Compliant Materials
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
3.1.2 Compliant Materials Product Design AQA A-Level
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What is a compliant material
A material that can be easily worked using basic hand tools
What are the four types of compliant materials
Paper
Board
Foam
Film
How is paper made
Plant fibres are converted into a pulp before being pressed and rolled into sheet form
What are the generic properties of paper
Comes from a sustainable source
Available in a wide range of finishes, colours and weights
Easily recyclable as paper products have short lifecycles
What are the 5 types of paper
Treated paper
Layout paper
Bleedproof paper
Cartridge paper
Watercolour paper

What are the properties and uses of treated paper
High quality paper available in a range of thicknesses and finishes
Used for printing high quality images and graphics

What are the properties and uses of layout paper
A strong paper with a degree of transparency
Used in the production of technical drawings and as overlays when tracing designs

What are the properties and uses of bleedproof paper
Coated on one side to prevent ink bleeding
Used with markers

What are the properties and uses of cartridge paper
Available in a range of finishes and weights
Used for quality drawings and graphics

What are the properties and uses of watercolour paper
An extremely heavyweight paper produced from cellulose and cotton fibres
Used in water based drawings as it does not distort with water
What is cardboard
Any multi-layered paper product
What is the generic properties of cardboard
Inexpensive
Can be scored, cut and folded into a net
Can be mass produced using die cutting
Can be easily printed on using flexography
Increased rigidity
Why is cardboard being inexpensive good
Important in a mass-produced disposable product
Why is cardboards increased rigidity useful
Makes it suitable for packaging boxes
What are the 5 types of cardboard
Corrugated card
Duplex board
Laminated / foil-backed card
Metal effect card
Mountboard
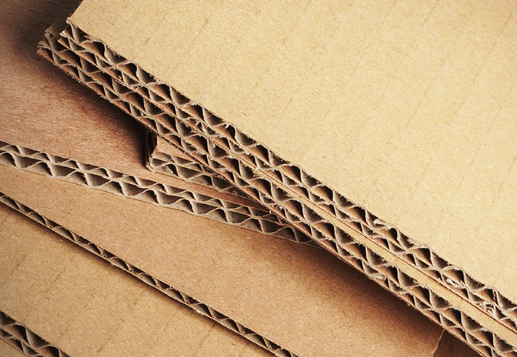
What are the properties and uses of corrugated card
Smooth on both sides with flutes inside to increase rigidity and shock absorption, easily printed on with flexography
Used in transportation boxes

What are the properties and uses of duplex board
Card with one high quality face suitable for printing onto and one natural card face
Used in the production of cereal and dried food boxes

What are the properties and uses of laminated / foil-backed card
Card with aluminium foil or metallised polyester film on one side for decoration / hygiene. difficult to recycle
Used in the production of drink cartons and food packaging

What are the properties and uses of metal effect card
Card with a metallic finish applied to one side
Used in the production of packaging and gift boxes

What are the properties and uses of mountboard
Card with greater than 1mm thick with high quality faces for displaying photographs or sketches
Ideal for model making
What is foam
A lightweight polymer construction with air pockets used for model making
What are the generic properties of foam
Lightweight cellular construction
Cushions impact due to elasticity of material
Easily workable with simple hand tools
Lack of grain structure means finish is uniform and stable
What are the 3 types of foam
Foamboard
Plastazote foam
Styrofoam

What are the properties and uses of foamboard
Two external layers of high quality gloss card with expanded foam centre for lightweight and rigidity, available in a bright white finish for aesthetics
Used for 3D architectural modelling and displays for printed graphics

What are the properties and uses of plastazote foam
A close celled polyethylene foam available in a wide range of colours
Used for model and prop making

What are the properties and uses of styrofoam
An easily shaped polystyrene foam with lightweight and fine surface finish
Used extensively in quick concept generation by designers
What is film
Thin flexible polymer materials used for hygeine / aesthetic purposes
What are the generic properties of foam
Thin flexible sheet material
Produced using calendaring
Used in packaging for aesthetic appeal
What is the name of the film
Cellulose Acetate

What are the properties and uses of cellulose acetate
Easily printed on and die cut film
Used in transport and packaging for its bright colours and clear windows
What is a polymer sheet
Polymer sheets are used in packaging and product design due to their flexibility and weather resitance
What are the generic properties of polymer sheets
Thin flexible sheet material
Produced using calendaring
Moisture and weather resistant
What are the 4 types of polymer sheets
Fluted polypropylene sheet
Translucent polypropylene sheet
Low density polyethylene sheet
Polyactide sheet and film
What are the properties and uses of fluted polypropylene sheet
Low density, rigid structure of polymer with hollow box section channels running between two thin polymer sheets, weather resistant and suitable external use
Suitable for printing on using flexography
What are the properties and uses of translucent polypropylene sheet
Flexible polymer, chemically resistant, easily laser cut, suitable for repeat bending
Used in packaging
What are the properties and uses of low density polyethylene sheet
A low density polymer sheet, chemically resistant, suitable for flexographic printing
Used in carrier bags
What are the properties and uses of polyactide sheet and film
A biodegradable alternative to low density polyethylene sheet
What are the properties and uses of moulded paper pulp
Made from recycled paper with water added to break down the fibres, reformed using heat and pressure to press into a mould, fully compostable meaning can be thrown into a compost bin, can be printed on once formed
Used in packaging such as egg boxes and to support electronic products as a replacement for expanded polystyrene.
What is a substrate
The material that the print ink is applied.
What is screen printing
A printing process used to apply an ink design to a flat surface.
What is the main use of screen printing
Ideal for small production runs and is very popular in producing personalised t-shirts, clothing and poster designs
What is the advantages of screen printing
-Stencils are easy to produce using a photo emulsion technique
-Versatile - can print on any flat surface
-Economical for short, hand produced runs
-Fully automatic methods capable of producing large volumes
What are the disadvantages of screen printing
-Generally difficult to achieve fine detail
-Requires long drying times
-Can only be done on a flat surface
What is the main use of offset lithography printing
Mainly used for large scale production (100,000 +) copies on porous substrates only. Mainly used on printing of card and paper for packaging
What is the advantages of offset lithography printing
-Consistent high image quality
-Suited to higher volumes print runs of 100,000 or more
-Quick and easy production of printing plates
-Long life of printing plates because they only come into contact with the printing blanket which is softer and less abrasive than the substrate
What are the disadvantages of offset lithography
-Expensive setup and running cost for small quantities
Name the 4 process colours used in offset lithography
CMYK
Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black
What are registration marks used for
To check that the colours are correct and that everything is aligned
What are the 4 printing processes
-Screen printing
-Offset lithography printing
-Digital printing
-Flexography printing
What is flexography printing mostly used for
Large scale production (100,000 +), copies on porous and non-porous substrates. An ideal alternative to Offset Lithography due to fast setting inks and suitability for printing on polymers, metals and corrugated card
What are the advantages of flexography printing
-High print speed
-Ideally suited for long production runs
-Prints on large variety of substates including both porous and non-porous
What are the disadvantages of flexography printing
-Cost of printing plates is high (they last for millions of runs though)
-Take a large amount of substrate to set up so there might be excess material wasted
-Any alterations to the graphic is time consuming and expensive as new printing plates must be produced
What is digital printing
Digital printers looks similar to large photocopiers and produce full colour, highly detailed print runs with the option for different designs and to print on both sides. They work similar to laser printers allowing the the ink to sit on top to be dried.
What is the main use of digital printing
Can be use for both low and high volume of prints. Used for mass customisation particularly for business flyers or cards
What are printing processes
They allow the designer and manufacturer to attract a consumer to a product as well as communicate information to the consumer. Colours images and text can provide aesthetic appeal as well as communicate barcodes, safety informations and ingredients
What are surface graphics
The process of adding a graphic to something already been printed on to enhance the aesthetic of functional properties of the design.
What are the 4 surface finishes
-Laminating
-Embossing / debossing
-Foil blocking
-Varnishing
What are the 2 types of lamination
-Lamination via encapsulation
-Lamination via a surface coating
What does lamination do
Coat the paper to protect it making it more durable
How is lamination via encapsulation applied
Seals a sheet of paper inside a polymer pouch creating a non-porous layer on both sides of the paper around the edge. The paper is fed through a laminating machine creating a heat seal around the paper
Lamination via a surface coating
Liquid lamination - can be applied with a roller or spray and is used for applications such as signage to protect from the effects of moisturise and dirt or UV light
Film lamination - can be done via hot or cold process and is used for products such as menu cards and business cards. Usually made of PP with an adhesive to make the laminate stick to the paper. The lamination is fed from a roller and pressure is applied as the paper is fed through
What does embossing do
Creates a raised design on the surface to give it a visual and tactile effect
What does debossing do
Creates an imprints/ lower design on the surface
What is embossing/ debossing used for
Popular to decorative techniques greeting cards, invitation cards and products such as chocolate boxes or packaging where the trade name or special feature is a raised area
How does embossing/ debossing work
1) Uses 2 dies (a male and a female) made for stainless steel or brass, they can be hot or cold
2) The substrate sheet is placed between two dies and held under pressure until the area is formed
3) Raised/ lowered area can have ink or foil applied to it or left natural (called blind debossing / embossing)