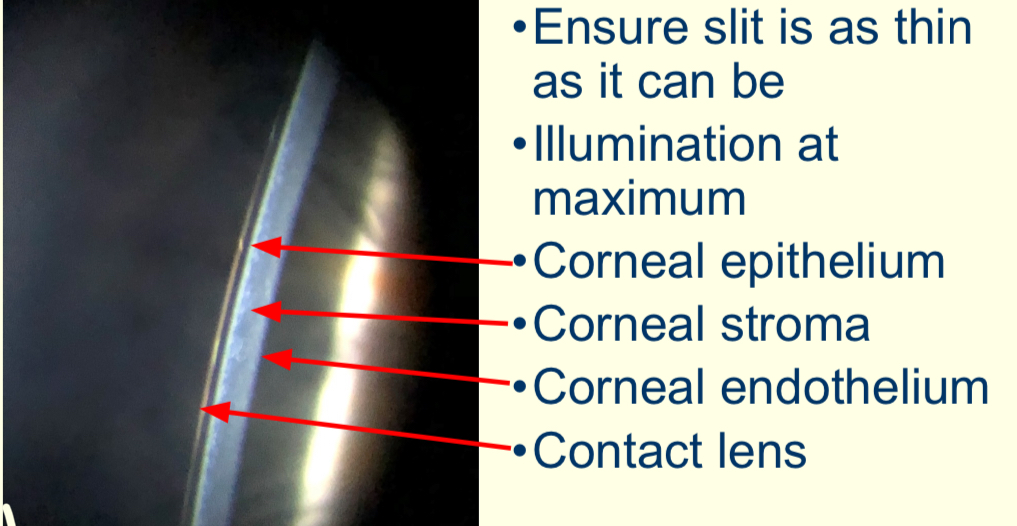
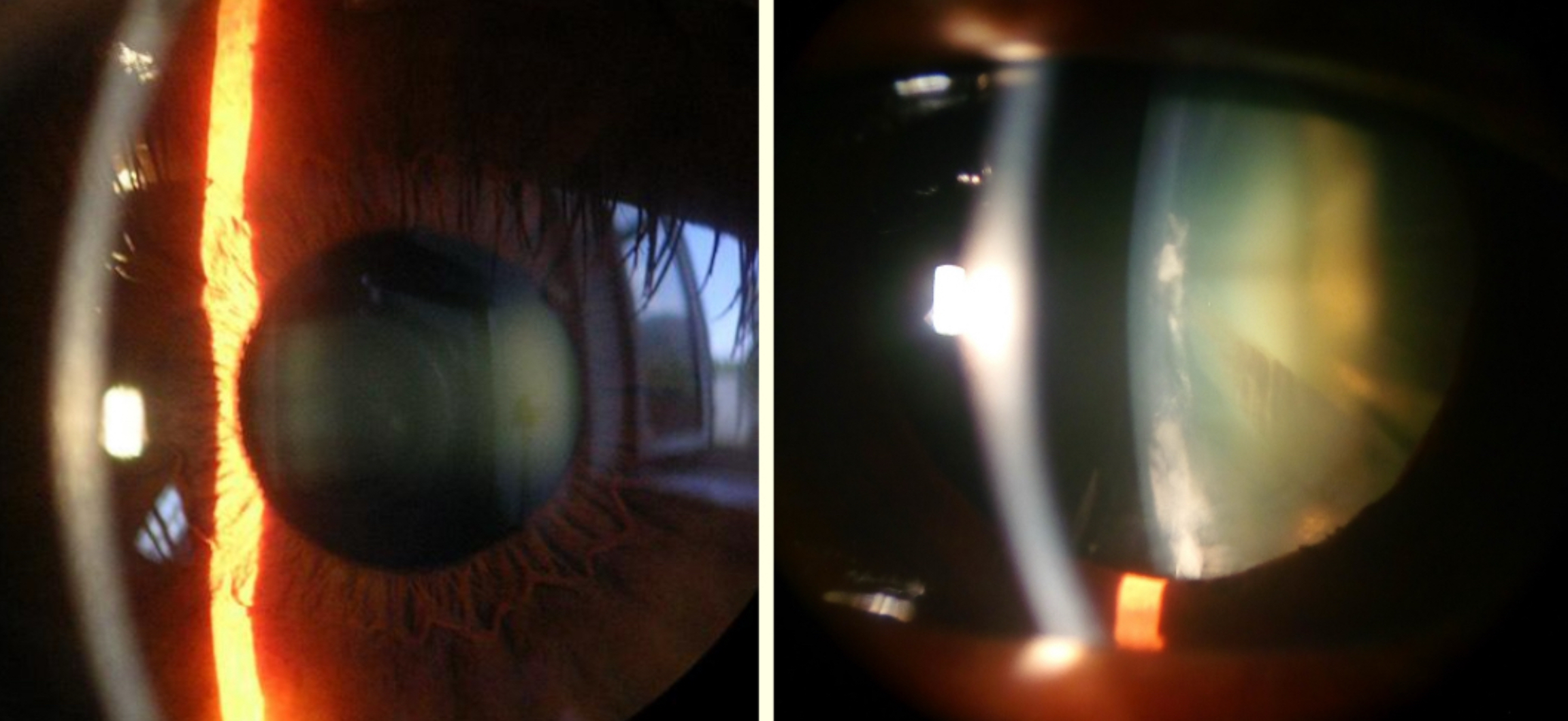
What method is used for this?
Optic section
What do you use van herick’s for?
The anterior chamber
Compare AC depth to the cornea
What are key aspects of van herick’s?
angle 60 degrees
beam just inside limbus
Ensure high brightness

Describe this method and what structures can be seen
van herick’s
Cornea, anterior chamber and iris
Looking for 1:1 ratio (100%)
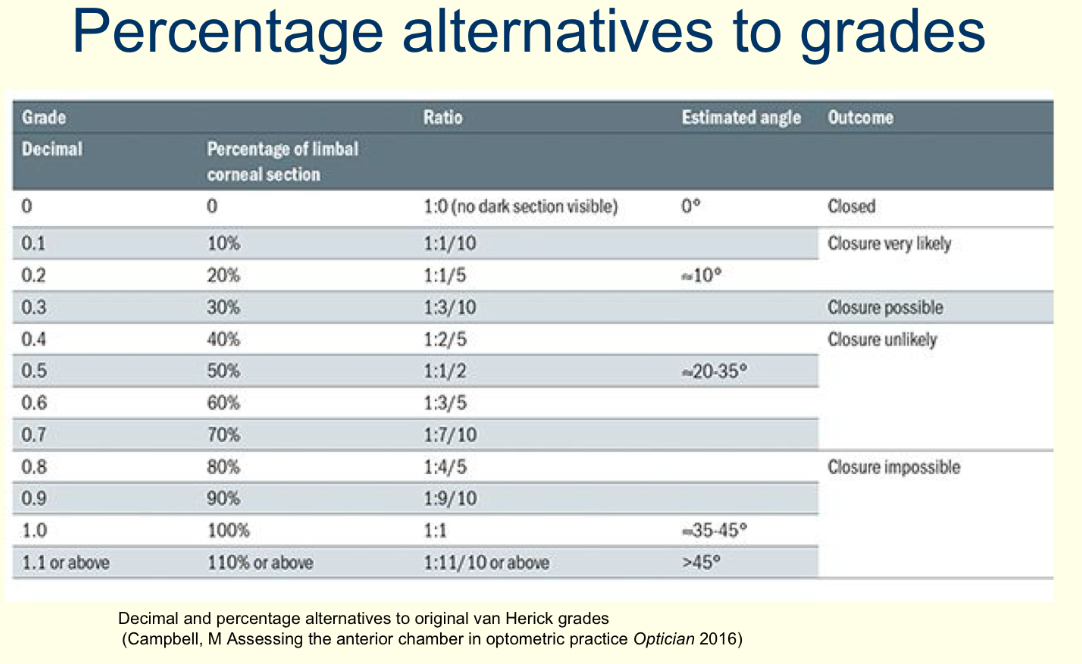
What grading scale do you use for van herick’s?
0-4 grading scale or percentage
Eg: 1:1 = 100%
1:0.25 = 25%
What angle percentage do you consider a referral?
Less than 15%
Memorise

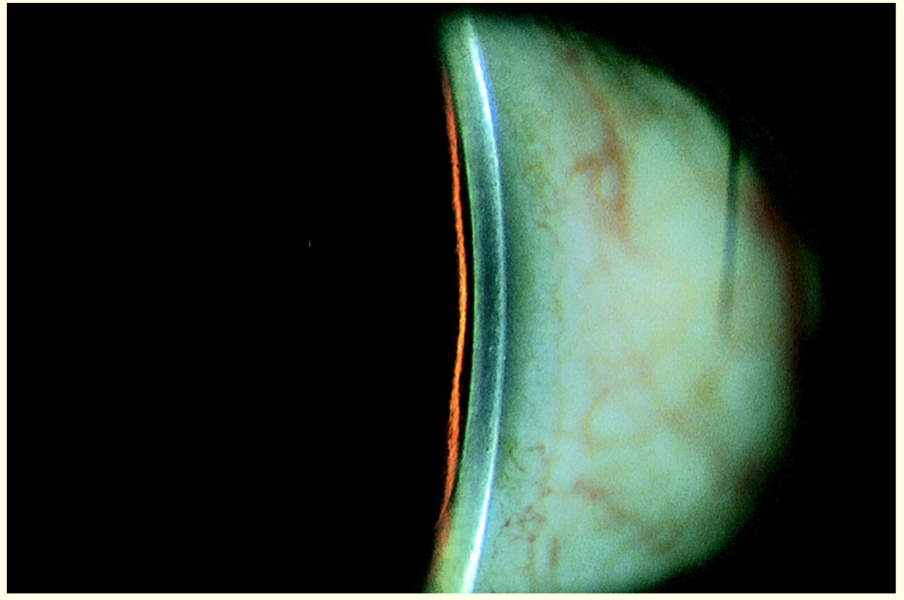
What % is this?
1:1 = 100%
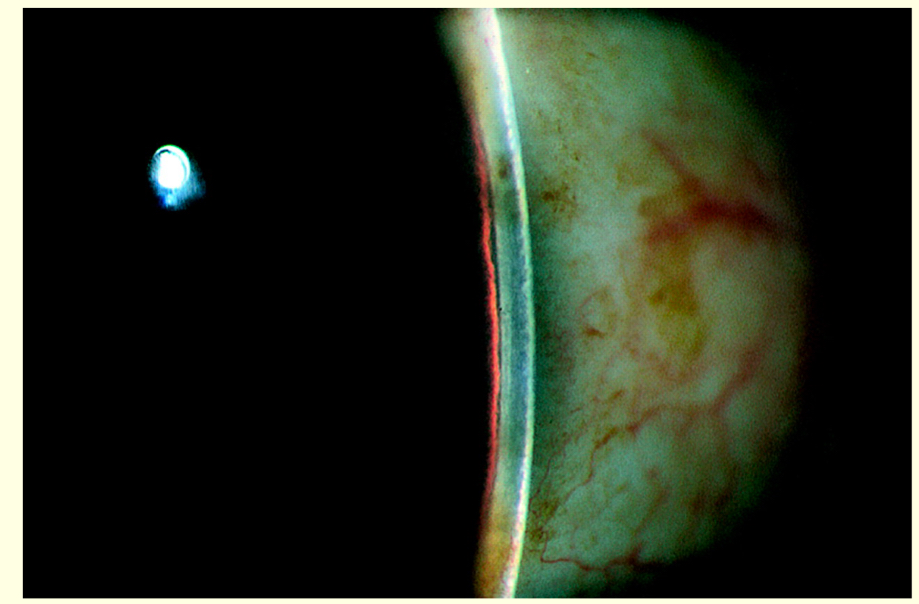
What % is this?
1:0.25 = 25%
What % is this?
5%
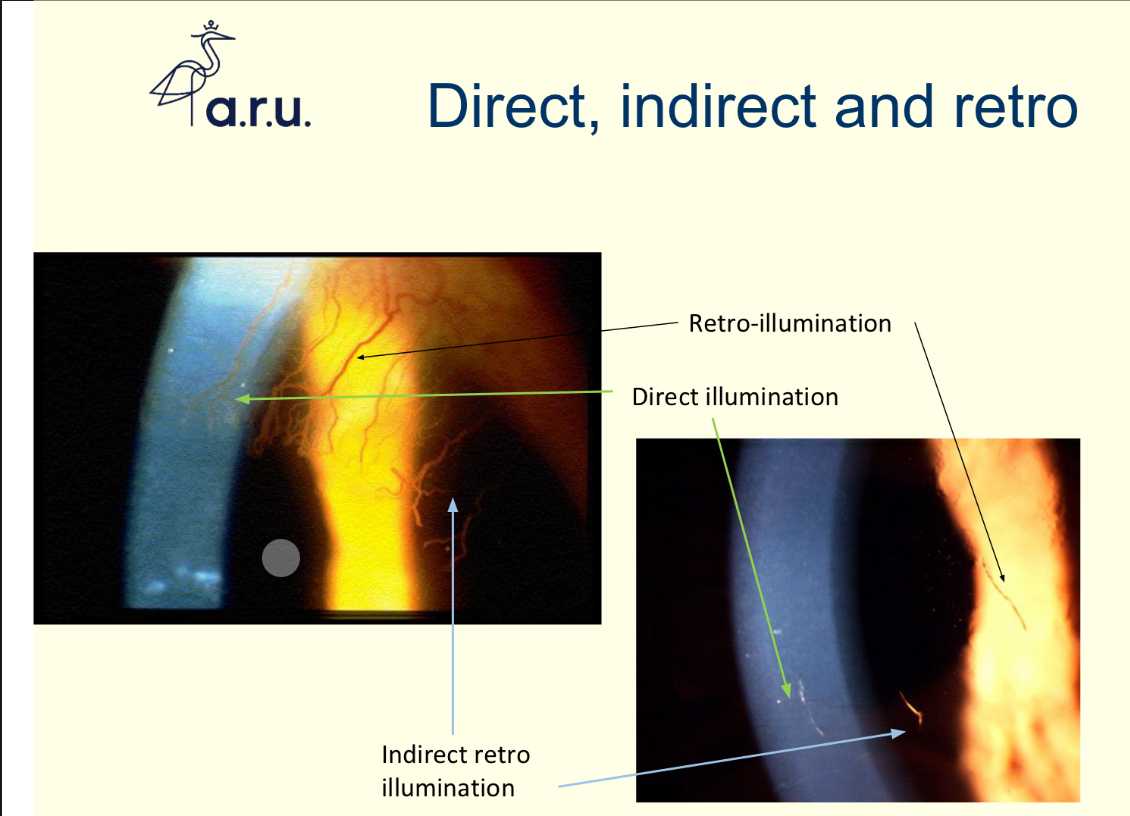
Describe direct, indirect and retro illumination
What do you use specular reflection to observe?
Corneal endothelium, espc prior to cataract surgery and tear film
What are the key aspects of specular reflection?
medium illumination
Highest mag
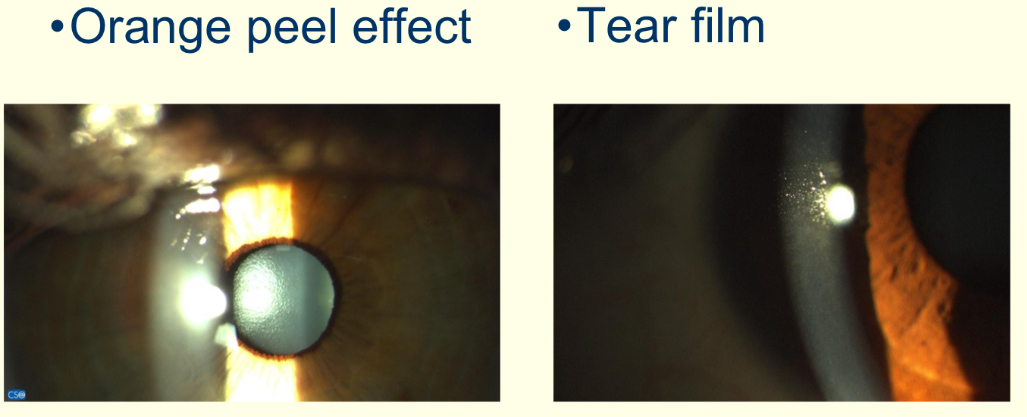
What method is being observed and what structures are being viewed?
Specular reflection
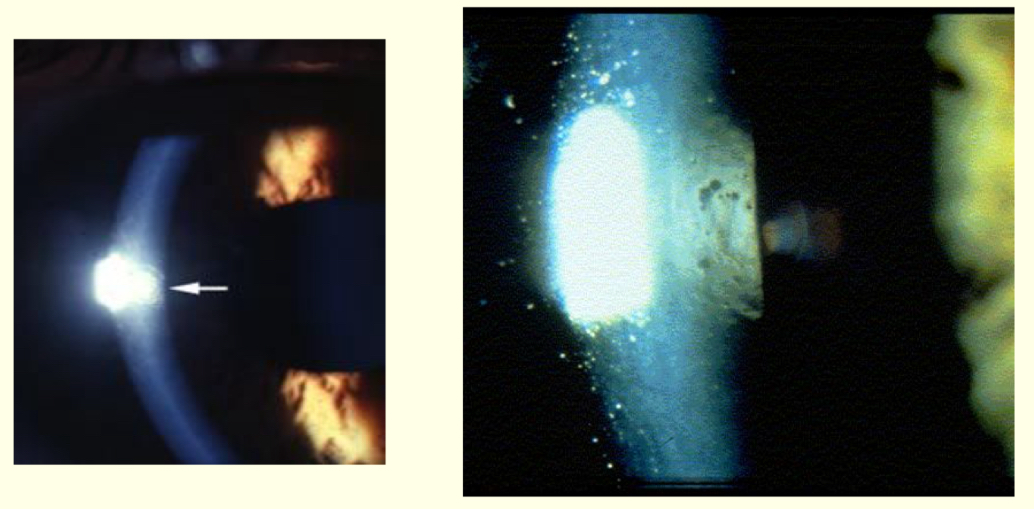
Whst method and what structures is being observed?
Specular reflection and endothelium
What is the purpose of decoupling the slit lamp?
places light at a different place than the eyepieces are viewing
What method uses decoupling a slit lamp?
Sclerotic scatter
Which structure is being illuminated in sclerotic scatter?
The limbus
What do you use fluroscein for?
Corneal staining caused by dryness or abrasion
How do use corneal staining?
instil fluroscein
Use cobalt blue and written filter
Look with wide beam and low mag
Then scan using a parallel piped and x16 mag
Check whole cornea
Record by drawing
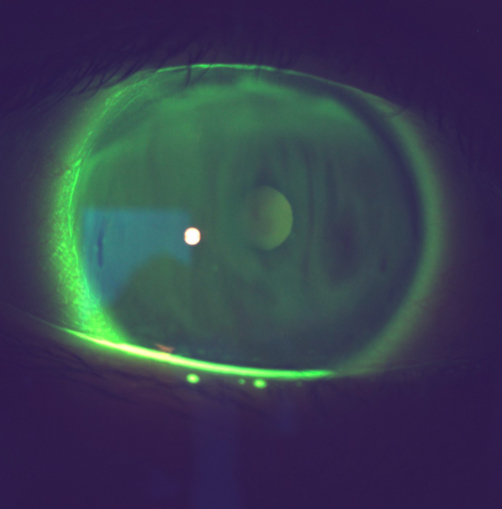
What’s going on here?
Corneal staining
Tear break-up
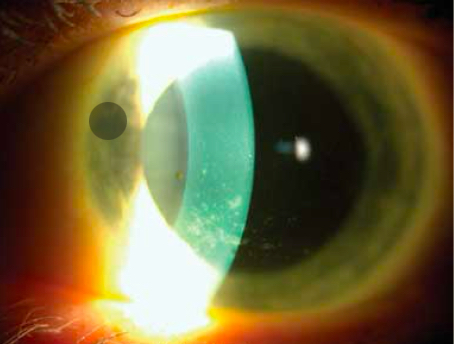
What’s going on here?
Dryness
What’s going on here?
Punctate staining
What are grade findings?
compare your findings to photograph
Use 0.5 steps
Same scale each visit
Support finding with drawing where appropriate
What are the advantages of grading scales?
improves record keeping
Allows change monitoring
Improves decision making
Improves reliability
Reduces intra and inter practioner variability