Biology GCSE Year 9 End of year
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
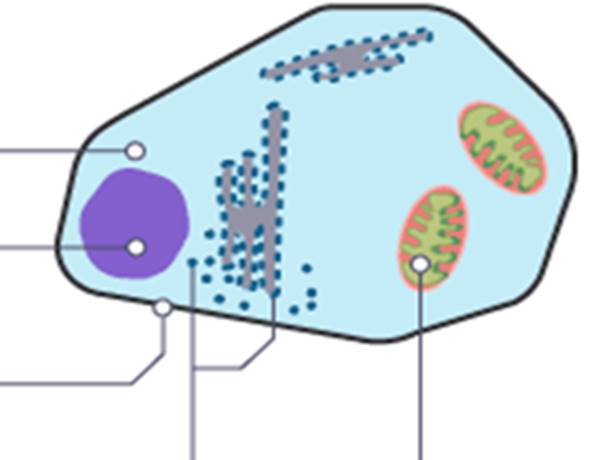
Name everything inside a animal cell
Cytoplasm, nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, cell membrane
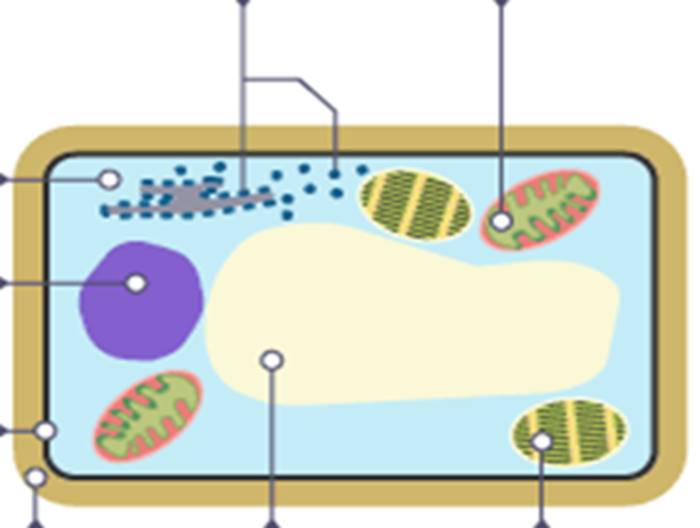
Name everything inside a plant cell
Cytoplasm, nucleus, cell membrane, vacuole, chloroplast, mitochondria, ribosomes
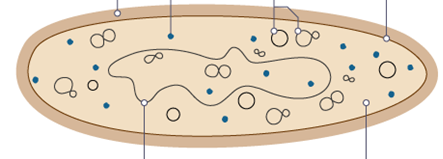
Name everything inside a bacteria cell
cytoplasm, cell membrane, plasmids, ribosomes, cell wall, free floating DNA
Red Blood cell (specialised structure and function)
Specialised structure: No nucleus, flexible, large surface area
Function: carry a lot of oxygen, can pass through narrow capillaries.
Root hair cell (specialised structure and function)
Specialised structure: Large surface area,
Function: absorbs a lot of water
Sperm cell (specialised structure and function)
Specialised structure: long tail, pointed head, lots of mitochondria Function: streamlined to travel efficiently, mitochondria to release energy for movement.
Nerve cell (specialised structure and function)
Specialised structure: Long, many connections at the end, can carry electrical signals
Function: Can transfer electrical signals to many other cells.
Egg cell (specialised structure and function)
Specialised structure: only has half as much DNA as other cells, has a thick outer coating,
Function: Only one sperm can fertilise the egg, to make cells with the normal number of chromosomes.
How to calculate total magnification
Total magnification = objective lens magnification X eyepiece lens magnification
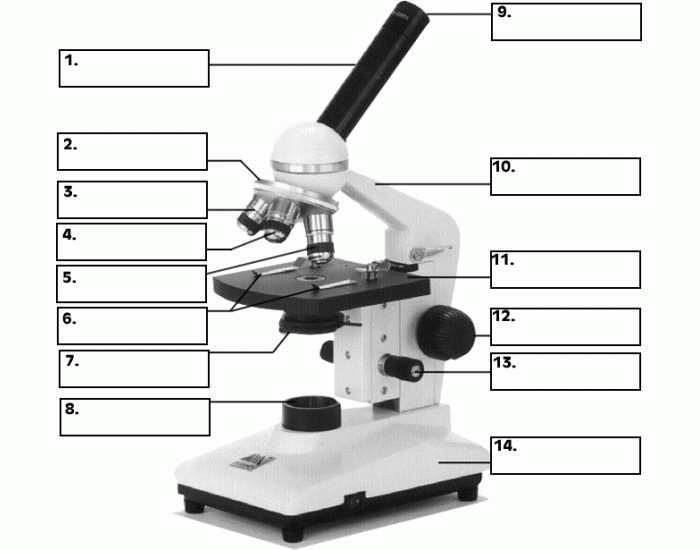
Label all the part of a microscope
body tube
Revolving nose piece
Low-power objective lens
medium power objective lens
stage
stage clips
Diaphragm
Light source
ocular lens/ eye piece
arm
rack stop
course adjustment knob
fine adjustment knob
base
Converting units
Unit name | Unit abbreviation | Fraction of a metre |
Centimetre | cm | 1/100 |
Milimetre | mm | 1/1000 |
Micrometre | µm | 1/1000000 |
Nanometre | nm | 1/1000000000 |
cm - mm = x10
mm - µm = x1000
µm - nm = x1000
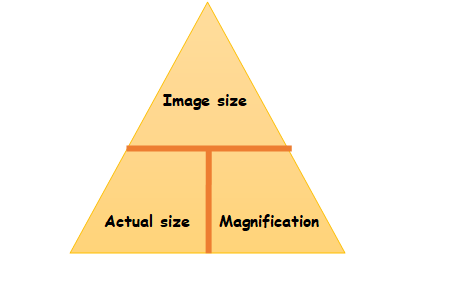
How to calculate image size
IAM
Optical, Transmittion EM, scanning EM
Microscope | Visualize specimen using | Max magnification | Min. resolution (nm) | Type of image seen | Used to observe |
Optical | Visible light | 2000x | 200nm | 2D image or 3d is the living sample | Living or dead samples |
Transmission EM | Electron beam | 2 000 000x | 0.1nm | 2D image black and white | Dead samples- organelles inside cells |
Scanning EM | Electron beam | 2 000 000x | 20nm | 3D image black and white | Dead samples - surface of cells. |
Define magnification
How many times bigger the image compared to the original. If the image gets to zoomed in it will go blurry
Define resolution
Minimal distance apart that 2 objects can be in order for them to appear separate.
Electron and light microscopes
Electron microscopes have much higher levels of magnification and resolution than light microscopes, so they show us much more details of the inside of cells. We can see the different organelles and learn more about them in the cell. Light microscopes have the advantage that they are cheaper, so we can buy them in school, and we can use them to look at living organisms.
How to answer a 6 mark question
6 mark question = When evaluating you write three paragraphs:
1st = 2 positive points
2nd paragraph - 2 negative points
3rd paragraph = justified conclusion.
4 mark = no conclusion.
4a Cells key words
Aseptic | Transferring bacteria without contamination |
Binary fission | Asexual reproduction by doubling |
Nutrient broth solution | A soup like solution with nutrients for bacteria |
Agar | Jelly which you put in the petri dish which grows bacteria |
Colony | A group of bacteria |
Contaminate | To infect with bacteria |
Disinfectant | A solution used to sterilise the surface |
Antibiotics | A medication used to remove only bacteria |
Petri dish | A circular shaped plastic container where agar jelly is placed. |
Sterilise | To clean / remove all traces of bacteria. |
Inoculating loop/ spreader | A wire loop use to transfer bacteria from one place to another. |
Transfer | To move something from one place to another. |
Incubate | Keep something at a certain temperature in a container/box |
Anaerobic conditions | Without oxygen |
Cross-sectional area | Area |
πr2 | Pi and radius squared |
Zone of inhibition | Zone of bacteria which is unable to form |
Standard form | 10 to the power of x to make equations and answers easier to use |
Chromosome facts
Inheritance is where genetics are passed on from your parents.
Sex cells are also called gametes.
The genetic information is contained in the nucleus of the cell.
DNA is a double helix made up of two strands twisted into a helix
Humans have 46 chromosomes in a normal body cell.
he gene is the unit of inheritance.
How do genes work
Genes in side the nucleus contain DNA. They send messages into the cytoplasm for proteins to be synthesised at the ribsomes. These proteins allow the cells to become specialized to perform a specific function. This determines our physical characteristics. All our characteristics are product of our genes.

Explain this diagram
The normal body has 4 chromosomes in 2 pairs.
In the first stage of the cell cycle, a copy of each chromosome is made,
The cell is divided in two forms two daughter cells, each with a nucleus containing 4 chromosomes identical to the ones in the original parent cell.
Why are stem cells special
They are unspecialised, so they cannot do specific functions in the body
Where do you find stem cells
Mostly live in bone marrow
How can stem cells be used
To treat conditions in which bone marrow is damaged and is no longer able to produce healthy blood cells
Define mitosis
Mitosis is a process in reproduction where a single cell asexually divides into two genetically identical daughter cells.
Why are the cells produced identical?
If something goes wrong the cell won’t do what it is supposed to be and will create a tumour and give you cancer.
What would be a benefit of reproducing whole organisms in this way?
To have the same thing twice/ clone something. E.g If a chicken lays loads of eggs then you would want to have that same chicken to get way more eggs.
What are stem cells and why do we need them
Stem cells are undefrenciated/non-specialised which can change into any type of cell.
Stem cells can copy themselves and differentiate themselves (change)
Adult organisms have cells that have different jobs, These cells are specialised to carry out a certain function.
What is Mitosis
Mitosis is the process in reproduction which produced 2 genetically identical cells called daughter cells.
Name the 3 stages of Mitosis
There are 3 stages. In the first stage before a cell can divide it needs to increase the number of sub cellular structures like ribsomes and mitochondria. Then the DNA duplicates to form 2 copies of each chromosome and then spindle fibres pulls one set of chromosomes to each end of the cell. Then the nucleus divided. The last stage of mitosis the the cell membrane and the cytoplasm divide
Specialised animal cells and their functions
Red blood cell (imports oxygen)
Hair cell
nail cell
eye cell
root hair cell
Specialised plant cell and their functions
mineral lines
parastates cells (absorbs maximum amount of light)
Where are STEM cells
Adult stem cells location
Bone marrow
Skin
Brain
Eye
The Adult stem cells remain in a non-dividing state for years until activated by disease or tissue injury.
What is diffusion
The net movement of particles from a region where they are at a higher concentration to a lower concentration ( down the concentration gradient.) This is a passive process
Link diffustion to where it happens in the body
Diffusion happens across membranes in lots of parts of your body. This is usually to move substances into the blood or remove substances from the blood.
Urea diffuses out of the blood into the kidney tubes to make urine.
Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the lungs into the alveoli sacs to be exhaled.
Oxygen diffuses into the blood from the alveoli so it can be carried to the cells.
Feautures of a succesful exchange (MRS.L)
Moist
Rich blood supply (Maintains concentration gradient)
Short diffusion distance (Thin membrane)
Large surface area
The effectiveness of an exchange surface is improved by:
Having a large surface area
A thin membrane which ensures a short diffusion distance
(in animals) an efficient blood supply
(in animal gas exchange) being ventilated (good circulation of air)
When will diffusion become more difficult
As surface area to volume ratio decreases diffusion becomes more difficult.
Define osmosis
The movement of water from a dilute solution to a more concentrated one through a partially permeable membrane. It can’t dilute water. This is a passive process so it does not require any energy
How to calculate the percentage change
Percentage change = (final value - original value / original value ) x100
Define active transport
Moving particles up the concentration gradient using energy This process requires energy
Why do cells that perform active transport have lots of mitochondria?
Mitochondria is the sight of respiration and respiration releases energy
Process of active transport
Molecules moving up the concentration gradient move by active transport. Substances such as glucose in the small intestine, K+ in the lung membranes and nitrates in the soil will be moved against the concentration gradient, to where they are already in higher concentration. This requires energy from respiration and can only happen through protein channels in the membrane.
Where does active transport take place
Glucose from intestines into the blook. This is an active transport as it requires energy. Nitrates into roots from the soil. There is a higher concentration in the inside of the root of the plant. This is an active transport. You go from a less concentrated to a higher concentration
How are specialised cells adapted for active transport?
There would be lots of mitochondria to provide energy from anaerobic respiration. There needs to be lots of channel proteins.
How would cells adapt for diffusion and osmosis be specialised?
Large surface area to volume ratio. Provide by extensions to the cell membrane such as microvilli.
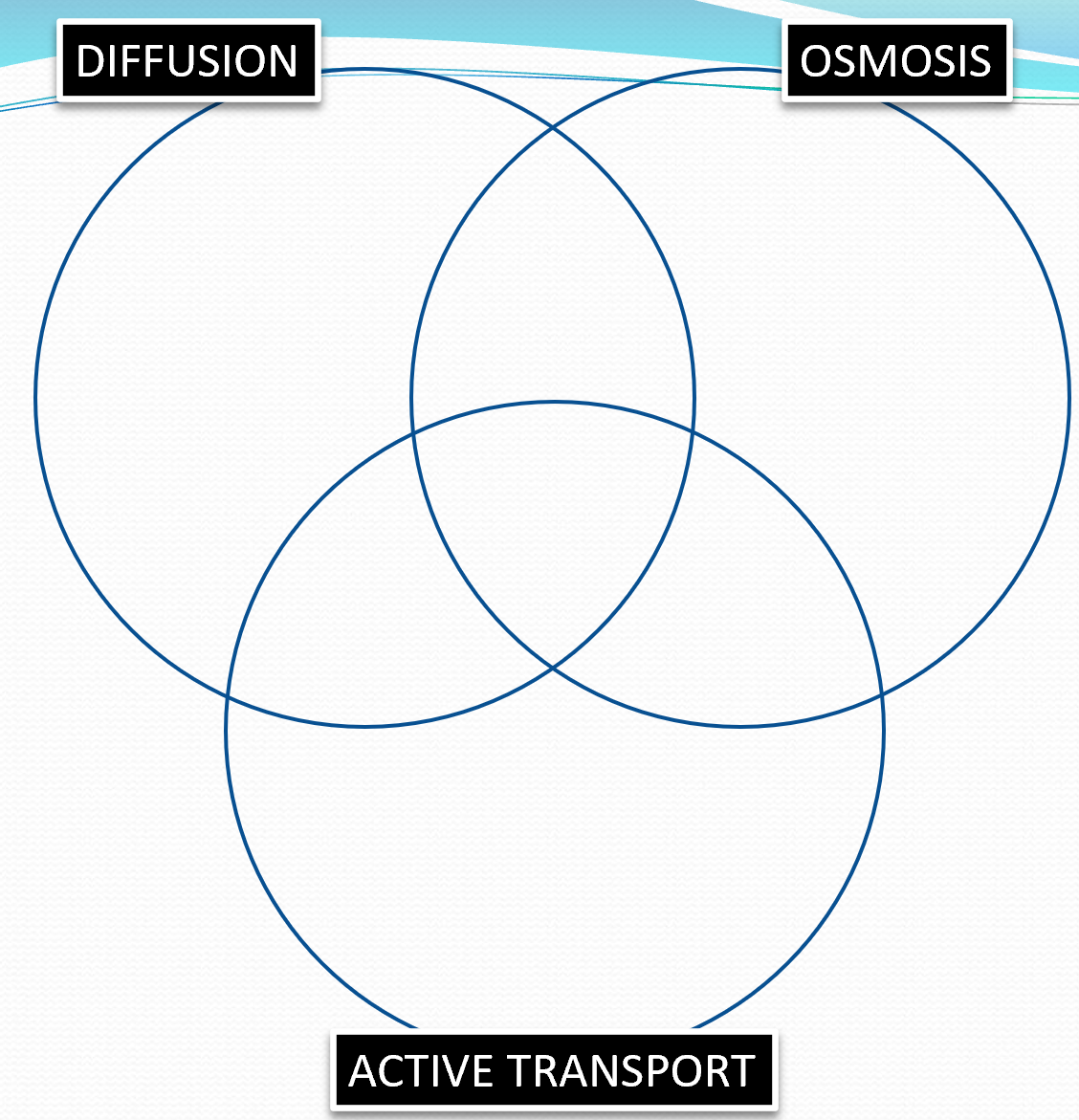
Compare diffusion, osmosis and active transport
Diffusion - high concentration to low concentration
diffusion and active transport - The transport of solutes
Diffusion and osmosis - Large surface area to volume ratio. Passive process
Osmosis - Water goes from a dilutes solution to a more concentrated one
Osmosis and active transport - They both need partially permeable membrane
Active transport - Mitochondria for respiration to release energy, goes from a low concentrated solution to a higher concentration.
All of them - Movement of particles, occurs in plants and animals
Word equation for photosynthesis
water + Carbon Dioxide ------- glucose + Oxygen
Symbol equation for photosynthesis
6H2O + 6CO2 --------- C6H12O6 +6O2
2 more things needed for photosynthesis to occur
Energy + chlorophyll
Why would starch be found in leaves
glucose
How do we test for presence of starch
We use iodine to stain the leaf. If it is blue black it is positive
Types of leaf
Variegated | In all of the white part of the leaf it will turn a light browny/orange and the green part will turn blacky blue |
Partially covered | The covered part goes a light browny orange and the not covered part turns blacky blue |
Full light | Goes blacky blue |
How many ways could you speed up this reaction?
Increase temperature
Increase light intensity
Increase concentration of carbon dioxide
Higher concentration of chlorophyll
What does describe and explain mean
Explaining is when you say why something is happening. Describe is what you can physically see happen. (Appearance). Paint a picture in words.
Example of a describe and explain
Describe
Part 1 of the graph shows As the light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis also increases. Part 2 of the graph shows As the light intensity increases the rate of photosynthesis stays the same.
Explain
The limiting factor in the first part of the graph is the light intensity. The second limiting factor in the graph are other external reactants which are required for photosynthesis such as temperature and concentration of carbon dioxide.
5 uses of glucose
Respiration - glucose is broken down to release energy
Synthesis - cellulose from cell wall and giant structures
Synthesis - animo acids glucose + nitrate is amino acids
Storage - fat/oil glucose is converted to glucose
Storage - starch insoluble easily broken down and doesn’t affect the movement of water
What is cellulose
Cellulose is the substance that makes up most of a plant's cell walls. Since it is made by all plants, it is probably the most abundant organic compound on Earth.
Evaluating data vocab
Accurate measurements | Closest to the true value |
Precise measurements | These measurement are close together. (consistent results each time the activity is repeated) |
Reproducible measurements | The same answer is obtained by a different person over and over again |
Repeatable | The same answer is obtained by the same person over and over again. |
Random error | An error that occurs without your control (e.g. loose count so you make up the answer.) |
Systematic error | A error that is wrong with your system so you make the same error again and again |
Anomalous value | Is a value that is outside the pattern of results. (one that sticks out) |
Validity | The more i control the variable the more valid my data will be. (V for variable and V for Valid.) |
Define respiration
Respiration is the process where all living things release energy from glucose.
word equation for aerobic respiration
Glucose + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water
Where does respiration take place
Mitochondria
Why do cell respire
To release energy for :
Muscles to contract
Build larger molecules from smaller ones
In mammals and birds its needed to produce heat to keep them warm
Respiration chemical equation
C6H12O2 + 6O2 ----> 6CO2 + 6H2O
Define anaerobic respiration
Respiration in the absence of oxygen
Partial breakdown of glucose without any oxygen to release a small amount of energy
GLUCOSE ---> LACTIC ACID
ONLY IN ANIMALS
It is the incomplete break down of glucose.
There is less energy released per glucose molecule during anaerobic respiration.
Anaerobic respiration takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.
Lactic acid is a toxic waste product if it builds up in muscles it can cause muscle fatigue.
When might muscle cells need to do anaerobic respiration
you need to put in a lot of energy. E.G sprint to catch the train.
Why do we respire anaerobically
When we do strenuous exercise we may not be able to provide enough oxygen to our muscles for aerobic respiration to take place. The muscles still need energy to contract. If they have enough glucose they use anaerobic respiration to provide this energy so the exercise can continue for longer.
Can you now explain why holding your bags out at the start of the muscle caused the effects you noticed?
Anaerobic respiration is occurring because not enough oxygen was reaching the muscle cells to your arms which causes the build up of lactic acid then your get muscle fatigue.
Restricted blood flow
How is anaerobic respiration used in fungi
Glucose ---> ethanol + carbon dioxide (+ energy) only happens in yeast
Compare Aerobic and anaerobic respiration
Aerobic | anaerobic |
Occurs in Mitochondria | Occurs in cytoplasm |
Complete breakdown of glucose | Incomplete breakdown of glucose |
Carbon dioxide and water are waste products | Lactic acid is a waste product |
Releases large amounts of energy slowly | Releases smaller amounts of energy quickly |
Glucose is the reactant | Glucose is the reactant |
Requires oxygen | Doesn't require oxygen |
What increases when you start exercising
Your breathing deeper
Your body temperature increases
Your breathing is more rapid
Body aches
Your hearts beats faster
Blood going to your muscles
Define lactic acid
The build us of products from a chemical reaction that happens when you resipre anaerobically. Toxic product. Acid built up in the muscles causes by the incomplete oxidation of glucose
Muscle fatigue
The lactic acid builds up in the muscles making the muscles feel tired/ fatigue
Oxygen debt
When we have to give the necessary amount of oxygen to the muscles after exercising to remove any remaining lactic acid. The amount of oxygen needed to break down lactic acid after exercise is finished.
Metabolism
Metabolism is the sum of all the reactions in a cell or the body