Operation System & Networks
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What does OS stand for?
Operating System
Operating System (definition)
Essential software that manages computer hardware, coordinates basic system operations, and provides services for running application software e.g. Linux. Windows
Name the functions of an operating system (6)
Resource management. Process management. User Interface. Multitasking. File Management. Security
How do operating systems perform resource management?
Allocates and monitors CPU and memory usage
How do operating systems perform process management?
Manages the lifecycle of all running programs
How do operating systems contribute to user interface?
Provide tools and environments for user interaction
How do operating systems allow multitasking
Allow the operation or multiple programs at once
How do operating systems allow for file management?
They organize. Store. Retrieve files and directories.
How do operating systems allow for security
Controls access and permissions for users and software.
Draw the layer model of an operating system
…
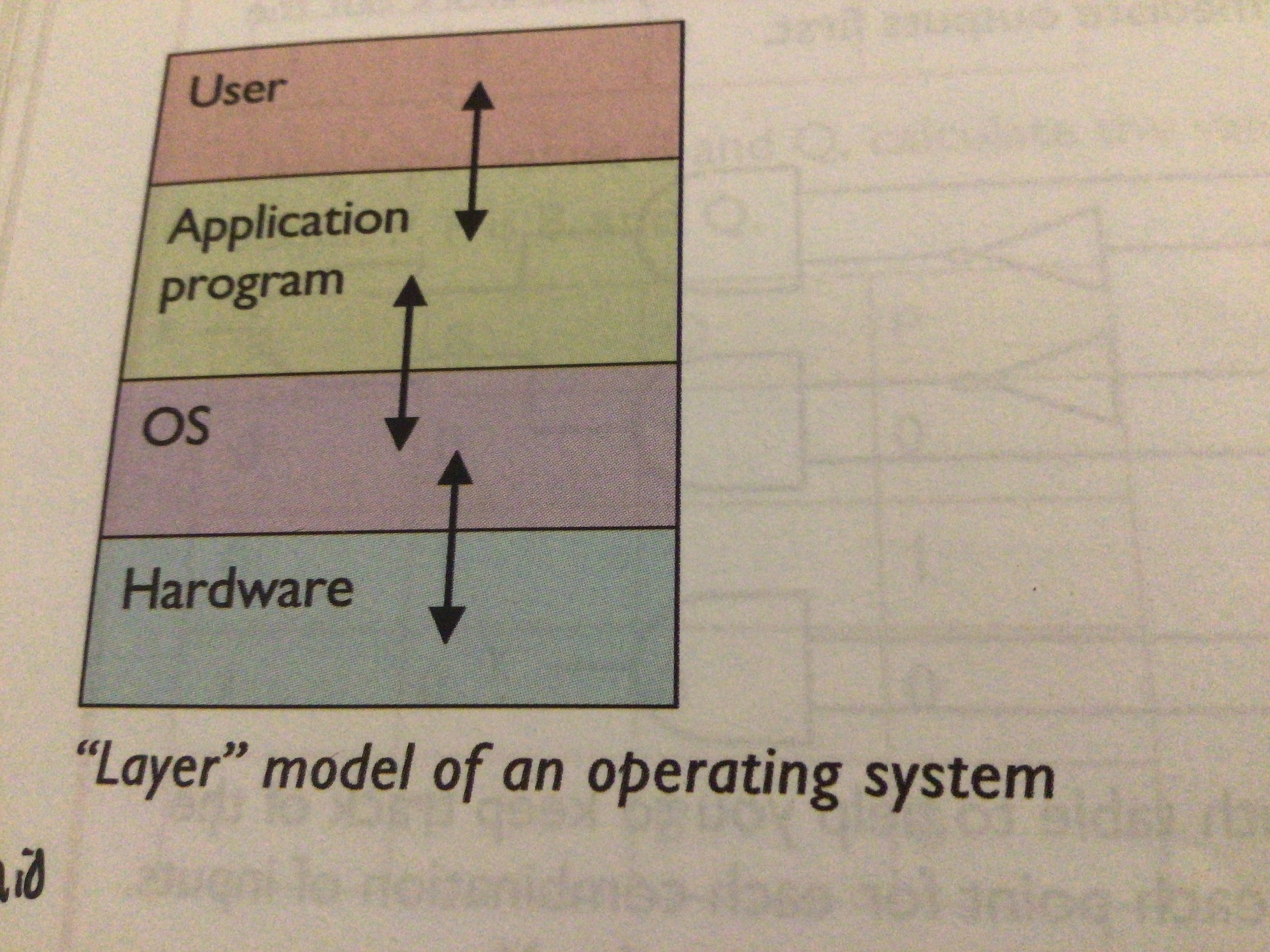
Explain the layer model of an operating system
User interacts with the application program. Application programs carry out specific tasks e.g. Microsoft Word. Application program interacts with OS which controls how the application program interacts with the hardware
LAN (definition)
(Local Area Network) Covers a small area like a building. E.g. Loreto Kilkenny.
WAN (definition)
(Wide Area Network) Spans large geographical areas. Utilises external infrastructure e.g. telecommunications (internet)
Client-Server (definition)
Centralised server manages resources
Describe a client-server model
Computer makes a request which arrives at the server. Server carries out request and the information e.g. webpage is transmitted to the computer (client)
Advantages of client-server
Security. Scalability
What is scalability?
The ability of hardware or software to continue to function when put under pressure e.g. more users, tasks, data
Disadvantages of client-server networks
Single point of failure
What is a peer-to-peer network?
All devices act as both client and server.
Advantages of peer-to-peer
Simple. Low cost
Disadvantages of peer-to-peer
Poor security
NIC (definition)
(Network Interface Card) Allows devices to connect to a network
Router (definition)
Forwards data between networks e.g. LAN to WAN
Switch (definition)
Connecte devices within a network, intelligent data packet routing.
What does Hyper Text Protocol stand for?
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
What layer is HTTP?
Application
What is the purpose of HTTP?
Deliver web pages over the internet
What does HTTPS stand for?
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure
What layer is HTTPS?
Application
Function of HTTPS
Securely deliver web pages over the internet
What does TCP stand for?
Transmission Control Protocol
What layer is TCP?
Transport
Function of TCP
Provide Reliable. Ordered. Error-checked delivery of a stream of data
What does IP stand for?
Internet Protocol,
What layer is IP?
Network
Function of IP
Handle the addressing and routing of data packets
What layer is TCP/IP?
Network
Function of TCP/IP
Communicate over the internet using combinations of protocols
What layer is Wi-Fi?
Physical
Function of Wi-Fi
Connect devices to the internet wirelessly
What does VoIP stand for?
Voice over Internet Protocol
What layer is VoIP?
Application
Function of VoIP
Enable voice communication over the internet
What does FTP stand for?
File Transfer Protocol
What layer is FTP?
Application
Function of FTP
Transfer files from one host to another
What is an IP address?
A unique string of numbers (IPv4 or IPv6) that identifies each device connected to a network which enables data to be sent and received accurately e.g. 192.168.1.1
What is dynamic IP?
Changes with each connection
What is static IP?
Permanent
Data packets (definition)
Data sent across the internet is split into small packets
Structure of Data Packets
Header (source/destination). Data. Error check
What is packet switching?
When a packet takes a different route to reach their destination (sequence number)
What does TCP do to packets?
Splits data into packets and reassembles them
What does IP do to packets?
Routes packets to the correct destination
What kind of format does IPv4 use?
32-bit format
What kind of format does IPv6 use? Why is it used?
128-bit. More combinations to accommodate the growing up number of devices on the internet.
MAC Address (definition)
A hardware identification number that uniquely identifies each device on a network. It is assigned to the network interface card (NIC) by the manufacturer and used for network communication within the local network segment.
WWW (World Wide Web) (definition)
Collection of websites accessible via the internet
Firewalls can be … firewalls or … firewalls
Hardware. Software
Firewalls (definition)
Control data entering and leaving a network based on security rules, acting as a barrier between trusted internal networks and untrusted external ones like the internet.
How does a firewall protect?
Filtering and blocking unauthorised access and cyber threats.
Encryption (definition)
Ensures data is securely transmitted e.g. HTTPS
What does DNS stand for?
Domain Name System
DNS (function)
Looks for the address of a website. A DNS checks other DNSs for a website address if they don’t have it.
What does SSL stand for?
Safe Sockets Layer
What does TLS stand for?
Transport Layer Security
Function of SSL
Encrypts websites
Function of TLS
Encrypts communication between websites
What does it mean when a web application is obsolete?
Works perfectly, but it’s out of date
What does URL stand for?
Uniform Resource Locator
Function of URL
Address of websites
What is a GET Request?
Computer requests to receive a webpage from a server
What is a POST request?
You send information e.g. Logging in. Cookies Data
What is a Cookie ID?
Everyone assigned a number (cookie ID). App uses it to remember you.
Bandwidth (definition)
The maximum transmission capacity of a device
Bit Rate (definition)
Number of bits that we can send over a given period of time.
What is a fibre optic cable? (Compsci)
Thread of glass engineered to reflect light
Fibre optic cable VS. Ethernet cable (Fibre optic cable) (4)
Light signals. Expensive. Signal doesn’t degrade over long distances. Multiple signals can use 1 cable
Fibre optic cable VS. Ethernet cable (Ethernet cable) (3)
Digital signals. Cheap. Used in LAN as signals degrade over relatively short distances
Why are static IP addresses used for servers? (2)
Ensures constant access. Prevents conflicts
Why are dynamic IP addresses used for personal devices? (2)
Ensures flexibility. Efficient use of addresses