Psych unit 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Depressants - function
slow neural activity and slow body functions
3 Depressants
Alcohol, Bariturates, Opiates
Stimulants - function
excite neural activity and speed up body functions
4 stimulants
caffeine, nicotine, cocaine, ecstasy
Hallucinogens function
distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input
1 Hallucinogen
LSD
Bariturates
what r they perscribed for (2 things)
what do they do
what r they also known as
what happens if mixed with alcohol
perscribed for sleep issues and anxiety
impair judgement and memory
known as tranquilizers
death is mixed w alcohol
Opiates
2 examples
what do they do
what is withdrawal like
opium and heroin
diminishes endorphins
extreme pain if discontinued use
2 narcotics
what they do
codeine, morphine
stops endorphins
Ecstacy
what type of drug
what is withdrawal like
can cause _
what type of neurotransmitter is released and what does this cause
stimulant
depressed mood days after
can cause hyperthermia
releases serotonin —> euphoria
Cocaine
what type of drug
what does it do
stimulant
blocks reuptake therfore seroonin levels highly increase
Bio-Psycho-Social Approach
3 types
what they take into account
Biological influences - genetics, illness
psychological influenes - mental illness, personal experiences, behavioral habits
Social/ cultural influences-relationships and surroundings
Neuroplasticity
the brain’s ability to change an adapt its structure and function through life
Lesioning
intentionally damaging or removing brain tissue
3 types of brain scans
EEG, MRI, PET scan
what does EEG scan record
Brain waves
what does MRI scan record
how does it do this
body and brain tissue, uses magnetic fields and special radio receivers
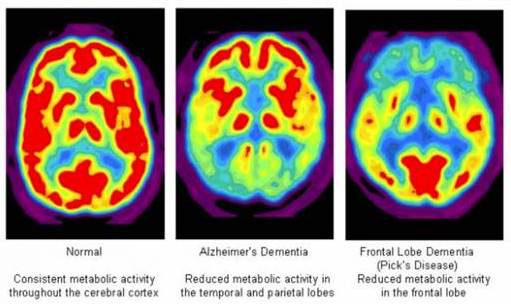
what does the PET scan record
Biochemical activity
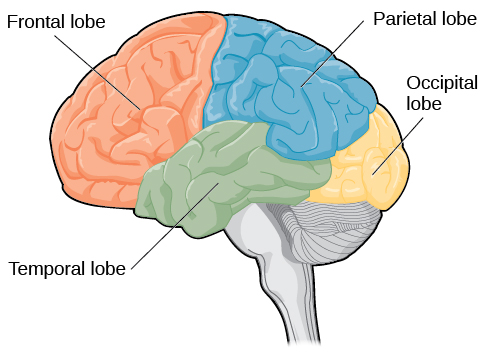
Four major lobes of the brain
Frontal lobe
Parietal lobe
Occipital lobe
Temporal lobe
Medulla
where is it located
what is its function
Hindbrain (Brainstem) – Regulates cardiovascular & respiratory systems (involuntary)
Pons
where is it located
what is its function
Hindbrain (Brainstem) – Bridge between brain areas; coordinates movement with cerebellum
Cerebellum
where is it located
what is its function
Hindbrain – Balance, posture, coordination (walking straight, etc.)
Midbrain
where is it located
what is its function
Brainstem – Controls visual & auditory reflexes (involuntary)
Reticular Formation
where is it located
what is its function
Inside Brainstem – Arousal, alertness, sleep cycle, respiratory control, pain modulation
Reticular Activating System
where is it located
what is its function
Brainstem → Thalamus – Alerts brain to important stimuli (like hearing your name)
Thalamus
where is it located
what is its function
Above Brainstem (Forebrain) – Relays sensory info to the forebrain for interpretation
Hypothalamus
where is it located
what is its function
Forebrain (Below Thalamus) – Maintains homeostasis; regulates hunger, thirst, body temp, hormones
Cerebrum
where is it located
what is its function
Forebrain – Higher-level processes not needed for survival
Corpus Callosum
where is it located
what is its function
Between Hemispheres – Connects left and right hemispheres of the brain
Frontal Lobe
where is it located
what is its function
– Forebrain – Higher thinking, planning, judgment, speech, voluntary movement
Prefrontal Cortex
where is it located
what is its function
Frontal Lobe – Decision making, foresight, judgment, complex thought
Broca’s Area
where is it located
what is its function
Frontal Lobe – Controls physical movement for speech
Motor Cortex
where is it located
what is its function
– Back of Frontal Lobe – Controls voluntary movement
Parietal Lobe
where is it located
what is its function
– Forebrain – Processes sensory information (touch, spatial awareness)
Somatosensory Cortex
where is it located
what is its function
– Front of Parietal Lobe – Registers touch and body movement sensations
Occipital Lobe
where is it located
what is its function
– Back of Brain – Processes vision; interprets visual info from both eyes
Visual Cortex
where is it located
what is its function
– Occipital Lobe – Interprets visual signals from left and right eyes
Temporal Lobe
where is it located
what is its function
– Forebrain (Side) – Hearing, smell, memory, face recognition, balance
Auditory Cortex
where is it located
what is its function
– Temporal Lobe – Processes hearing info from opposite ear
Wernicke’s Area
where is it located
what is its function
– Temporal Lobe – Language comprehension
Angular Gyrus
where is it located
what is its function
– Temporal/Parietal Junction – Translates written words into auditory code (reading)
Limbic System
where is it located
what is its function
– Forebrain (between Brainstem & Cerebral Cortex) – Emotions, learning, and memory
Hippocampus
where is it located
what is its function
– Inside Temporal Lobe (Limbic System) – Creates new memories and helps learning
Amygdala
where is it located
what is its function
– End of Hippocampus arms – Controls emotions like fear, anger, anxiety
Acetylcholine
functions
malfunctions
muscle action, learning and memory
alzheimers disease
Dopamine
functions
malfunctions
movement, learning, attention, emotion
high= schizophrenia, low= parkinsons
serotonin
mood, hunger, sleep, arousal
low=depression
norepinephrine
functions
malfunctions
alertness, arousal
low=depressed mood
GABA
functions
malfunctions
inhibitory
low=seizures and insomnia
Glutamate
functions
malfunctions
memory, excitatory
high= migranes, seizures